Cell Structure
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
What are the two types of cells?
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
What are 2 examples of eukaryotic cells?
Plant and Animal
What is an example of a prokaryotic cell?
Bacteria
Eukaryotic cells contain _________ _______ ____________ and a nucleus containing genetic material.
membrane bound organelles
Prokaryotic cells are much _____ than eukaryotic cells.
smaller
What is the prokaryotic cell wall composed of?
Peptidoglycan
How is genetic information stored in a prokaryotic cell?
Found free within the cytoplasm as chromosomal DNA and plasmid DNA
What is chromosomal DNA?
A single large loop of circular DNA.
What are plasmids?
Small, circular loops of DNA found free in the cytoplasm.
Are plasmids part of the main DNA within prokaryotic cells?
No, they are separate from the main DNA.
What kind of genes do plasmids carry?
They carry genes that provide genetic advantages e.g. antibiotic resistance.
What is order of magnitude?
A power to the base 10.
What are orders of magnitude used to do?
They are used to quantify and compare size.
What is a centimetre (cm)?
1 × 10⁻² metres
What is a millimetre (mm)?
1 × 10⁻³ metres
What is a micrometre (μm)?
1 × 10⁻⁶ metres
What is a nanometre (nm)?
1 × 10⁻⁹ metres
What is the difference in order of magnitude between a human hair (100 μm) and the HIV virus (length = 100 nm)?
3 orders of magnitude
List the components of both plant and animal cells (5)
Nucleus, Cytoplasm, Cell membrane, Mitochondria, Ribosomes
List the additional cell components found in plant cells (3)
Chloroplasts, Permanent vacuole, Cell wall
Other than storing genetic information, what is the function of the nucleus?
Controls cellular activities
Describe the structure of the cytoplasm
Fluid component of the cell. Contains organelles, enzymes and dissolved ions and nutrients.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
Site of chemical reactions. Transport medium.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
It controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
What is the function of the mitochondria?
Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration.
What is the function of the ribosomes?
Site of protein synthesis.
What is the plant cell wall made of?
Cellulose
What is the function of the plant cell wall?
It provides strength and prevents the cell bursting when water enters by osmosis.
What does the permanent vacuole contain?
Cell sap (a solution of salts and sugars).
What is the function of the permanent vacuole?
Supports the cell and keeps it turgid.
What is the function of chloroplasts?
It is the site of photosynthesis, it contains chlorophyll which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
Adaptations of sperm cells: _______ nucleus contains genetic information.
Haploid
Adaptations of sperm cells: Tail enables ________.
movement
Adaptations of sperm cells: Mitochondria provide ______ for tail movement.
energy
Adaptations of sperm cells: Acrosome contains ______ that digest the egg cell membrane.
enzymes
Adaptations of nerve cells: Long axon allows ________ impulses to be transmitted all over the body from the _______ ________ _______.
electrical, central nervous system
Adaptations of nerve cells: Dendrites from the cell body connect to and receive _______ from other nerve cells, ________ and ______.
impulses, muscles, glands
Adaptations of nerve cells: Myelin sheath ________ the ____ and speeds up the transmission of ________ along the nerve cell.
insulates, axon, impulses
Adaptations of muscle cells: Arrangement of ______ filaments allows them to slide over each other to produce muscle __________.
protein, contraction
Adaptations of muscle cells: ____________ to provide energy for muscle contraction.
Mitochondria
Adaptations of muscle cells: Merged cells in ______ muscle allow muscle fibre contraction in _____.
skeletal, unison
Adaptations of root hair cells: _____ surface area to absorb ________ and water from surrounding soil.
Large, nutrients
Adaptations of root hair cells: ____ walls that do not restrict water _________.
Thin, absorption
Adaptations of xylem cells: No upper or lower _______ between cells to provide a ___________ route for water to flow.
margins, continuous
Adaptations of xylem cells: _____, woody side walls strengthen their structure and ________ collapse.
Thick, prevent
Adaptations of phloem cells: ______ plates let dissolved _____ acids and sugars be transported up and down the ____.
Sieve, amino, stem
Adaptations of phloem cells: __________ cells provide energy needed for ________ __________ of substances along the phloem.
Companion, active transport
What is cell differentiation?
The process by which cells become specialised.
Why is cell differentiation important?
Allows production of different tissues and organs that perform various vital functions in the human body.
At what point in their life cycle do most animal cells differentiate?
Early in their life cycle
For how long do plant cells retain the ability to differentiate?
Throughout their entire life cycle
What is the purpose of cell division in mature animals?
Repair and replacement of cells
What changes does a cell go through as it differentiates?
Becomes specialised through acquisition of different sub-cellular structures to enable a specific function to be performed by the cell.
Define magnification
The number of times bigger an image appears compared to the size of the real object.
Define resolution
The smallest distance between two objects that can be distinguished.
How does a light microscope work?
Passes a beam of light through a specimen which travels through the eyepiece lens, allowing the specimen to be observed.
What are the advantages of light microscopes? (4)
Inexpensive
Easy to use
Portable
Observe both dead and living specimens
What is the disadvantage of light microscopes?
Limited resolution
How does an electron microscope work?
It uses a beam of electrons which are focused using magnets.
The electrons hit a fluorescent screen which emits visible light, producing an image.
Name the two types of electron microscope
Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
What is the advantage of electron microscopes?
Greater magnification and resolution.
Why do electron microscopes have a greater magnification and resolution?
They use a beam of electrons which has a shorter wavelength than photons of light.
How have electron microscopes enabled scientists to develop their understanding of cells?
Allow small sub-cellular structures (e.g. mitochondria, ribosomes) to be observed in detail.
Enable scientists to develop more accurate explanations about how cell structure relates to function.
What are the disadvantages of electron microscopes? (4)
Expensive
Large so less portable
Require training to use
Only dead specimens can be observed
How can magnification be calculated?
magnification = size of image / size of real object
What is standard form?
A way of expressing numbers - written as a figure between 1 and 10 multiplied by a positive or negative power of 10.
Write 0.005 in standard form
5 × 10⁻³
Write 10382 in standard form
1.0382 × 10⁴
How do bacteria multiply?
Binary fission
How often do bacteria multiply?
Once every 20 minutes.
What are the conditions bacteria need to multiply? (2)
Enough available nutrients
Suitable temperature
State 2 ways in which bacteria can be grown
Nutrient broth solution
Colonies on an agar gel plate
What nutrients make up a nutrient broth solution?
All nutrients required for bacteria to grow including nitrogen for protein synthesis, carbohydrates for energy and other minerals.
What are uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms needed for?
Investigating disinfectant and antibiotic action.
Preparation of an uncontaminated culture using aseptic technique: Step 1
Use pre-sterilised plastic Petri dishes or sterilise glass Petri dishes and agar gel before using with an autoclave.
Preparation of an uncontaminated culture using aseptic technique: Step 2
Pour the sterile agar gel into the Petri dish and allow time to set.
Preparation of an uncontaminated culture using aseptic technique: Step 3
Sterilise the inoculating loop by passing it through a Bunsen burner flame.
Preparation of an uncontaminated culture using aseptic technique: Step 4
Dip the inoculating loop into the solution of microorganisms and make streaks with the loop on the surface of the agar.
Preparation of an uncontaminated culture using aseptic technique: Step 5
Put the lid on the Petri dish and secure it with tape. Label accordingly then turn and store upside down.
Preparation of an uncontaminated culture using aseptic technique: Step 6
Incubate the culture at 25°C in school laboratories.
Why must Petri dishes and culture media be sterilised before use?
To kill any bacteria already present.
Why must inoculating loops be sterilised by passing them through a Bunsen burner flame?
To kill any bacteria present on the inoculating loop.
Why must the Petri dish lid be secured with adhesive tape?
Stops bacteria in the air contaminating the culture.
Why is the lid of the Petri dish not fully sealed?
The lid is not fully sealed to prevent the growth of anaerobic bacteria in a lack of oxygen.
Why must the Petri dish be stored upside down?
To prevent condensation from forming and dripping down onto the colonies.
Why are cultures incubated at 25°C in school laboratories?
To avoid growing pathogens that could be harmful to humans.
What is the formula used to calculate cross-sectional area of a bacterial colony or clear area around a bacterial colony?
πr²
Calculating the number of bacteria in a population after a certain time from the mean division time: Step 1
Calculate the number of times the bacteria will divide in the given time period from the mean division time.
Calculating the number of bacteria in a population after a certain time from the mean division time: Step 2
Use the equation to calculate the number of bacteria.
What equation is used to calculate the number of bacteria in a population at the end of a time period.
Number of bacteria in population at end of time period = number of bacteria at the beginning of the time period × 2ⁿᵘᵐᵇᵉʳ ᵒᶠ ᵈᶦᵛᶦˢᶦᵒⁿˢ ᶦⁿ ᵗʰᵉ ᵗᶦᵐᵉ ᵖᵉʳᶦᵒᵈ.
Calculate the number of bacteria that will be present after 3 hours for a population that divides every 15 minutes and has 5 bacterium present now. Express your answer in standard form.
2.048 × 104
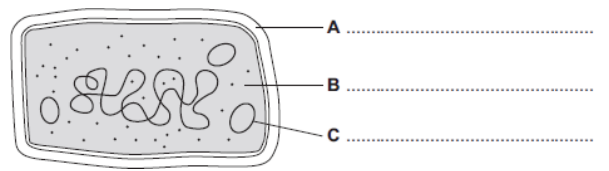
The diagram shows the structure of a bacterial cell.
Label structures A, B and C.
A: Cell wall
B: Cytoplasm
C: Plasmid
Give one difference between the structure of the bacterial cell and an animal cell.
Animal cells have their genetic material in a nucleus. Bacterial cells have their genetic material free in the cytoplasm as chromosomal DNA and plasmid DNA.
Name two structures that are found in a plant cell but are not found in a bacterial or an animal cell.
Permanent vacuole and chloroplasts
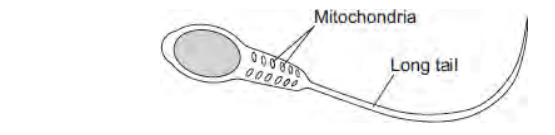
Cells can be specialised for a particular job. The diagram shows the structure of a human sperm cell.
Describe how the long tail and the mitochondria help the sperm to do its job.
The long tail allows sperm cell to swim towards the egg. The mitochondria release energy for movement in respiration.
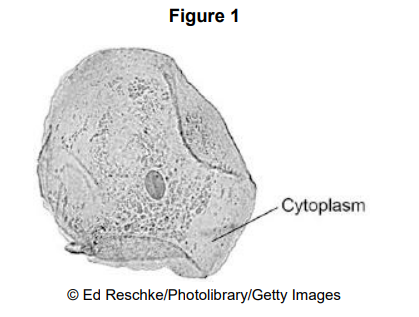
Ribosomes and mitochondria are not shown in Figure What type of microscope is needed to see ribosomes and mitochondria?
Electron microscope
A red blood cell is 8µm in diameter. A bacterial cell is 40 times smaller. Calculate the diameter of the bacterial cell.
0.2µm
Antibiotics cannot be used to treat diseases caused by viruses. Why?
Viruses live inside cells.
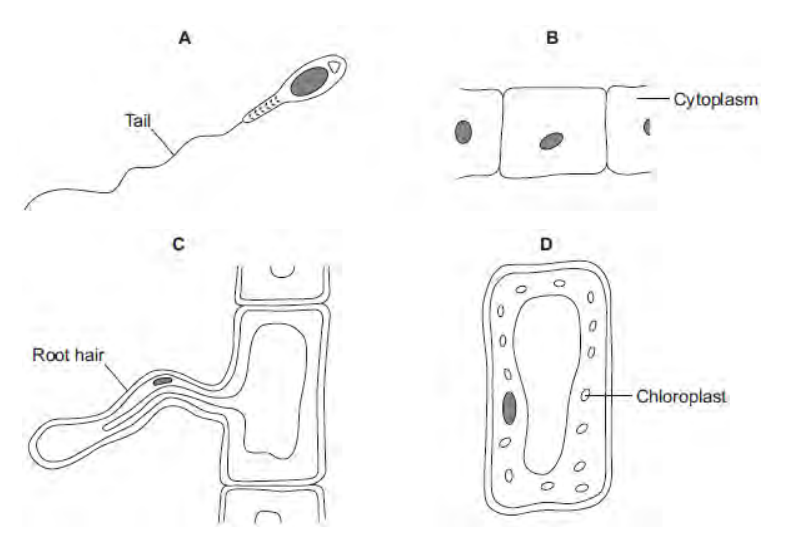
The diagrams show four types of cell, A, B, C and D. Two of the cells are plant cells and two are animal cells. Which two of the cells are plant cells? Give two reasons for your answer.
C and D; They have cell walls and permanent vacuoles.
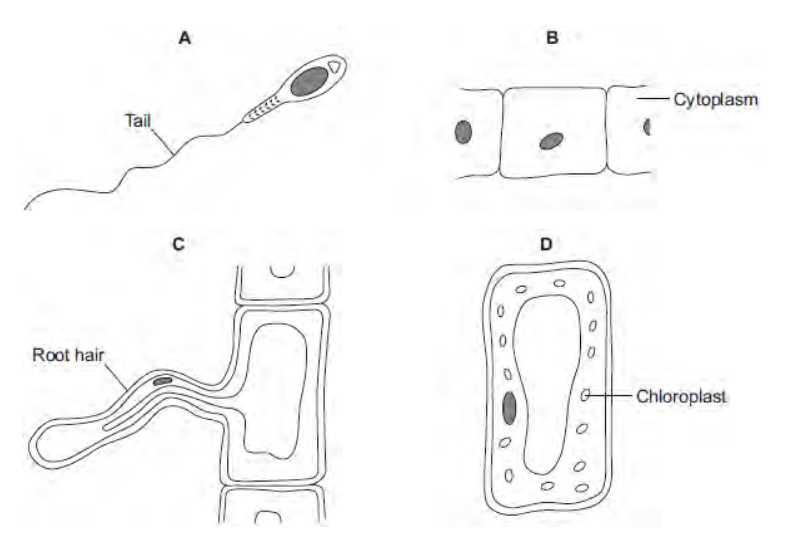
Which cell, A, B, C or D, is adapted for swimming?
A