cumulative cms 3 review
1/330
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
331 Terms
agent that prevents bacteria from multiplying = bacterioSTATIC
agent that kills bacteria = bacteriCIDAL
what is the prion-causing neurodegenerative disease that patients can get from contaminated endoscopes?
what do we use to clean endoscopes?
creutzfeldt-jakob disease
gas sterilization
KNOW
what is the purpose of the surgical hand scrub? (2)
a. to make our skin sterile
b. to kill all of the microbes present
c. to decrease bacterial skin flora
d. to remove the pathogenic organisms
c. to decrease bacterial skin flora
d. to remove the pathogenic organisms
how long of a contact time do scrub solutions need to contact the skin to be effective?
3 minutes
what should you do if the BRUSH becomes contaminated during surgical scrub?
what should you do if your ARM becomes contaminated during surgical scrub?
start over
add 1 minute to the contaminated arm
when scrubbing in we use betadine. what can be used if someone has an anaphylactic allergy?
do you scrub in before or after mechanically cleansing the patient's skin?
plain chlorhexidine scrub (pink bar)
after! you don't want to scrub in and then get urself dirty/exposed to bacteria again
instant surgical hand sanitizers for scrubbing in
**remember: these are non-mechanical, do not require a scrub brush, and you should start at fingers & go 2 inches above elbow, and you do not need to towel before gowning & gloving
- sterillium rub
- avagard
- triseptin
how long of a drying time does chloraprep need on the patient's skin before we drape them?
when should we NOT use chloraprep (or any other alcohol-based prep, such as duraprep)?
3 min
on mucous membranes, vaginal orifices, or eyes --> use betadine instead!!
circulating nurse: goes b/w sterile & non-sterile areas, and is NOT sterile or scrubbed in!! they will tie your gown, prep the pt and supplies, collect specimens, and are responsible for legal documentation.
KNOW
scrub tech: collects needles, sponges, etc. at the end of surgery
positioning pt for surgery
- pillows under knees to prevent back strain
- pad bony prominences
- do NOT let sacrum hang off table
- avoid excessive flexion/extension n
- avoid pressure on common peroneal nerve
- avoid skin touching metal surfaces
pt cannot dorsiflex, raise foot at ankle, invert/evert ankle, foot appears floppy, sensation is lost over the area, and pt has a "steppage"/"foot drop" gait with high-step walk.
which nerve was likely injured during surgery d/t pressure from drapes, mayo stands, stirrups?
COMMON PERONEAL NERVE
branch of sciatic nerve
dorsal recumbent = supine = most basic position
ventral decubitus = prone
what is the preferred position for colonoscopy?
a. lateral kidney
b. prone
c. semi-prone (sims)
d. dorsal lithotomy
e. reverse trendelenburg
c. semi-prone (sims)
know
max time of tourniquet use
2 hours --> risk of ischemia to limb
remember pre-ob abx BEFORE starting the pressure
we need to give antibiotics within 1 hour of making the incision, ideally. when will we consider re-dosing?
at 4 hours
kocher = RUQ scar representing cholecystectomy
pfannenstiel = C-sections
midline incision = most common abdominal incision & usually spares the umbilicus
lanz = modified mcburney in the RLQ that runs more transverse
mcevedy = runs from femoral canal to inguinal region
muscle splitting loin = used for kidney transplants
stages of anesthesia
1. analgesia --> loss of pain + pt is conscious
2. excitement --> want to avoid
3. surgical anesthesia
4. medullary paralysis --> must not go into this stage
all of the following are reasons we would use benzos as a pre-anesthetic agent EXCEPT....
a. amnesia
b. analgesia
c. sedation
d. anxiety-relief
b. analgesia
benzos do not work for pain relief
diazepam = most used outpatient
midazolam = most used inpt
which opioid is used for post op shivers?
meperidine (demerol)
**high abuse risk
which halogenated agent has the LEAST degree of bronchospasm?
sevoflurane
KNOW
agents that can cause malignant hyperthermia
halogenated agents (isoflurane, desflurane, halothane, etc.)
succinylcholine
PROPOFOL is the most commonly used IV anesthetic agent, but who should we AVOID using this in d/t its SEs?
who is etomidate CI in?
who is ketamine CI in?
kids --> risk of severe acidosis in kids who has resp infx
cardiac instability / shock / emergency surgery -->
b/c propofol SE is severe hypotension
seizure patients
adrenocortical suppression
neurosurgery pts
increased ICP or HTN
relative CI = healthy adults (can reduce post op psych effects with a benzo)
post-op causes of fever:
first 24 hours: resp problems (atelectasis)
48-72 hrs: urinary tract complications
>72 hrs (3-5 days): wound infections, thrombophlebitis, DVT, PE
#1 MCC of surgical site infection
staph aureus
go thru types of wounds (clean ---> contaminated)
what level of post op fever is considered concerning & warrants an investigation?
>100.4 F / 38 C
what is the drug of choice for IV anesthesia when CV instability & cardiac contractile dysfunction is a concern?
etomidate!!
no effect on BP/HR/pulm pressure and only a mild effect on CO
tx for delirium tremens
librium or valium
which of of the following has a SE of myoclonus during induction?
a. propofol
b. etomidate
c. ketamine
b. etomidate
KNOW
IV induction agents of choice for asthmatics
propofol or ketamine
____________________ is a combo of IV sedation & local anesthesia.
TIVA (total IV anesthesia)
succinylcholine we would use for ET intubation & quick cases requiring fast intubation.
rocuronium & vecuronium are used for procedures > 30 minutes (aka in the OR).
what is the REVERSAL AGENT for roc/vec? (**does not work for succ**)
neostigmine or sugammadex
SEs of local anesthetics
seizures
cardiac arrest
metallic taste
HTN
tinnitus
lightheadedness
longest acting local anesthetic
bupivacaine
what can be added to local anesthetic to help decrease the burning caused by the acidity of the local anesthetic agent?
bicarb in a 1:10 ratio
reversal agents for anticoags
warfarin: vit K, FFP, PCC
unfractionated heparin: protamine
pradaxa: praxbind
eliquis, xarelto, lixiana: andexanet alfa
most common cause of post-op morbidity?
pulm complications --> #1 = ATELECTASIS
know
**remember that serum albumin < 3 is one of the strongest predictors of post-op pulm complications too
how long after drug-eluting stent placement do we need to wait?
how long after a MI do we need to wait to consider elective surgery?
how long after balloon angioplasty do we need to wait?
12 months (KNOW!!)
6 months
14 days
who to give BBs to perioperatively
already taking them
vascular operations
high cardiac risk (3 RCRI risk factors)
CAD/ischemia on pre-op testing
**start within 1 week of surgery
conditions requiring IE prophylaxis
heart transplant
prosthetic heart valve
prior rheumatic heart disease
CHD (unrepaired, prosthetic)
REMEMBER: prophylaxis is NOT needed for GU or GI procedures (so like a cystoscopy or hysterectomy you don't give prophylaxis for)
blood sugar goal in surgery for diabetics
how do we manage insulin?
how do we manage oral hypoglycemics?
100-180
insulin: decrease dose by 1/2 the morning of surgery
oral hypoglycemics: HOLD dose on day of surgery
**restart these when pt starts eating again post-op, unless it is METFORMIN then you need to wait until their renal function is stabilized d/t risk of fatal lactic acidosis!!!!!
child pugh class mortality risks
A: <10%
B: 40%
C: >80%
adrenal suppression in surgery:
patients who have taken >____mg of prednisone for > ______ weeks within the last year are considered at risk for adrenal suppression.
what do they require during surgery?
5 mg; 3 weeks
IV hydrocortisone
how long are type and cross units held for?
72 hours (3 days)
know
we should advise our patients to stop all narcotics before surgery EXCEPT for which one?
methadone
meds HELD on day of surgery
oral hypoglycemics
loop diuretics
ACEIs --> prils
ARBs --> sartans
how long is it recommended to fast solid & non-human milk (formula) prior to surgery?
how long is it recommended to human milk (breastfeeding) prior to surgery?
> 6 hours
> 4 hours
patient is undergoing surgery in which they were given succinylcholine for ET intubation, and halothane for inhaled anesthesia induction.
during surgery, they have a rapid rise in body temperature, muscle rigidity/stiffness (sustained tetany), increased HR, and dark brown urine (indicating rhabdomyolysis).
what is this condition called and how will you treat?
malignant hyperthermia
d/c the causative medication
DANTROLENE via rapid IVP
ice for cooling
**can do an in vitro contracture test prior to surgery to see if they're at risk
diabetic patient is 2 days post-op after ACL repair. you are suspicious of a soft tissue infection. the wound is inflamed, hot, red, and there is ***crepitus*** present. WBC >14,000, BUN > 15, and the patient is hyponatremic. you obtain a gram stain + culture, and it comes back with strep and clostridium.
what will you rx?
a. 1st gen cephalosporin only
b. fluoroquinolone
c. PCN G
d. PCN G + clindamycin
d. PCN G + clindamycin
**this is NECROTIZING SOFT TISSUE INFX.
the crepitus makes us think CLOSTRIDIUM and the culture confirms it
**if it was only strep present, we could do just a 1st gen ceph
what imaging should we get if we suspect an intra-abdominal post-op infection?
what will we rx?
CT scan --> to look for abscess
ampicillin + clindamycin + gentamicin
minimum urine output for an adult patient on maintenance IV fluids
minimum urine output for an adult trauma patient
30 ml/hr
50 ml/hr
**URINARY OUTPUT IS THE BEST WAY TO ASSESS FLUID STATUS
best indication of traumatic injury to the urinary system?
hematuria
risk of spontaneous bleeding in surgery if platelet count is less than what?
10,000 to 20,000
why is glucose/dextrose CI with bolus fluids?
why do we give it with maintenance fluids?
because body will not use sugar in times of acute stress, so we will become hyperglycemic and --> osmotic diuresis
it is given with maintenance fluids, in the absence of shock, to stimulate basal insulin secretion & prevent muscle breakdown
which of the following functions as a grasper, dissector, coagulator and cutter, and does so via ultrasonic vibration?
**there is no thermal spread, limiting injury to tissue, and is better suited for bowel and OBGYN cases.
a. laser
b. ligasure
c. enseal
d. harmonic scalpel
d. harmonic scalpel
electrothermal bipolar devices
ligasure + enseal
** don't need pad
vicryl rapide is well-suited for _____________ procedures.
dental
a wound becomes chronic if it doesn't heal in how many months?
3
which med is used as an antiemetic and decreases gastric volume, and is commonly given to diabetes or patients with gastric hypomotility prior to surgery?
metoclopramide (reglan)
*gastric motility stimulant
most common of breast cancer
#1 = DCIS
#2 = LCIS
MCC of mastitis
staph aureus
s/s of breast malignancy
unilateral spontaneous discharge
firm, fixed mass
non-cyclic (aka constant) pain
peau d'orange
complex findings on imaging
what is the gold standard for diagnosis of breast cancer?
what is the imaging of choice for a breast implant rupture?
mammo
MRI
how often should a patient receive bilateral mammograms after a lumpectomy + radiation?
how often should a patient receive a contralateral mammogram after a modified radical mastectomy?
how often should all pts after breast cx treatment have a PE of the breasts?
6 months after, and then annually
annually
every 3-6 months x 3 years, then annually
TRAM flap can be used for breast reconstruction when the pt desires a more "natural" breast reconstruction. what does this involve?
transverse rectus abdominal flap from the CONTRALATERAL side
which nerves, found in the tracheoesophageal grooves behind the cricothyroid muscle, must we be careful of during a thyroidectomy because they control our vocal cords and airway control?
RECURRENT LARYNGEAL NERVES
unilateral --> hoarseness + weak/breathy voice + dysphagia
bilateral --> loss of speech + airway control + stridor (REQUIRES TRACHEOSTOMY)
superior laryngeal --> loss of voice quality (deep/quiet)
gold standard for dx a thyroid nodule? definitive way to characterize the nodule?
gold standard = US (<1cm = we don't rly do anything)
definitive = FNA
tx for papillary thyroid cancer
MC thyroid cancer
total thyroidectomy
papillary
type of thyroid cancer that is associated with Men 2A/2B, has early cervical mets, and is tx with a total thyroidectomy?
medullary
what does hyperparathyroidism most commonly occur secondary to?
a single hyperfunctioning adenoma
MC visual defect seen in pituitary adenoma
bitemporal hemianopsia
s/s of prolactinoma
women:
galactorrhea
oligomenorrhea
amenorrhea
infertility
men:
gynecomastia
dec libido
erectile dysfunction
infertility
medication treatment of choice for a prolactinoma?
if this doesn't work, what surgery will we do?
BROMOCRIPTINE (know)
transsphenoidal pituitary surgery
PHEPO for pheochromocytoma
palpitations
headache
excessive sweating
pallor
orthostasis
**rapidly rising HTN**
triggers --> SUCCINYLCHOLINE, tyramine foods, physical exertion, propranolol
tx for pheochromocytoma is surgical excision, but what must be do before surgery to prevent a hypertensive crisis?
1. alpha blockade --> phenoxybenzamine
2. beta blockade --> phentolamine
tx for testicular torsion
surgical de-torsion + bilateral orchidopexy WITHIN 6 HOURS
post-void residual volume that indicates need for surgical intervention for BPH
>100
gold standard for diagnosis of prostate cancer
biopsy
radical prostatectomy
removes the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, and part of the urethrah
pantaloon hernia
indirect + direct hernias at the same time
INDIRECT V. DIRECT INGUINAL HERNIAS
INDIRECT: **OVERALL MOST COMMON**
- inguinal hernia protrudes through the deep and superficial inguinal rings into the inguinal canal.
- this commonly occurs congenitally d/t a patent process vaginalis
DIRECT:
- inguinal hernia protrudes through Hesselbach's triangle into the inguinal canal.
**this commonly occurs due to weakness in the abdominal wall with age
males = SI --> follows spermatic cord (vas deferens)
females = ovary/fallopian tubes --> follows round ligament
when can we do a laparoscopic approach (TAPP or TEP) for hernia repair?
what are the types of open repairs?
if it is reducible
lichtenstein --> mesh sutured around sperm cord
proline hernia system --> overlay mesh & underlay portion that is inserted thru the internal ring
incomplete rim sign think of what type of hernia?
ventral/umbilical hernia
#1 most common surgery among women
C-section
#2 = hysterectomy
partial/subtotal/supracervical hysterectomy: removes just the upper part of the uterus, and the cervix is left in place.
total hysterectomy: removes the uterus + the cervix.
radical hysterectomy: removes the uterus + the cervix + the upper part of the vagina + lymph nodes
**often done with uterine cancer
hysterectomy + BSO: removes the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tube
fibroids removed from the uterus to promote fertility or reduce bleeding =
myomectomy
what is the 1st thing we come into contact with once we enter the peritoneal cavity?
thick layer of omentum
charcot's sign
choledocholithiasis
1. RUQ pain
2. fever
3. jaundice
jaundice + a palpable, non-tender GB =
what does it indicate?
courvoisier's sign
periampullary tumor (pancreatic cancer)
referred pain to the LEFT shoulder when the pt is lying down with legs up significies a possible splenic hemoperitoneum.
what is this sign called?
kehr's
MC site of bleeding in gastric ulcer = left gastric + splenic vessels
MC site of bleeding in duodenal ulcer = gastroduodenal artery
billroth procedure is done for peptic ulcers > _______ cm.
3
**billroth 1 = more likely for a stricture to occur
MC cause of pneumoperitoneum
how to dx?
perforated ulcer
CT = standard of care
3 reasons for spleen surgery
hemorrhage 2/2 trauma
ITP
sickle cell disease
**splenorrhaphy = tx of choice
**splenectomy = if pt is hypotensive & has lots of abd injuries
MC bacterial causes of overwhelming post splenectomy sepsis
strep pneumo
h flu (HIB)
n meningitidis
need to vaccinate against these before splenectomy!!
pancreatic cancer
MC type = ductal adenocarcinoma
courvoisier's = 95% specific to pancreas HEAD carcinoma
CT = diagnostic
things removed in whipple procedure
tumor/head of pancreas
duodenum
GB
portion of common bile duct
gallstones have a SHADOW on US (polyps will not).
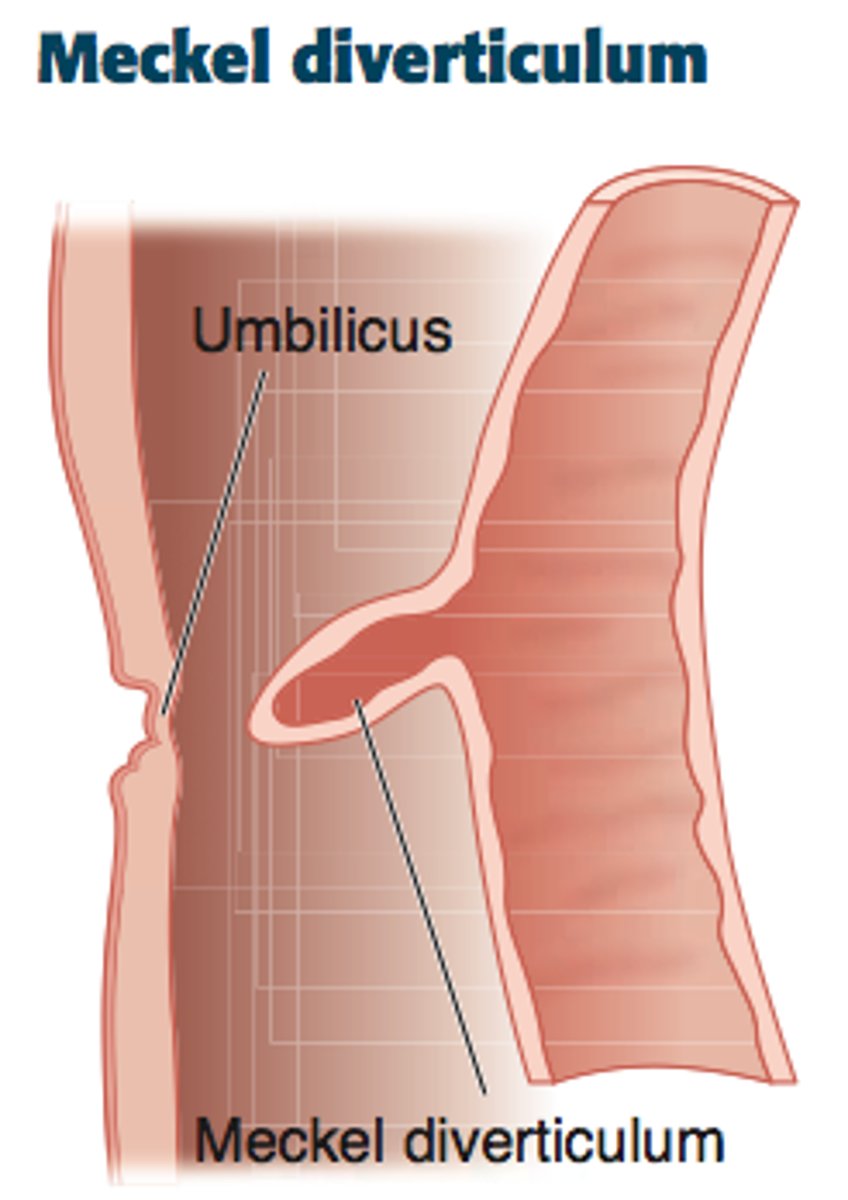
MC congenital abnormality of the SI, and the most common cause of GI bleeding in kids
meckel's diverticulum --> get an abdominal CT
2% of population
2" in length
2 yo
2 types of mucosa
tx if kid has s/s of bleeding = laparoscopic ileal resection