Exam 3 - Normal Carotid Anatomy & Waveforms
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Transducer used for carotid exams
Linear - low/medium frequency
Small footprints - when catheters present
CCA
Left - from AO arch
Right - from brachiocephalic A.
Bifurcates into ICA & ECA
ICA
Scan more lateral
3 segments - cervical, petrous, intracranial
Ophthalmic A is first branch
Cervical branch of ICA
Lies lateral and posterior
No extracranial branches
Petrous branch of ICA
Lies vertical and horizontally
Through temporal bone
Intracranial branch of ICA
Divides into cavernous and supraclinoid segments
Ophthalmic Branches of Periorbital Circulation
Supraorbital A
Frontal A
ECA
Scan more medial
8 branches to head/face/neck
Superficial thyroid A. is first branch
ECA Branches of Periorbital Circulation
Facial A
Nasal A
Indications of Collateral Flow
Internalization of ECA
Reversal of flow in Ophthalmic A
Veterbral A
Find CCA, angle posteriorly
Originates from posterior portion of subclavian A
Courses beside ICA
Left is larger/prominent
Enters transverse processes of spine at C6
Enters cranium via foramen magnum
Jugular Veins
Main source of head/neck drainage
Internal Jugular V
Flows into brachiocephalic V
External Jugular V
Flows into subclavian V
Carotid Protocol
Prox CCA - close to AO arch
Mid CCA
Distal CCA - just before bulb
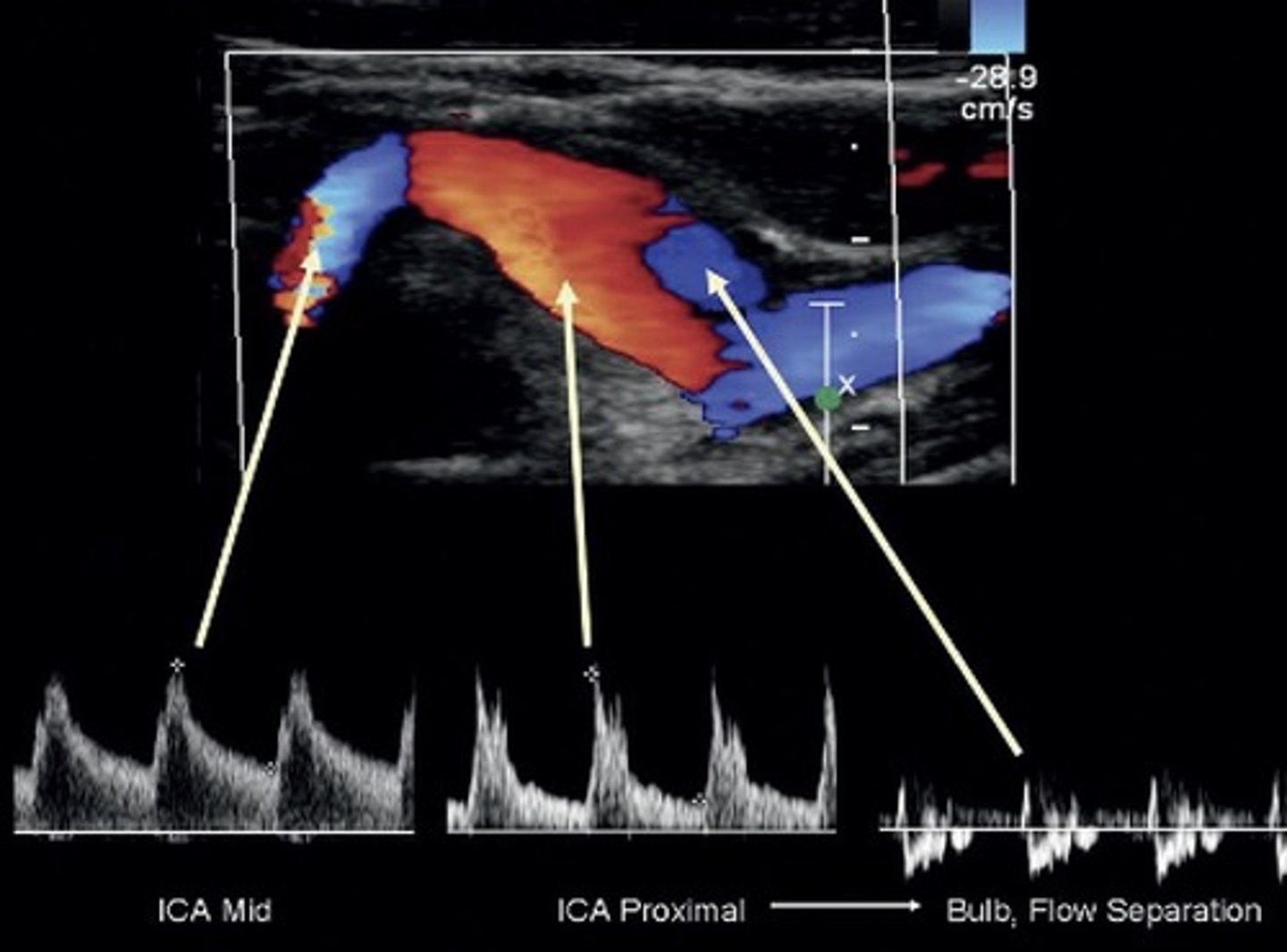
Prox ICA - just after bulb
Mid ICA
Distal ICA
Prox ECA - showing first branch if possible
Spectral Doppler with PSV at each point
Doppler Characteristics of Carotid A
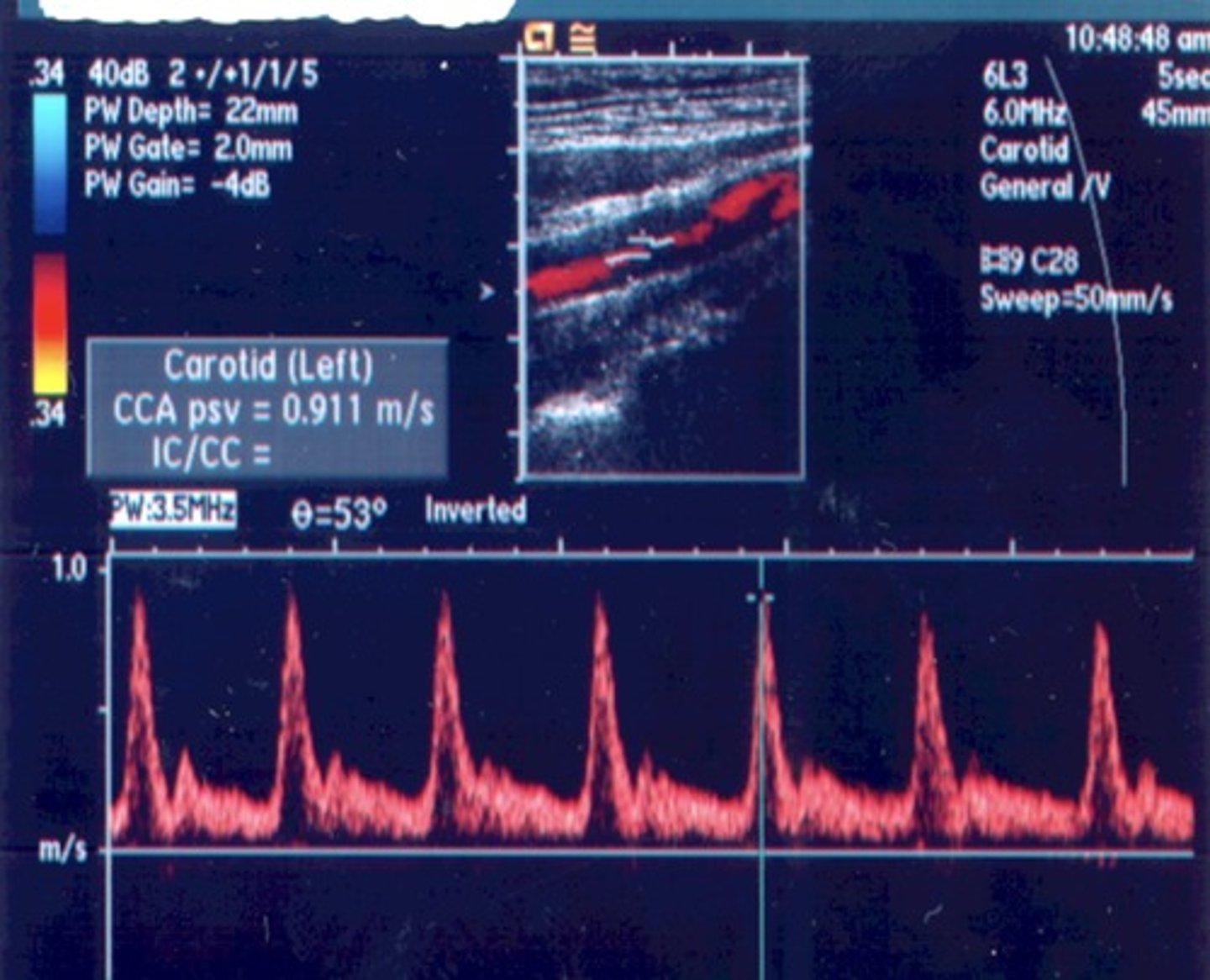
Low resistant - except prox. CCA & ECA
High off baseline
Spectral window
Continuous forward flow
Normal Prox CCA Waveform

Normal CCA Waveform
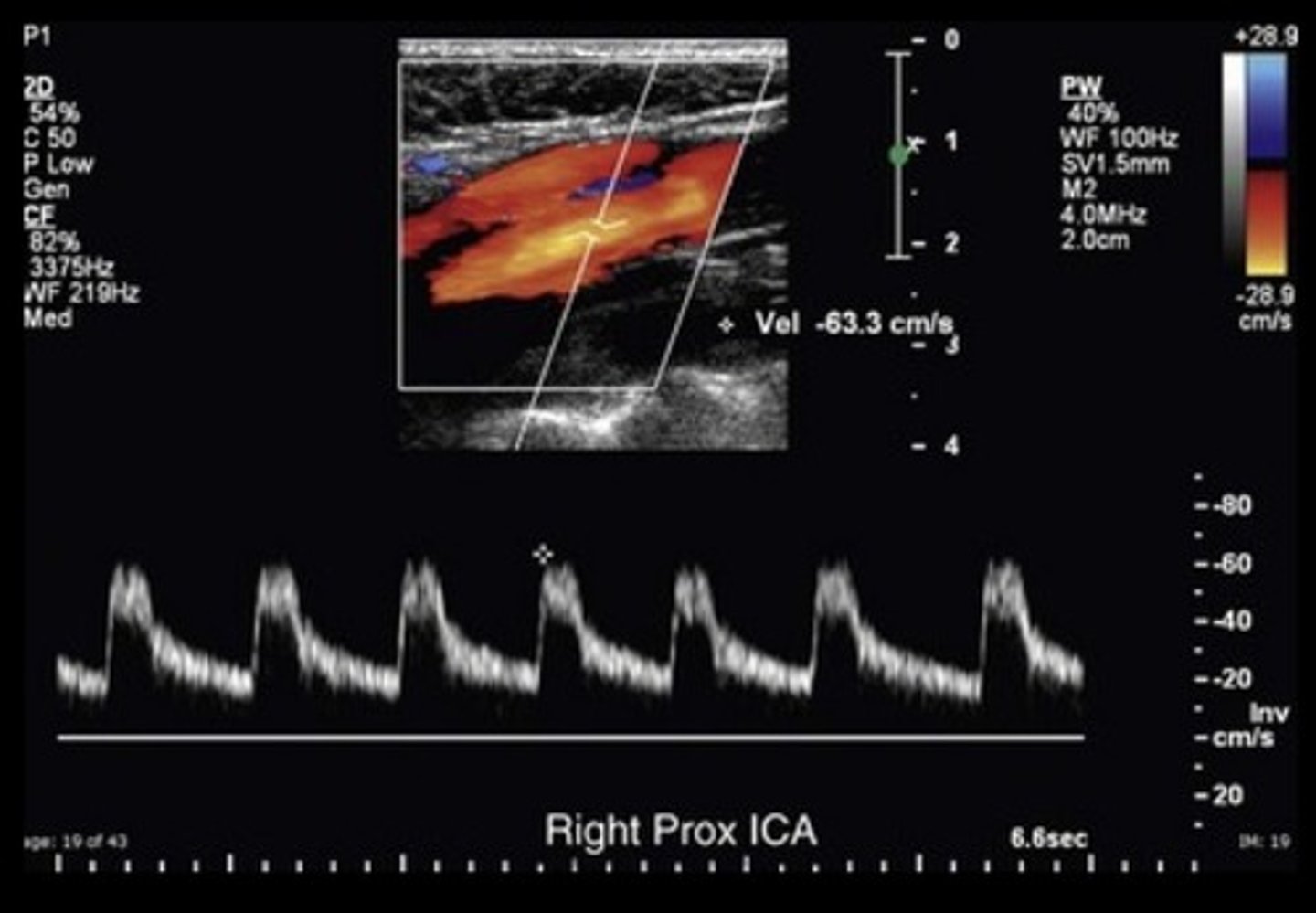
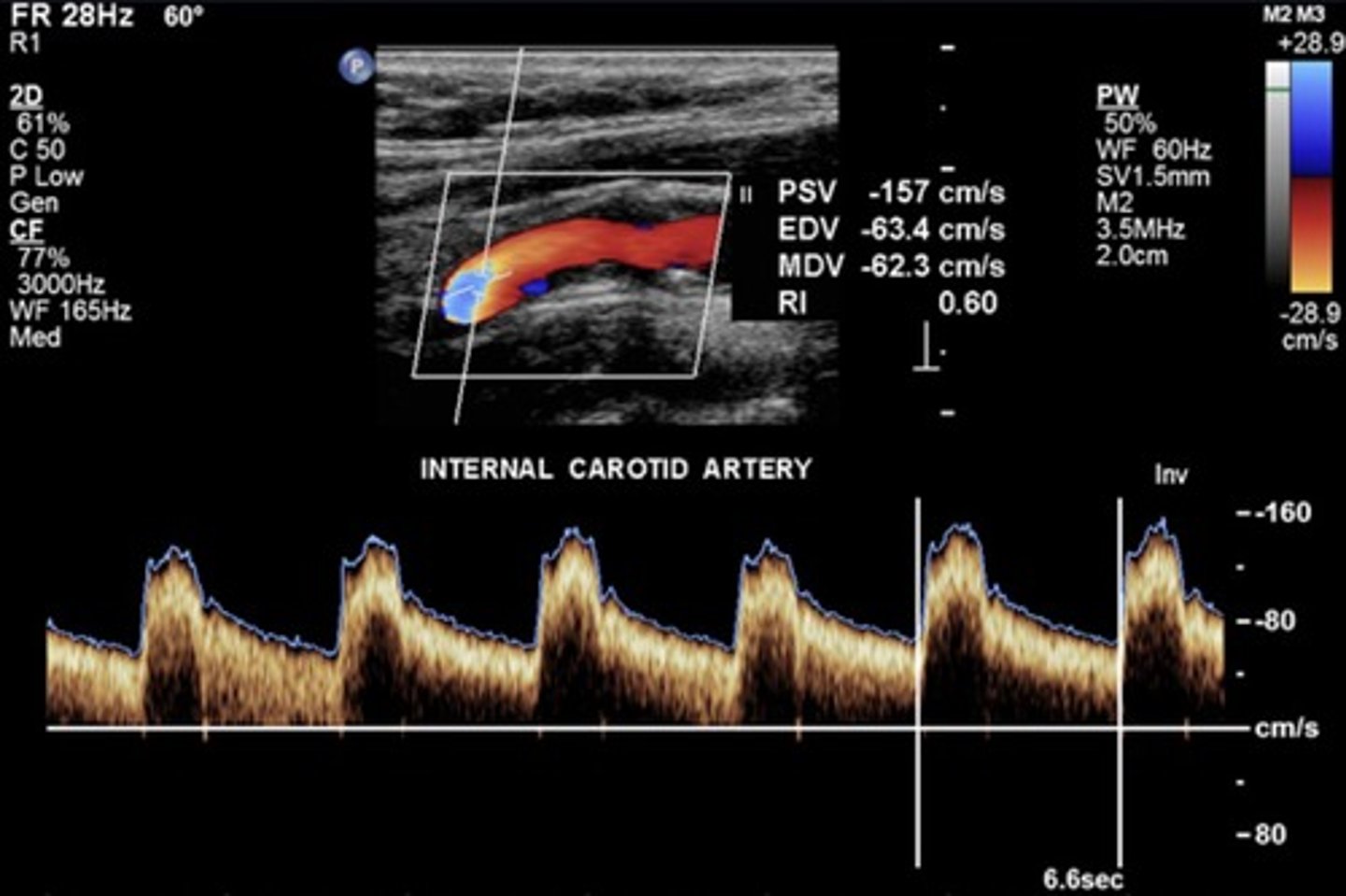
Normal ICA Waveform
Lowest resistance
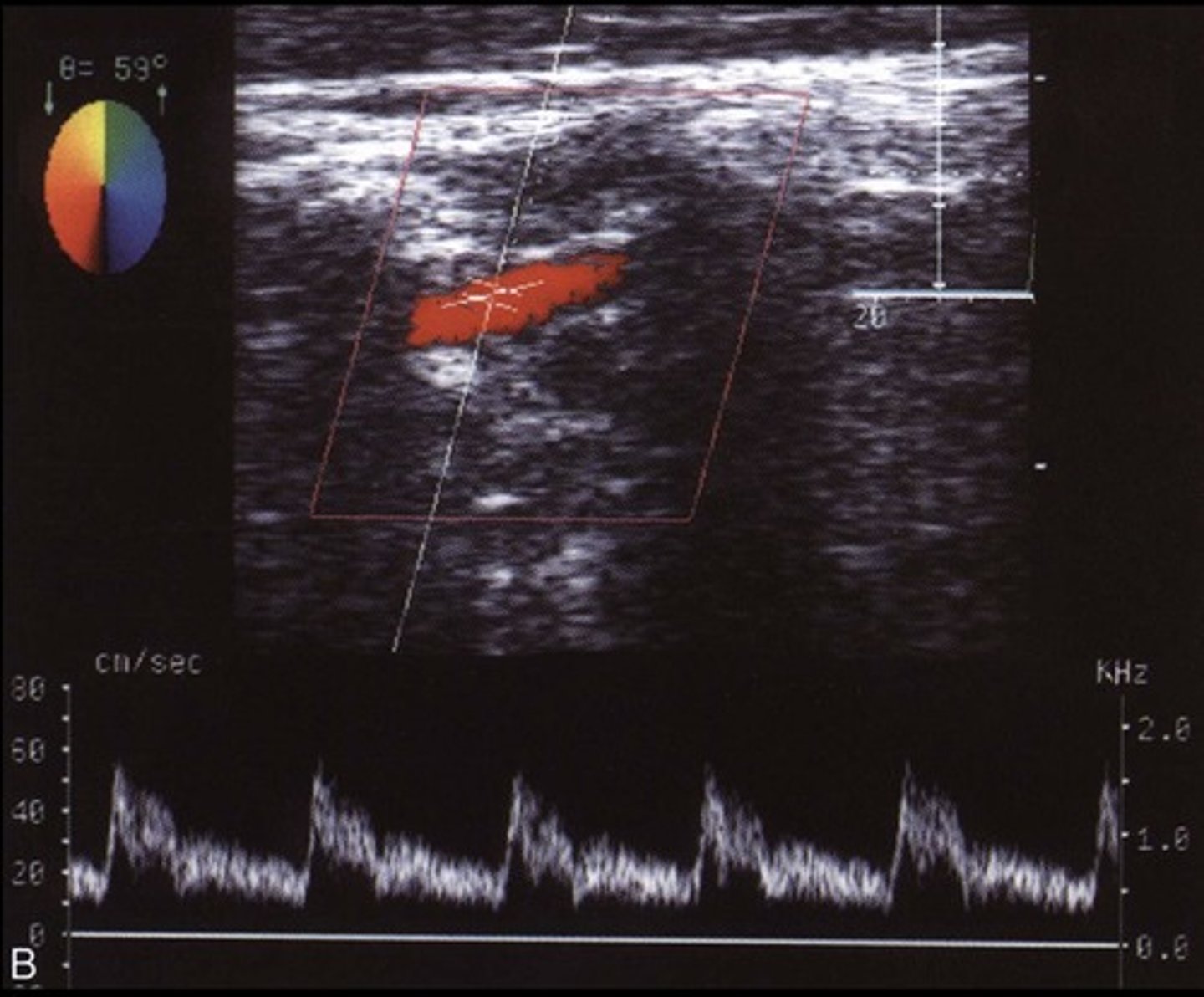
Carotid Bulb
Normal to have turbulent flow at separation/divider
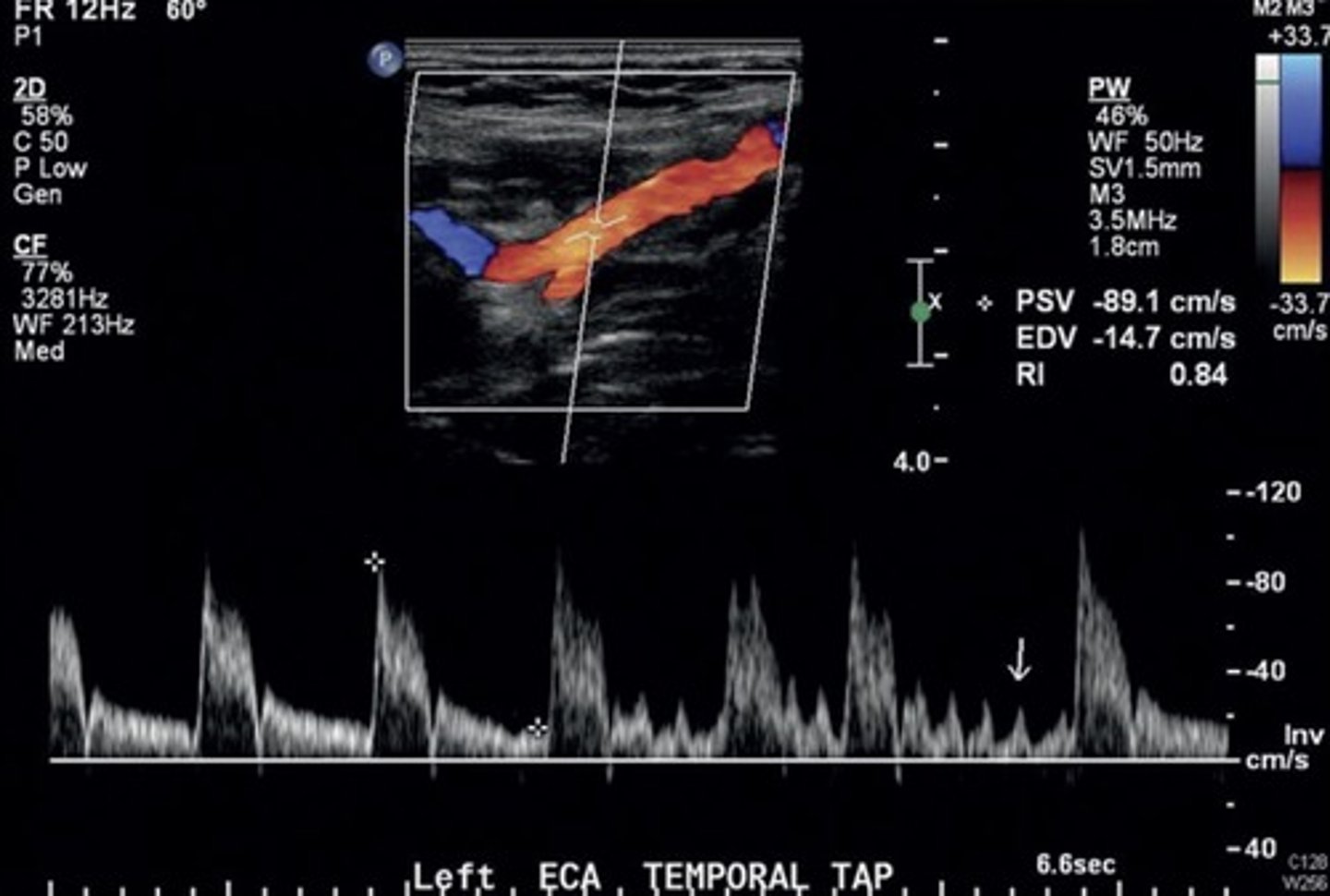
Normal ECA Waveform (with temporal tap)
High resistant
Normal Vertebral A Waveform