Oral Biology
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Type of cells that teeth develop from
Epithelium (from oral ectoderm) - Determines shape of tooth (permissive influence)
Ectomesenchyme (from neural crest cells) - Determines fate of tooth
Morphology vs Differentiation
Morphology - Changes in shape of developing tooth
Differentiation - Different cell type/function (odontoblast vs ameloblast)
When does odontogenesis begin?
6 weeks in utero
Dental Lamina Stage
Initial induction
Primary Epithelial Band - Horseshoe thickening of oral ectoderm in upper and lower jaw
Dental lamina - Sheet growing on epithelial band where tooth buds can develop
Vestibular lamina (vestibule) - Space separating lips/cheek from teeth/gingiva (found buccal to teeth)
Bud Stage
Proliferation
Bud forms on dental lamina (epithelial cells)
10 buds on each jaw
Ectomesenchyme condense around bud
Congenital absence from interruption in this stage
Cap Stage
Proliferation, Differentiation, Morphogenesis
Shape of tooth becomes evident from unequal proliferation of bud cells (morpho-differentiation)
Successional lamina forms on lingual side of teeth
Enamel knot - Cluster of non-dividing epithelial cells
All teeth have primary knots
Molars have additional secondary knots
Tooth germ becomes enamel organ, dental papilla, and dental sac
Enamel Organ
From Oral Epithelium
Forms ameloblasts and eventually enamel for crown shape
Induces dentin formation
Dental Papilla
From ectomesenchyme
Forms odontoblasts which is responsible for dentin and pulp shape
Determines tooth made
Dental Sac
From ectomesenchyme
Forms cementoblast and cementum
Also forms periodontium, PDL, and alveolar bone
Early Bell Stage
Proliferation, Differentiation, Morphogenesis
DEJ location is determined
Enamel organ differentiates to 4 layers
Cervical Loop is junction of IEE and OEE. Dental papilla cells proliferate to outer dental papilla (future odontoblasts) and inner dental papilla cells
Outer Enamel Epithelium
Outer protective barrier
Capillary Plexus
Aids with transport of material inwards for oxygen and nutrients
Stellate Reticulum
Secretes GAGs which draw water into enamel organ and increase volume
Provides support so crown shape is maintained until hard tissue is formed
Stratum Intermedium
Enables IEE cells to become ameloblasts
Forms functional unit with IEE
Contains alkaline phosphatase for mineralization
Inner Enamel Epithelium
Become ameloblasts
Initiate dentin formation (reciprocal induction)
Forms enamel knots in cap stage
Makes cusps, fissures, and ridges of final crown pattern
Late Bell Stage
Proliferation and Induction
Hard tissue is formed
Ameloblast (forming enamel) and Odontoblast (forming dentin) using reciprocal induction
Reciprocal Induction
IEE becomes preameloblast
Preameloblast helps dental papilla cells differentiate to preodontoblast
Preodontoblast becomes odontoblast and secretes predentin
Odontoblast induces preameloblast to become ameloblasts
Ameloblasts secrete enamel until they reach 30% calcification
Additional Reciprocal Induction Notes
First enamel and dentin formed at DEJ
Dentin formed before enamel
Last enamel formed at outermost layer of tooth
Last dentin formed at dentino-pulpal junction
Hertwig’s Epithelial Root Sheath
Sheath formed when IEE and OEE join
Cervical loop grows apically
HERS does not form root but induces root odontoblast differentiation to synthesize dentin
Eventually detach and migrate so dental sac mesenchymal cells take their place and become cementoblasts to lay cementum around root
Each medial ingrowth of HERS causes additional tooth root
Epithelial Rests of Malassez
HERS remnant that detaches from root surface
Can become tumor-forming cells
Those that do not disappear will calcify and become “cementicles”
Lateral periodontal cysts occur
Usually in adult males and not associated with pain
Does not need treatment unless pulpal tissue is necrotic
HERS disturbance anomalies
Exposed Root Dentin - HERS detaches too late for dental sac mesenchymal cells to be placed on dentin and cementum will not appear on that portion of the tooth as a result
Enamel Pearls - HERS cells do not detach, causing odontoblasts to form enamel pearls
Accessory Root Canals - Lack of HERS prevents dental papilla cell differentiation, causing lack of dentin and cementum formation
Amelogenesis
Presecretory Stage - IEE → Pre-ameloblast → Ameloblast
Secretory Stage - Ameloblast → Enamel
~30% mineralized
Initial secretory ameloblasts secrete prism-less enamel
Secretory ameloblasts secrete enamel prisms (Tome’s Process)
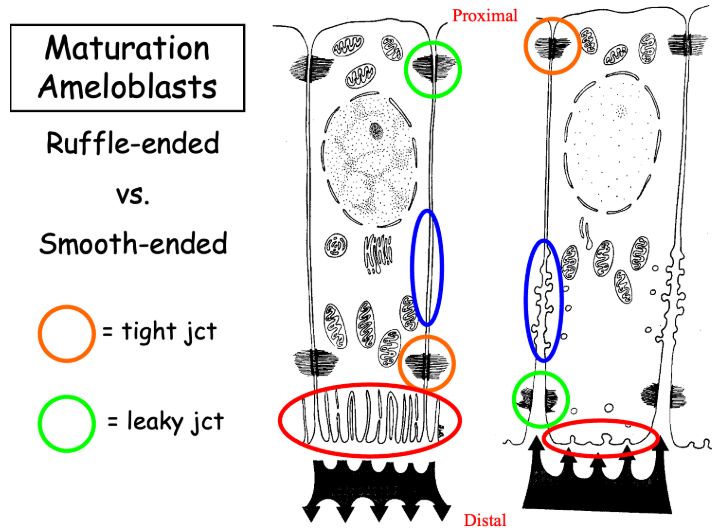
Maturation Stage
>96% mineralized
Ruffle-ended ameloblasts - Have tight junctions in distal end to prevent enamel from leaking
Smooth-ended ameloblasts - Have leaky junctions in distal end to remove water and organic proteins
Protective - Ameloblasts become cuboidal covering mature enamel
Reduced Enamel Epithelium
Remnant of enamel organ
All 4 enamel organ layers and papillary layer contribute to REE
Mature Dentin
Light yellow color
Resilient and hard
70% inorganic (HA), 20% organic (Collagen I), 10% water
Derived from dental papilla
Apatite crystals with collagen fibers (not parallel to dentin tubules) in matrix
Odontoblasts
Only cells in dentin
Reside within dentin tubules
Projection as odontoblastic process (Tome’s fiber)
Dentinogenesis Process
Differentiation of odontoblasts (IEE induces dental papilla cells to become odontoblast)
Predentin formation
Mantle mineralization
Predentin formation
Circumpulpal mineralization
Mantle Dentin
Outer, first-formed layer
Thick von Korff’s fibers (Type III collagen)
Circumpulpal Dentin
Outlines pulp
Has part of primary, and all of secondary and tertiary dentin
Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Dentin
Primary Dentin - Formed prior to and during tooth eruption. Forms fast
Secondary Dentin - After root formation and continuous through life, causing pulp recession. Has directional change and deposition is not even
Tertiary Dentin - Responds to stimuli and has osteodentin cells
Reactive Dentin - Pre-existing odontoblasts
Reparative Dentin - Newly differentiated odontoblasts
Dentinal Tubules
Contain odontoblastic process and interstitial fluid
1 in 10 have nerves
S-shaped in crown and straight in roots
Tapered contour
Canaliculi
Intratubular vs Intertubular Dentin
Intratubular Dentin
Lines wall of tubule
40% more mineralized than intertubular dentin
Dentin Sialoprotein, No Collagen fibers
Not in mantle or interglobular dentin
Intertubular Dentin
Type I collagen
Between dentinal tubules
Interglobular Dentin
Irregular and hypomineralized
Between circumpulpal and mantle dentin
Caused by Vitamin D deficiency or high fluoride during development
Incremental growth lines of von Ebner
5 day cyclic growth lines
Exaggerated change in fiber orientation
Contour Lines of Owen
Wider, thicker incremental lines
Deficiencies during mineralization
Neonatal Line
Thickest line
Made during birth
On all primary teeth and cusp of first permanent molar
Sclerotic Dentin
Occludes dentin tubules with material
Appears transparent
Commonly in apical 1/3 of root and crown
Increases with age
Caused by mineral deposition and spread of peritubular dentin
Dead Tract Dentin
Empty dentinal tubules caused by sclerotic dentin
Odontoblastic process retracts/dies
Appears black when transmitted light
Sealed off by tertiary dentin
Granular Layer of Tomes
In ground section only
Granular appearing layer in root dentin between dentin and cementum
Caused by arrangement of collagenous and noncollagenous proteins
Age effects on Dentin
Secondary Dentin - Decreases volume of pulp with age and may cause pulp stones
Tertiary Dentin - Decreases volume of pulp
Sclerotic Dentin and Dead Tract dentin - May appear
General Enamel Details
Epithelial origin
Made by ameloblasts
Has no cells and can’t self-repair
96% mineralized (HA crystal arrangement)
Permeable
Can be demineralized/remineralized
Has long and thin crystals (larger than dentin crystals)
5 Enamel Physical Properties
Color
Birefringence - light double refracts (splits to two rays)
Not translucent in young enamel
Thickness
Thicker at crown and thins until it reaches gingival level
Hardness
Mature enamel has higher enamel to protein ratio than earlier stages
Hard and brittle
Solubility
Organic acid decalcifies enamel → increases soluble calcium → increases caries susceptibility
Permeability
Permeable to dyes and radioactive isotopes
Makes demineralization and remineralization possible
Dehydrated enamel looks chalky and lighter in color
Calcium HA Substitutions
Carbonate replace phosphates
Magnesium replaces calcium
Fluoride replaces hydroxyl ion (more resistance from acid dissolution)
Organic matrix composition in enamel
Proteins (amelogenins and non-amelogenins) and lipids (cell membrane remnants)
Distributed between HA crystals
Rods and Interrods
Rods - Long axis
Interrod - Angled from rod
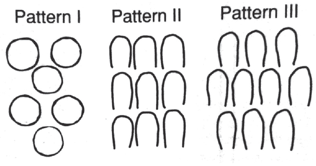
Enamel Patterns
Pattern 1 - DEJ and Surface (formed slowly)
Pattern 3 - Keyhole patterns
Head - Occlusal (parallel to long axis)
Tail - Cervical (65-70 degree angulation to long axis)
4 Ameloblasts needed to make a single enamel rod
Enamel Rod Orientation and Support
Perpendicular to DEJ and surface
Slightly S-shaped
Enamel rods unsupported by dentin fracture
Full-length and shortened enamel rods that are supported will remain
Rod Sheath
Boundary between rod and interrod containing organic matter
Has amelogenin and ameloblastin
Caries penetrate through sheath
Etching Patterns
Type 1 - Remove rods
Type 2 - Remove interrods
Type 3 - Random removal pattern
Cross Striations
Diurnal (every 24 hours)
Perpendicular to long axis of enamel prisms
Striae of Retzius
Weekly
Striae of Retzius
Increased organic content
Perikymata
Imbrication lines of Pickerill
Found on surface of tooth
Hunter-Schreger Band
Optical phenomenon making light and dark bands
Gnarled Enamel
Complex twisting of rods near DEJ
Harder and can break burs
Resists masticatory load at cusps/incisal edges
Non-prismatic enamel
Outer layer of enamel
First formed and is highly mineralized due to lack of organic material and rods
Caused by absence of Tomes process of ameloblasts in first and last stages of enamel deposition
Enamel Spindles
Elongated odontoblastic process extending into enamel
Enamel Tuft
Tuft of grass in DEJ
Contains organic enamel proteins
Developmental origin
Enamel Lamellae
Crack across enamel
Contains organic material
Developmental and post-eruptive origin
Attrition, Abrasion, Erosion
All cause enamel loss
Attrition - Tooth to tooth contact
Abrasion - External object
Erosion - Acidic agents (including bulimic erosion)
Enamel Coatings
Developmental coatings
REE/Nasmyth’s membrane (primary enamel cuticle) - Worn away after mastication and eating
Afibrillar Cementum (Secondary enamel cuticle)
Acquired coatings
Pellicle
Plaque
Calculus
Orders of DEJ
1st order - Scallops
2nd order - Microscallops
3rd order - Nanostructual interaction between collagen of dentin and enamel
Age effects on enamel
Attrition
Decreased permeability
Stains and dark color
Less water content
More brittle
Increase fluoride use and reduced complex carbs → Decrease in caries
Enamel Disturbances during Tooth Development
Febrile disease
Tetracycline defects (bands of color)
Fluoride-induced defects (hypermineralized)
Ectodermal dysplasia (can cause loss of teeth or modified tooth shape)
Amelogenesis Imperfecta (teeth are colored, sensitive, and at risk of decay)
Enamel pearl (Enamel sphere in crown or root furcation of teeth)
Enamel in furcation (enamel surface extends to root furcation)