Concept 13.2: Fertilization and meiosis alternate in sexual life cycles
1/14
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Life cycle
The generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism
Chromosmal behavior is related to this in organisms
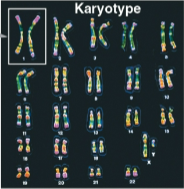
Karyotype
An ordered display of the pairs of chromosomes from a cell
Humans display 23 pairs
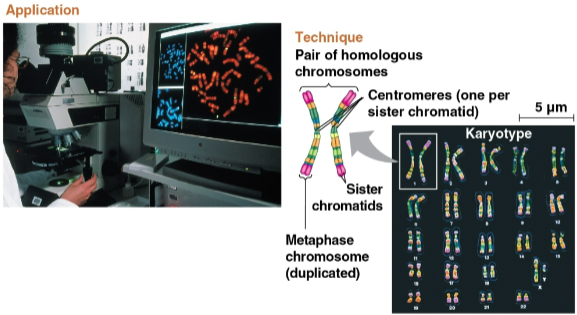
Homologous chromosomes (homologs)
The two chromosomes in each pair of chromosomes
Each has the same length, centromere position, and staining pattern with one set of chromosomes from each parent cell for inherited characteristics
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of the individual
X and Y in humans
Females have a homologous pair of X chromosomes
Males have one X and one Y chromosome
Autosomes
The remaining pairs of chromosomes that do not determine sex
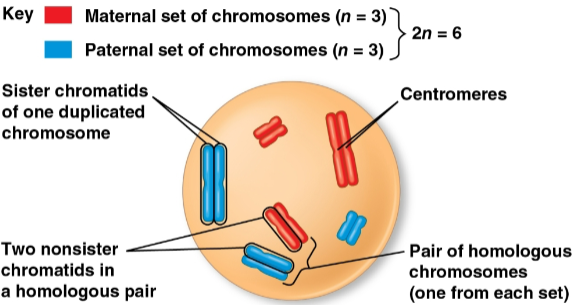
Diploid cell (2n)
A cell with two sets of chromosomes
Is 46 in humans, representing two half-sets
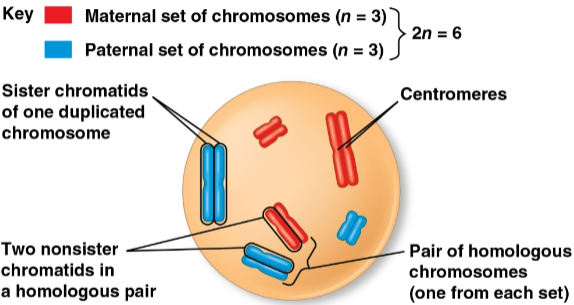
Chromosome replication
The replication of each chromosome into two identical sister chromatids
Haploid cell (n)
A cell that contains a single set of chromosomes
Includes gametes (sperm and eggs)
Is 23 in humans, representing one half-set with a single sex chromosome
Eggs (ovum) have a single X chromosome
Sperm have either an X or Y chromosome
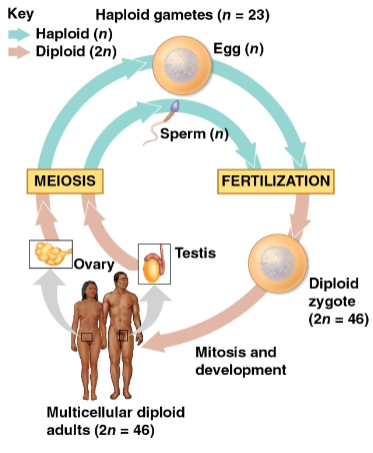
Fertilization
The union of gametes (sperm and egg) to create a zygote
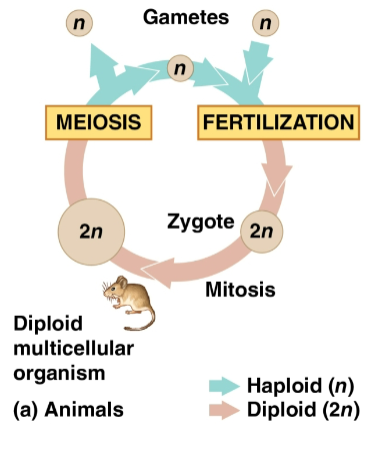
Zygote
A fertilized egg with one set of chromosomes from each parent
Produces somatic cells by mitosis and develops into an adult
Often the only diploid stage in most fungi and some protists with no multicellular diploid stage; these grow by mitosis into haploid multicellular organisms
Meiosis
Type of cell reproduction that creates gametes
Found in the ovaries and testes in humans
Results in one set of chromosomes in each gamete (n) as only diploid cells can undergo this
Alternates with fertilization to maintain chromosome number
Gametes
Reproductive cells produced by meiosis that undergo no further cell division before fertilization
Often the only haploid cells in most animals
Fuse to form a diploid zygote that then divides by mitosis to a multicellular organism
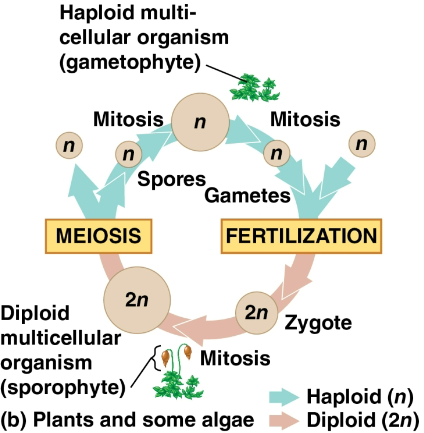
Alternation of generations
A life cycle exhibited by plants and some algae that include both a diploid and haploid multicellular stage
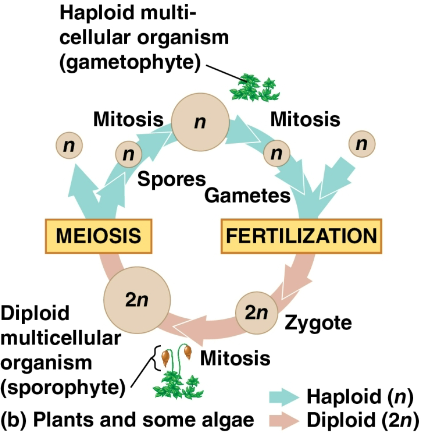
Sporophyte
A diploid organism that makes haploid spores by meiosis
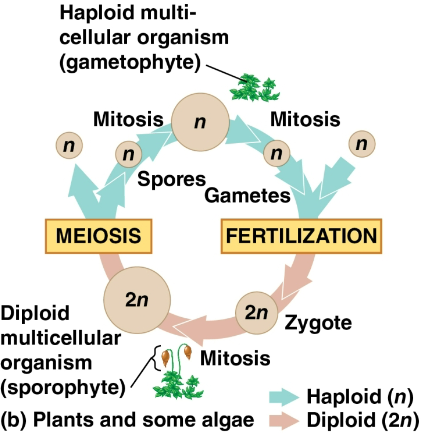
Gametophyte
A haploid organism that grew from a sporophyte by mitosis that then makes haploid gametes by mitosis
Fertilization of these gametes results in a diploid sporophyte