Cranial nerves
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
The cranial nerves provide ______ _____ of ____ ____ that control visceral functions such as ____, ____ ___, ___ ___, ___, ___.
The cranial nerves provide parasympathetic innervation of the autonomic ganglia that control visceral functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, coughing, swallowing
Sensory afferents entering the brainstem are generally the central processes of ________ ____ ___ located in ____ ___ - exceptions include afferents associated with cranial nerves ___, ___ and ____
Sensory afferents entering the brainstem are generally the central processes of pseudounipolar ganglion cells located in sensory ganglia - exceptions include afferents associated with cranial nerves I, II, and VIII
Cranial nerve sensory nuclei arise from the _______ ____ and motor nuclei from the ____ ____
Motor neurons are located ______ and sensory neurons are located slightly ____ and ____ to the ____ ___
Within motor grouping, somatic tend to be _____ to _____
Within the sensory grouping visceral tend to be _____ to _____
Cranial nerve sensory nuclei arise from the alar plate and motor nuclei from the basal plate
motor neurons are located anteromedial and sensory neurons are located slightly lateral and posterior to the motor neurons
Within the motor grouping somatic tend to be medial to visceral
Within the sensory grouping visceral tend to be medial to somatic
The midbrain mediates ____ and ___ reflexes
Contains the _____ nucleus and the _____ nucleus which innervate _____ ____ ____
Contains center for _____ _____ ____
Gives rise to two cranial nerves (they are?)
Contains the ______ nucleus of ____ which is the sensory component for the ____ ___ of the jaw - contains ____ ____ Neurons and arise from the ____ ____
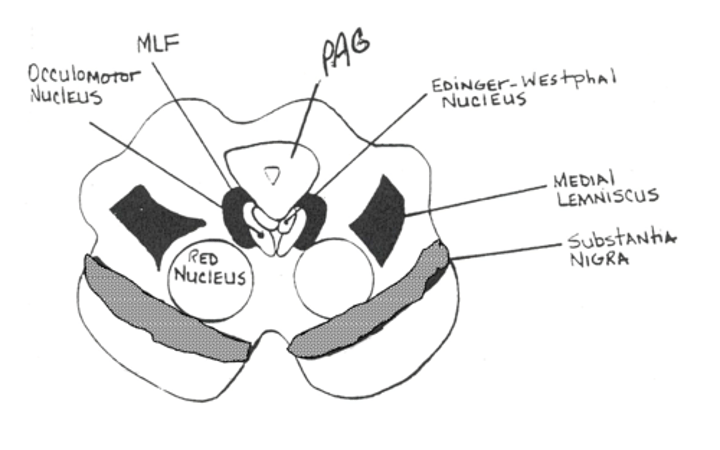
The midbrain mediates auditory and visual reflexes
Contains the oculomotor nucleus and the trochlear nucleus which innervate extraocular eye muscles
Contains center for vertical conjugate gaze
Gives rise to CN III, IV
Contains the mesencephalic nucleus of V which is sensory component of the stretch reflex of the jaw - contains primary sensory neurons and arise from the neural crest
Superior colliculus receives ____ input from the ____ and ____ ___
Receives ____ input from the ____ ___ to mediate _____ ____
Superior colliculus receives visual input from the retina and eye fields
Receives auditory input from the inferior colliculus to mediate audiovisual reflexes
The periaqueductal gray contains a high density of ____ ____ and is involved in _____ ___
The periaqueductal gray contains a high density of opiate receptors and is involved in pain modulation
The edinger westphal nucleus gives rise to _____ _____ fibers that terminate in the _____ ____
____ fibers from the ___ ___ innervate the _____ ___ and ____ of the _____
The edinger westphal nucleus gives rise to preganglionic parasympathetic fibers that terminate in the ciliary ganglion
Postganglionic fibers from the ciliary ganglion innervate the ciliary body and sphincter of the iris
The ascending component of the MLF contains _____ fibers that coordinate ____ ____ and interconnects the ____ ____ cranial nerves
The ascending component of the MLF contains vestibular fibers that coordinate eye movements and interconnects the oculo motor cranial nerves
The red nucleus receives ____ input from the ____ ____
Receives _____ input from the cerebellar nuclei
Gives rise to crossed _____ and uncrossed ______ tracts
Exerts facilitatory influence on ____ muscles of the ____ ____
The red nucleus receives bilateral input from the cerebral cortex
Receives contralateral input from the cerebellar nuclei
Gives rise to crossed rubrospinal and uncrossed rubro-olivary tracts
Exerts facilitatory influence on flexor muscles of the upper extremity
Substantia niga contains large _____ cells (____)
Part of the ____ ___
Contains ____
Substantia nigra contains large pigmented cells (melanin)
Part of the motor system
Contains dopamine
Medial lemniscus carries ____ ____ modalities to the ____
Medial lemniscus carries dorsal column modalities to the thalamus
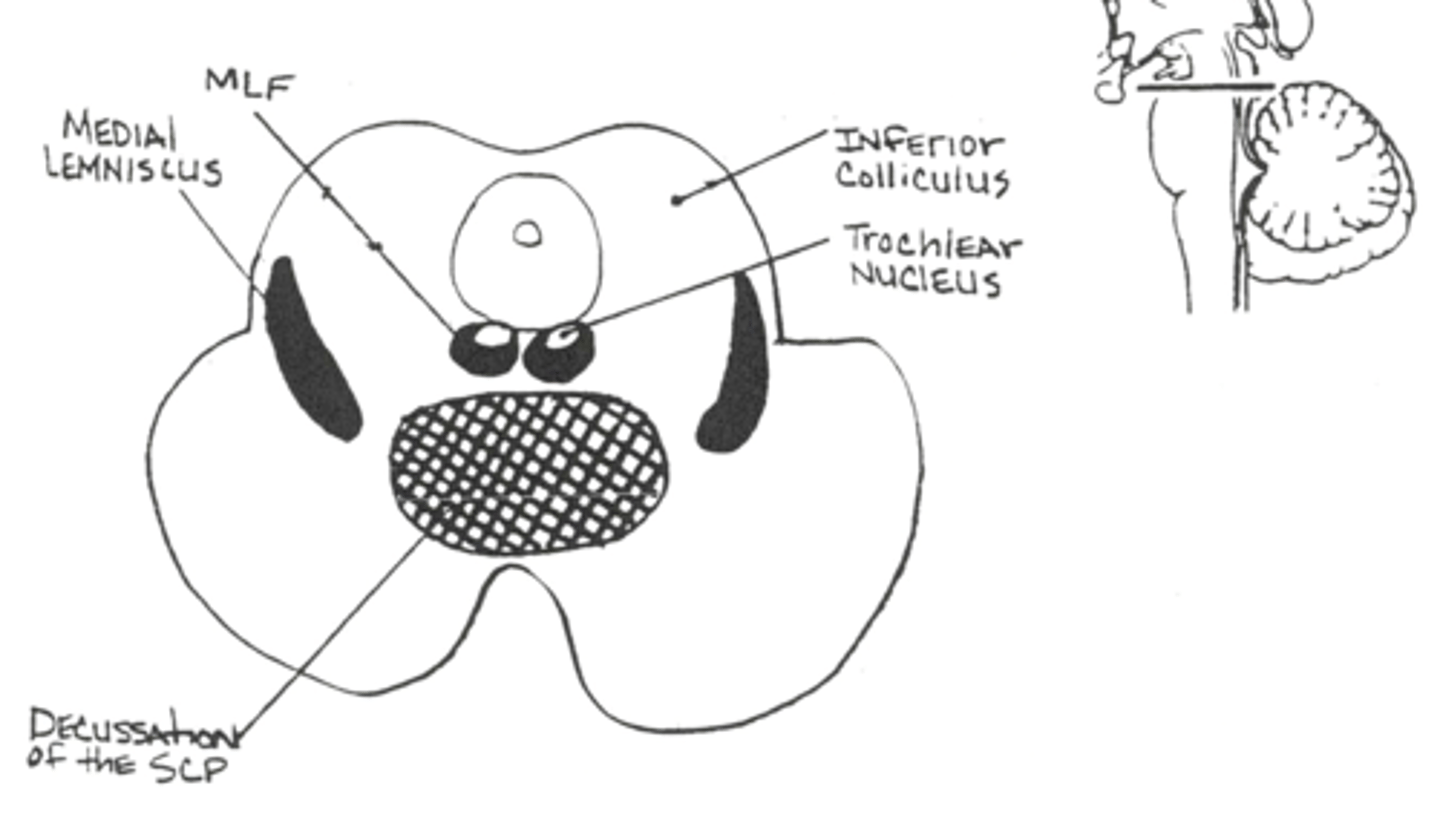
Nucleus of the inferior colliculus is an _____ relay nucleus
Projects via the _____ of the ____ ___ to the ____ ____ body
Nucleus of the inferior colliculus is an auditory relay nucleus
Projects via the brachium of the inferior colliculus to the medial geniculate body
The trochlear nucleus innervates the _____ _____ ___
This is the only ____ ____ _____ that innervates a ______ target - the axons ____ prior to exit from the ____
Thus the cranial nerve in the periphery innervates the _____ _____ ___ but the axons in the nerve arise from cell bodies in the ______ _____ _____
The trochlear nucleus innervates the contralateral superior oblique
This is the only cranial nerve nucleus that innervates a contralateral target - the axons decussate prior to exit from the midbrain
Thus the cranial nerve in the periphery innervates the ipsilateral superior oblique but the axons int he nerve arise from cell bodies in the contralateral trochlear nucleus
Decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle (X/SCP) is an important landmark that occurs at the level of the ____ ____ in the _____
Decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle (X/SCP) is an important landmark that occurs at the level of the inferior colliculus in the midbrain
Section at the superior colliculus
Section at the inferior colliculus
Section at the level of the principle sensory and motor nucleus of V
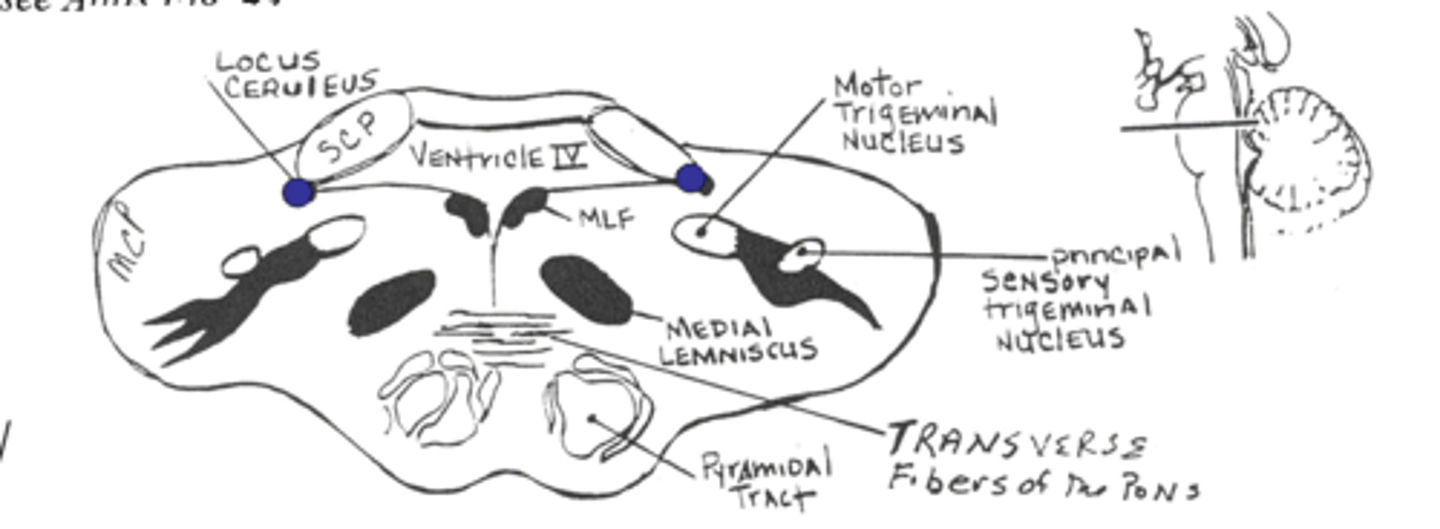
Motor nucleus of V gives rise to fibers that innervate the ____ of ____
Motor nucleus of V gives rise to fibers that innervate the muscles of mastication
Principal sensory nucleus of V lies ____ to the motor nucleus of V
Receives ____ and ____ input from the face
Gives rise to the ____ ___ which terminates in the _____ _____
Principal sensory nucleus of V lies lateral to the motor nucleus of V
Receives pressure and touch input from the face
Gives rise to the trigeminal lemniscus which terminates in the contralateral thalamus
The locus ceruleus is a small pigmented nucleus that synthesizes and releases ______ and is found at the level of the ______ ____ and ______ ____ of ___
The locus ceruleus is a small pigmented nucleus that synthesizes and released norepi and is found at the level of the primary sensory and motor nucleus of V
Section at the level of the facial colliculus
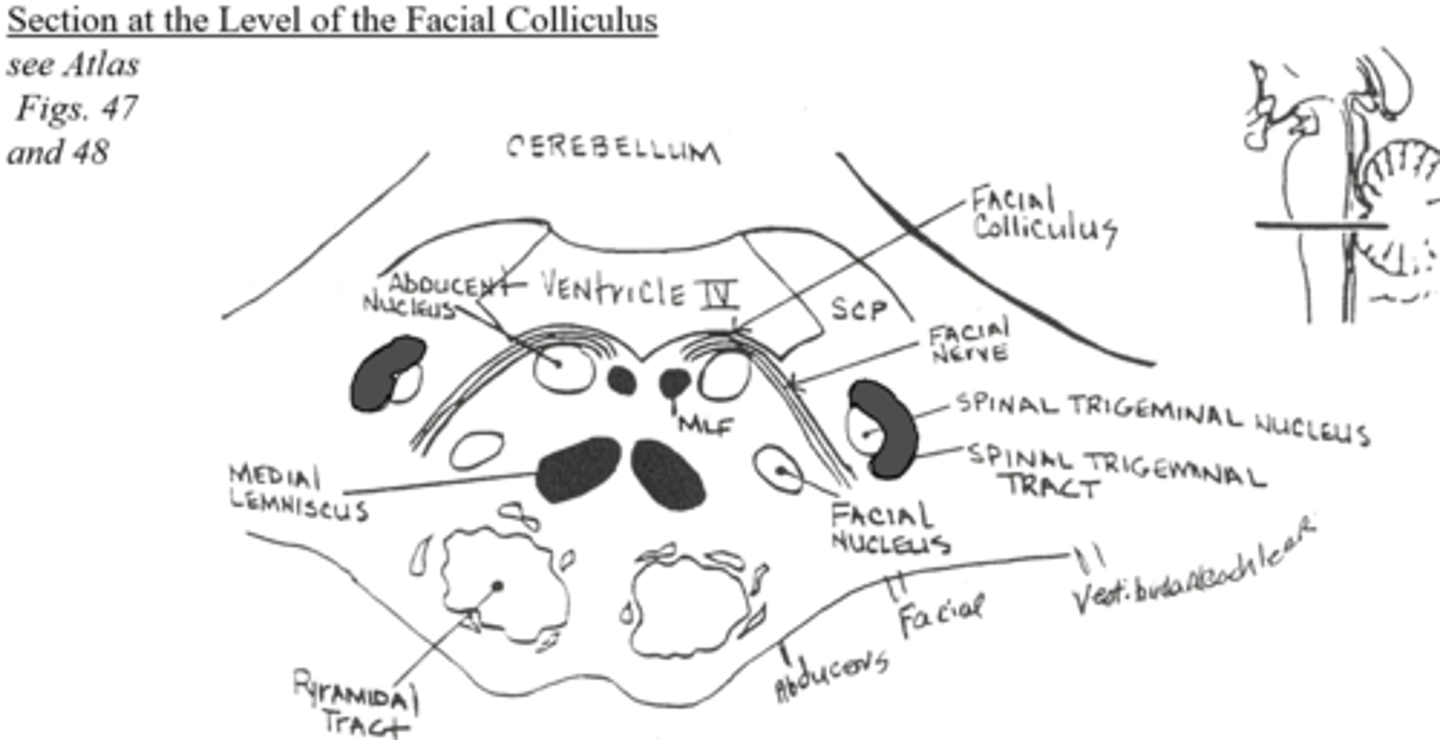
The abducens nucleus occurs at the level of the _____ ____ and receives input from the _____ _____ center for ____ ____ ___ - which receives commands from the ______ ____ eye field
The abducens nucleus occurs at the level of the facial colliculus and receives input from the adjacent pontine center for lateral conjugate gaze - which receives commands from the contralateral frontal eye field
The facial nucleus occurs at the level of the ____ _____ and its fibers project _______ to encircle the ____ ____ and then course ______ to exit the brainstem at the ______ _____ - a common tumor, a ____ ____ is a ____ of the ______ nerve which grows in this space
The facial nucleus occurs at the level of the facial colliculus and its fibers project dorsomedially to encircle the abducens nucleus and then course ventrolaterally to exit the brainstem at the cerebellopontine angle - a common tumor, a vestibular schwannoma is a schwannoma of the VIIIth nerve which grows in this space
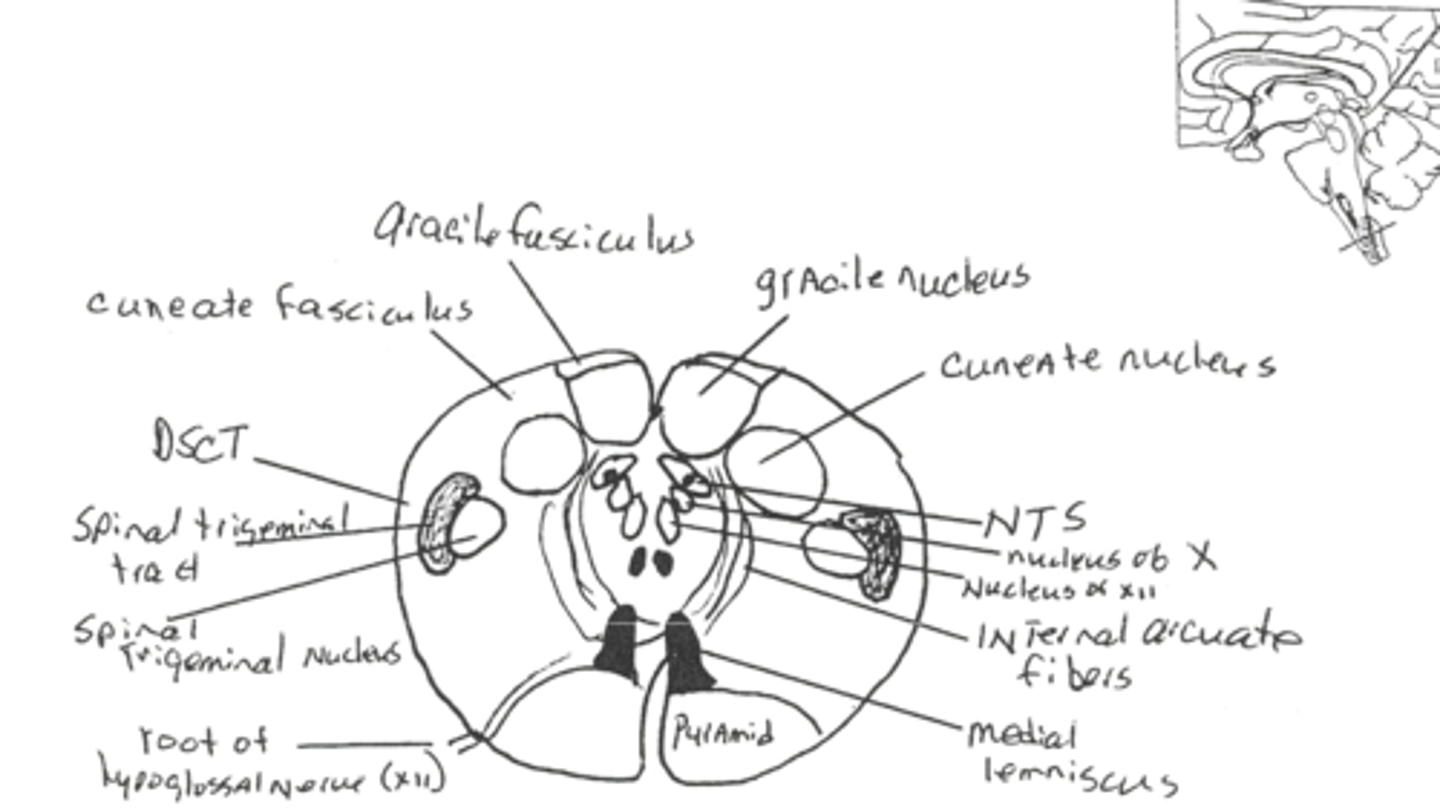
The spinal trigeminal tract can be seen at the level of the _____ ____ - this is the equivalent of the spinal cord ___ ____
Axons arising from cells in the spinal nucleus of V cross ____ and project to the ____
This contains fibers that mediate ____, _____, and ___ __ from the face
The spinal trigeminal tract can be seen at the level of the facial colliculus - this is the equivalent of the spinal cord substantia gelatinosa
Axons arising from cells in the spinal nucleus of V cross midline and project to the thalamus
This contains fibers that mediate pain, temp, and crude touch from the face
Section of the medulla at the level of the middle of the inferior olive
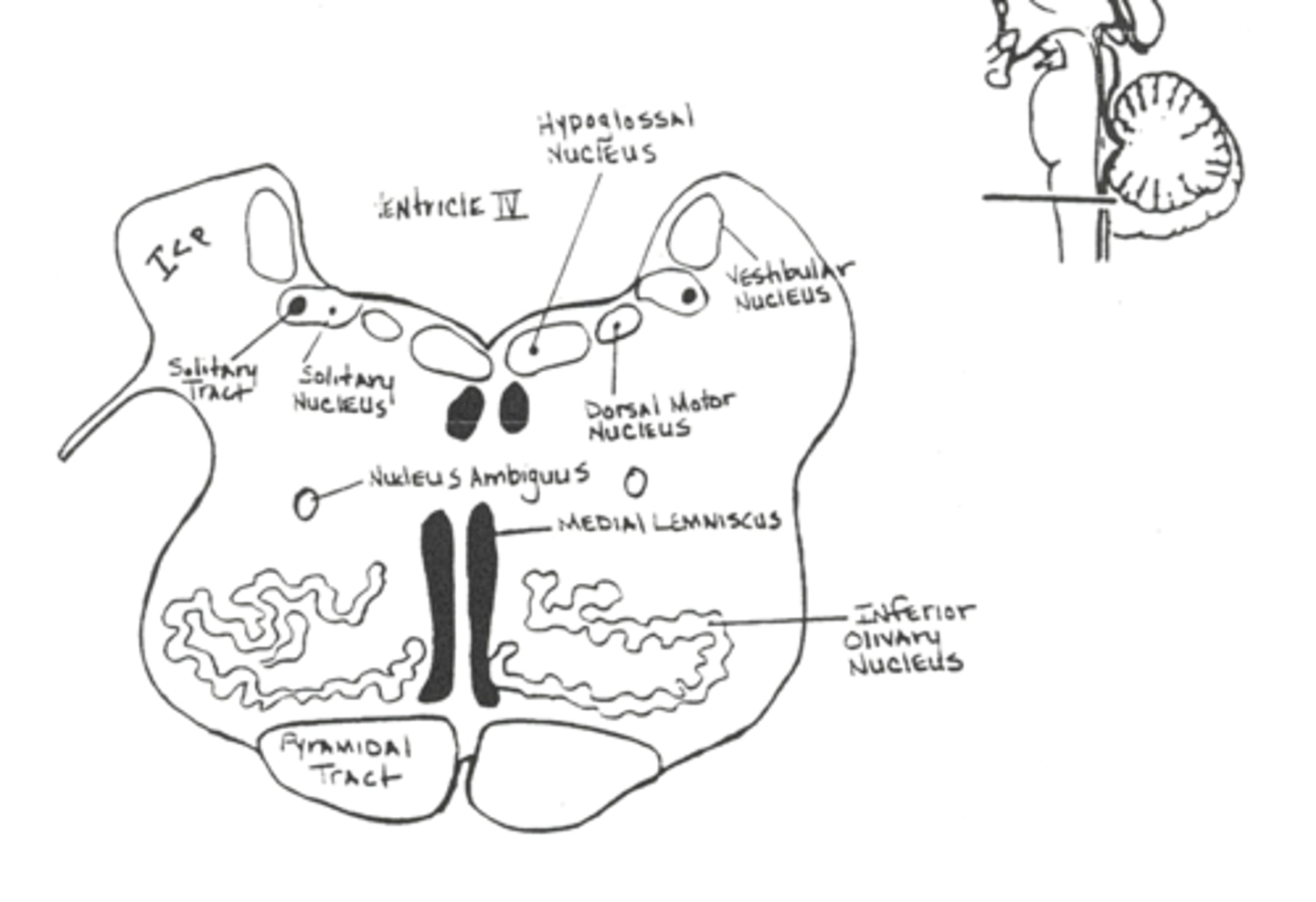
The olive conveys _____ ____ to the ____
involved in _____ _____
The olive conveys excitatory impulses to the cerebellum
involved in motor learning
The DMV can be found at the level of the ____ of the ___ ___
This is _____ _____ neurons that run in the ____ ___ and decrease ___ ___ and promote _____ in the ___
The DMV can be found at the level of the middle of the olivary nucleus
This is preganglionic parasympathetic neurons that run in the vagus nerve and decrease heart rate and promote peristalsis in the gut
The NTS is an ____ nucleus that receives input from ____, ___ and ___
The rostral portion is the ______ center and gets ____ input from ____, ____, ___
The caudal portion is involved in ______ control and also input from ____ and ____
The NTS is an afferent nucleus that receives input from VII, IX and X
The rostral portion is the gustatory center and gets taste input from VII, IX, and X
The caudal portion is involved in cardiovascular control and also input from IX and X
The nucleus ambiguus is the _____ nucleus for ____ and ____
It innervates _____ muscles in the ____ and ____ that control ___ and ____
Contains _____ _____ projecting via the _____
Seen at the level of the ____ of the _____ ____
The nucleus ambiguus is the motor nucleus for IX and X
It innervates striated muscles in the larynx and pharynx that control speech and swalloing
Contains preganglionic parasympathetics projecting via the Vagus
Seen at the level of the middle of the olivary nucleus
The vestibulocochlear nuclei mediates ____ and _____ reception
The vestibulocochlear nuclei mediates hearing and equilibrium reception
Axons of neurons from the _____ _____ ____ form the ____ ____ - these cross the ____ as the ___ ___ __
Axons of neurons from the dorsal column nuclei form the medial lemniscus - these cross the midline as the internal arcuate fibers
Section from the sensory decussation
The vestibuloocular reflex is a response that allows the brain to compensate for ___ ___ with opposite rotation of the ____ and is mediated by the ____ portion of the ____
Normally the vestibuloocular reflex is inhibited by the ____ ____ however, in comatose patients stimulation should evoke the vestibuloocular reflex - if it cannot be elicited it is an indication the ____ ____ may be damaged and the _____ and ____ centers may be compromised
The vestibuloocular reflex is a response that allows the brain to compensate for head movement with opposite rotation of the eyes and is mediated by the ascending portion of the MLF
Normally the vestibuloocular reflex is inhibited by the cerebral cortex however in comatose patients stimulation should evoke the reflex - if it cannot be elicted it is an indicated the brainstem tegmentum may be damaged and the respiratory and CV centers may be compromised
Gaze to the right requires coordinated activity of the right ____ ____ (__) and the left _____ ____ (____)
Integration of this activity occurs at the _____ ____ ____ formation and specifically is known as the ____ ___ ___
The ____ is essential in _____ ____ ____
Gaze to the right requires coordinated activity of the right lateral rectus (VI) and the left medial rectus (III)
Integration of this activity occurs at the paramedia pontine reticular formation and specifically is known as the horizontal gaze center
The MLF is essential in conjugate eye movements
Lesions of the MLF _____ to the ____ ___ (preserving ____ ___ function) produce a disturbance of _____ ____ known as ______ _____ - most common cause is _____
Disruption of ____ ___ leads to _____ and ______
Lesions of the MLF rostral to the abducens nuclei (preserving lateral rectus function) produce a disturbance of conjugate gaze known as internuclear opthalmoplegia
Most common cause is MS
Disruption of conjugate gaze leads to strabismus (cant focus) and diplopia (double vision)
Unilateral lesion of the MLF produces impaired _____ (____ rotation) of the ____ _____ ____ on an attempted lateral gaze to the ____ ___
Contralateral horizontal ______
Unilateral lesion of the MLF produces impaired adduction (medial rotation) of the ipsilateral medial rectus on an attempted lateral gaze to the opposite side
Contralateral horizontal nystagmus
Since the MLFs are in close apposition, a brainstem lesion almost always involves ______ _____ bundles.
Bilateral lesions rostral to the ____ ____ results in dissociated ____ _____ on attempted ____ gaze to either side - impaired _____ and ____ _____ function
Since the MLFs are in close apposition, a brainstem lesion almost always involves both fiber bundles
Bilateral lesions rostral to the abducens nuclei results in dissocated eye movements on attempted lateral gaze to either side - impaired adduction and medial rectus function
The facial nucleus also innervates the _____ muscle so a lesion would cause ______ as there is an inability to dampen ___ ___
The facial nucleus also innervates the stapedius muscle so a lesion would cause hyperacuity as there is an inability to dampen loud noises
The facial nucleus also innervates the ____ ____ and ____ ____
The facial nucleus also innervates the orbicularis oculi and orbicularis oris
A lower motor neuron syndrome of VII causes ___ ___ of the _____ side of the face
______ reflex is lost on that ____ because _____ ___ are lost
Facial LMN syndrome can be caused by _____ _____
A LMN syndrome of VII causes muscle paralysis of the ipsilateral side of the face
Corneal reflex is lost on that side because motor fibers are lost
Facial LMN syndrome can be caused by vestibular schwannoma
Idiopathic facial paralysis is called ____ ___ and involves ____ _____ _____ usually at or just distal to the ____ _____
Idiopathic facial nerve paralysis is called Bell's palsy and involves VII nerve inflammation usually at or just distal to the stylomastoid foramen
In central facial palsy (aka a _____ syndrome) the facial muscles above the _____ retain their tone, but there is paralysis of the facial muscles in the ___ ____ of the _____ ____. This is known as _____ paralysis
This occurs because there is _____ innervation of the ____ quadrants but _____ innervation of the ____ quadrants from the cortexes (ie....)
In central facial palsy (aka a UMN syndrome) the facial muscles above the cheek retain their tone, but there is paralysis of the facial muscles in the lower quadrant of the opposite side (of the central lesion) This is known as quadrantic paralysis
This occurs because there is bilateral innervation of the upper quadrants but contralateral innervation of the lower quadrants from the cortexes - (ie UMN for upper are bilateral but UMN for lower contralateral)
The NTS is important for coordinating ________ reflexes
The NTS is important for coordinating cardiovascular reflexes
The NTS helps coordinate the _____ _____ reflex which responds to ______ ____ and _____ of the blood and adjusts ____ accordingly
The NTS helps coordinate the carotid body reflex which responds to carbon dioxide and oxygen of the blood and adjusts breathing accordingly
Injury to the midbrain can cause ______
Injury to the rostral pons can cause _____ ____
Injury to the lower pons or upper medulla can result in ____ that is ____ and of ___ ____ (called____ ___) - this often transitions to ____ ___
Injury to the midbrain can cause hyperventilation
Injury to the rostral pons can cause apneustic breathing
Injury to the lower pons or upper medulla can result in breathing that is irregular and of uneven depth (called ataxic breathing) this often transitions to respiratory arrest
RVLM provides _____ drive to _____ ____ neurons in the _____
RVLM is the ____ ___ - lesions here produce a _____ in _____
NTS connection to RVLM is _____
So an increase in ______ causes a _____ in RVLM activiy
RVLM provides tonic drive to preganglionic sympathetic neurons in the IML
RVLM is the pressor center - lesions here produce a drop in BP
NTS connection to RVLM is inhibitory
So an increase in BP causes a decrease in RVLM activity
NTS connection to DMV is ______ so an increase in ____ will cause _______ outflow from the ____ resulting in _____ ____
NTS connection to DMV is excitatory so an increase in BP will cause increased outflow from the DMV resulting in lower HR
Trigeminal fibers are involved in the ____ _____
Injury to the ____ division of the ____ _____ causes loss of ____ ____ and ____ on the _____ side because the _____ limb of the reflex arc is lost however the _____ ____ remains intact
stimulation of the _____ side will result in _____ ____ indicating the ____ limb of the reflex arc is ____ on the _____ side
Trigeminal fibers are involved in the corneal reflex
Injury to the opthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve causes loss of corneal sense and reflex on the ipsilateral side because the afferent limb of the reflex arc is lost however the opposite side remains intact
stimulation of the opposite side will result in bilateral blinking indicating the efferent limb of the reflex arc is intact on the injured side
In patients with peripheral facial palsies, corneal ____ will be present on both sides, but no ____ ____ can be elicited on the side of the ____ because the ____ __ of the reflex arc is lost.
however, stimulation of the _____ on the side of the ____ will cause ____ and ____ of the ____ eye
In patients with peripheral facial palsies, corneal sensation will be present on both sides, but no corneal reflex can be elicited on the side of the lesion because the efferent limb of the reflex arc is lost
However, stimulation of the eye on the side of the lesion will cause blinking and closure of the opposite eye (because sensation is present and efferent limb of opposite side intact)
Loss of LR function would result in...
Double vision