EXAM 2 BIO 111
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Describe the greenhouse effect
a natural process where certain atmospheric gases, called greenhouse gases, trap heat and keep Earth warm enough to support life
Explain why water is slow to change temperature
water has a high specific heat capacity so it takes large amounts of energy to heat up or cool down
Compare and contrast the water cycle and carbon cycle.
the water cycle primarily focuses on physical state changes of water (evaporation, condensation), while the carbon cycle involves biological and chemical transformations of carbon atoms in living organisms and geological formations. Key differences include that the carbon cycle is central to life and climate regulation through photosynthesis and respiration, whereas the water cycle focuses on providing freshwater and maintaining habitats.
Discuss the origin of fossil fuels and their relationship to the carbon cycle.
Fossil fuels originate from the anaerobic decomposition of ancient plant and animal remains buried under intense heat and pressure over millions of years, forming coal, oil, and natural gas. Their relationship to the carbon cycle involves the removal of carbon from the active cycle for millennia.
State the basic equation of photosynthesis.
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
Describe the light reactions of photosynthesis.
convert light energy into chemical energy by using pigments, primarily chlorophyll, to absorb sunlight within the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
Explain the events that occur during the Calvin cycle, and describe the relationship between the light reaction and the Calvin cycle.
The Calvin cycle uses energy from ATP and NADPH (produced in the light reactions) to convert atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) into sugars, a process that occurs in three main stages: carbon fixation by the enzyme Rubisco, reduction of intermediate molecules, and regeneration of the starting molecule, RuBP. The light reactions provide the essential chemical energy (ATP) and reducing power (NADPH) for the Calvin cycle, while the Calvin cycle regenerates ADP and NADP+ to be used by the light reactions, creating a crucial two-way relationship between these stages of photosynthesis.
Explain the role of stomata in balancing photosynthesis and water loss.
Stomata act as regulated pores, primarily on leaves, that balance the conflicting needs of gas exchange for photosynthesis (carbon dioxide uptake) and water conservation (preventing water loss via transpiration). They achieve this by opening to allow CO2 in for photosynthesis and then closing to minimize water loss, particularly under unfavorable conditions like drought, with guard cells controlling the pore's aperture in response to environmental cues such as light, humidity, and CO2 levels.
Discuss how our own activities contribute to or reduce the risk of global climate change
burning fossil fuels, deforestation, industrial processes, and agriculture. these activities all create greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming.
Describe the cellular basis of cancer
normal cells that acquire genetic mutations that disrupt the normal processes of cell growth, division, and death
Compare and contrast benign and malignant tumors.
benign
non cancerous
grow size
usually harmless
malignant
cancerous
grow rapidly
potentially harmful
List several risk factors for cancer development that are under your control.
avoiding tobacco
eating healthy foods
getting regular physical activity
limiting alcohol consumption
List the normal functions of cell division.
involves the creation of new "daughter" cells from a "parent" cell, ensuring the continuity and maintenance of life at both the cellular and organismal levels.
growth
cell replacement
repair
Describe the structure and function of chromosomes.
thread-like structures in the cell nucleus, made of DNA and proteins (especially histones), that organize and carry the genetic instructions for growth, development, and function
Outline the process of DNA replication.
a semi-conservative process where a DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules, each containing one original and one new strand
******
Describe the events that occur during interphase of the cell cycle.
G1
cell growth
metabolic activity
organelle duplication
protein and RNA synthesis
S
DNA replication
G2
continued growth
protein synthesis for mitosis
quality control
Diagram two chromosomes as they proceed through mitosis of the cell cycle.
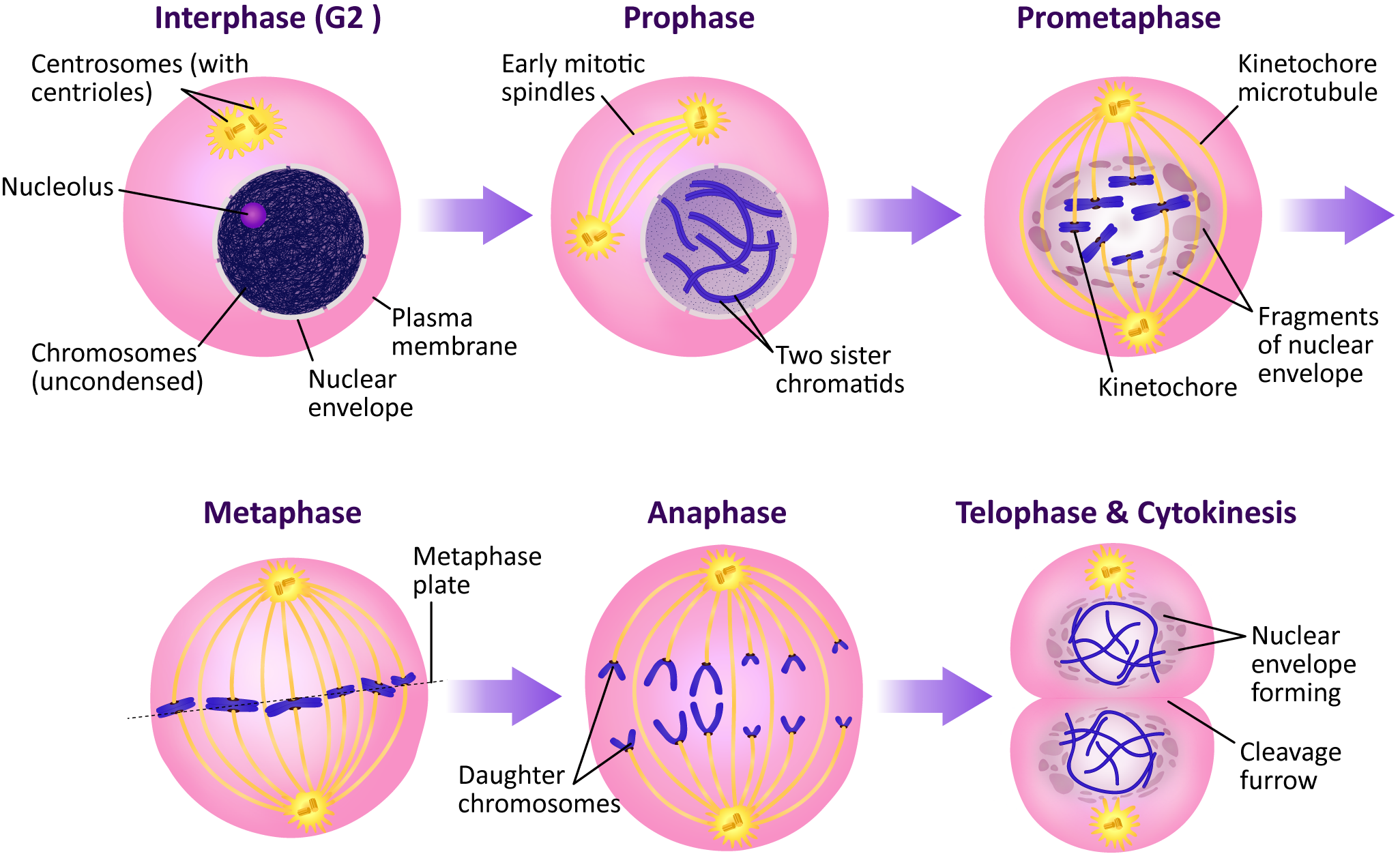
Describe the process of cytokinesis.
the process of cell division where the cytoplasm divides, following mitosis, to form two genetically identical daughter cells
Describe how the cell cycle is regulated and how dysregulation can lead to tumor formation.
the cell cycle is regulated by checkpoints in metaphase (middle), G1(end), and G2(end). (NOT S). Unregulated cell cycles can leave room for error and possible uncontrollable duplication leading to cancerous cells.
Describe why chemotherapy and radiation are used to treat cancer.
chemotherapy: selectively kills duplicating cells
interrupts cell division
prevents resistance to drugs
radiation: use of high-energy particles to destroy
damages DNA of cancer cells to prevent cell division
after surgical removal of tumor
Describe the relationship between genes, chromosomes, and alleles.
Explain why, although each cell in your body contains identical genetic information, the cells produced by your body are different from each other.
Define segregation and independent assortment and explain how these processes contribute to genetic diversity.
Distinguish between homozygous and heterozygous genotypes and describe how recessive and dominant alleles produce particular phenotypes when expressed in these genotypes.
Demonstrate how to use a Punnett square to predict the likelihood of a particular offspring genotype and phenotype from a cross of two individuals with known genotype.
Differentiate incomplete dominance from codominance.
Outline the pattern of inheritance seen in the ABO blood system.
Describe the mechanism of sex determination in humans.
Explain the pattern of inheritance exhibited by sex-linked genes.
Explain the utility of a genetic pedigree.
Explain what types of cells undergo meiosis, the end result of this process, and how meiosis increases genetic diversity.
Explain the significance of crossing over and random alignment in terms of genetic diversity.
Explain how altered meiosis affects fertility.
Explain how the male and female reproductive structures and their functions are important for fertility.
Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis