Chapter 2: Anatomy and Physiology Marieb - Anthony Morgan St
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
matter
anything that occupies space and mass
energy
the capacity to do work
kinetic energy
energy in action
potential energy
stored energy that has potential to do work but is not doing so
Name and define four types of energy and give examples of where they can be found in the body
chemical energy (breaking or forming of chemical bonds, e.g. digestion to create ATP); electrical (movement of charged particles e.g. nervous system uses nerve impulses); mechanical (energy involved in moving matter e.g. moving muscles to run); electromagnetic (wave energy e.g. x-rays and ultraviolet rays to make vitamin D)
Energy conversions
Not very efficient, and a lot of supply lost as heat. ex. lightbulbs emit light and heat
elements
substances that can't be broken down into simpler substances
4 elements prevalent in body
CHON
atoms
Building blocks of matter
atomic symbol
first letter(s) of elements name ex. Ca stands for calcium
Protons
Positive charge subatomic particle (1 amu)
neutrons
neutrally charged subatomic particles (1 amu)
electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles (0 amu)
Why are atoms electrically neutral?
Same number of protons and electrons
orbitals
regions around nucleus in which electrons are to be found most of the time
atomic number
number of protons in nucleus
mass number
masses of the protons and neutrons
isotopes
same number of protons but different number of neutrons
atomic weight
average of all relative abundance mass numbers of all isotopes / number of isotopes
radioisotopes
isotopes that are unstable that decompose into stable forms, used in cancer research to localize and illuminate damaged tissue
molecules
combination of two atoms of the same element held together by chemical bond
compound
two or more different kinds of atoms binding e.g. H2O
Mixtures
PHYSICALLY INTERMIXED not chemically intermixed unlike compounds
solutions
homogenous mixtures of components, substance present in largest amount is solvent (dissolving medium), smaller amount is solute, naturally transparent and don't scatter life
What is the units of a solution
percent (parts per hundred percent) or milligrams per deciliter, or molarity (moles per liter indicated by M)
mole
molecular weight (sum of atomic weights) weighed out in grams
colloids
heterogenous mixtures, solute particles are larger. cytosol is a colloid
suspensions
heterogenous mixture with large solutes that settle out. blood is a suspension
valence shell
outermost shell of atom with electrons
octet rule
atoms react by gaining or losing electrons so as to acquire the stable electron structure of a noble gas, usually eight valence electrons
ionic bond
atoms formed by transfer of one or more electrons. Atom that gains one or more electron is the electron acceptor (anion negative charge), and atom that loses electrons is the electron donor (cation and has positive charge)
Describe ionic bond NaCl
Na has one electron in valence, Cl has 7 electrons in valence. Na is the electron donor and gives electron to Cl, and Cl is electron acceptor. most ionic compounds are salts.
Covalent bonds
shared electrons produce molecules that occupy single orbital common to both atoms. single covalent bond is when two atoms share one pair of electrons. some atoms share two or three electron pairs and these are double and triple covalent bonds
Polar vs non polar-covalent bond
unequal sharing of electrons (slight negative change at one end of molecule, slight positive charge at other end-- dipole) vs equal sharing of electrons (charge balanced among atoms)
electronegative vs electopositive
electronegative hog electrons and gain them due to valence shell with 6,7 electrons, and electropositive tend to lose valence shell electrons
hydrogen bonds
attractions rather than two bonds, ex. oxygen from one H2O attracts hydrogen from another so they cling together forming surface tension
chemical reaction
when bonds are formed, rearranged, broken
chemical equation
reactants --> products in equilibrium
synthesis reaction
anabolic activities such as joining small molecules into large protein molecules
decomposition reaction
broken down into smaller molecules (catabolic)
exchange or displacement reactions (give example)
both synthesis and decomposition e.g. ATP to ADP reaction; redox reaction. reactant losing electrons is the electron donor and is oxidized. reactant taking up electrons is electron acceptor and is reduced.
exergonic reactions
A chemical reaction associated with the release of energy to the surroundings, oxidative and exergonic
endergonic reactions
chemical reactions that require energy, typically anabolic
chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, the state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, so that the relative concentrations of the reactants and products do not change with time.
What influences the rate of chemical rxns
temperature (higher faster), concentration (higher faster), particle size (smaller faster), presence of catalysts e.g. enzymes
biochemistry
study of chemical composition and reactions of living matter
organic compounds characteristics
contain carbon, covalently bonded, large
inorganic
water, salts, acids, bases
Why is water so useful to life
high heat capacity (low resistance to temperature changes), high heat of vaporization (efficient cooling while sweating), universal solvent, it is important reactant in body with respect to hydrolysis (add water to break bond) and dehydration synthesis (remove water to make bond), and cushioning around organs
salts
ionic compounds containing cations other than H+ and OH-. they dissociate in water and conduct electricity. electrolytes help with nerve impulse and muscle contratction
acids
releases hydrogen ions and is just a hydrogen nucleus, called proton donors because they release hydrogen ions and anions.
e.g HCl--> Cl- + H+
bases
proton acceptors and they take up hydrogen ions. They dissociate to form hydroxyl ions and cations.
e.g. NaOH --> OH- + Na+ and OH- + H+ -> H2O . bicarbonate ion and ammonia (waste product) are found in body
pH units
more hydrogen ions more acidic, more hydroxyl ions more basic. 7 is neutral.
strong acids
strong acids: dissociate irreversibly and completely in water and dramatically change the pH
Buffer
They resist changes in pH by releasing H+ ions when pH increases and binding H+ when pH decreases. Homeostasis of acid base balance is regulated by kidneys and lungs by buffers. Weak acid and conjugate base or weak base and conjugate acid.
weak acids
weak acids: partial dissociation, only some dissociate fully into ions and others don't. e.g. acetic acid
100 HAc--> 90 HAc + 10 Ac- + 10 H+ ; also HAc ⇌ Ac- + H+
When you add H+ to the acetic acid solution, some of ti combines with Ac- and goes to HAc. When you add strong base, equilibrium shifts to teh right and more HAc molecules dissociate to release H+
It's a buffer system.
strong base
hydroxides dissociate easily in water and tie up H+, like hydroxides
What happens when acids and bases are mixed?
react in displacement to form water and salt. It neutralizes the solution.
weak base
ionizes incompletely and reversibly and accept only a few protons
carbonic acid-bicarbonate system
H2CO3 ⇌ HCO3- + H+
weak acid weak base proton
When pH rises, the rxn shifts right and carbonic acid dissociates and releases protons, when pH lowers, rxn shifts left and as bicarbonate ions bond with protons
exceptions to generalization of organic compounds
Carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide are considered inorganic compounds
electroneutral
carbon never loses or gains electrons, only shares them, can join long rings in the body
polymers
chainlike molecules made up of units called monomers which are joined in dehydration synthesis
carbohydrates
sugars and starches that contain CHON, larger the carbohydrate molecule the less soluble
monosaccharide and give examples
simple sugar, single chain, single ring structure. pentose (deoxyribose) and hexose (glucose, galactose, fructose) sugars are examples of monosaccharides
isomers
same molecular formula, different arrangements of atoms. galactose and fructose are isomers of glucose
disaccharide and give example
double sugar formed from two monosaccharides from dehydration synthesis, can't move through membranes so they break apart by hydrolysis (sucrose, lactose, maltose)
sucrose = which two monosaccharides
lactose = which two monosaccharides
maltose = which two monosaccharides
glucose + fructose
glucose + galactose
glucose + glucose
polysaccharides and give examples
large polymers of simple sugar, fairly insoluble. Starch is storage carbohydrate and cellulose is a polysaccharide. in animals it is glycogen (storage for animals in muscle and liver cells)
functions of carbohydrates
energy storage that is ready and useable
Properties of lipids and name three main types
insoluble in water. types include triglycerides, phospholipids, steroids. don't have much oxygen in comparison
Another name for triglycerides
Neutral fats
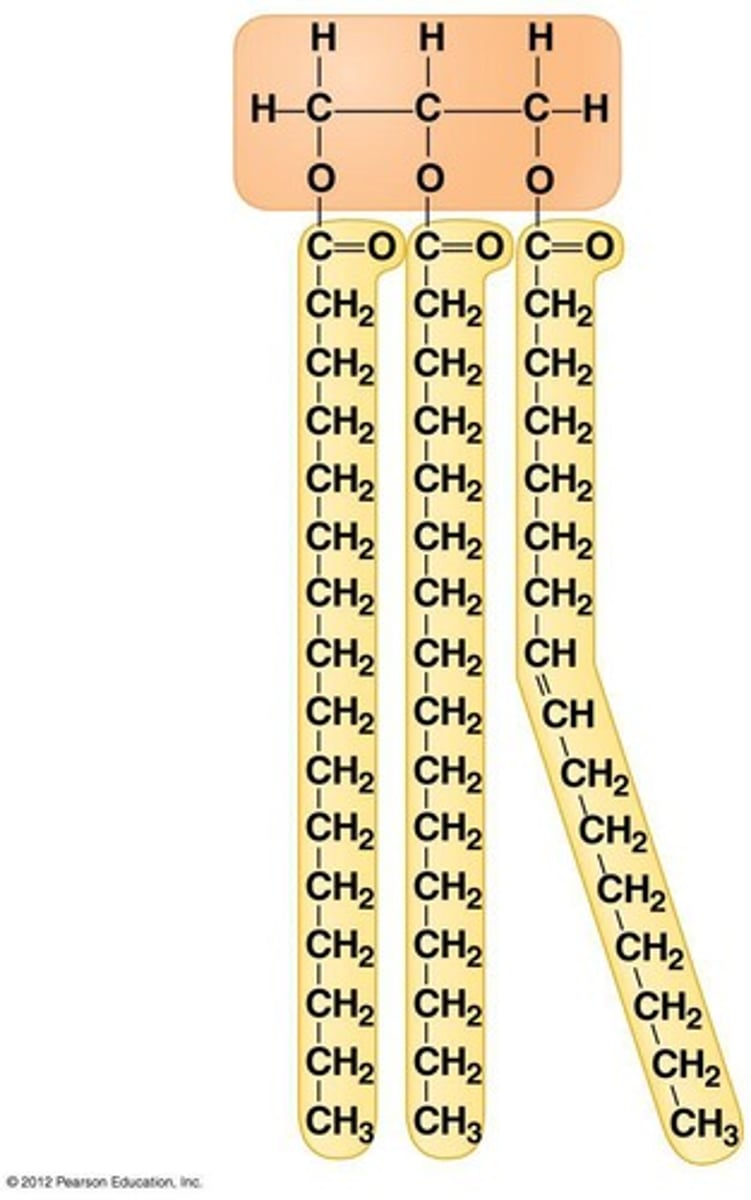
triglyceride
fats when solid, oil when liquid. Made up of fatty acids and glycerol in 3:1 ratio. MOST efficient and compact form of stored energy. found mainly beneath skin and insulate from heat loss, and protect from trauma. can be saturated or unsaturated
fatty acids make up?
Fatty acids are linear chains of hydrocarbons and an organic acid group (-COOH) at one end.
glycerol make up?
glycerol is a modified simple sugar (sugar alcohol)
How are triglycerides made?
dehydration synthesis to attach fatty acid chains to glycerol
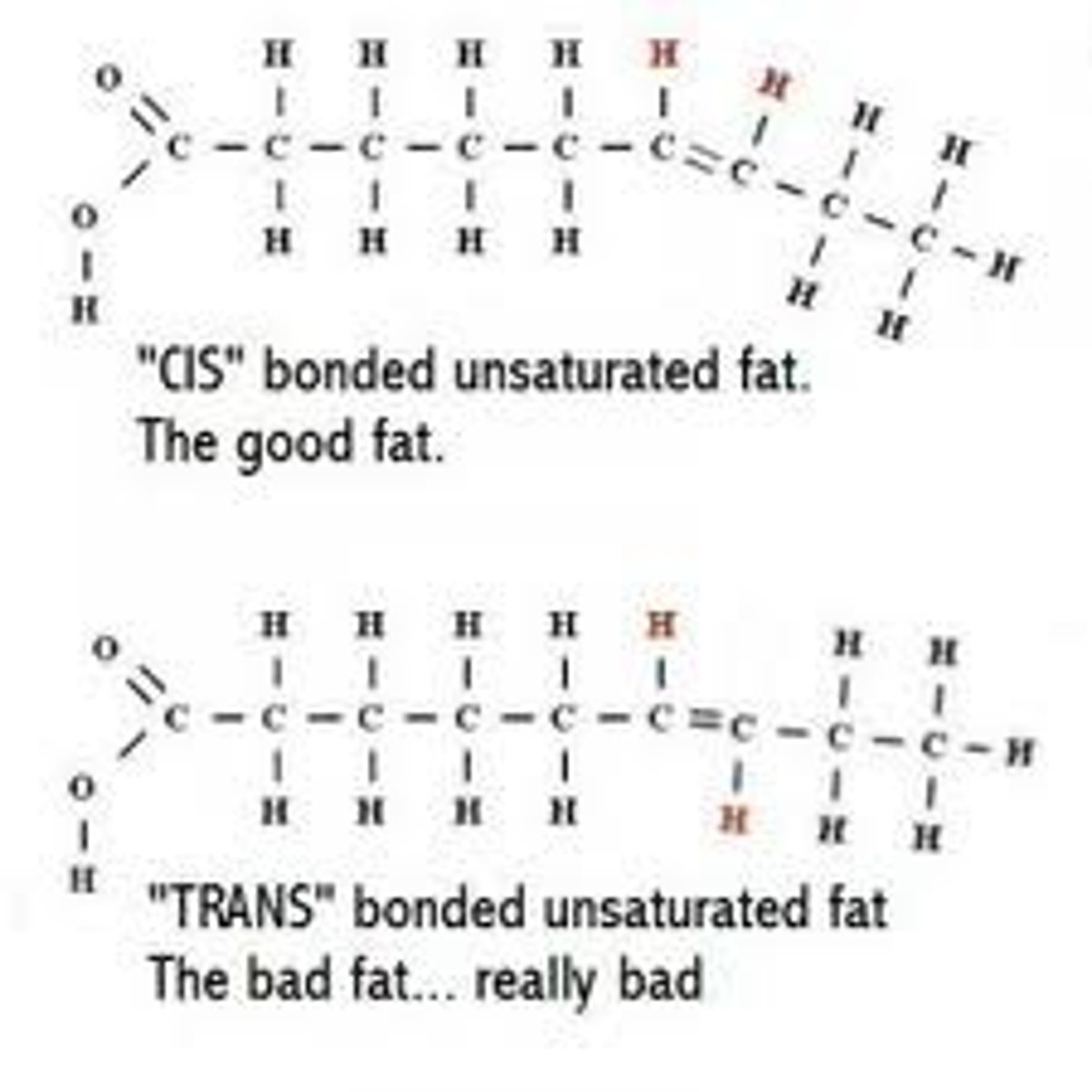
Properties of saturated fatty acids
solid at room temperature. single covalent bonds only, and completely straight. mostly found in animal fats.
Properties and types of unsaturated fatty acids
2 types, mono and polyunsaturated). Double covalent bonds between carbon atoms that cause them to kin, remain liquid at room temperature. found in plants.
Trans fats
oils that have been solidified by addition of H atoms at sites of carbon double bonds. Increase risk of heart disease.
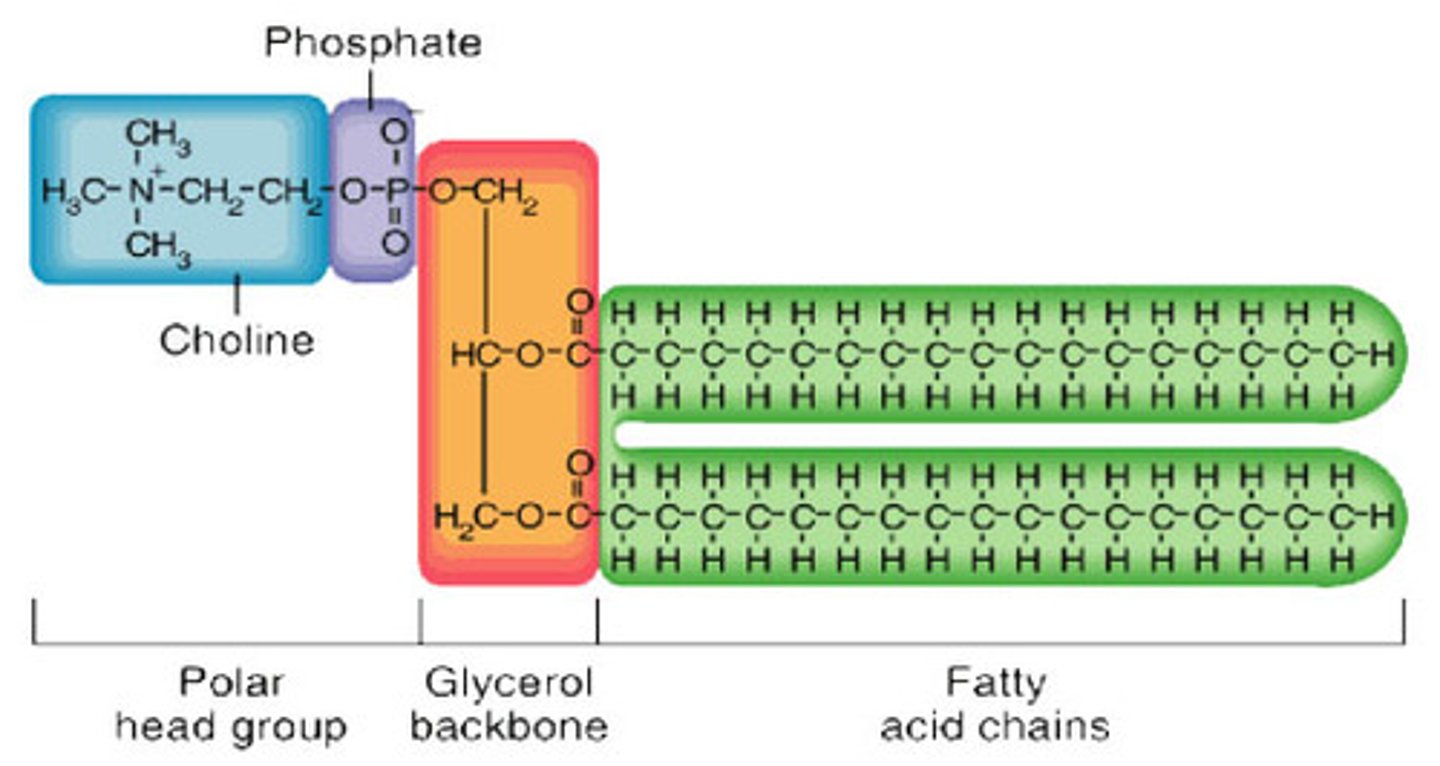
Phospholipids make up and where you can find in body
phosphorous containing group called the polar head + glycerol back bone + 2 fatty acid chains. hydrocarbon portion is nonpolar tail, and phosphorous containing head is polar and attracts water and ions. it is used in cell membranes (e.g. phospholipid bilayer)
Steroid make up and where to find them in body
flat molecules of four interlocking hydrocarbon rings. fat soluble and contain little oxygen. example is cholesterol. found in cell membranes and vital to homeostasis.
Eicosanoids
diverse lipids from 20 carbon fatty acid chain. most important is prostaglandins which play roles in blood clotting, regulation of blood pressure, labor contractions etc
Proteins
structural material of body (e.g. keratin in skin and nails, muscles), enzymes, hemoglobin, insulin. contain CHNOPS (only proteins have nitrogen)
Amino acids and make up
building blocks of protein. Made up of amine group (NH2), a functional R group and organic acid group -COOH. They can act as either an acid (proton donor) or base (proton acceptor).
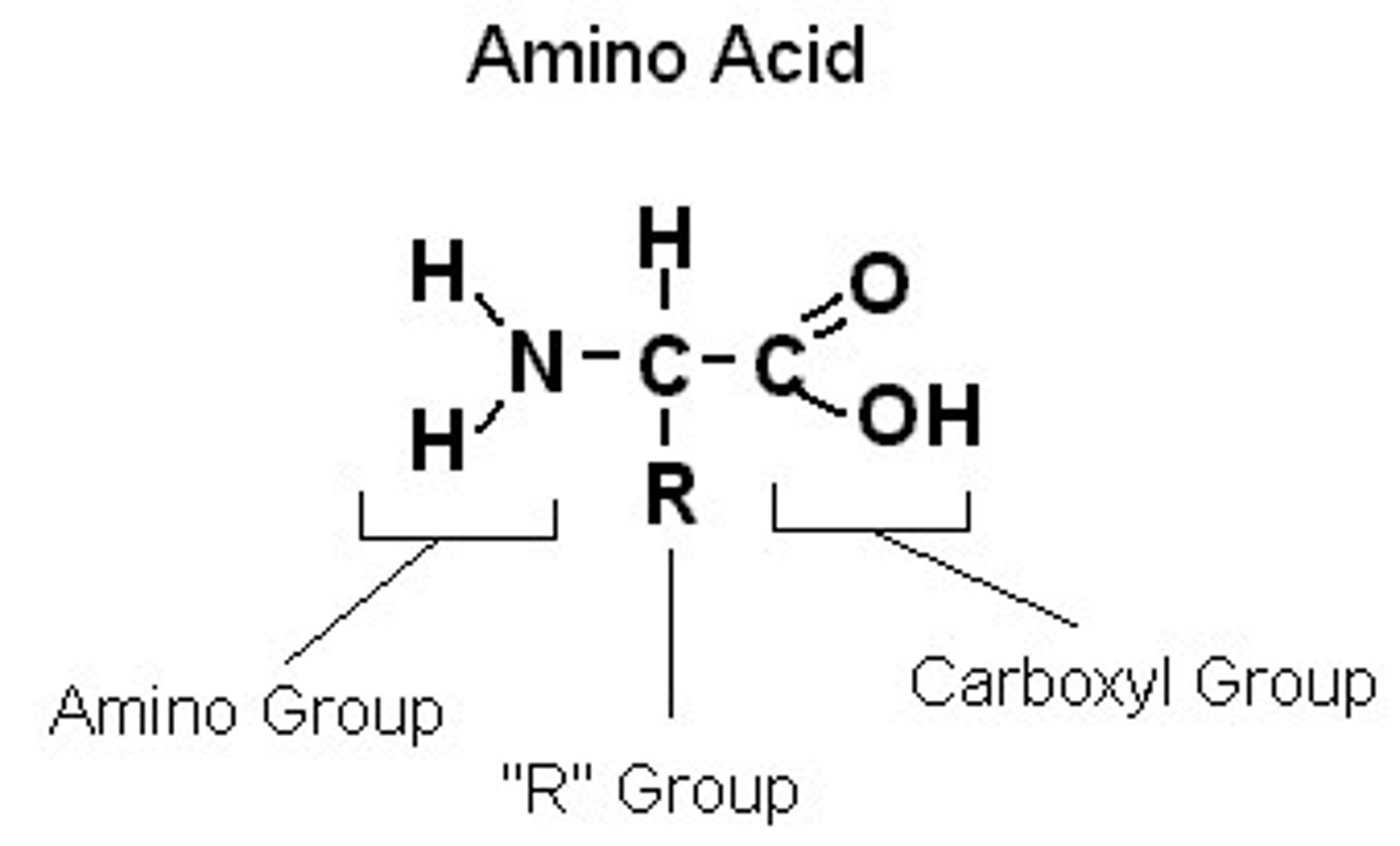
What makes amino acids chemically unique
differences in the R group
Peptide bond
Long changes of amino acids joined together by dehydration synthesis. Amine is linked to -COOH in the next. Two joined is dipeptide, 3 is tripeptide, 4+ is polypeptide, 50+ is a protein
macromolecules
most proteins are large and complex containing from 100 to 10,000 amino acids joined by peptide bonds in which amine is connected to carboxylic acid via dehydration synthesis
How many amino acids are there?
20. Using some combination of these, thousands of different types of proteins are constructed
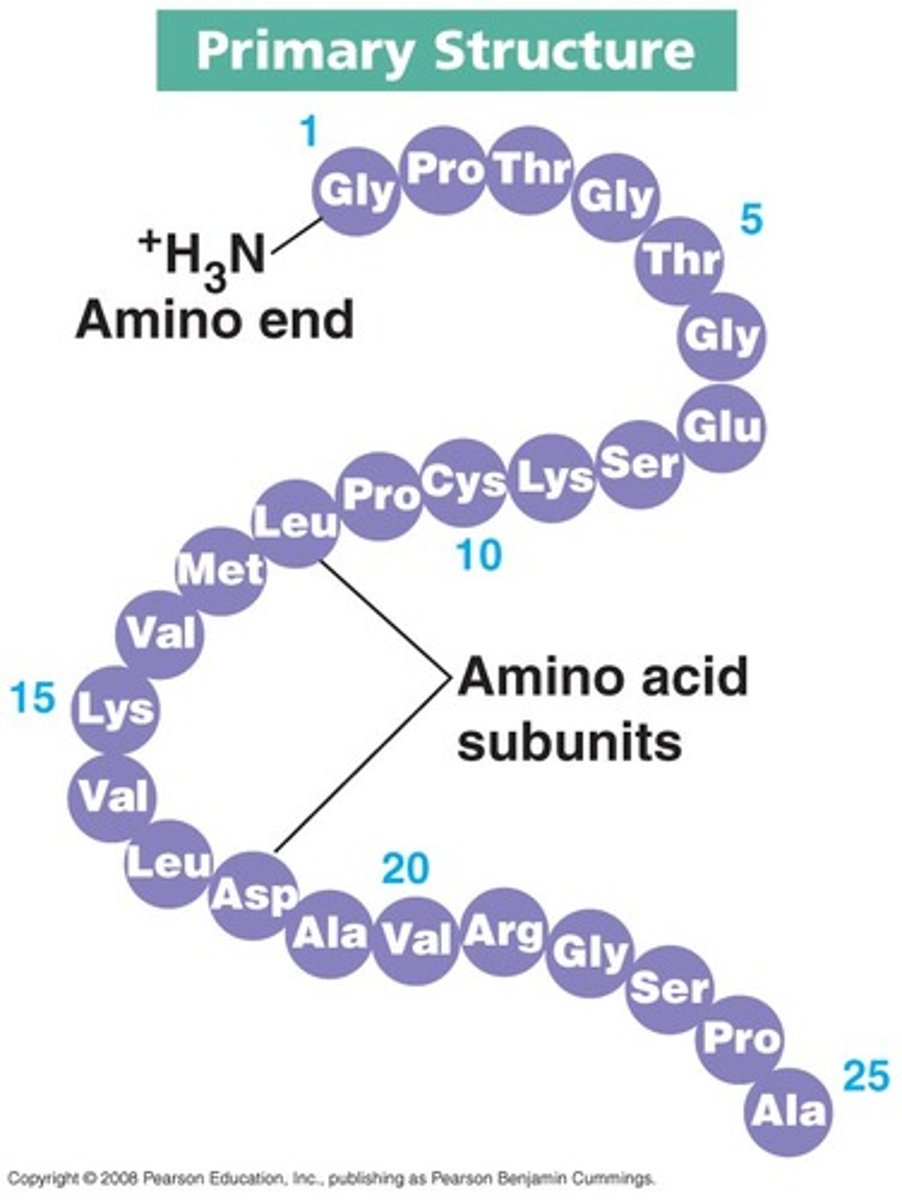
Primary structure of protein
amino acid beads are the backbone of protein molecule
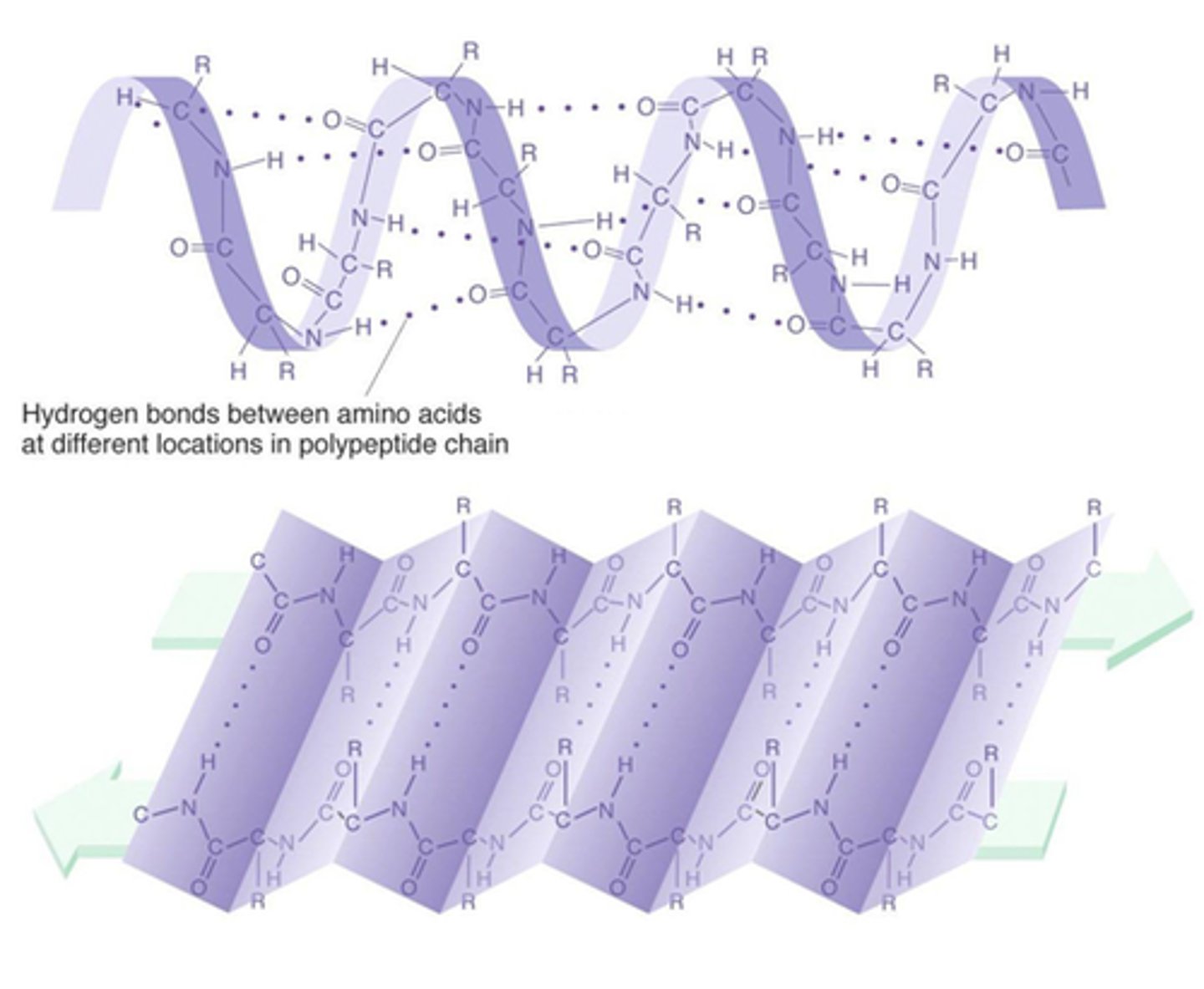
Secondary structure of proteins
Alpha helix (primary chain coiled to form spiral structure stabilized by hydrogen bonds). and beta sheets (primary chain zig zags forming pleated sheet and adjacent strands are held together by hydrogen bonds).
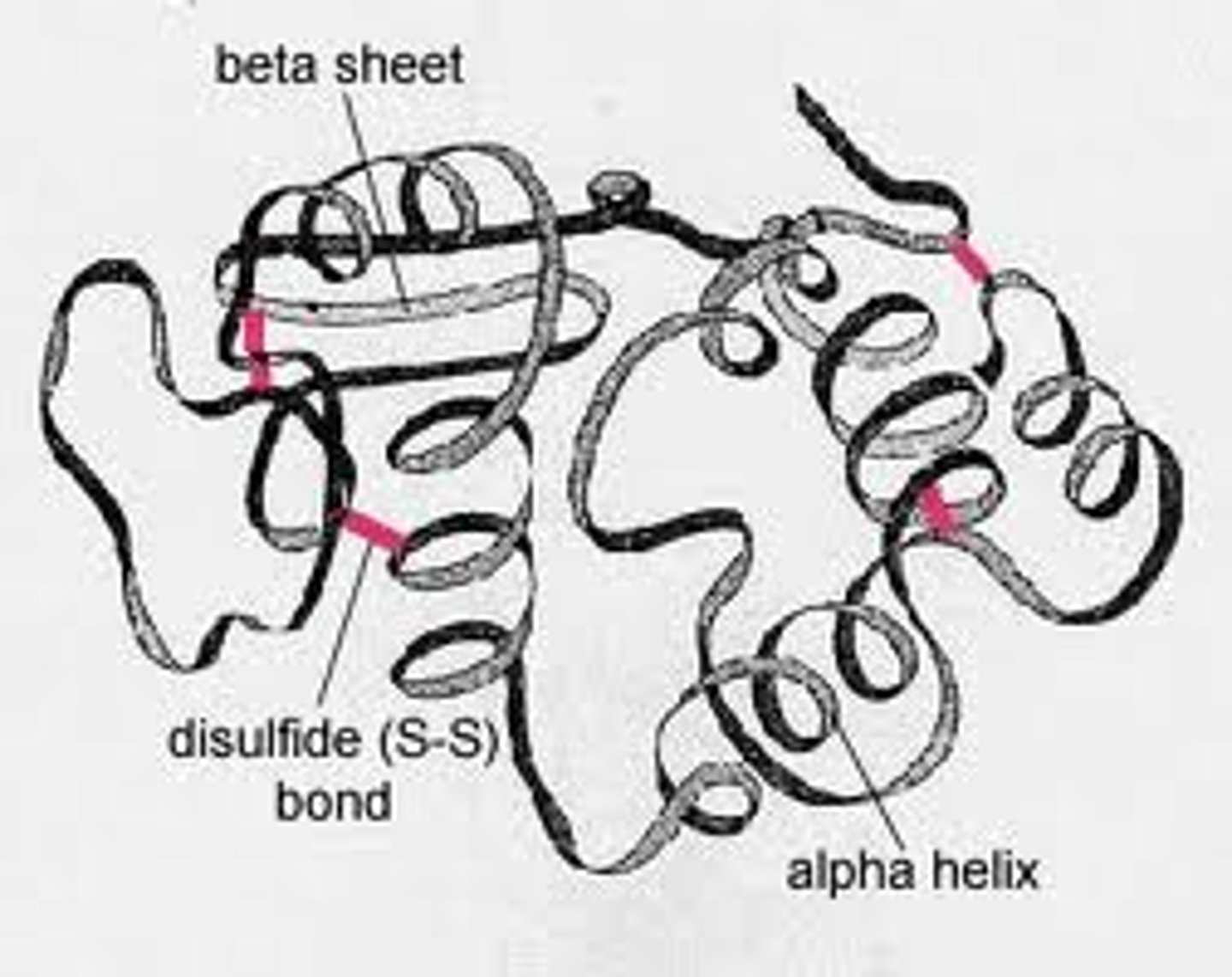
tertiary structure
A helical or B pleated sheets of the polypeptide chain fold to form a compact globular molecule. Structure maintained by both covalent and hydrogen bonding
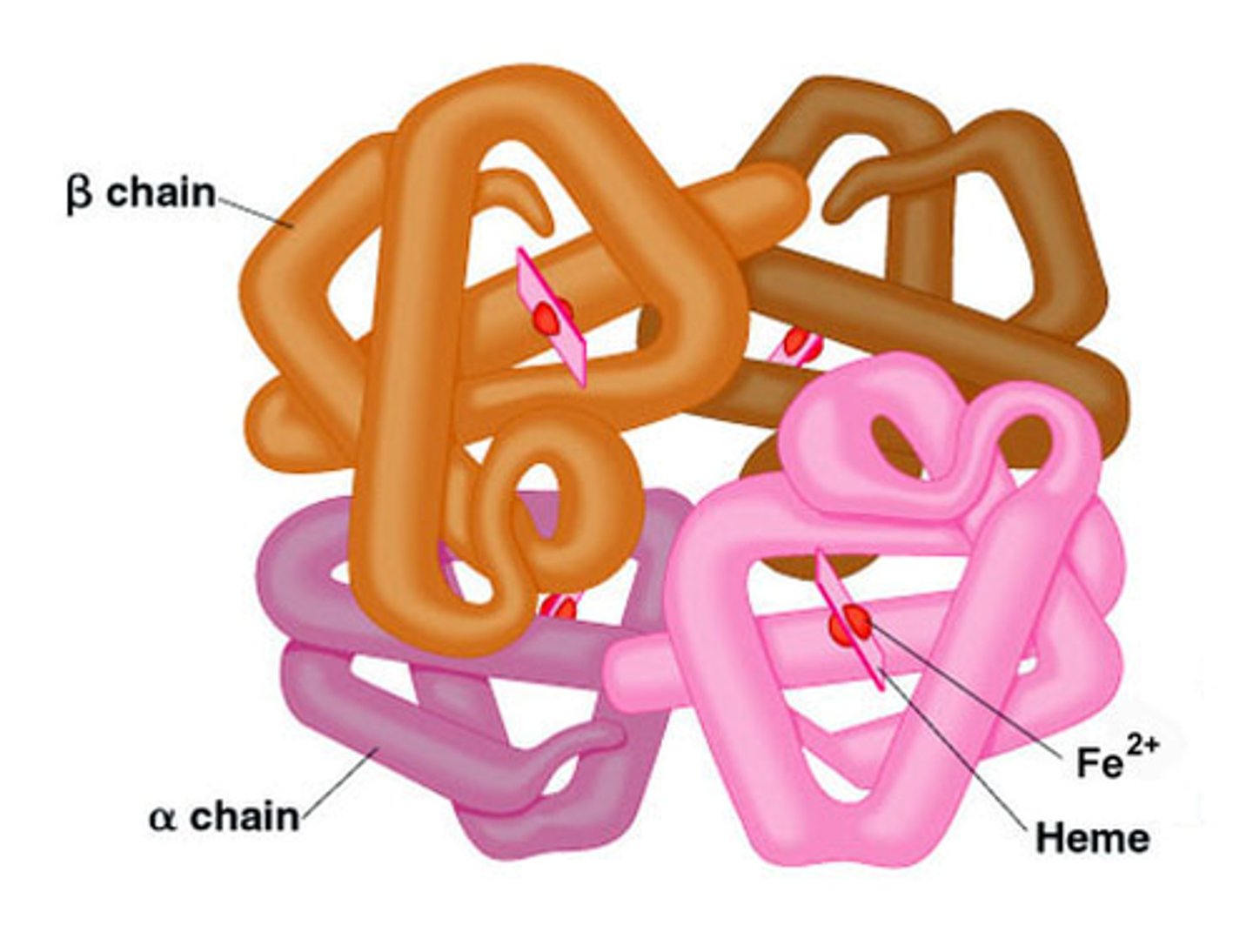
Quaternary structure
two or more polypeptide chains with tertiary structure combine to form functional protein
Fibrous proteins and another name for them
also called structural proteins. extended and strand like. insoluble and stable. some secondary structure, and most have tertiary or even quaternary structure as well. collagen, keratin, elastin, and contractile proteins of muscle
globular proteins and another name for them
functional proteins. have at least tertiary structure. water soluble, chemically active and unstable. prone to denaturation. examples include antibodies for immunity, enzymes like amylase in saliva to breakdown starch, hemoglobin for oxygen transport in blood, albumin for regulation of pH, molecular chaperones to create new proteins and breakdown damaged ones
Factors causing denaturation
hydrogen bonds are fragile and can break easily due to low pH, high temperature and loses its shape and functionality
Denaturation
Can be restored, but if its too damaged then it can't be cured. For globular proteins, the active sites can be destroyed and they no longer work. if blood ph to acidic, hemoglobin will not be able to bind and transport oxygen.
molecular chaperones
Molecular chaperones aid folding of new proteins in both healthy and damaged cells and transport of metal ions into and within the cell. They also promote breakdown of damaged protein. ex. stress proteins produced in variety of traumatizing stimuli and can patch up damaged proteins and refold them
Enzymes
biological catalysts that accelerate rate of biochemical reactions but are not used up. they lower the activation energy (energy amount required to break bonds of reactant) required for a reaction.
two parts of enzyme, what is it called? what are the two parts.
collective is called holoenzyme. there is apoenzyme (protein portion) and cofactor (metal ion like copper or iron) /coenzyme (usually vitamins)
substrate
substance on which an enzyme acts