Lecture 24: type IV hypersensitivities
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
immune mechanism of type IV hypersensitivity
-CD4 T cells
-CD8 CTLS
mechanism of injury: type IV hypersensitivity
-macrophage activation, cytokine inflammation
-cell lysis
type IVa hypersensitivity is mediated by
-IFN-gamma, TNF-alpha (Th1 cells)
-macrophage
EX: tuberculin reaction
type IVb hypersensitivity
Mediated by Th2 cells --> IL-5, IL-4, IL-13
-eosinophils
ex: chronic asthma, allergic rhinitis, exanthema
type IVc hypersensitivity
Mediated by cytotoxic T cells --> perforin, granzymes
-T cells
EX: contact dermatitis
type IVd hypersensitivity
-mediated by IL-8, GM-CSF
-neutrophils
EX: AGEP
type IV hypersensitivity is aka
T-cell mediated
delayed type
type IV hypersensitivity mechanisms of injury
-for a, b, and d: cytokines induce inflammation
-for c: directly killing target cells
name some antigens that cause TIVH response
-infectious agents (TB)
-environmental antigens/chemicals
-autoantigens
-transplanted organs
describe patch tesing
-used to diagnose type IV hypersensitivity
-used to diagnose suspected contact dermatitis
-apply thick panels of allergens to skin, check reactions after several days
list some TIVH diseases
rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, type I DM, IBS, psoriasis
-transplant rejection
p-i reactions
-pharmacologic interaction with immune receptors
-drug binds to MHC or TCRand stimulates T cell
direct p-i reaction
drug binds to TCR
indirect p-i reaction
drug binds MHC-peptide
type IVa hypersensitivity is mediated by what cells?
-primarily Th-17 (IL-17) and Th1 cells
-IL-17 recruits neutrophils
-IFN-y activates macrophages' and TNF recruits leukocytes
types of IVa reactions
-tuberculin reaction: mantoux (PPD) test
-granuloma formation
-tuberculoid granuloma
-allergic contact dermatitis
what causes the induration of PPD skin tests?
-TH1 effector cel recognizes antigen and releases cytokines which act on vascular endothelium
-recruitment of macrophages mediates tissue damage
false positives of tuberculin skin tests often appear with
-previous infection to non-TB mycobacterium
-prior BCG vaccination
-incorrect administration or interpretation of test
false negatives of tuberculin skin tests result from
-very recent or very old TB infection
-very young age
-recent live virus vaccine
-some viral diseases
what causes granuloma formation
CMI removes most intracellular organisms
-continuous stimulation/accumulation of macrophages
what causes contact dermititis?
-haptens penetrate skin and trigger immune response
-langerhans cells present Ag to T cells
-keratinocytes secrete cytokines
-damage is rash is monocyte/cytokine mediated
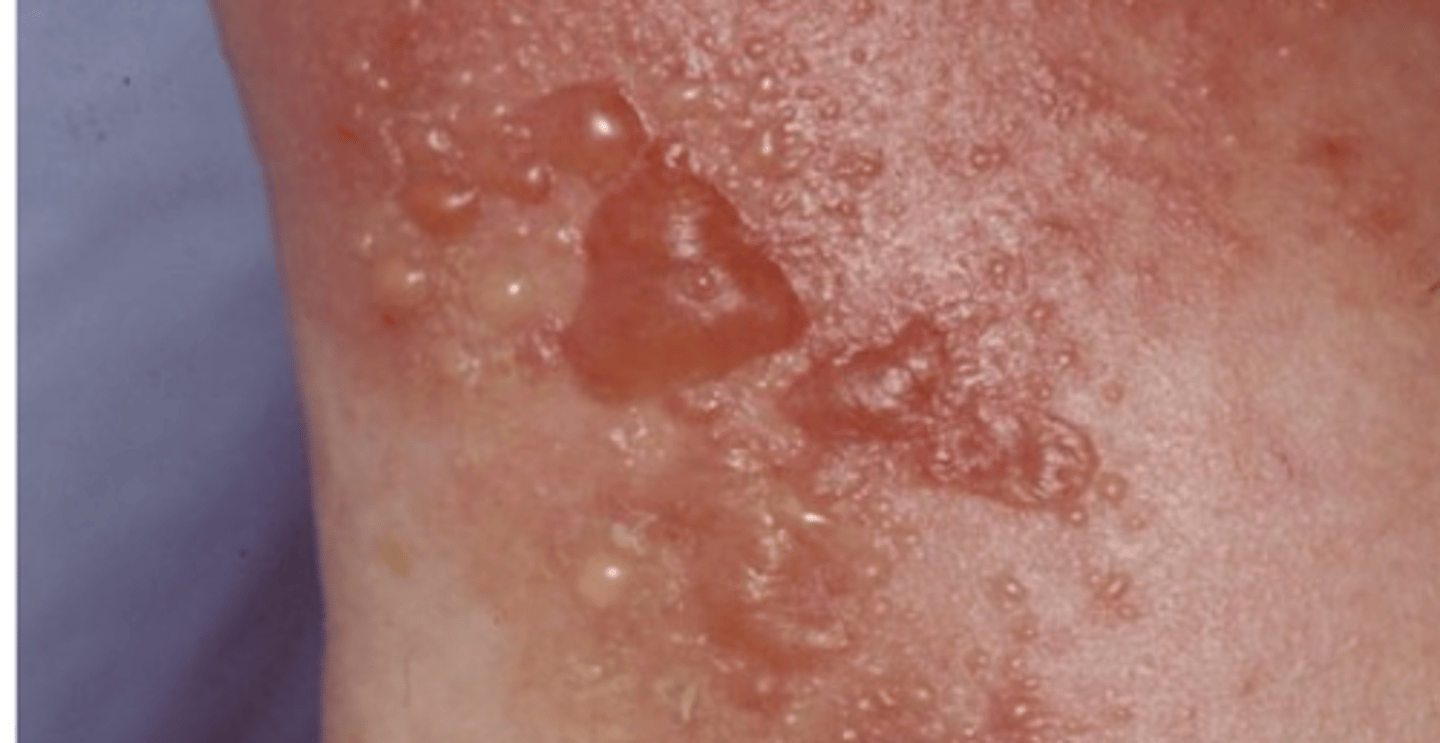
list some common allergens that cause contact dermatitis
poison ivy most common
-nickel, gold
-laatex, rubber
-plant resins/saps
-formaldehyde
-bacitracin, neomycin
-cosmetics
what are the two phases of contact dermatitis/DTH?
-sensitization: keratinocytes activated by allergen; produce TNF, IL-1, GM-CSF
-challenge: subsequent exposure, rapid activation of Th1 cells; IFN-y causes macrophage infiltration
Type IVb reactions
-eosinophil activation, triggered by Th2 type immune response
-seen in chronic asthma airway remodeling
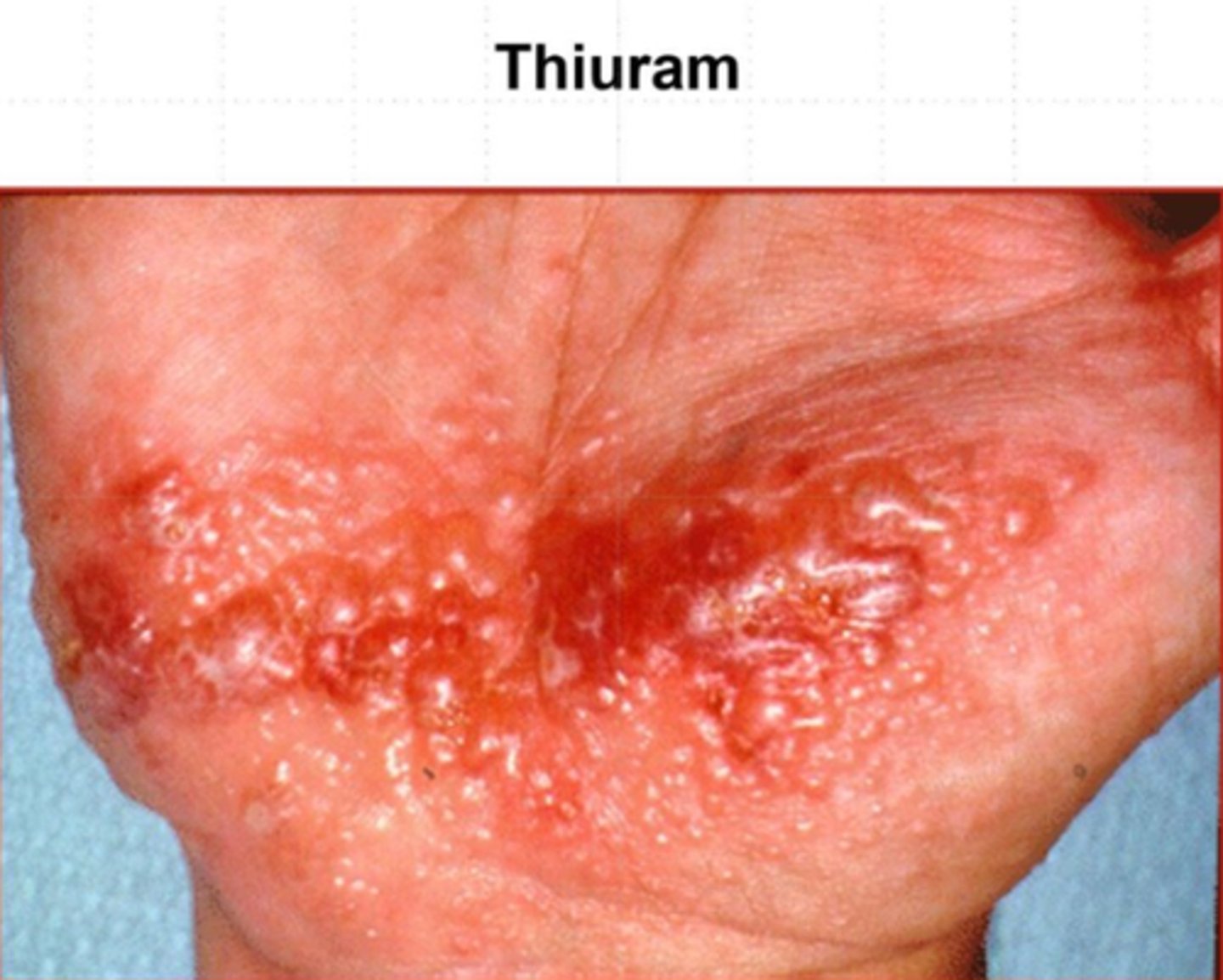
type IVd reactions
-neutrophilic inflammation mediated by T cells
-acutee generalized exanthematous pustulosus
Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP)
type IVd disease
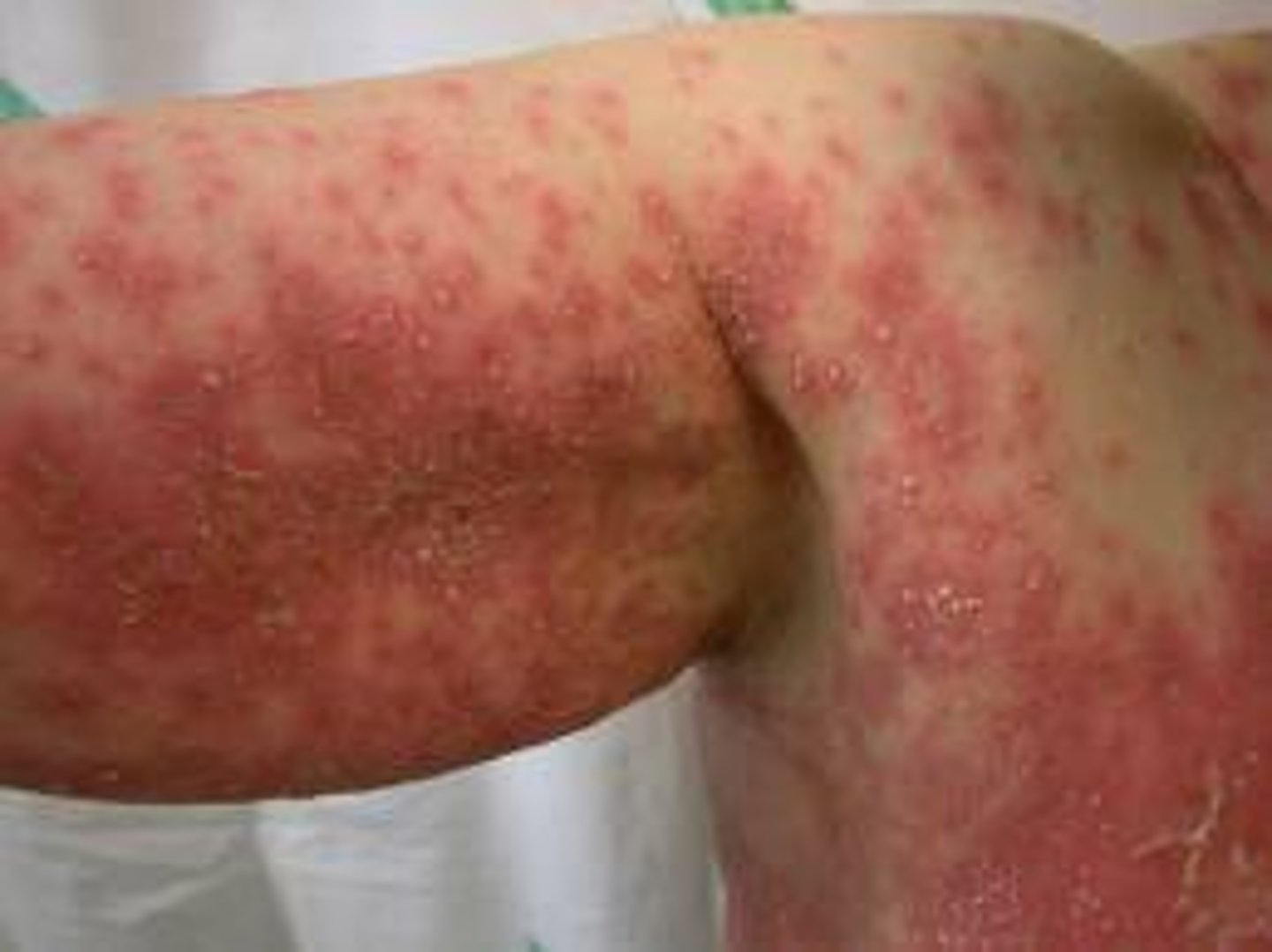
type IVc hypersensitivity is aka
delayed type hypersensitivity
mediation of type IVc hypersensitivity
-CD4 T cells recognize Ag on APC, become Th1 cells
-Th1 cells secrete IL-2 and IFN-y
-takes 24-48 hours
type IVc hypersensitivity is found in
contact dermatitis, drug reactions, hepatitis, graft rejections
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
skin detachment of <10% of body
type IVc
-commonly cauased by meds
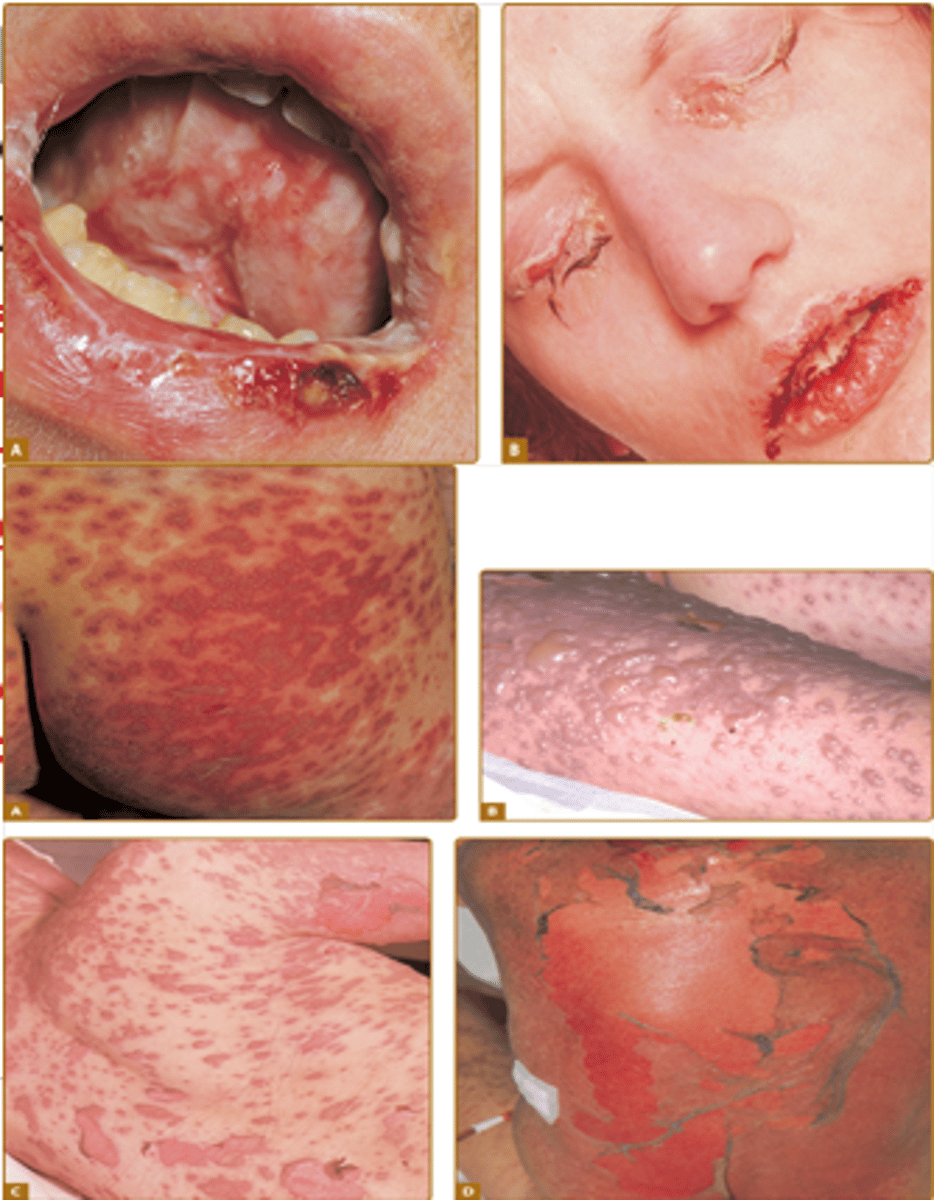
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
detachment of >30% of the body
Type IVc
-commonly caused by meds
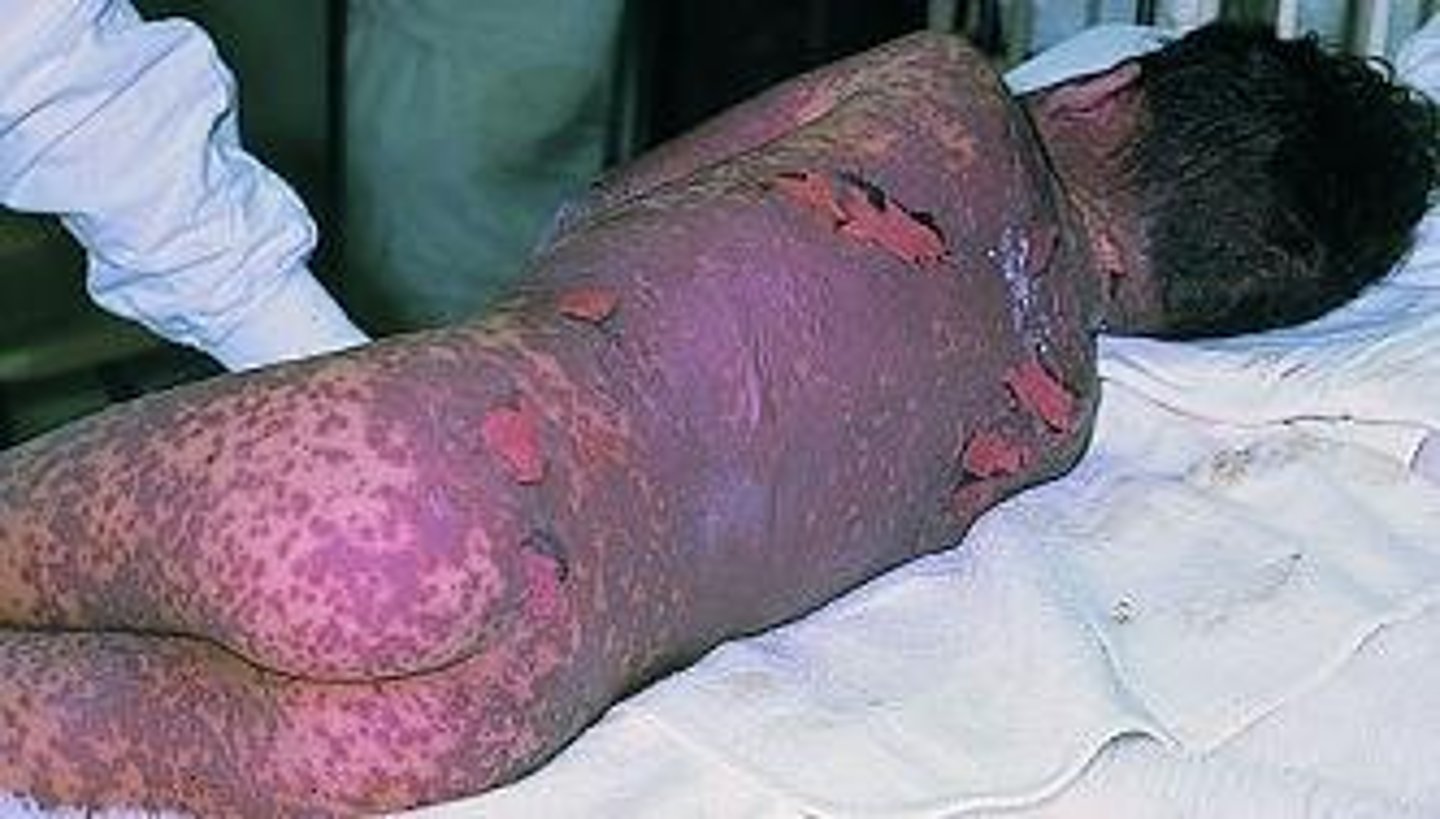
IVc reactions cause what?
the cell death causes epidermis to separate from dermis (ex TEN and SJS)
which type has no cytokines involved
type IVc; uses cell death by cytotoxic T cells