Cards Straight Outta the Review
1/99
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Remember this in the course eval guys
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
20%
No state has an adult prevalence less than
4 (louisiana, alabama, mississippi, west virginia)
How many states had an obesity prevalence over 35%
US SOUTH, 2ND Midwest (30.7%), Northeast (26.4%), West (25.2)
Highest geographical prevalence of obesity (31.2%)?
Genetics (30-40% of risk), Environment, Metabolic, Behavioral issues
Etiology of obesity
40%
Prevalence of obesity has increased __ in the last ten years
CVD, Type II DM, Hypertension, Dyslipidemias
The major obesity-related comorbidities are:
Dyslipidemias
Which obesity related comorbidity is the last to change with weight loss?
80%
__ of type II Diabetics are obese?
40x
BMI > 31 INCREASES risk of Type II DM in women by What ?
40x
BMI > 35 in Men INCREASES risk of Type II DM in men by What
57%, 37%
Obesity prevalence in African American Women? Men?
47%, 36%
Obesity prevalence in Hispanic women? Men
Weight, Height, BMI, pinching fat, Recent weight loss (Intentional or not), Labs (fasting etc), Clinical/History, Dietary Evaluation, 24 hr recall, Food frequency, Food diary, Diet/Nutrition history
What are the components of a nutrition assessment?
Physical fitness
a state of being created by the interaction between nutrition and physical activity
Cardiopulmonary fitness, MSK fitness, Flexibility, Optimal Body composition
4 Domains of physical fitness
physical activity
muscle movement that increases energy expenditure
Heart disease, Stroke, HTN, Diabetes II, Falls/Hip fractures/Osteoporosis, Early Mortality, decreased risk of endometrial and colorectal cancer
A lifestyle of physical activity has been shown to independently decrease which common morbidities?
1/4
In spite of the benefits what percentage of US adults admitted to no leisure activity
less than 50%
In spite of the benefits what percentage of US adults perform the recommended amount of physical activity
30%
In spite of the benefits what percentage of US adolescents participate in at least 60 min per day (data suggest this number is increasing)
usually yes
If you lack exercise as a teen, does this trend continue as an adult
West (colorado, cali, oregon) Highest, South lowest
Rates of physical activity based on states
Lowest in non-hispanic black adults, highest in white adults
Rates of physical activity based on ethnic groups
Lower in those with less education, Lower in those living at the poverty level
Rates of physical activity based on education and SES
60 minutes a day - muscle strengthening 3x/week and Bone strengthening 3x/week
Exercise recommendations for Children and teens
150 minutes/week of moderate intensity exercise every week - 2 or more days of muscle-strengthening
Exercise recommendations for adults
Trying to maintain or improve overall health, Trying to significantly improve physical fitness, Training for athletic competition, Advise related to training injuries (Strains, Inflammation, etc.), Guide on recuperation is key
An individual’s fitness program will be different if they are?
Health risk
the severity or likelihood of an adverse health outcome due to an exposure to environmental, biological, or social conditions
Health risk appraisal
refers only to the INSTRUMENTS used to assess health risk
Health risk assessment
refers to the overall process in which the health risk appraisal instruments are used
Health improvements in a population, Reduce healthcare costs, Has a significant impact on direct healthcare spending within 5 years, Want to move them from high to low risk, Foster a healthy quality of life culture, Smoke, ETOH consumers, elevated BMI, Text while driving, no seat belts, Risky behaviors
HOW DO HRAS PROVIDE BASELINE DATA TO TRACK HEALTH IMPROVEMENTS IN A POPULATION
Worksite stress, Unprotected sex with multiple, short-term partners, Use illicit drugs, or abuse prescription medications, Can be a wake up call for the patients when they receive the results, Allows you as the healthcare provider an opportunity to broach sensitive topics
HOW DO HRAS PROVIDE BASELINE DATA TO TRACK HEALTH IMPROVEMENTS IN A POPULATION
the sooner we lower the risk the cheaper it is
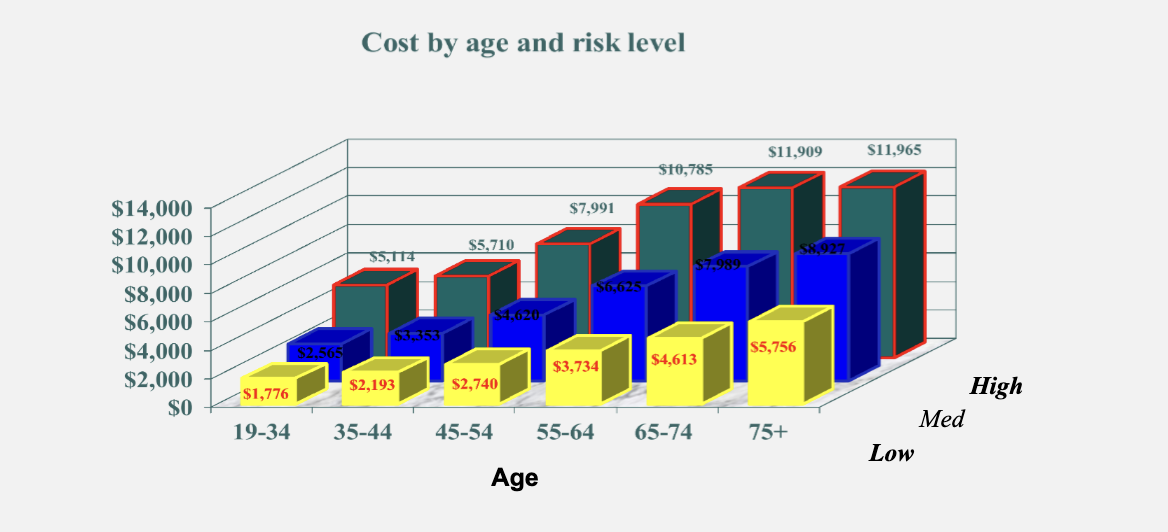
Sum up this chart
Address underlying determinants of health, Tailor approaches to each individual’s unique environment and circumstances, Transfer day-to-day responsibility for personal healthcare management to the patient, Emphasize ongoing communication & education, Normalize healthy behavior, Change attitudes, Promote healthy environments (Healthy eating options/exercise etc.)
Uses of HRAs
Do use them to be more efficient and effective, Do select the right tool, Do realized advantages and limitations, Don’t assume HRA equals clinical eval (patients may lie), Don’t neglect the ethics (HIPAA, DV)
Dos and Don’ts of HRAs
32% Heart disease and stroke, 29% from lung cancer, 21% from COPD, 8% other cancer (renal, esophageal, oral), 10% other causes
How do smokers die?
Bluish- colored skin and lips, Tend to take deeper breaths but cannot secure the optimal level of O2
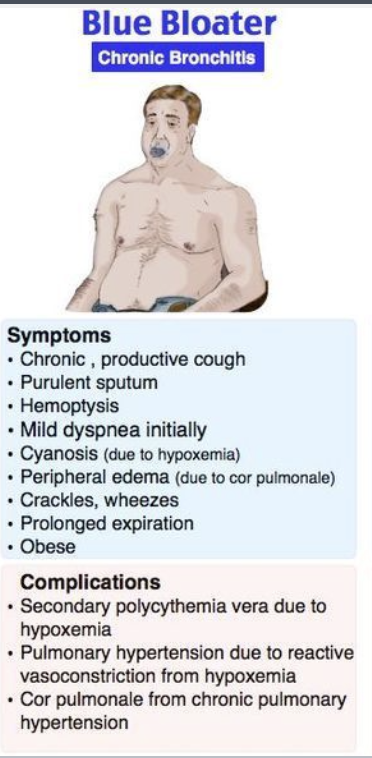
Describe a blue bloater (chronic bronchitis)
Thin, breathing rapidly, and is pink, Pursed lip breathing
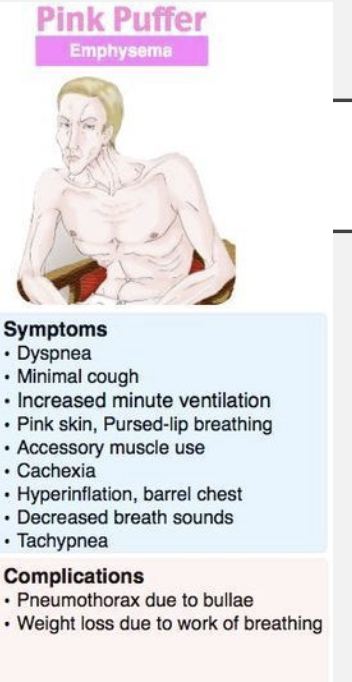
Describe a pink puffer (emphysema)
low education, males, young adults, south and midwest, LGBTIAQ+, below poverty level, disabled, certain races/ethnicities
Smoking remains high among which population
3-5%
A 10% increase in cigarette has reduced overall consumption
young adults (2-3x)
A price of cigarette affects which populations smoking choices?
10 years
If you quit at 30 y/o this increases your lifespan by
8 years
If you quit at 40 y/o this increases your lifespan by
6 years
If you quit at 50 y/o this increases your lifespan by
3-4 years
If you quit at 60 y/o this increases your lifespan by
Nicotine is highly addictive, causes euphoria, reaches the brain quickly, cravings, becomes a pavlov response
Why do people smoke
Dysphoria/depressed mood, Insomnia, Irritability, frustration, or anger, Anxiety, Difficulty concentrating, Restlessness, Decreased heart rate, increased appetite/weight gain
Big time withdrawal symptoms of smoking
Ask about smoking, Advise about smoking, Assess their willingness to quit, Assist those are willing to quit, Arrange for follow up
5As of smoking
Every patient, every visit, every H&P, Include in vital signs, Congratulate never smokers, encourage former smokers, advise current to quit
Ask about smoking includes:
First Line -Nicotine delivery systems, Bupropion (Wellbutrin), Varenicline (Chantix); Second line - Clonidine, Nortripyline
Pharm therapy for smoking
treatment focus is to provides steady nicotine levels to eliminate withdrawal and reinforcing "hits” (Patch, gum, lozenge, inhaler, nasal spray) - 8-12 weeks (if smoking >10 cigs/d, apply highest dose patch daily Q 6 wks, then titrate to lower doses Q 2 wks each sequentially)
Tell me about nicotine therapy
low risk for heart disease could be 10x more likely to a false positive, Could lead to an unnecessary cath (approximately 39% of asymptomatic have had an EKG despite this)
Should Healthy and 40-60 → EKG or stress test (ER VISITS DO NOT COUNT)
if there’s no symptoms there’s no benefit, 75% of tests that reveal a high PSA level turn out to be false alarm, False postive leads to stupid unneeded stuff, CONSIDER 55-69 y/o, Don’t test if they are going to die in 10 years
Should Males over 40 → PSA
This is radioactive, Find the protein in 30-40% of people who are asymptomatic, Unable to predict which individuals with plaques will develop the disease
If you have a memory issue → PET
Only needed every 3 years, With 1 negative HPV test → only HPV test every 5 years, Over 65 y/o with normal pap smears → you can discontinue testing
All adult women → Pap smear
Mild osteopenia may not be cost effective, risk of fracture is low and the risk for significant side effects, no evidence that the medications provide much benefit
Women 50-65 → DEXA (osteopenia, osteoporosis)
Peeps with normal risk should begin screening at 50 and repeat every 10 years, If normal at 75 → never again
Over 75 → colonoscopy
Little evidence that annual check up keeps people healthy, Results of specific tests should be used to determine frequency, schedule based on need
All adults → annual checkup
Best imaging technology in the world is often inadequate at determining the cause of back pain, Most will go away in a month, imaging tests often leads to expensive procedures
Lower back pain →Xray, CT, MRI
DASH
A diet rich in fruits, veggies, and low fat dairy foods, can substantially lower bp in individuals with HTN and high normal bp. The greatest potential is in African Americans and the elderly
Decrease in systolic and diastolic in ENTIRE study group
Increased fruits and veggies to 8.5 servings
Significant decrease in systolic and diastolic bp in both groups, greatest drop was in systolic in HTN group (11.4 mmhg)
Combination - add 2-3 servings of low fat dairy to fruit and veggie diet
Linked to 27% less strokes, 15% decrease in heart disease
Study outcomes for DASH - 10 year follow up period
No (just eat them)
Are antioxidant supplements recommended?
MAY help with cholesterol level if use to replace animal products (minimal otherwise)
Benefits of Soy proteins
associated with decreased risk of CVD (use with caution as it is high fat)
Benefits of mediterranean diet
Control Macros and fiber, Increased fruits and veggies to 8.5 servings, Combination - add 2-3 servings of low fat dairy to fruit and veggie diet
DASH arms → not sodium restricted
7-8 servings of grains, 4-5 servings of veggies, 4-5 servings of fruit 2-3 servings of low fat dairy, 2 (or less) servings of meat, poultry, fish, 2-3 servings of fats and oils, limit sweets, nuts, seeds, and dry beans 4-5 times/week
The DASH diet includes
Cigarette smoking, Hypertension >140/90 mmHg or on medication, Low HDL-C (<40 mg/dl), Family history of premature CHD (male first degree relative<55; female<65), Age (men >45 years, women 55 years)
Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) targets LDL goals what can impede this
Beta Carotene → Higher risk of lung cancer in smokers taking this
Antioxidants and smoking
C. Botulinum
Home canned foods
campylobacter
Poultry, raw milk
Clyclospora
Imported berries
E. coli
Ground beef, produce, water, animal contact
listeria monocytogenes
Ready to eat meats, soft/pale cheeses
norovirus
Ill food handlers, produce, shellfish
★ M/C cause of viral gastroenteritis
salmonella
Meat, eggs, raw meat, animal contact
toxoplasmosis
cat feces, raw meat (pork, lamb, venison)
vibrio
Shellfish
yersinia
pork products (chitterlings)
final prep and cookin
What point in the chain of production of farm to table do we target?
ingestion of undercooked meat, contaminated food or water, contact with infected animals
Clin. Pres.: diarrhea, cramps, malaise, fever, N/V
TX: fluids + azithro (kids) or cipro (adults)
No risk to pregnancy
High burden in infants, especially <1 y.o.
★ M/C cause of bacterial gastroenteritis
Campylobacter quirks
#1 Cause of Traveler’s Diarrhea
Characterized by bloody diarrhea and cramps but can be ASx
cattle/deer via contaminated food/water or infected person to person
Unpasteurized dairy/undercooked ground beef
prevention=improved sanitation, personal hygiene, and avoid undercooked ground beef/unpasteurized dairy/fruit juices
TX: FQ for adults & azithro for kids
★ 6% of cases progress to HUS (hemolytic uremic syndrome)
E.Coli quirks
Acute viral infection
CP: fever, fatigue, dark urine, +/- jaundice, nausea, anorexia, abd pain or asymptomatic
Reservoir = humans
Resolves on its own, but very infectious viral infection
Primarily Foodborne transmission. Can be sexual transmission
Incubation 28-30 days
Children at high risk, vaccine available for 2+ y.o.
Typically seen in daycares and schools typically seen in school age kids and young adults
Hep A quirks
Parasite
Infections mild and symptoms include malaise, fever, fatigue, and
lymphadenopathy
Reservoir: cats and other felines (others=swine, cattle, sheep, goats, rodents, and birds)
Infections in immunocompromised are severe
TX: Sulfadiazine or Pyrimethamine
Ingestion of undercooked meat, Ingestion of oocytes passed in feline feces through contact w/ litter or soil, Vertical transmission
Toxoplasmosis Quirks
Bacterial Illness
Diarrhea, abd cramps, tenderness, N/V, and fever or ASx
2 types: Typhi and Non- typhi (m/c in US)
Serotypes: Contaminated egg products (enteritidis), beef (Newport), poultry (typhi)
TX: IV fluids + FQ for adults and azithromycin for kids
Infectious throughout course of infection
Amphibians/reptiles carry it
Children increased risk due to immature immune systems and hand-to-mouth contact
Quirks of salmonella
145
Cook steaks and roast to →
180
Cook whole poultry to →
160
Cook ground meat to →
165
Heat leftovers to →
40 or less
Refrigerate foods at →
Many different diseases are caused by contaminated foods (250+), For many of these, the source might be food, water, animal contact, or contact with ill people, For an individual case of illness, it is often impossible to know the source of the infection, Outbreaks let us learn specific course of infection, Individual cases are tracked regardless of whether or not they may be from food or other sources, Outbreaks of foodborne diseases, regardless of which microbes caused them (source-specific surveillance)
Core concepts in surveillance of food-borne outbreakes
17%
Obesity in children
start with 5 to 10 % of initial body weight
Guidance for obesity
Recent data suggest this may be better to estimate central adiposity, Correlates strongly with type II DM, CVD, HTN, and dyslipidemia risk (35” in women, 40” in men)
Waist Circumference
Weight loss has been shown to lower bp (independent of Na+ restriction), Weight loss from diet alone reduced both LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, Weight loss from a combination of diet and exercise decreased total cholesterol and increased HDL cholesterol
weight loss and chronic diseases
kg/height (meters) (25-29.99= overweight, 30 = obese, 40+ = extremely obese)
BMI formula
Osteoartritis really benefits from weight loss, Modest wt loss has been shown to improve both glucose tolerance and type II DM, lower BP
Benefits of weight loss
Lifestyle assessment (eating behavior, stress management, fitness assessment, work style) Disease/condition specific (Bronchitis and COPD, Pain, menopause, depression, PTSD, insomnia, skin cancer, heart disease, diabetes, osteoporosis), Age-based (adolescents, young adults, older adults, seniors), Gender-based (Cancers, Bone density loss, Depression, STI), Environmental (chemicals, biologicals, insects–safety, lead contamination, sports safety, hurricane prep, depleted uranium exposure, asthma triggers)
Types of HRAs
1. Don’t be afraid to address underlying determinants of health
2. Tailor approaches to each individual's unique environment and circumstances
3. Use shared decision making
4. Transfer day-to-day responsibility for personal healthcare management to the patient
5. Emphasize ongoing communication and education
Engaging and powering
