Understanding Weathering Processes and Their Effects
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Weathering
The breakdown and alteration of Earth's rocks and minerals.
Endogenic Processes
Internal energy / tectonic processes.
Exogenic Processes
Processes that wear away and/or rearrange landforms.
Landmass Denudation
The process of wearing away the land surface.
Geomorphology
The study of landforms and the processes that shape them.
In situ process
Material altered in place, 'not moved'.
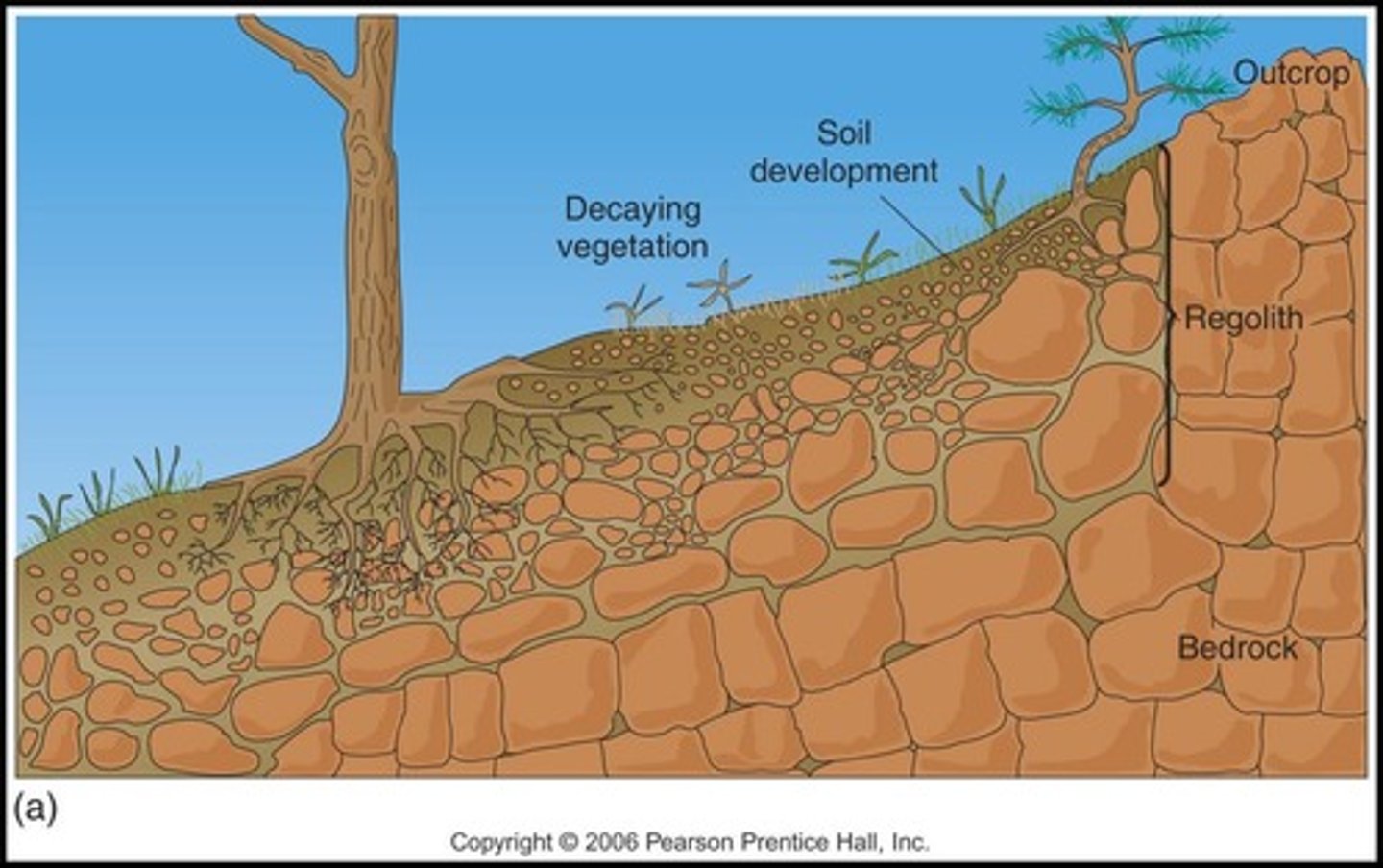
Regolith
Loose, broken-up bedrock material that helps make soil and move material.
Laterite
Highly weathered tropical soil found along the Rio Negro, Brazil.
Weathering Effects
1. Lowers resistance, 2. Drives soil development, 3. Forms unique landforms.
Material Resistance to Weathering
A function of internal resistance of material and magnitude/type of external forces.
Factors Influencing Weathering
Includes composition of rocks, areas of weakness, climate, temperature, and precipitation.
Composition of Rocks
Mineralogy including Quartz (SiO2), Calcium carbonate (CaCO3), Clay Minerals (Feldspars), etc.
Planes of Weakness
Stress at zones of weakness within material exceeds strength of the material.
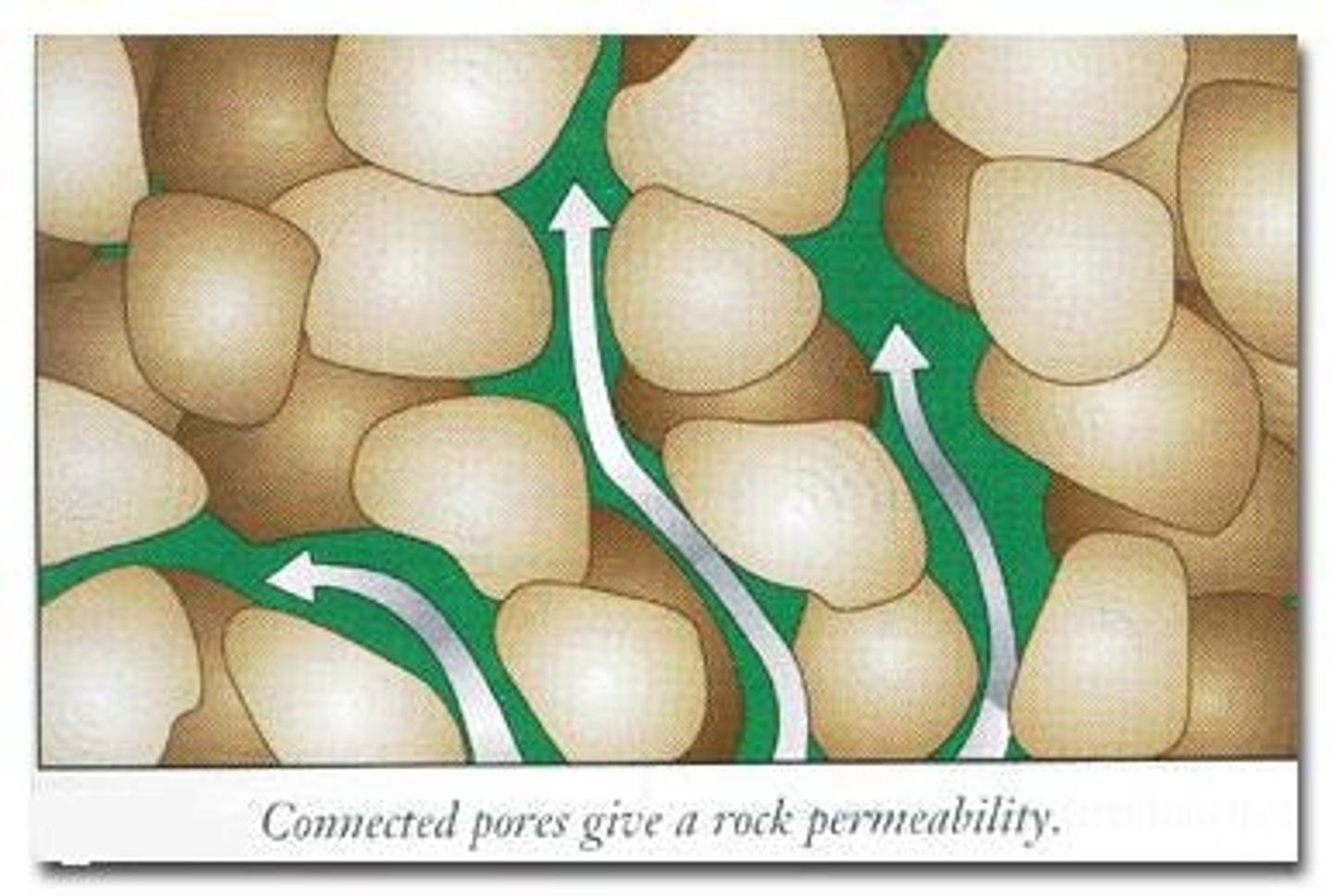
Porosity
Pore space within a rock.
Permeability
Ability of rock to transmit water.
Vegetation
Deflects water, stabilizes rock, and contributes to weathering.
Microclimates
Climates of small areas influenced by local variations in temperature and precipitation.
Mechanical Weathering
Also known as physical weathering, it involves the disintegration of rocks into smaller pieces.
Chemical Weathering
Involves the decomposition of rocks through chemical processes.
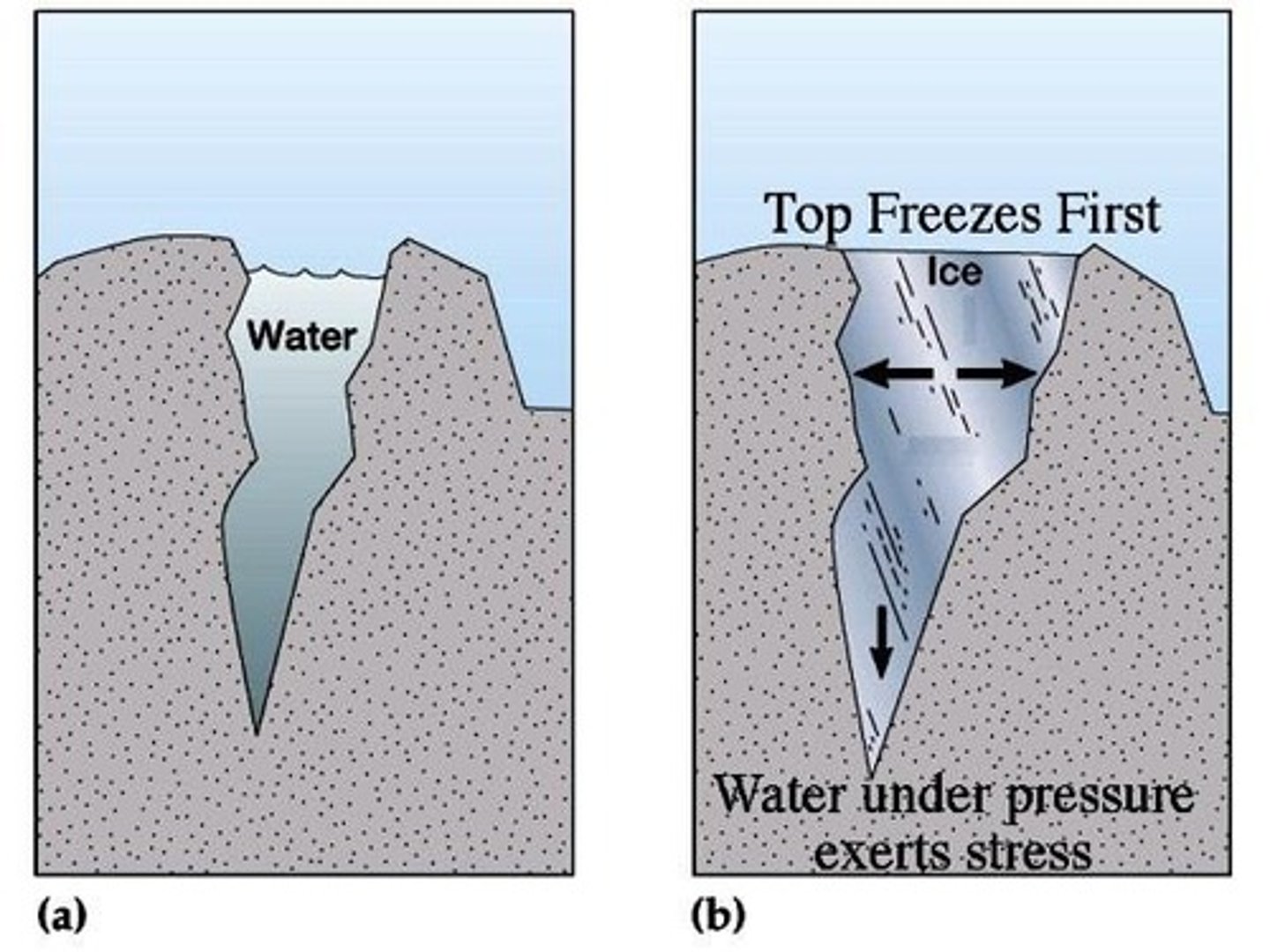
Freeze Thaw Weathering
Water freezes in cracks, increasing volume ~9%, leading to tensile stress that exceeds rock strength.
Talus
Rock apron at the base of steep slopes from mass wasting.
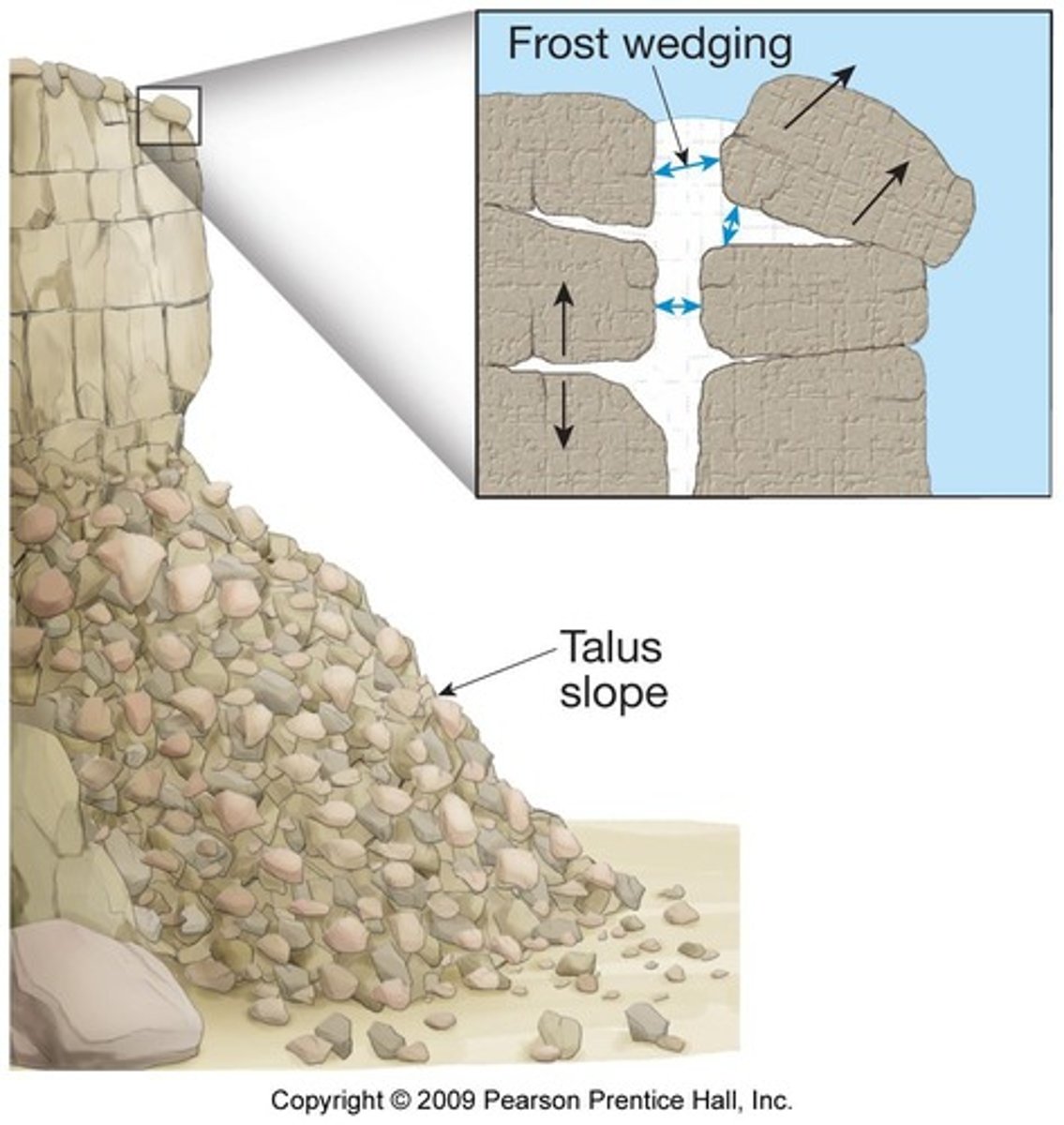
Angle of Repose
The maximum surface angle maintained by loose material.
Wetting and Drying
Minerals expand/contract in response to moisture changes, affecting rocks.
Salt Crystallization
The formation of salt crystals, which can contribute to weathering.
Physical Weathering
The process of breaking down rocks through physical forces without changing their chemical composition.
Salt Weathering
The process where salt enters in solution, water evaporates, crystals form, and crystals hydrate and expand, leading to disintegration of material.
Expansion of Clay Minerals
The increase in volume of clay minerals when wet, with specific expansions: Ca-montmorillonite (45-185%), Na-montmorillonite (1400-1600%), illite (15-120%), and kaolinite (5-60%).
Desiccation Cracks
Cracks that can form in clay-rich soils as a result of drying.
Expansive Clays
Clays that can cause damage to structures; estimated to affect 1/4 of all homes in the United States.
Exfoliation
The process of rock layers peeling away due to pressure release.
Thermal Expansion
The expansion of rocks and minerals due to temperature changes, such as those caused by fire or forest fires.
Biological Activity
The influence of living organisms, such as plants and animals, on the weathering of rocks.
Chemical Weathering Equation
The reaction where primary minerals react with water to produce dissolved ions and secondary minerals.
Role of Acidity
Acidity from the reaction of CO2 with water, which can enhance weathering processes.
Solution Weathering
The process where minerals dissolve in water into their constituent ions.
Carbonate Weathering
The reaction of carbonate minerals with acids, leading to the dissolution of minerals like limestone.
Carbonic Acid Formation
The formation of carbonic acid (H2CO3) from the reaction of water and carbon dioxide.
Pitting and Etching
Surface features that result from chemical weathering, particularly on limestone structures.
Surface Area Calculation
The measurement of surface area affected by weathering, with examples: 16 cm on a side = 1,536 cm²; joints 4 cm apart = 3,072 cm²; joints 1 cm apart = 24,576 cm².
Chemical Weathering Agents
Water and organic acids that facilitate the chemical weathering process.
Expansive Soils
Soils that expand and contract significantly, causing structural damage.
Half Moon Dome
An example of an exfoliation dome located in Yosemite National Park, CA.
CaCO3 + H+
HCO3
Oxidation
Reaction between metallic elements and oxygen, very effective with increased temperature and precipitation.
Oxidation of Iron
Fe2SiO4 + 4H2CO3 → 2Fe2+ + 4HCO3
Oxide
Metal + oxide ions (O2-).
Oxidized minerals
Often have yellowish brown to red color.
Basalt
Igneous rock that can show weathering effects.
Hydrolysis
Chemical reactions that produce different compounds, often involving water.
Hydrolysis of K-feldspar
2KAlSi3O8 + 2H+ + 9H2O → H4Al2Si2O9 + 4H4SiO4 + 2K+.
Weathering of feldspar in granite
A common form of hydrolysis weathering.
Residual clays
Form into soils and/or shale stone (sedimentary rock).
Quartz (SiO2)
Sand transported to beaches.
Differential Weathering
Not all materials weather at the same rate; varies over many scales.
Corestones
Relatively unaltered rock surrounded by weathered materials.
Grus
Coarse rock fragments from granular disintegration of rock.
Saprolites
Deeply weathered rock, largely converted to clay and Al or Fe oxides.
Weathering pits
Positive feedback loop in weathering processes.
Joints in sandstone
Formed by uplift and collapse, leading to weathering.
Chemical weathering activity
More active in warm, wet climates.
Forms of mechanical weathering
Include exfoliation, thermal expansion, and frost action.
Freezing of water in joints
Associated with mechanical weathering.