N470: Cardiac Disorders (exam 2)
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Any condition that impairs the ability of the ventricles to fill or eject blood can lead to this; the heart cannot pump blood at a volume required to meet the body's needs
heart failure
Hear failure occurs due to either (3)
- systolic dysfunction (poor contraction)
- diastolic dysfunction (poor filling)
or
- increased afterload
Causes of HF (5)
- CAD (CAD with damage to left ventricle is most common cause)
- valvular dysfunction
- infection (myocarditis or endocarditis)
- cardiomyopathy
- uncontrolled HTN
What clinical syndromes can lead to discovery of HF?
- acute MI
- decreased exercise tolerance
- fluid retention and JVP?
Which form of HF involves increased venous pulmonary and capillary pressures leading to interstitial edema?
left ventricular failure
S/S of left sided heart failure (13)*
L=Lungs (mostly respiratory)
-Pulmonary edema
-dyspnea
-restlessness
-tachycardia
-Orthopnea
-nocturnal dyspnea
- cyanosis
- fatigue
-crackles
-extra heart sounds
-weak pulses
-pale, cool extremities
- decreased CO
Which form of HF involves ineffective right ventricular contractile function
right ventricular failure
What is the most common cause of RVF (right ventricular failure)?
left ventricular failure
Causes of RVF (right ventricular failure) (3)
- LVF
- PE
- RV infarct
S/S of right sided heart failure (10)* systemic congestion
- JVD
- congestive hepatomegaly
- ascites
- dependent peripheral edema
- enlarged liver/spleen
- weight gain
- increased venous pressure
- weakness
- elevated CVP
- extra heart sounds
decreased contractility of the heart muscle during systole; s/s of HF combines with below normal EF (<50%)
systolic heart failure
What causes systolic heart failure? (2)
- CAD
- non-ischemic cardiomyopathy (dilated cardiomyopathy)
What can systolic heart failure lead to?
ventricular remodeling
inability of the heart muscle (L ventricle) to relax, stretch, or fill during diastole; has a preserved EF of 45% and above
diastolic heart failure
Causes of diastolic heart failure (8)
- CAD
- MI
- AFIB
- uncontrolled HTN
- L ventricular hypertrophy/dysfunction
- cardiomyopathy (hypertrophic/restrictive)
- infiltrative disease (amyloidosis/neoplastic)
- aging
clinical findings for DHF
- s/s of HF
- normal or slightly abnormal LV systolic dysfunction
- abnormal L ventricular relaxation, filling, diastolic distensibility, or diastolic stiffness
type of HF with a sudden onset and no compensatory mechanism in which the pt may experience pulmonary edema, low CO, or even cardiogenic shock
Acute heart failure
S/S of acute HF (6)
similar to chronic but severe and start/worsen suddenly
1) sudden fluid buildup
2) palpitations
3) S3 (d/t oscillation of blood back and forth between walls of ventricles from atria
4) sudden severe SOB
5) cough with pink frothy mucus
6) chest pain if caused by MI
Chronic heart failure structural heart changes
heart chamber dilation and hypertrophy
DX tests for HF (8)
1) blood tests- BNP
2) chest x-ray- looking for enlargement/fluid buildup
3) ECG
4) echo- to measure EF and structure
5) ejection fraction
6) stress test
7) CT/MRI
8) angiogram (coronary catheterization)
what is secreted by the atrial myocardium in response to atrial stretch?
atrial natriuretic peptide
What are the natriuretic peptides?
1) atrial natriuretic peptide
2) brain natriuretic peptide
what is secreted by the ventricular myocardium in response to ventricular stretch and is measured to confirm diagnosis of HF?
brain natriuretic peptide
Decreased CO causes the body to activate several major compensatory mechanisms including...
1) the sympathetic nervous system
2) the RAAS system
3) ventricular hypertrophy if HTN present
Describe the RAAS system
1) SNS (hypotension, sodium depletion, dehydration, serum albumin depletion, cardiac failure) signals the kidney to release renin
2) renin activates the conversion of angiotensinogen from the liver to form angiotensin II by an enzyme in the lungs
3) Angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor) stimulates aldosterone secretion
4) aldosterone acts on kidneys to retain water and sodium
5) angiotensin II also stimulates posterior pituitary gland to secrete ADH signaling kidneys to retain water therefore increasing vascular volume
When the failing heart undergoes changes in shape and dimension in an attempt to enhance contractility; hypertrophy of myocytes, increase in myocardial mass and fibrosis of interstitium; last effort to repair
ventricular remodeling
What does ventricular remodeling result in?
it results in increased stiffness, decreased compliance, and ventricular dys-synchrony
Medications used to halt or reduce the progression of HF remodeling
1) ACEI or ARB (losartan)
2) Aldactone
3) beta blocker
NYHA functional classification
I- normal ADLs do not initiate s/s
II- normal ADLs initiate onset of s/s although s/s resolve with rest
III- minimal activity initiates s/s, no s/s at rest
IV- any activity initiates s/s and a/a present at rest
A disease of the heart muscle affecting its ability to contract and adequately perfuse the body's vital organs; the weakening and/or inflammation of the heart muscle itself
cardiomyopathy
Goal of treatments for cardiomyopathy
- stop or slow the progression of damage to heart
-improve heart function
- reduce/eliminate s/s
- prevent sudden death
- treat common associated condition that worsen heart function ( sleep apnea, CAD)
cardiomyopathy diagnostic tests (6) *
- EKG wide QRS
- CXR
- echo
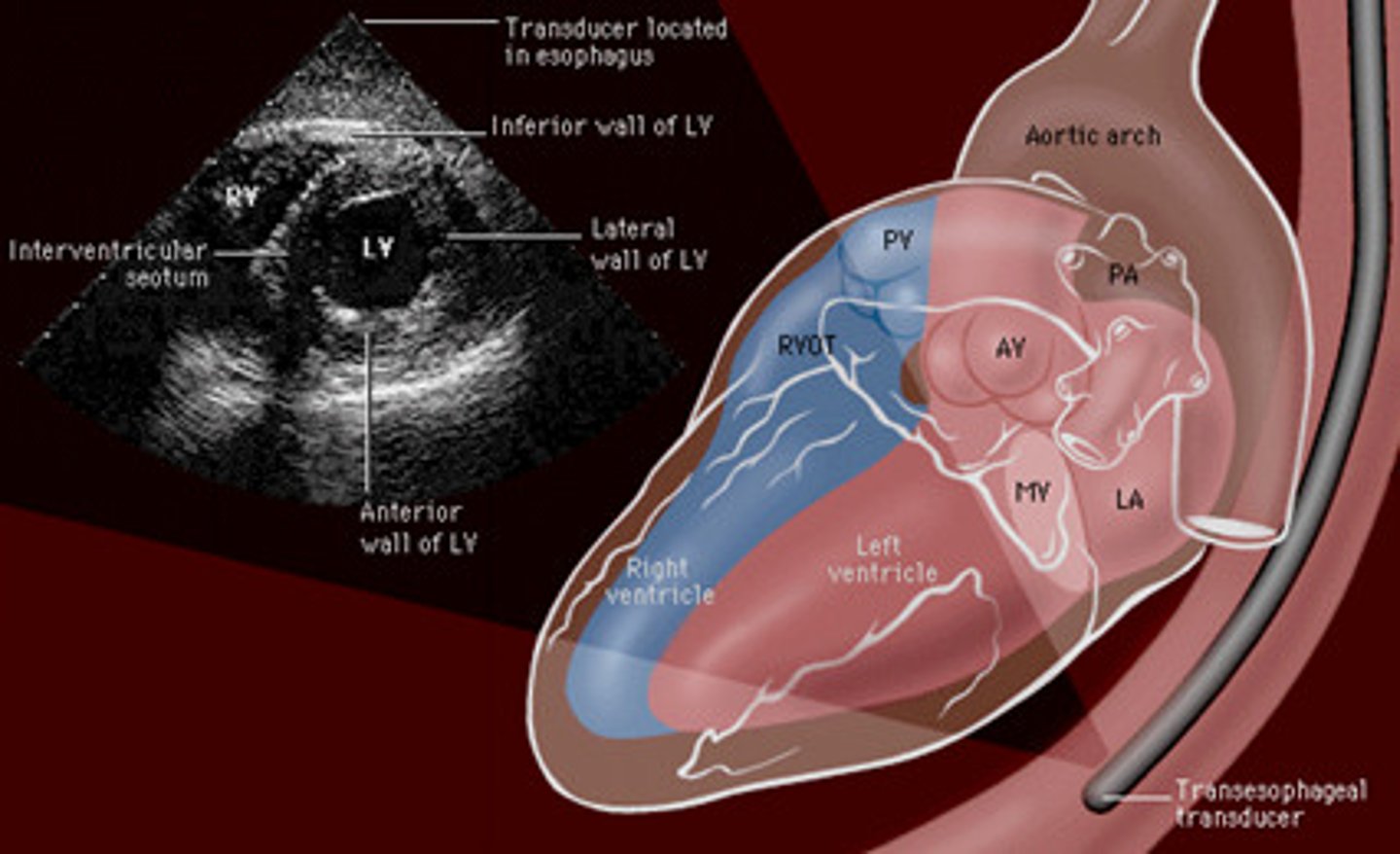
- transesophageal echo (TEE)***
- cardiac catheterization/ arteriography
- ventriculogram
Three types of cardiomyopathy
1. Dilated
2. Hypertrophic
3. Restrictive
primary cardiomyopathy
idiopathic- unknown cause but associated with risk factors
secondary cardiomyopathy
associated with other conditions like CAD, MI, valvular disease, ETOH, severe HTN, viral infections, AI disease
most common form of cardiomyopathy (60%)
dilated
type of cardiomyopathy involving:
- circular ventricles (usually both L/R)
- degeneration of myocardial fibers
- increased fibrotic tissue
- fibrotic tissue not pliable
dilated cardiomyopathy
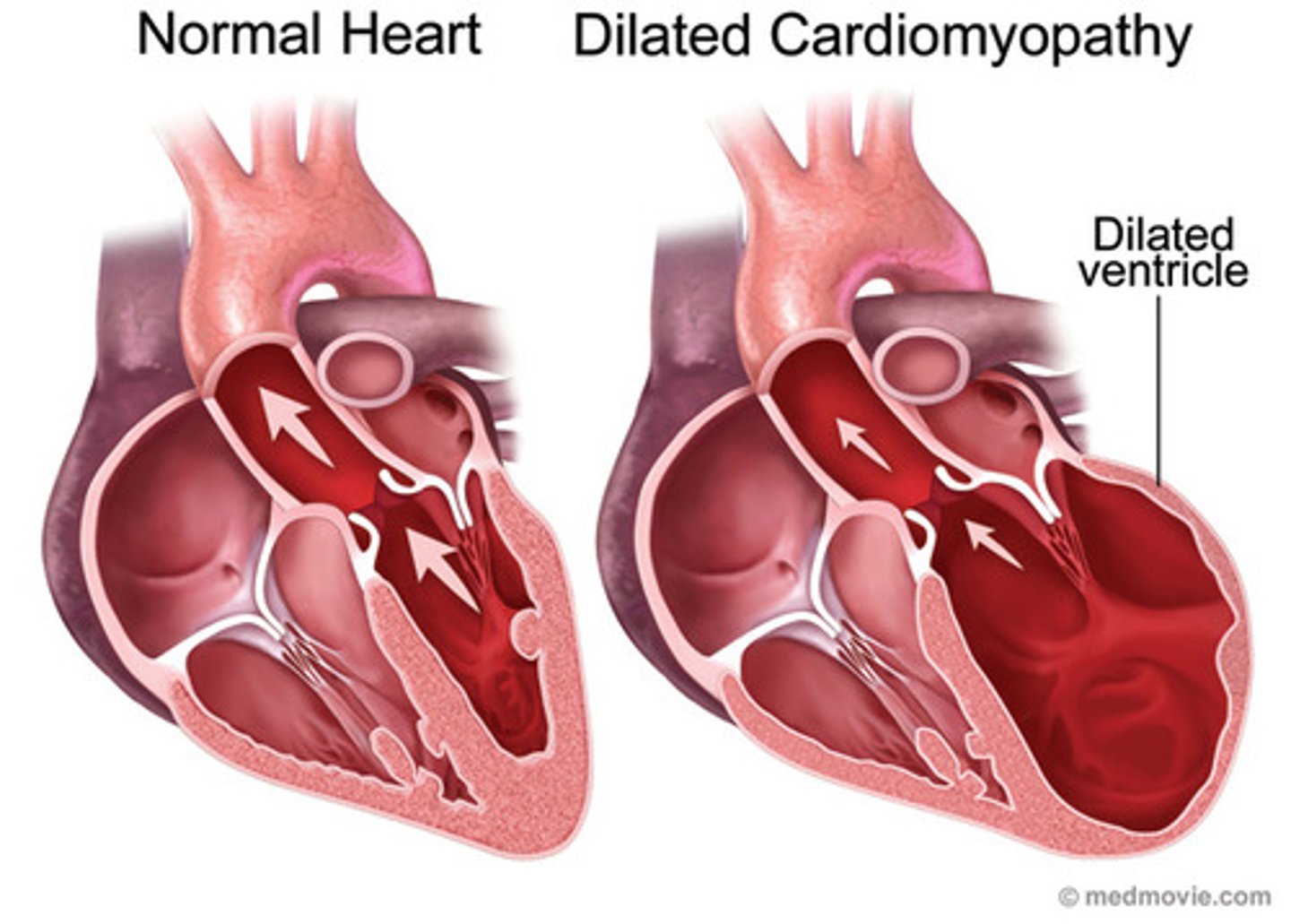
What is the patho of contractile dysfunction in dilated cardiomyopathy? (4 parts)
1) decreased SV and CO
2) grossly impaired systolic function
3) heart compensation by increasing HR
4) 5 year morbidity rate 75%
s/s of dilated cardiomyopathy (7)
1) syncope
2) fatigue
3) angina
4) pulmonary congestion
5) extra heart sounds/ murmurs
6) atrial and ventricular dysrhythmias
7) emboli formation within the heart muscle or pulmonary vasculature
Assessment findings in dilated cardiomyopathy (6)
- cardiomegaly
- aortic and mitral valve murmurs
- x-ray: cardiac enlargement
- left ventricular hypertrophy
- pulmonary HTN
- Abnormal EKG
Abnormal EKG findings in dilated cardiomyopathy
- sinus tachy
- atrial/ventricular dysrhythmias
- ST segment and T wave abnormalities
- conduction defects d/t myocardial enlargement
- vtach/vfib
dilated cardiomyopathy tx (9)*
- diuretics
- Na restriction
- antidysrhythmic
- blood thinners
- ACE inhibitors (vasodilator, lower BP improve blood flow and decrease work of heart)
- beta blockers (slow HR and increase filling time)
- nitroglycerine vasodilator
- inotropic agents (increase contractility)
- pacemakers*, AICDS, LVADS, heart tx
type of cardiomyopathy involving:
- thickening of interventricular septum
- enlargement of heart and heart cells
- genetic inheritance
- idiopathic caused by prolonged uncontrolled HTN
- young adults most affected resulting in sudden death
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
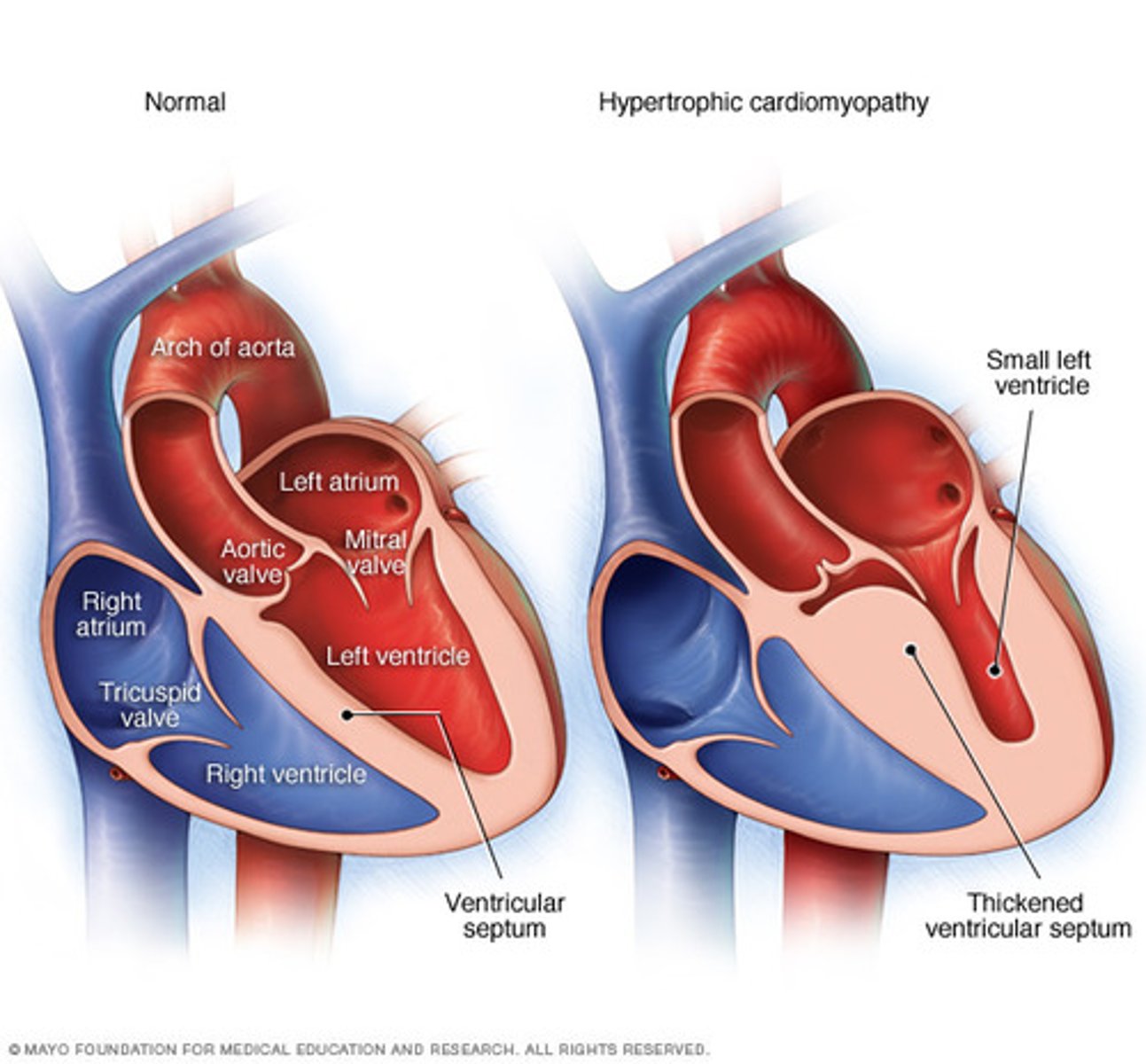
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) manifestations in the heart
- increase resistance to flow from left atrium
- left ventricle outflow restriction
- left ventricle hypertrophy and ventricle wall stiffness
- LVEDP increase
- increase in PA pressures/ wedge venous pressure
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) patient symptoms
- dyspnea
- angina
- fatigue
- syncope
- palpitations/ sudden cardiac death/ SVT/ Vtach
- nocturnal dyspnea
- SOB with exertion
diagnostic management for Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) (2)
- echo- determines the extent of ventricular septum/ventricle thickening
- holter monitor- presence of dysrhythmias and activity intolerance
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) assessment findings
- x-ray (mild/mod cardiomegaly)
- S4 sounds
- presence of systolic murmur
- EKG (ST segment and T wave abnormalities)
- Av dysrhythmias
What is the goal of HOCM treatment?
to reduce contractility and relieve left ventricular outflow obstruction
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) treatments (8)
- beta blockers (decreased HR/contractility/O2 consumption and prevents dysrhythmias)
- Ca channel blocker
- coumadin if in AFIB
- antidysrhythmic
- avoid inotropes and preload reduction meds
- AICD d/t sudden cardiac death risk
- permanent pacemaker
- mitral valve replacement
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) pt education
- promote oxygenation
- cardiac rehab consult for less intense exercise
- family genetic screening
- AICD
- heart transplant in a small percentage
- no basketball
- prophylactic abx (prevent infective endocarditis)
least common cardiomyopathy
restrictive cardiomyopathy
infiltrative process that results in fibrosis and thickening of myocardium d/t fibrotic infiltration into the myocardium, endocardium, and sub endocardium, which decreases ventricular stretch
restrictive cardiomyopathy
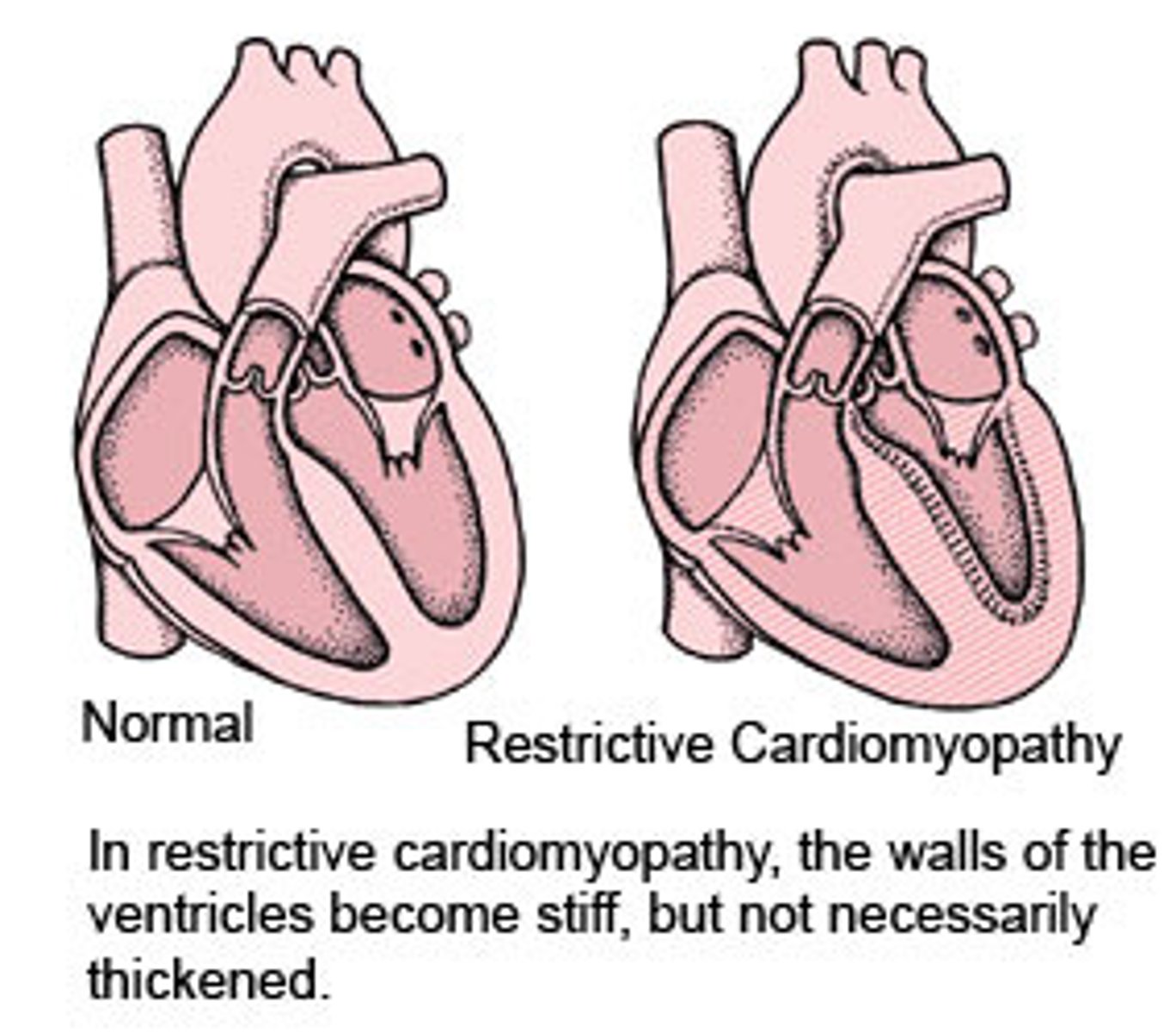
restrictive cardiomyopathy s/s (6)
1) CHF
2) cardiomegaly
3) refractory dysrhythmias
4) fatigue
5) persistent cough
6) activity intolerance
restrictive cardiomyopathy treatment (6)
1) Na restriction
2) pacemaker
3) AICD
4) diuretics
5) vasodilators
6) symptom management
patient education for restrictive cardiomyopathy
- disease
- medications
- diet
- exercise
- smoking cessation
- s/s to monitor/report
- daily weight
- support groups
- possible transplantation
What does AICD stand for?
Automated internal cardioverter defibrillator
What does and AICD do?*
- recognizes ventricular arrythmias
- cardiovert or defibs (shocks in HIGHER ENERGY LEVEL)
- ability to pace
- ability to store retrievable data
- implanted like a pacer (lasts 3-5 yrs)
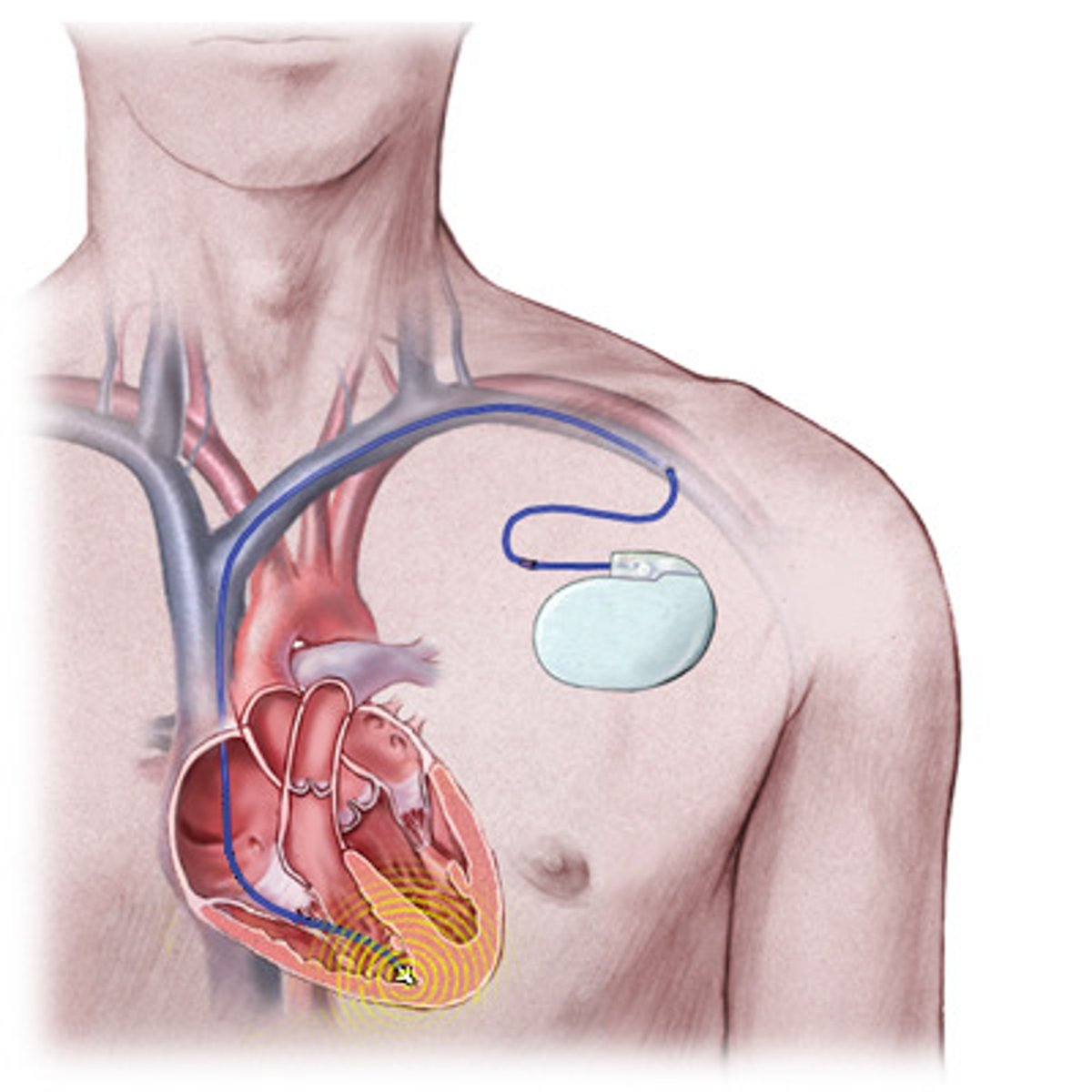
Nursing care for an AICD
- insertion is frightening (induced VF)
- know if device is on/off, place sign
- magnet to turn off
- mild shock w CPR
- follow ACLS
Patient education for an AICD
- extensive
- know difference between MI and cardiac arrest
- call MD/keep a diary
- driving, cell phones, MRI, arc welding
- shock (self and others)
a bridge to a transplant that takes over or assists the pumping role of the left ventricle
left ventricular assist device (LVAD)
a device that preserves perfusion by taking over both ventricles and valves; bridge to transplant for people who don't respond to treatment; imminent death likely
artificial heart
a device that is intended for people not eligible for heart transplantation; unlikely to live longer than one month without direct intervention
totally implanted permanent artificial heart
when the heart valves that move the blood efficiently through the heart chambers do not fully "open" or "close" distal perfusion to the heart and tissues is impaired, which puts a strain on the myocardium; aortic and mitral volves most commonly affected
valvular heart disease
two types of valvular lesions
1) stenotic
2) regurgitant
which valve disease causes a decrease in the blood flow from the left ventricle into the aorta and systemic circulation; causes increased left ventricular pressures causing left ventricular hypertrophy
aortic valve disease
aortic stenosis etiology
1. Congenital bicuspid aortic valve
2. Rheumatic aortic valve disease
3. calcific (senile) aortic stenosis
s/s of aortic valve stenosis
- chest pain
- sudden death from exertion (4%)
- syncope d/t decrease in CO
- fatigue
- nocturnal dyspnea
- palpitations
- systolic murmur
how is aortic valve stenosis diagnosed?
- echo- shows thick calcified valve and heart chamber size
- CXR- shows dilation of aorta
- EKG- reflects heart thickening
- heart catheterization- gold standard for knowing severity
aortic valve stenosis management
- Close observation (new onset), annual echocardiogram
- Avoid strenuous exercise
- Valve infection concern so antibiotic therapy prior to procedures.
- Significant stenosis will need balloon valvuloplasty or aortic valve replacement
When some of the blood that was just pumped out of the hearts left ventricle leaks back into it; can develop suddenly or over decades; has a wide variety of causes
aortic regurgitation
aortic regurgitation s/s (8)
1) fatigue and weakness with exertion
2) SOB w/ exertion or when lying flat
3) angina during exercise
4) syncope
5) arrythmia
6) heart murmur not commonly heard
7) heart palpitations
8) ankle/foot edema
aortic regurgitation treatment
- early surgical intervention recommended
- LVED pressure reduction
- dobutamine/primacor
- prevent infection
- in sever cases, IABP
when the leaflets of the mitral valve are weakened, causing blood to leak backward into the left atrium of the heart; the most common cause is valve prolapse in which the leaflets bulge back into the left atrium as your heart contracts
Mitral valve regurgitation
when the mitral valve becomes stiff or scarred. fails to open completely during diastolic filling
mitral valve stenosis
types of mitral valve disease
1) Mitral valve regurgitation
2) mitral valve stenosis
mitral valve regurgitation s/s
mild and progresses slowly
- murmur
- SOB on exertion or lying down
- fatigue especially with exertion
- lightheadedness
- cough, at night or when lying down
- heart palpitations
- pedal edema
- excessive urination
mitral valve regurgitation management*
- restrict activities that produce fatigue/dyspnea
- diuretics for preload reduction
- meds: ACE inhibitors, nitrates, digitalis for chronic patients
mechanical valves vs tissue valves
mechanical valves
1) increase durability
2) need anticoag therapy forever
3) used in clients <65 y.o.
Tissue valves
1) from porcine or bovine
2) NO anticoag therapy
3) don't last as long
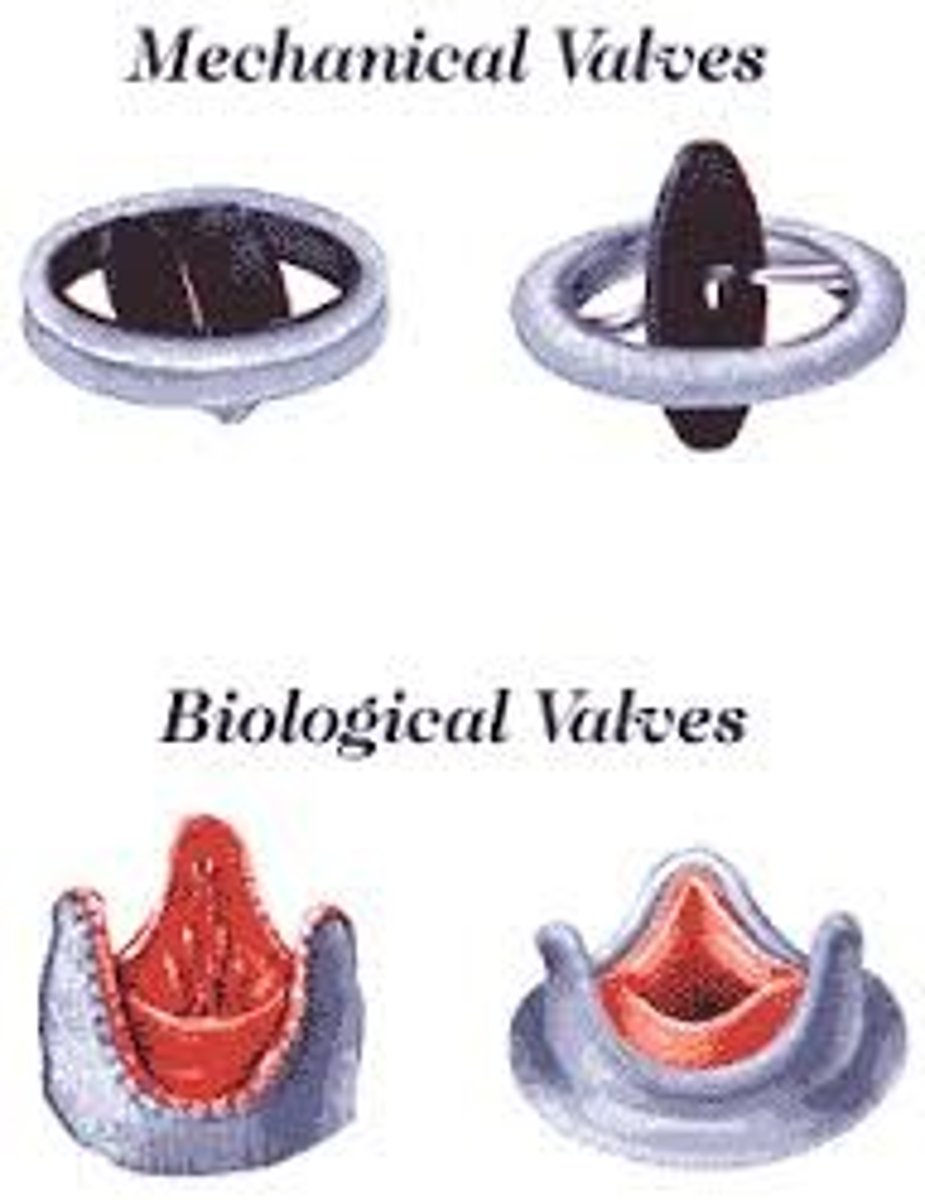
mitral valves stenosis management
- blood thinners
- mitral valve repair/replacement
- percutaneous balloon valvuloplasty (unless calcium buildup or clot present)
- abx pre procedures
priorities of care for valvular heart disease
- refer to POC for cardiomyopathy
- maintain adequate CO
- optimize fluid balance
- provide patient education
an inflammation on the endothelial surface of the heart; can be related to infectious or non-infectious sources; 4th most common cause of life-threatening infectious syndromes
infective endocarditis
Who is at risk for infective endocarditis
- pt with congenital dosease
- valvular heart disease
- prosthetic heart valves
- PMR/ AICD
- body piercings
- IV drug use
- degenerative valve disease
common pathogens in infective endocarditis
streptococcus, staphylococcus, enterococci
complications of infective endocarditis
- HF
- stroke- emboli
- pulmonary embolism
- embolisms of the liver, spleen, kidney, abdominal mesenteric artery, and peripheral vessels
Medical management of infective endocarditis
- IV anti-microbial therapy for 4-6 weeks
- cardiac surgery
- discharge with home abx therapy
Nursing management for infective endocarditis
- timely antimicrobial administration
- prevent complications
- provide pain meds
- individualize pt education
most common indication for a pacemaker*
cardiomyopathy
primary d/c teaching for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients*
promote oxygenation
Aortic valve complications*
1) pulmonary HTN
2) rheumatic fever group A strep
effects of DHF on hemodynamics with increased LVEDP? (including during exercise)
- increased LVEDP= decreased LVEDV
- during exercise: increased LVEDP = low SV and CO
what is the difference between the myopathies in cardiac anatomy?*
1) dilated- ventricles enlarge
2) hypertrophic- ventricles thicken and become stiff
3) restrictive- ventricles become stiff but not thick
Most important class of med in CHF*
ACE inhibitors