medsurge Respiratory
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
What is Fi02 and room air concentration of Fi02?
Fraction of inspired oxygen: room air is 21% oxygen
Define hypoxemia vs hypoxia
inadequate level of oxygen vs inadequate level of oxygenation
What is peak inspiratory pressure?
highest pressure in lungs during inspiration
What is PEEP?
controllable on a ventilator: positive end expiratory pressure (pressure at the end of respiration)
What are the five main respiratory procedures?
pulmonary function tests, peak flow meters, ABG lab test (arterial blood gas), bronchoscopy, and thoracentesis
What is a pulmonary function test?
measurement of lung volumes, function, flow rates, airway resistance etc. (like for asthma)
What is a peak flow meter?
track and observe lung function trends at home
What does an ABG lab test tell about lung function?
pH, Pa02, PaC02, HC03, Sa02: the oxygenation and acid/base balance of the blood
What is the Sa02 element of an ABG test?
percentage of oxygen bound to Hgb as compared with total amount that can be possibly carried (can be used to check accuracy of patients 02 monitor)
What is an arterial line?
an iv in an artery only for continuous blood pressure monitoring and ABG testing (only in the ICU)
What is nurse management for an arterial line removal?
direct pressure for at least 5 min. (20 if on anticoagulants), monitor ABG sampling site for bleeding, loss of pulse, swelling, changes in color/temperature
What is the normal pH of blood?
7.35 to 7.45
How does respiratory acidosis vs alkalosis occur?
lung weakness (COPD/pneumonia vs lung stress (fever, sepsis, pregnancy)
What is a bronchoscopy?
visualization of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi through either a flexible fiber‑optic or rigid bronchoscope
What are nurse management tips for bronchoscopy?
assess VS and LOC, for pneumothorax/infection, atropine for aspiration/bradycardia prevention, NPO
What is a thoracentesis?
perforation of the chest wall and pleural space with a large bore needle for evals/med placement/fluid removal (needle decompression removes air)
What are nursing considerations for patient oxygenation?
oxygenate 95 to 100 percent on as least amount of artificial oxygen possible
What are nursing considerations for oxygen face masks
no less than 5L02 or you suffocate your patient
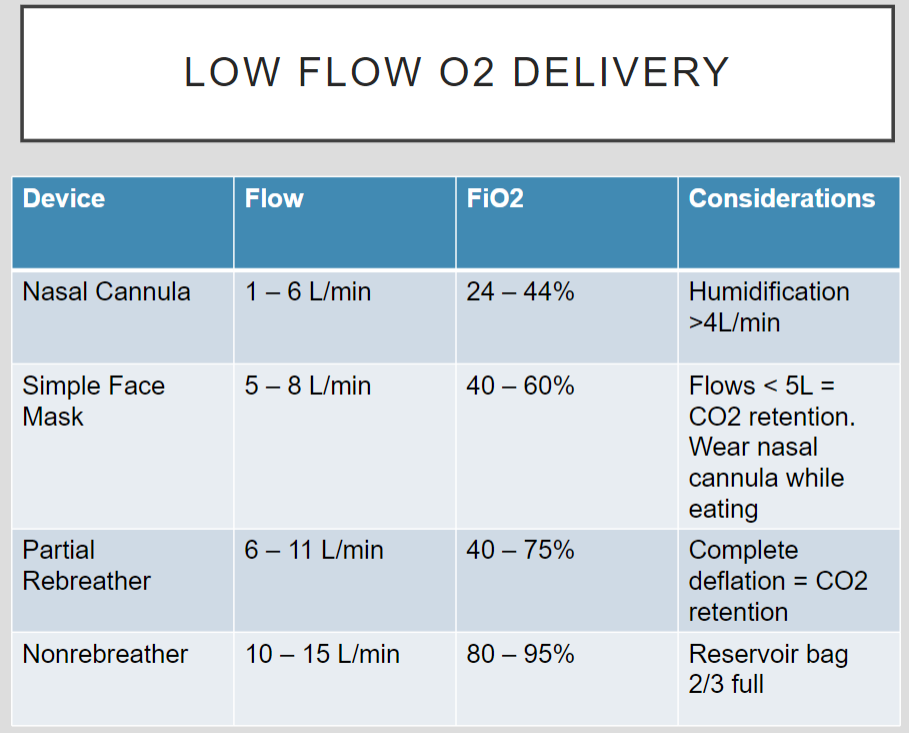
Low flow 02 delivery
see slide 16
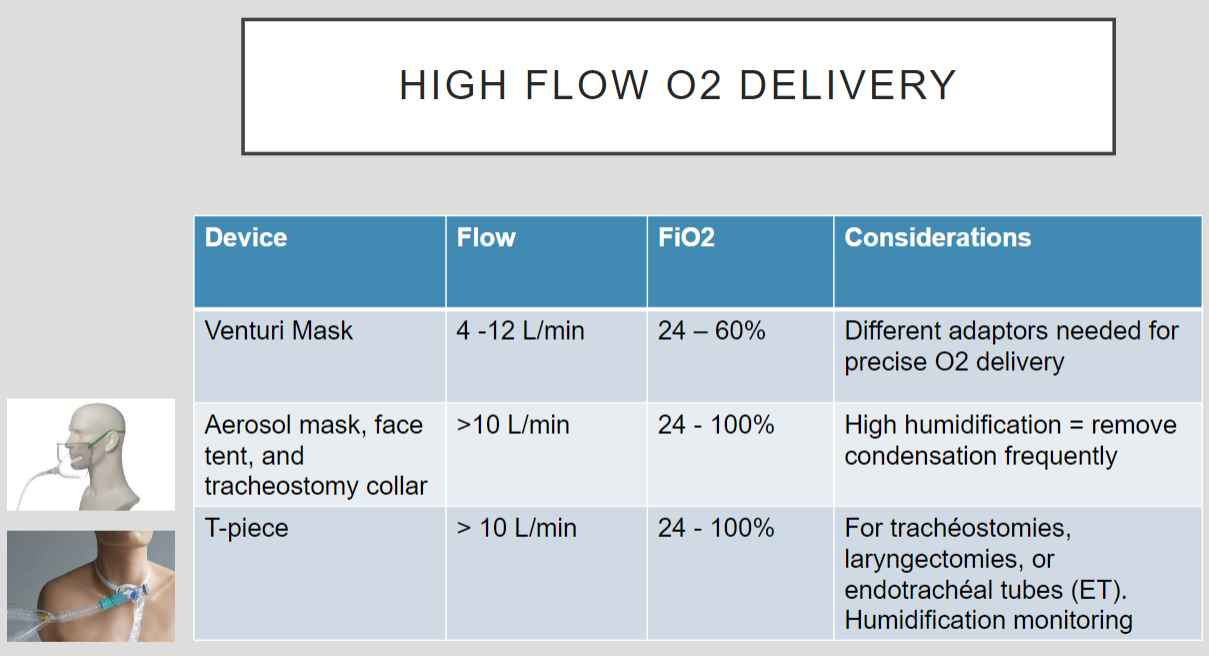
High flow 02 delivery
see slide 17
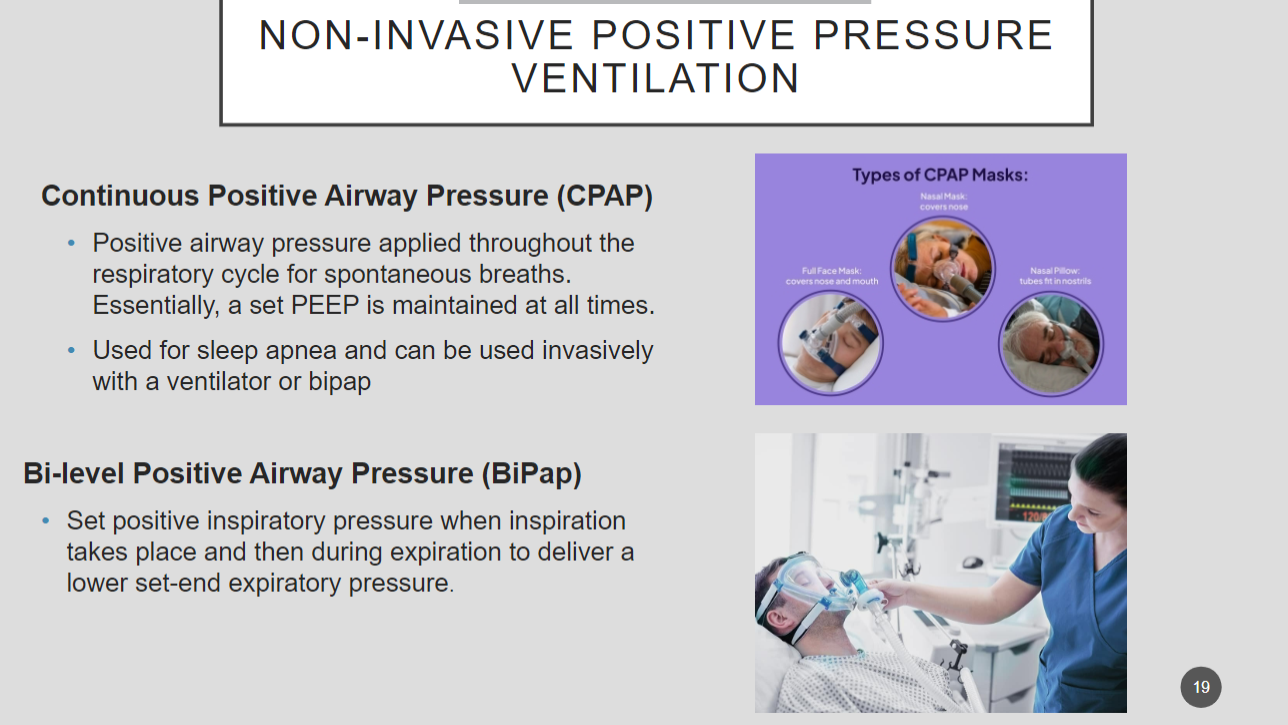
What are two ways to non invasively deliver positive pressure ventilation?
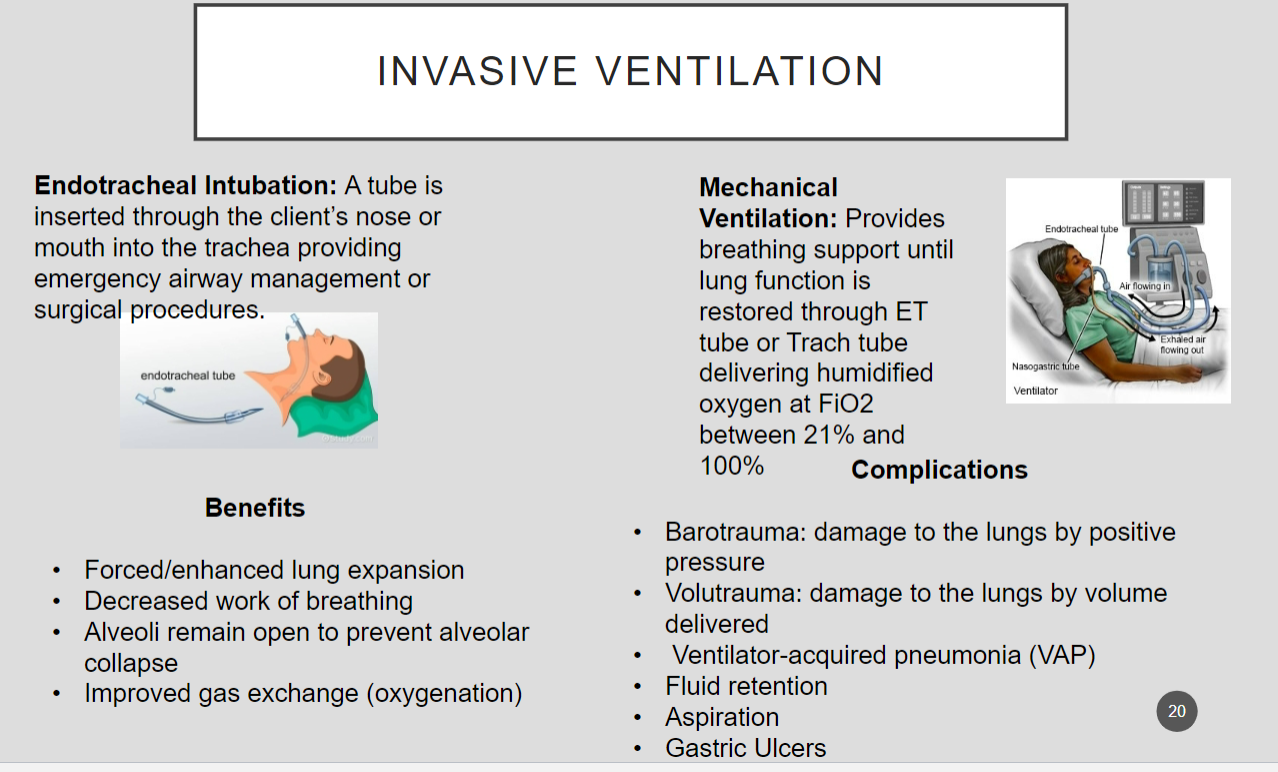
Go through invasive ventilation
see slide 20
What are the three main oxygen delivery complications?
oxygen toxicity, combustion, or oxygen induced hypoventilation
What concentration is oxygen toxicity?
high concentrations of oxygen 50% Fi02 for more than 24 to 48 hours
What is sinusitis?
inflammation of the mucus membranes of one or ore of the sinuses which can block the drainage of secretions and cause a sinus infection
What are findings for sinusitis?
nasal congestion, cough, headache/facial pressure/tenderness, bloody/purulent drainage, low grade fever
What are nursing cares for sinusitis?
increase rest and fluids, saline nasal spray, humidification, limit air travel
What is important patient education for sinusitis?
contact provider if severe symptoms present, self irrigate, use nasal sprays
What are the two types of influenza and what is it confused with?
it has to be respiratory (throwing up doesn’t count and rotavirus doesn’t count) can be seasonal (follows a fall/winter pattern) or pandemic (animal flu mutated to be contagious to humans and spread globally
What are findings for flu?
severe head/muscle ache, chills, fatigue, weakness, diarrhea and cough (avian flu), fever, hypoxia (almost never vomiting)
What are important nursing cares for flu?
droplet precautions, monitor I/Os, watch for pneumonia
What are findings for pneumonia?
fatigue, weakness, fever, chills, SOB, low SP02, cough, lung crackles/wheezes, sputum, chest pain
What are diagnostics for pneumonia?
sputum culture (before starting ABX), chest x ray
What is good nursing care for pneumonia?
high fowlers, suction/deep breathing, incentive spirometer, monitor VS
What are the three main complications for pneumonia?
atelectasis (lung collapse), sepsis, ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome)
What is good patient education for flu/pneumonia
good hygiene practice/coughing promotes secretion removal, annual flu vaccines
What are the 3 main characteristics of asthma and what are they due to?
mucosal edema, bronchoconstriction, and mucus production due to inflammatory hyperresponsiveness
What is good nursing care for asthma?
adjust nursing care dependent on acute event, high fowlers (60 to 90 degrees), monitor VS and ECG – tachycardia and/or PVCs
What is the best bed position for respiratory patients?
high fowlers
What are complications of asthma?
status asthmaticus: life threatening airway obstruction, emergency intubation
What is COPD?
chronic bronchitis and emphysema (alveoli level damage leading to a decreased surface area for gas exchange), co2 retention, and respiratory acidosis
What are signs of emphysema r/t COPD?
difficulty breathing out, barrel chest, daily dry cough, not reversible
What are general signs of COPD?
clubbed fingers, wheezing/lung crackles, etc.
What is tripod positioning? With what is it associated?
hunched over patient with their hands on their knees or on the edge of the bed to get help breathing: COPD
What is good nursing care for COPD patients?
high fowlers, productive coughing, supplemental 02,
What is good patient education for COPD patients?
breathing techniques (pursed lip and diaphragmatic), exercise as tolerated, incentive spirometer
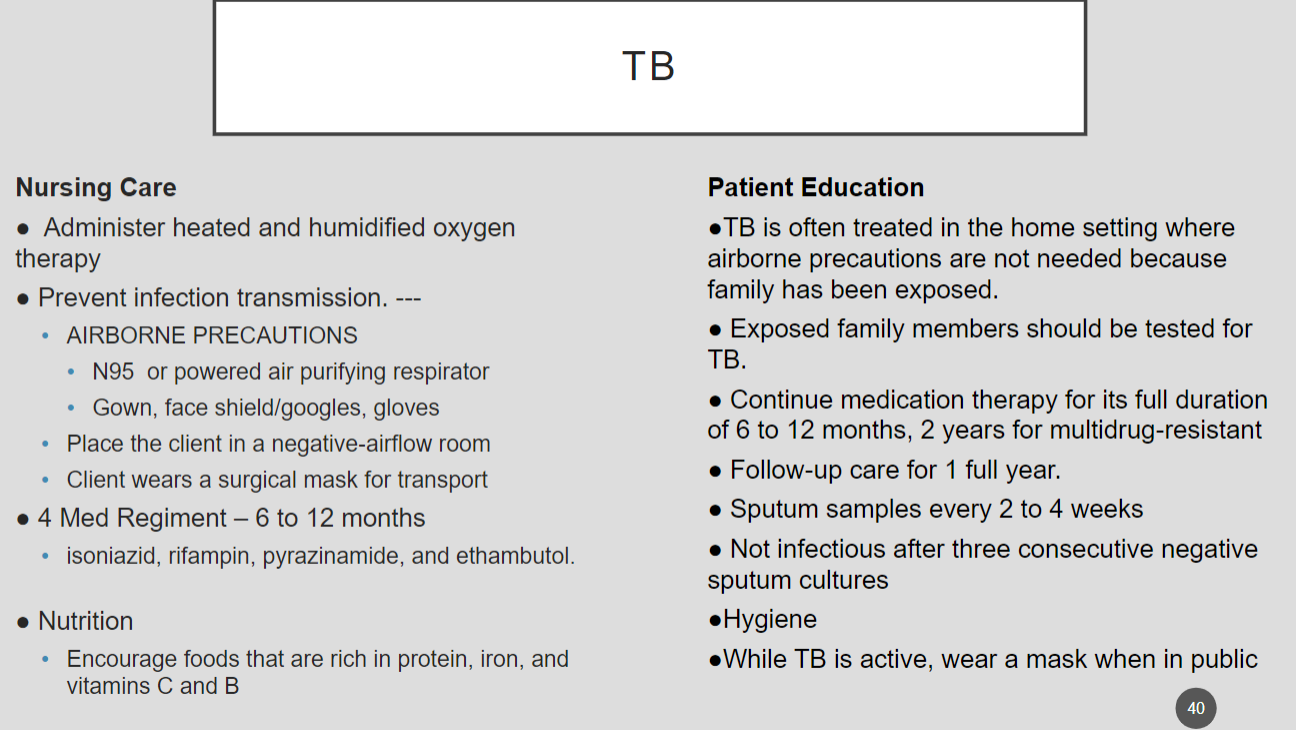
What is TB
airborne bacterial disease primarily in the lungs (can be infected but inactive)
What are findings for TB?
persistent cough, purulent sputum, fatigue, weight loss etc.
What is good nursing care for TB?
What is a pulmonary embolism?
a substance (solid gas or liquid) enters venous circulation and forms a blockage in the pulmonary vasculature and are a medical emergency
What are risk factors for PEs (pulmonary embolisms)
immobility, oral contraceptives and estrogen, substances, obesity,
What are nursing assessment findings for PEs?
pulmonary embolism: feelings of impending doom, anxiety, chest pressure (sudden onset tender), pain upon inspiration, dyspnea, cough, hemoptysis,
What are diagnostics/labs for PEs (pulmonary embolism)?
D dimer for clot formation, CT scan, pulmonary angiography, ABGs
What is good nursing care for PEs (pulmonary embolisms)?
high fowlers, assess respiratory/cardiac status often, oxygen
What is good patient education for PEs (pulmonary embolisms)?
don’t cross legs, avoid immobility, compression socks, etc.
What is WOB?
work of breathing (part of respiratory assessment)
What is a hemo vs pneuomo vs hemopneumothorax
blood in the lungs vs air in the lungs vs blood and air in the lungs
What are findings for pneumothorax/hemothorax?
anxiety, pleuritic (sharp stabbing) pain, respiratory distress, asymmetrical chest wall movement, subcutaneous emphysema (damaged lung air sacs)
What is a tension pneumothorax?
air or fluid in the pleural space displaces mediastinal structures and creates cardiac disfunction
What are findings for a tension pneumothorax?
hypotension, hypo breath sounds, JVD (jugular vein distension), tracheal shift towards unaffected side, chest pain, etc.
When do you clamp a chest tube as a nurse?
trouble shooting, if there is air in the catch below the clamp that’s where this issue is, if there is no bubble it’s above the clamp
What is the difference between wet suctioning and dry suctioning chest tubes?
a little water and a secondary suction dial vs just water
What is flail chest?
a free floating rib segments cause the lung below to cave in on inhalation and balloon out on exhalation and below the segment cannot participate in gas exchange
What is good nursing care for flail chest?
humidified oxygenation, assess lung sounds, promote lung expansion, mechanical ventilation as needed, pain meds, IV fluids, I/Os
What is respiratory failure?
unable to exchange enough oxygen and carbon dioxide to meet the body’s needs: life threatening
What are findings for respiratory failure?
SOB, orthopnea (breathing lying flat), tachypnea, cyanotic, hypotension, decreased Sa02, cardiac arrhythmias etc.
What is acute respiratory failure?
hypoxemia and/or hypercapnia (increased PaC02) and acidosis (pH less than 7.35)
What is ventilatory failure vs oxygenation failure?
acute respiratory failure: air movement abnormality vs lack of perfusion to capillary bed/altered gas exchange
What are causes/risk factors for ventilatory failure?
COPD, pneumothorax, fibrosis lung tissue, neuromuscular disorders (impair RR), elevated ICP (intracranial pressure
What are causes/risk factors for oxygenation failure?
hypoventilation, hypovolemic shock, pulmonary embolism, low hemoglobin
What are causes/risk factors for both ventilatory and oxygenation failure?
ARDS, asthma, pulmonary edema
What is acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
a systemic inflammatory response that injures the alveolar/capillary membrane making it permeable to large molecules filling the lungs with fluid
What is mortality rate for ARDS?
58%
What are causes for ARDS?
sepsis, pneumonia, trauma, DIC (diseminated intravascular coagulation - clotting spread around the body)
What are findings of ARDS?
respiratory distress, lung crackles, 100%02 hypoxemia (refractory hypoxemia