Enterprise Data Management: DBMS Architecture and Types
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the main focus of Chapter 2 in the course?
The architecture and classification of Database Management Systems (DBMSs).
What are the key components of a DBMS architecture?
Key components include user privilege verification, database connection setup, DDL parsing, and query processing.
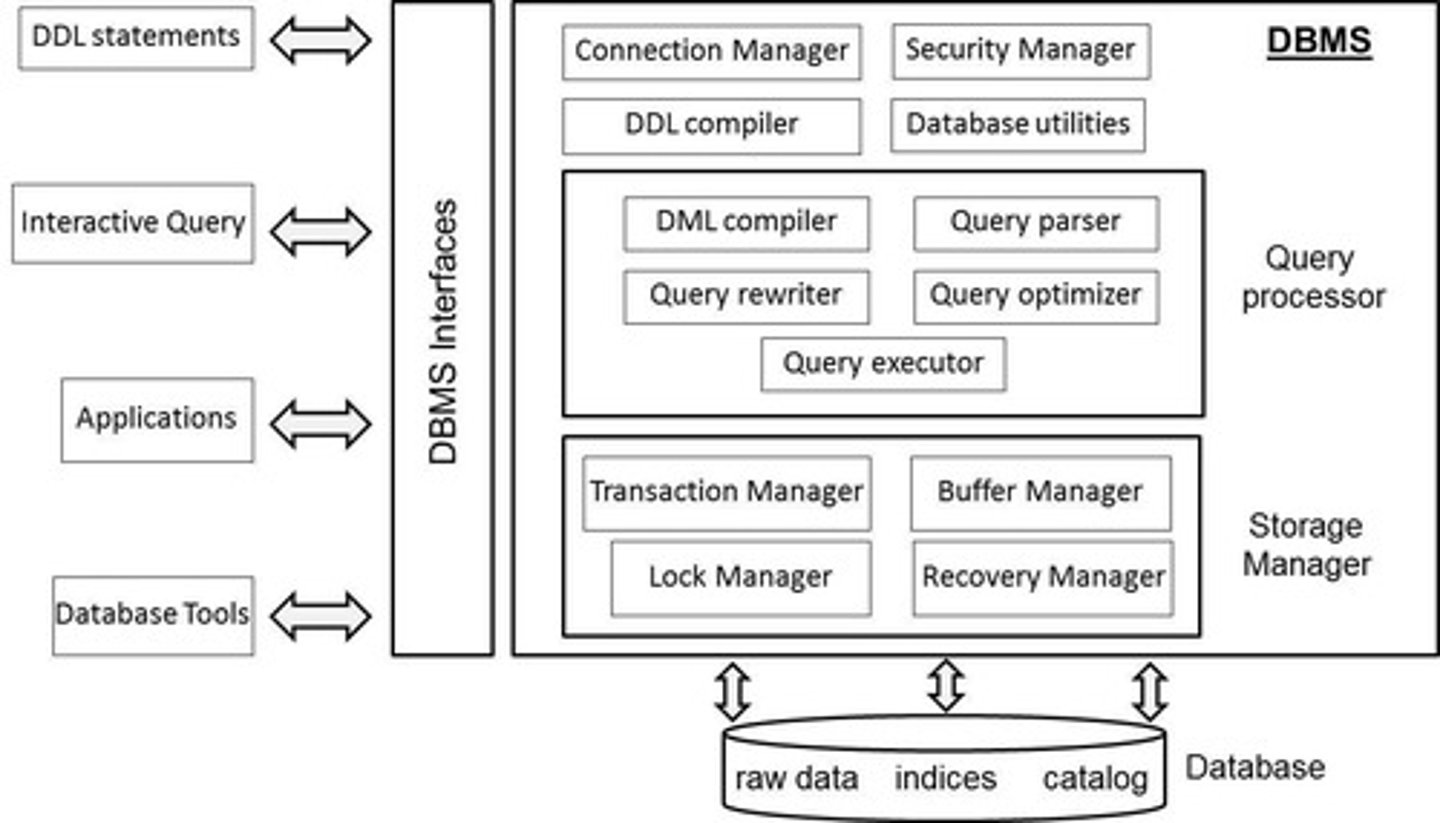
What is the role of the Query Processor in a DBMS?
It assists in executing database queries, compiling DML statements, optimizing queries, and executing them.
What does the Storage Manager do in a DBMS?
It governs physical file access, supervises data storage, manages transactions, and ensures concurrency control.
What are some types of DBMS interfaces?
Types include web-based interfaces, stand-alone query language interfaces, command-line interfaces, and graphical user interfaces.
What were the early database applications based on?
They were based on hierarchical and network models, which dominated during the 1960s and 70s.
What is a characteristic of the relational data model?
It features a strict separation between logical and internal data models and uses SQL for querying.
What are Object-Oriented DBMSs (OODBMSs) designed for?
They are designed for complex data processing in applications like CAD.
What is the significance of XML in modern databases?
XML is used to store data and has led to the development of XML-enabled DBMSs.

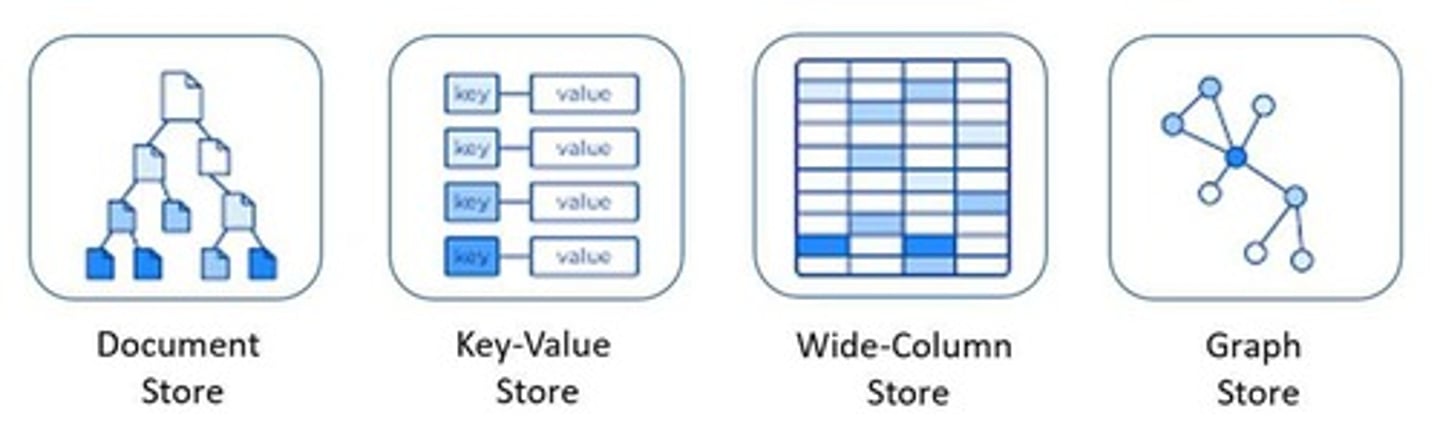
What are NoSQL databases primarily used for?
They are targeted at storing big, unstructured data and focus on scalability.
What is the difference between OLTP and OLAP?
OLTP manages operational data with many short, simple queries, while OLAP uses operational data for decision-making with fewer complex queries.
What is a characteristic of mobile DBMS?
They run on mobile devices, are always online, and have a small footprint.
What does a centralized DBMS architecture entail?
Data is maintained on a centralized server, with all queries processed by a single host.
What is the purpose of a federated DBMS architecture?
It provides a unified interface to multiple underlying data sources.
What is the role of the dispatcher in a multi-user DBMS?
It manages incoming connections to the database server.
What is the focus of new functionalities being added to DBMSs?
They include support for scientific applications, multimedia, data warehousing, and complex data structures.
What is the main advantage of in-memory DBMS?
It stores all data in internal memory for real-time processing.
What is the next topic to be covered in the course?
The next lecture will cover Conceptual Data Modeling.
What is the purpose of the data loading and reorganization utility in a DBMS?
It helps with performance monitoring, user management, backup, and recovery.
What is a key feature of the hierarchical data model?
It organizes data in a tree-like structure.
What is the significance of SQL in relational DBMS?
SQL is a declarative and set-oriented language used for querying relational databases.
What are some examples of NoSQL databases?
Examples include Apache Hadoop, MongoDB, and Neo4j.
What is the function of the log file in a Storage Manager?
It keeps track of database operations for crash recovery.