Law and Social Change: Institutionalization, Elias, State Formation, and Legal Profession
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
What are the two interrelated processes of law as an instrument of social change?
Institutionalization and internalization of patterns of behavior.
What does institutionalization of a pattern of behavior refer to?
The establishment of a norm with provisions for its enforcement.
What does internalization of a pattern of behavior mean?
The incorporation of the value or values implicit in law.
How does law affect behavior directly?
Through the process of institutionalization.
Who was Norbert Elias?
A researcher known for his adventurous theories, often overlooked by North American academics.
What is the title of Norbert Elias's work that is considered offensive?
The Civilizing Process.
What does Elias suggest about interdependent societies?
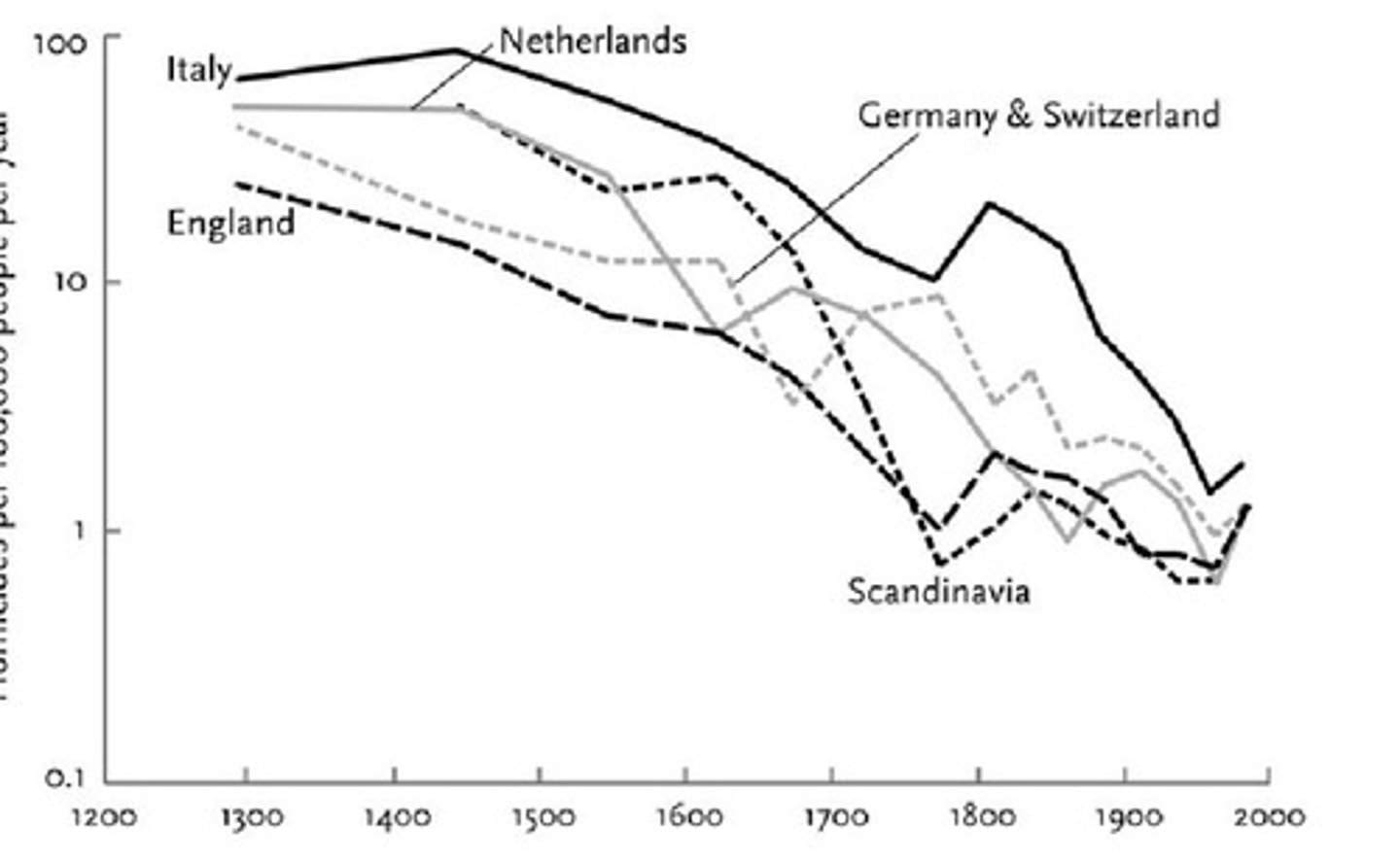
The more interdependent society is, the kinder and more respectful individuals will be to one another.
What was the real land in feudal times according to the text?
The few dozen or hundreds of square miles controlled by local warriors, not the state.
What two classes of people existed in feudal times?
A rich upper class of territorial lords and their warrior associates, and the downtrodden peasantry.
What was the biggest threat to the stability of late medieval and early modern nation-states?
Violent change in leadership.
What are the two main ways an emerging king could be killed?
Internal attack (assassination, regicide) and external attack (being conquered by another nation).
What distinction did kings introduce to protect themselves from internal threats?
The distinction between illegal and legal homicide.
What types of homicide were considered illegal?
Acts like regicide and standard murder.
What types of homicide were considered legal?
Acts supported by the state, like capital punishment and warfare.
What was the significance of the division between illegal and legal homicide?
It ensured that serious laws attracted harsh punishments for crimes like regicide and treason.
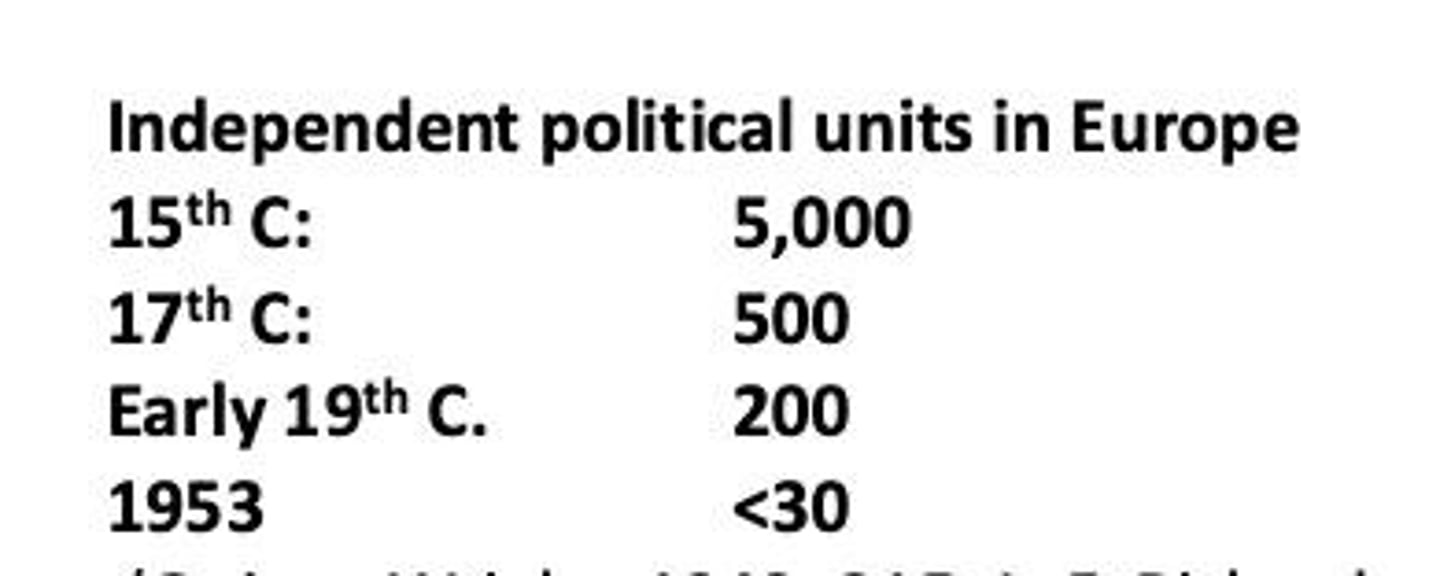
What did the formation of court societies encourage kings to do?
Invest tax into strengthening their military forces.
What was the benefit of forming massive armies?
They were stronger than a band of upper-class knights and increased the king's power.
What did the emergence of the middle class signify?
Successful trading peasants formed a new middle class of merchants and professionals.
How did the middle class adapt to fit into upper-class circles?
They imposed self-restraints on their emotional volatility.
What perception did the French bourgeoisie have of the nobility by the end of the 18th century?
They viewed the nobility as a useless and functionless class.
What ambitions did the upper middle class have regarding the lower class?
To elevate and civilize the lower class through controlling institutions.
Who was Charles-Henri Sanson?
The royal executioner of France during King Louis XVI's reign, executing nearly 3,000 people.
What does the term 'villain' historically refer to?
Originally an inhabitant of a villa, it evolved to mean a deliberate scoundrel or criminal.
What connection does the term 'villain' have to the civilization process?
It reflects the negative connotation of rural dwellers as society evolved.
What period saw the nobility and rising middle class become more emotionally controlled?
Early modern period (1500-1700)
What type of conduct did criminal courts begin to prosecute during the early modern period?
Violent conduct
What were the key emerging differences in values between the nobility and the rising middle class?
Nobility valued honour, prestige, and respect for ceremony; the bourgeoisie valued entrepreneurialism, thrift, temperance, hard work, materialism, and honesty.
What was the 'bloody code' in 18th century England?
A legal code that imposed the death penalty for over 200 offences.
How many offences were punishable by death in England in 1689?
50 offences
How many offences were punishable by death in England in 1776?
Around 200 offences
What was the number of offences punishable by death in England in 1800?
220 offences
What significant legal change occurred under King Henry II regarding crimes?
Crimes such as murder, theft, and robbery became crimes against the state.
What was the median salary for Canadian lawyers in 2016?
$88,000
What is the projected median salary for Canadian lawyers in July 2024?
$116,000
What is notable about the income range for lawyers?
It is unusually large.
What trend has been observed regarding law school education costs?
It has become progressively more expensive.
Who are increasingly finding law school education accessible?
Applicants of little wealth and little or no social prominence.
What professions did the parents of early law entrants typically belong to?
Blacksmiths, farmers, stonemasons, and laborers.
What significant change occurred in the law professions in 1826?
The law professions became progressively more exclusionary.
In what year did a ruling state that women could not become lawyers?
1905.
What was a barrier for minorities in the legal profession historically?
Minorities were unable to find a lawyer to accept them as articling students.
What percentage of law students in Canada were female in 1965?
6%.
What percentage of law students in Canada were female in 2014?
51-52%.
What recommendations were made in 1994 regarding law school admissions?
Law schools should review admission criteria, ensure fair treatment of aboriginal and racialized communities, add diversity to admissions committees, and expose students to critical race theory.
What percentage of visible minorities aged 25-34 were lawyers in Ontario in 2013?
27.5%.
What challenges do women lawyers face compared to their male counterparts?
Women lawyers quit at a significantly higher rate due to low pay, lack of support for maternity leave, and being treated differently by judges.
What is the first method of data collection mentioned in the research?
Historical research.
What are the strengths of historical research?
Excellent for detailing processes that lead to the present and collecting data on topics that cannot be observed.
What is a limitation of historical research?
Uncertainty about the accuracy or truthfulness of documents.
What are the two types of observational research mentioned?
Utilization of human observers and mechanical observers.
What is a strength of observational research?
Provides the opportunity to record information as events unfold.
What is a limitation of observational research?
Not applicable to large social settings and relies on the researcher's memory.
What does experimental research involve?
Manipulation of variables to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
What is a common criticism of experimental research?
It can be too artificial, as it often occurs in controlled laboratory settings.
What are common sources of data in survey methods?
Face-to-face interviews and self-administered questionnaires.
What is an advantage of survey methods?
If the sample is large and representative, results can be generalized to a wider population.
What is a limitation of survey methods?
Low response rates; less than 60% is considered poor.