conditions module2 quiz 2
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
The most common type of cerebral palsy and the one most associated with contractures is:
Spastic
What is the most common type of Muscular Dystrophy (MD)?
Duchenne
When should an OT assess possible adaptive equipment needs when working with a client with Muscular Dystrophy (MD)?
At initial evaluation and at any time when there is a change or decline in the client's function
Which of the following conditions are always present in cerebral palsy (CP)?
Abnormal muscle tone and stereotypical patterns of movement.
In treating a client with cerebral palsy, occupational therapists may address the following:
A.
Navigating public spaces
B.
Interacting with family and peers
C.
Caring for a pet
D.
All of the above
The focus of occupational therapy assessment and intervention for a person with an intellectual disability (ID) is:
Adaptive behavior
A significant problem that OTs must be aware of when working with clients with Down Syndrome is:
Hypotonicity
The essential criteria for measuring limitations in conceptual, social, and practial skills in clients with intellectual disability (ID) is:
Performance that is typical for that client
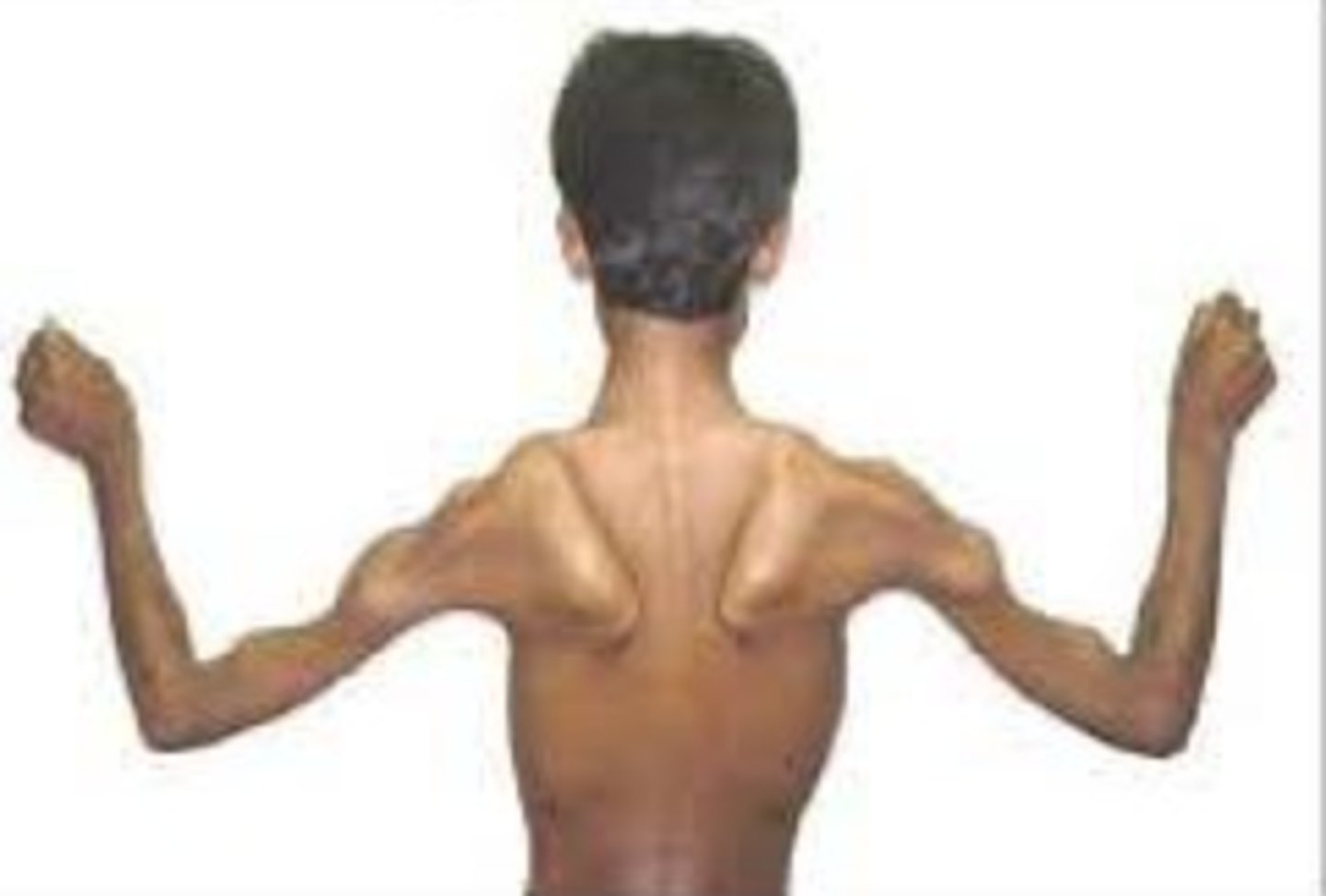
What is represented in this picture?
Valley sign
When cerebral palsy is present, it is most often first suspected:
When the child does not achieve early motor milestones, such as sitting.
When the occupational therapist passively extends a patient's elbow to full extension and little or no resistance to movement is felt, this is a sign of:
Hypotonicity
The strongest risk factor for the development of cerebral palsy is:
Prematurity
OTs will often consult with this specialty due to half of persons with Down Syndrome having complications in this area:
Cardiology
For a client with cerebral palsy (CP), tetraplegia means:
All four limbs are involved
What severity levels are used to further refine and categorize a diagnosis of ID based on severity of function?
Mild, moderate, severe, profound
How are the nine different types of MD distinguished clinically?
Clinical observation of the distribution and rate of progression of the muscle weakness
What is the Gower's maneuver?
The inability to rise off the floor without using arms to "walk up" the legs
What is a condition that can mimic Muscular Dystrophy (MD)?
A.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
B.
All of the above
C.
Myasthenia Gravis
D.
Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease
Which type of Muscular Dystrophy is the fastest progressing with the shortest lifespan?
Duchenne
The most complete definition of intellectual disability (ID) is as follows:
A significant limitation in intellectual functioning and adaptive behavior originating before age 18.
What are the initial symptoms that may lead a physician to suspect a child has Muscular Dystrophy (MD)?
Muscle cramping, muscle weakness, increased falls, and increased fatigue
Which of the following is a perinatal factor that may contribute to intellectual disability (ID)?
Hypoxia
B.
Maternal exposure to drugs or chemicals
C.
Herpex simplex II passed from mother during birth
D.
All of the above
Of the following, which is the most important factor for a positive prognosis for a person with ID?
Social inclusion
Which of the following statements is NOT true about intellectual disability (ID)?
The criteria for measuring performance is to compare to peers of the same age.
Which is NOT true of cerebral palsy (CP)?
CP cannot be acquired after birth. A child is always born with CP.
Classification of cerebral palsy in which slow, writhing, and involuntary movements characterize the condition.
Athetosis
Which of the following is NOT true about the incidence and prevalence of Muscular Dystrophy (MD)?
Not all forms of MD are inherited genetic disorders