Trauma II
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Shoulder down
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Young adults (high energy trauma), elderly patients (osteopenia, low energy injuries)
Humerus fractures make up 3-5% of all broken bones who are they commonly seen in?
Proximal, middle (most common), distal
Location of humerus fractures
spiral, transverse, comminuted
Common patterns of humerus fractures
radial (loss of sensory on dorsal part of hand, loss of wrist, finger, and thumb extension)
What nerve are we worried about with humeral shaft fractures
Varus (bow leg)
Humeral shaft fractures often fall into what angulation
Coaptation spint (hard to place in peeps with boobs, swole chest, or obese) → Sarmiento brace; DO NOT SLING
Non-operative management for humeral shaft fractures (takes 3+ months to heal)
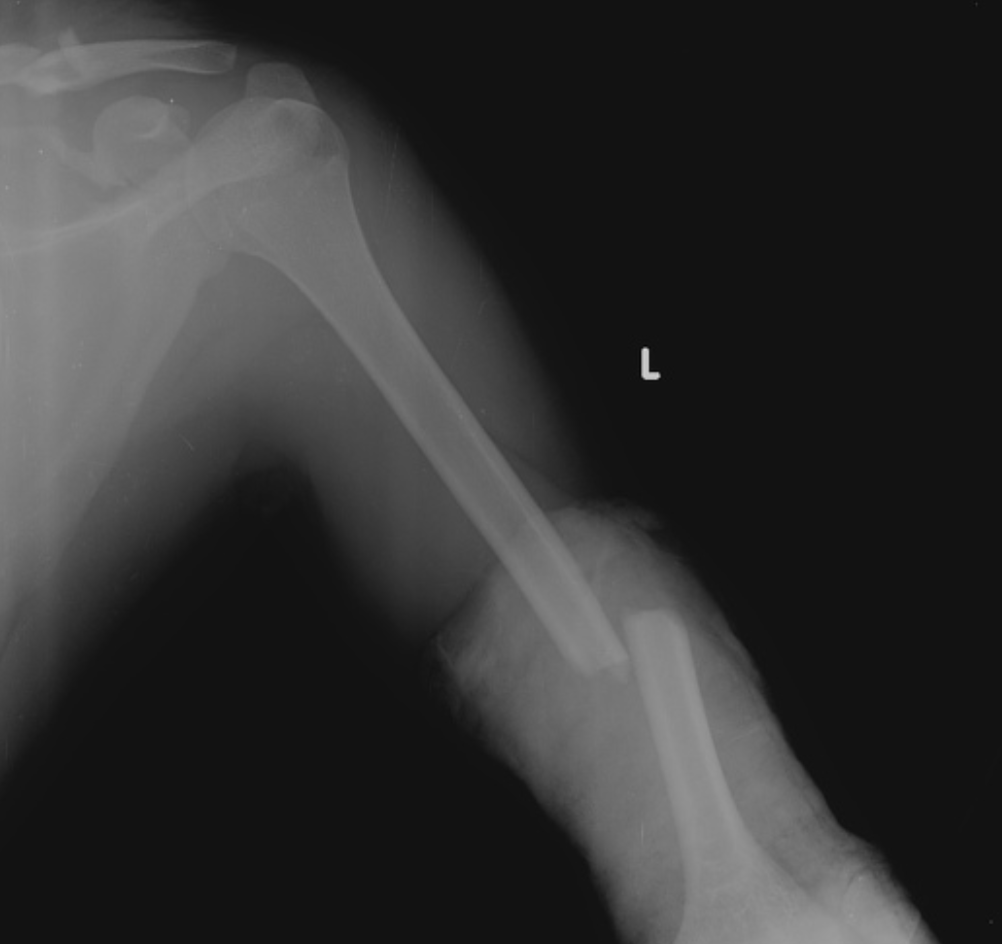
less than 20 degree anterior angulation, less than 30 degree varus/valgus, less than 3 cm shortening
Criteria for humeral shaft fractures to be treated non-op (depends on location, displacement, fracture type, other ipsilateral injuries)
open, brachial plexus injury, angulation over 20 anterior and 30 varus/valgus, floating elbow, compartment syndrome
Indications for surgical humeral shaft fracture management (RISK OF DAMAGING THE RADIAL NERVE)
Normal elbow
Normal elbow
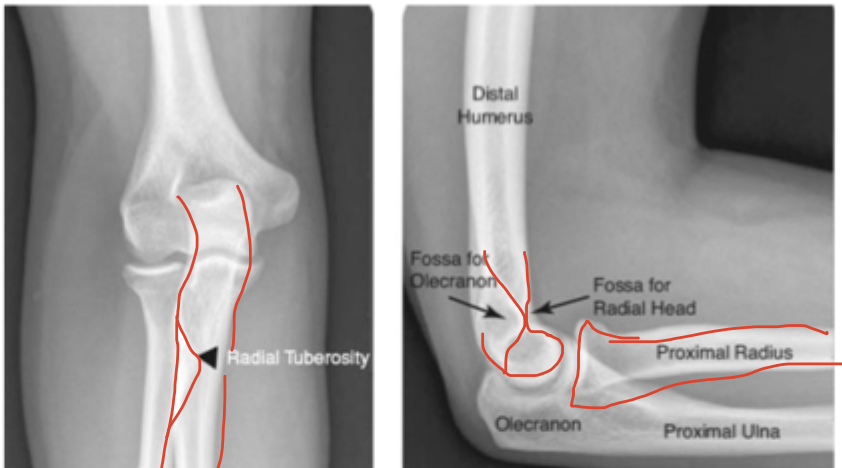
radial head
Most common elbow fracture in adults
limitations in extension and supination, tender on palpation on lateral side, pain on movement
What might you find in a radial head fracture on physical exam
posterior splint for 3-5 days then ROM especially extension and supination (test); sling (IRL)
Game plan for radial head fracture
Condylar fractures (peds), radial head fractures (adults)
What are fat pad signs associated with
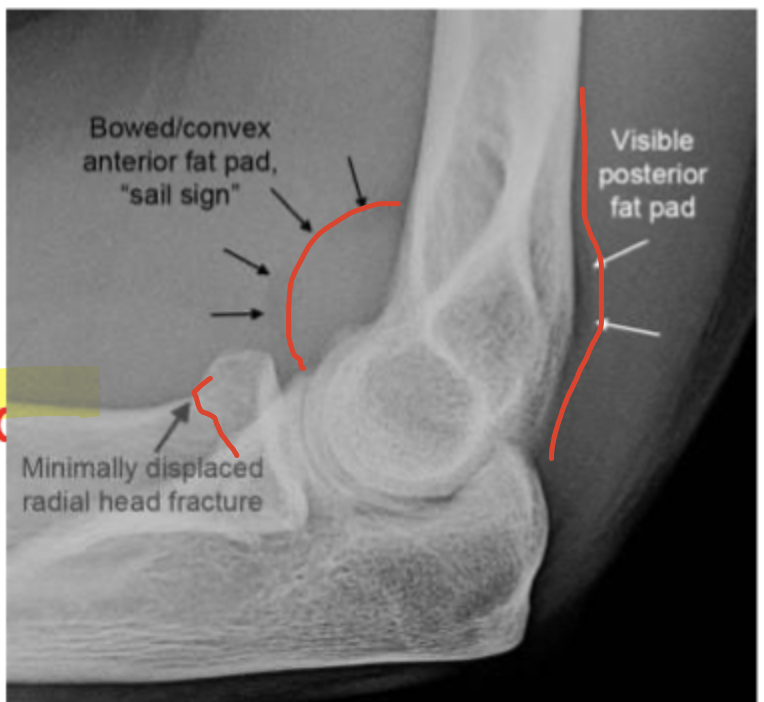
NEVER normal, occult non-displace fracture
If you see a posterior fat pad or a GIANT anterior fat pad (sail sign)…
Direct trauma (high energy in young, low energy in old)
What is the MOI for olecranon fractures?
NO extension (triceps gone, flapping in the wind)
If the olecranon breaks what do you lose
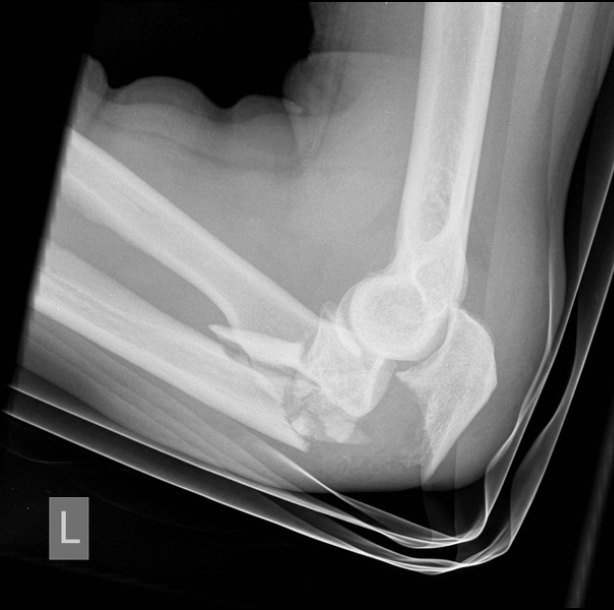
long-arm splint at a 45 degree angle
Non-operative management for olecranon fractures (non-displaced, intact extensor mech)
extensor mechanism is gone, displaced
Indications for surgical management (hook plate) of olecranon fractures
elbow dislocation
Most common dislocation in kids (second in adults)
Posterior
Elbow dislocation usually occurs in which direction
extension (more unstable)
What position does elbow dislocation often occur in
elbow dislocation, radial head fracture, coronoid process fracture
Terrible triad of the elbow
Reduction in the ER (Grab the forearm, Pull out into extension, Flex, Clunk it back in), long arm splint at 45 for 7-10 days, throw it in a sling for early ROM (no loss of extension)
treatment plan for elbow dislocation
associated fracture, persistent instability, failed closed reduction
Indications for surgical management of elbow dislocation
Both bone, monteggia, galeazzi, nightstick
Adult forearm fractures
both bone, buckle, greenstick
Peds forearm fractures
Both bone forearm fracture
A fracture of both the radius and the ulnar that usually needs surgical intervention
NV exam (test anterior interosseous with the OK sign, posterior interosseous with thumbs up), Elbow and wrist x-rays, evaluate for compartment syndrome, sugar tong splint for stability and patient comfort (prevents flexion, extension, supination, and pronation)
Initial eval of Both bone forearm fracture includes
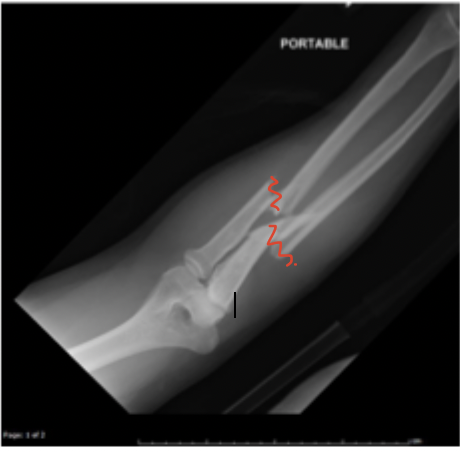
Fall from a height
Both bone fractures are very common in kids, what is their MAOI
Closed reduction, flexible intermedullary nailing (operative)
Game plan for both bone fractures in kids
Buckle fracture
A fracture that results due to a failure of cortex compression side 2-3 cm proximal to physis that is common in young children (FOOSH) and the volar cortex remains intact
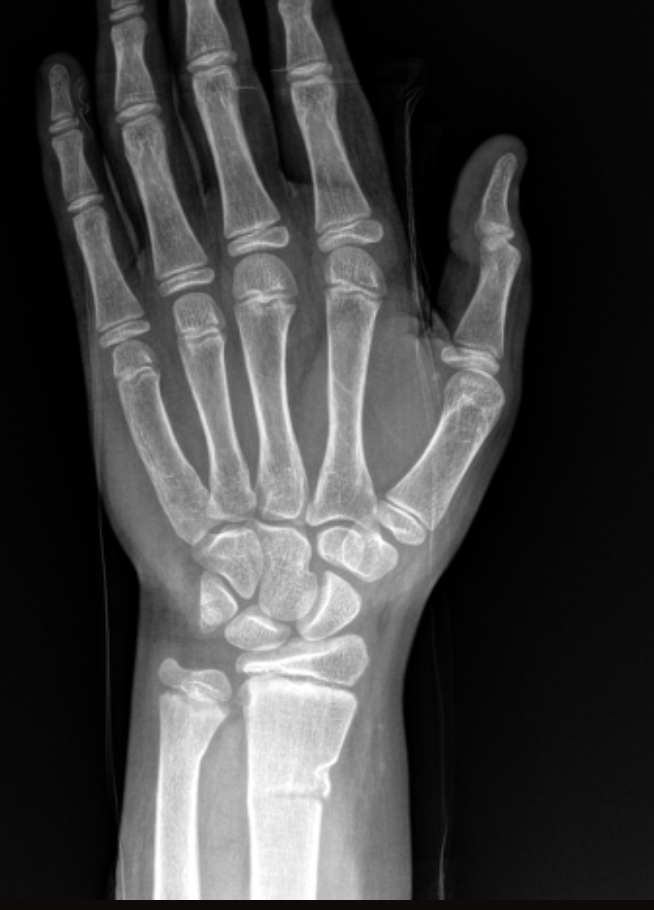
volar splint, short arm cast
Gameplan for buckle fracture
Greenstick
An incomplete fracture of the cortex - typically in children
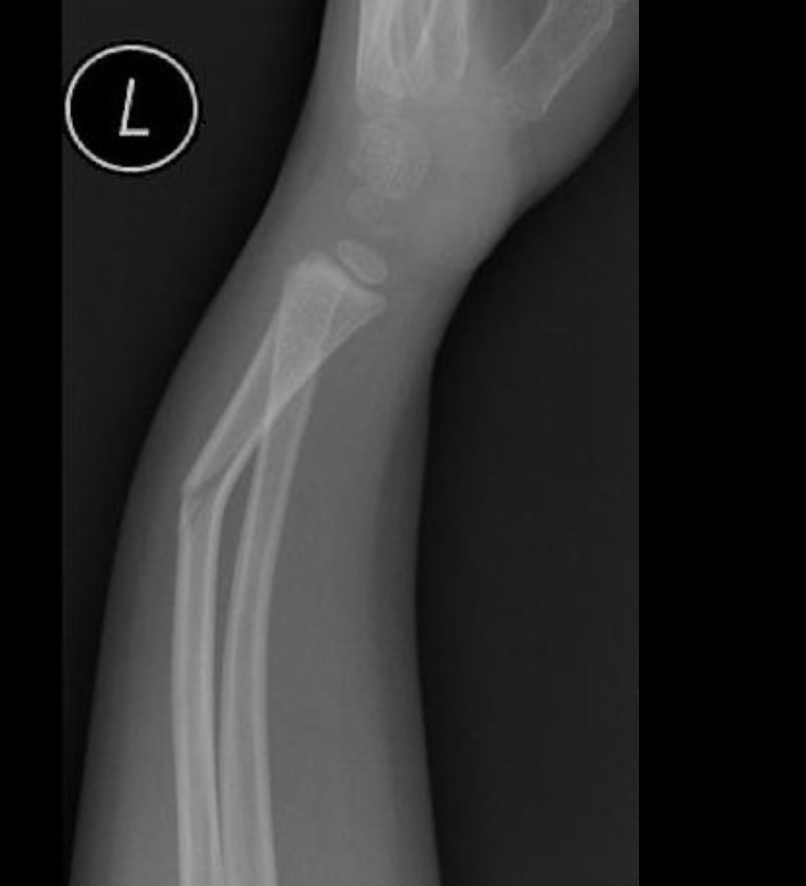
Do not overcorrect in reduction, long arm cast (4-6 weeks)
Gameplan for greenstick fractures
Galeazzi fracture
A fracture of the distal 1/3 radial shaft with injury of the DRUJ (bust it wide open) - get and document nerve function
FOOSH
MOI of Galeazzi fracture
ORIF (usually pretty unstable)
Treatment for Galeazzi fracture
Monteggia fracture
A fracture of the proximal 1/3 of the ulna with dislocation of the radial head
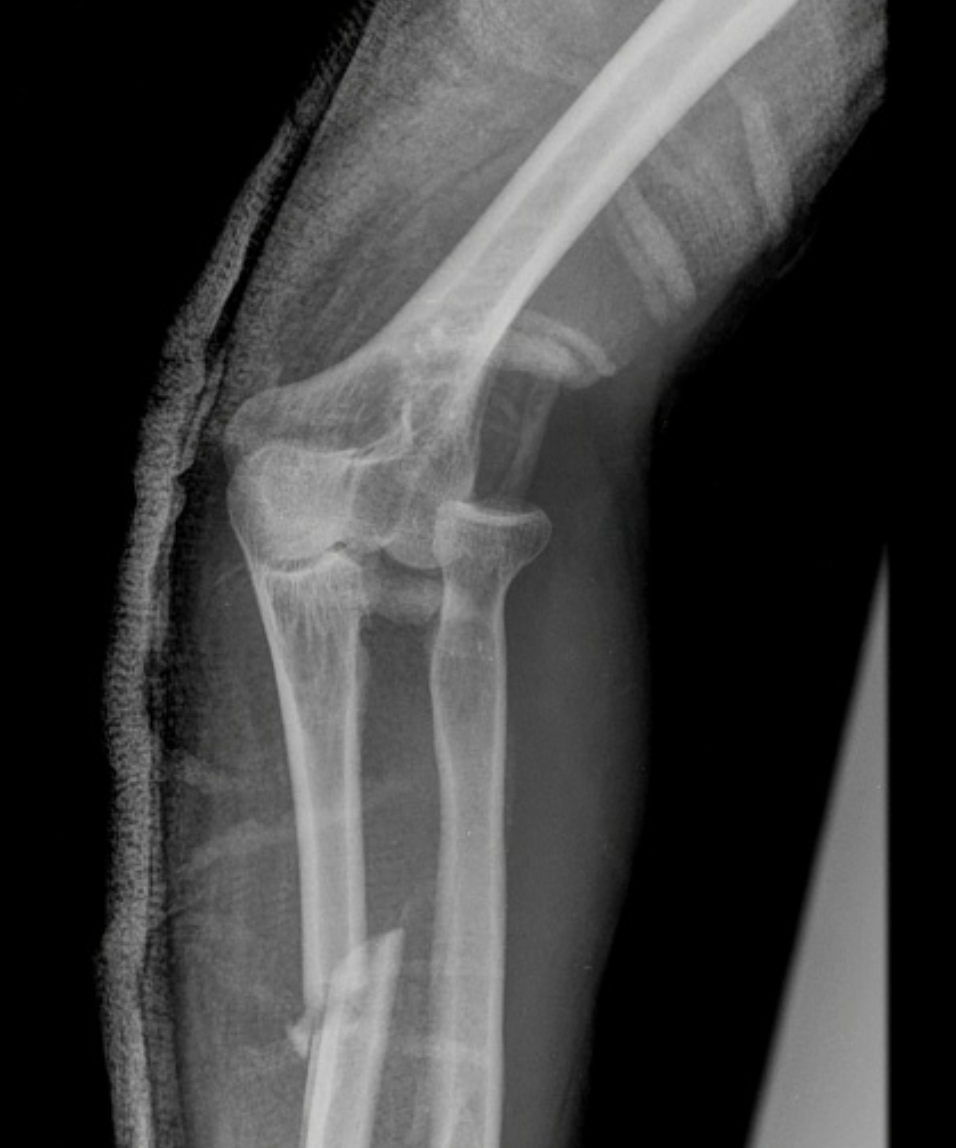
hyper-pronation
MOI for Monteggia fracture
operative (unstable), once ulna is brought back to the length of the radial head it typically reduces
Game plan for Monteggia fracture
Nightstick fractures
Ulnar shaft fracture usually at the distal 1/3 junction due to a direct blow when trying to block/shield
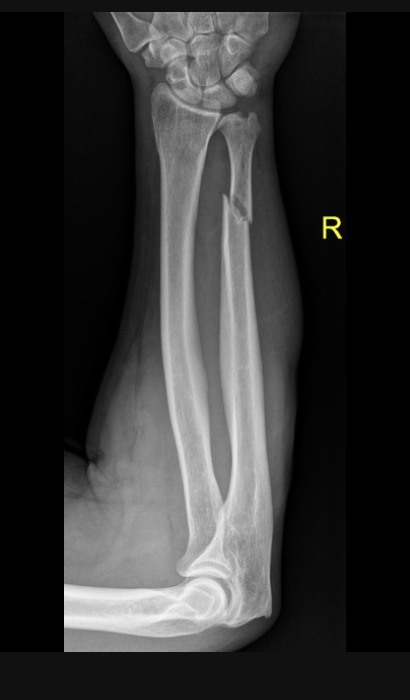
If less than 50% displaced → muenster cast
Gameplan for nightstick fractures
normal wrist
normal wrist
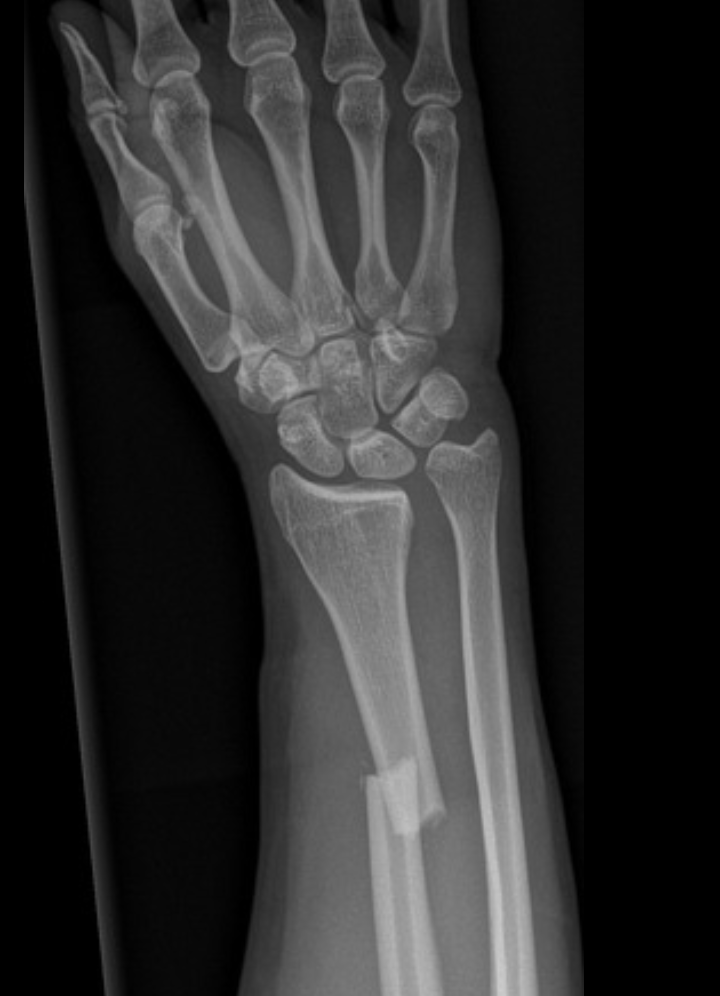
Distal radius fracture
A very common fracture that is often due to a FOOSH injury in the elderly
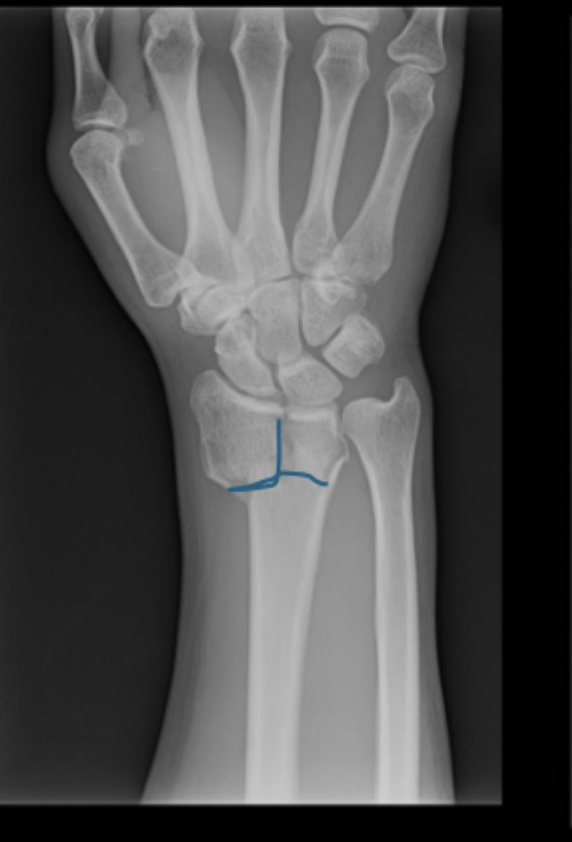
Reduce and immobilize IMMEDIATELY (sugar tong), can be treated non-op if stable and non-displaced
With a Distal radius fracture, what is the gameplan
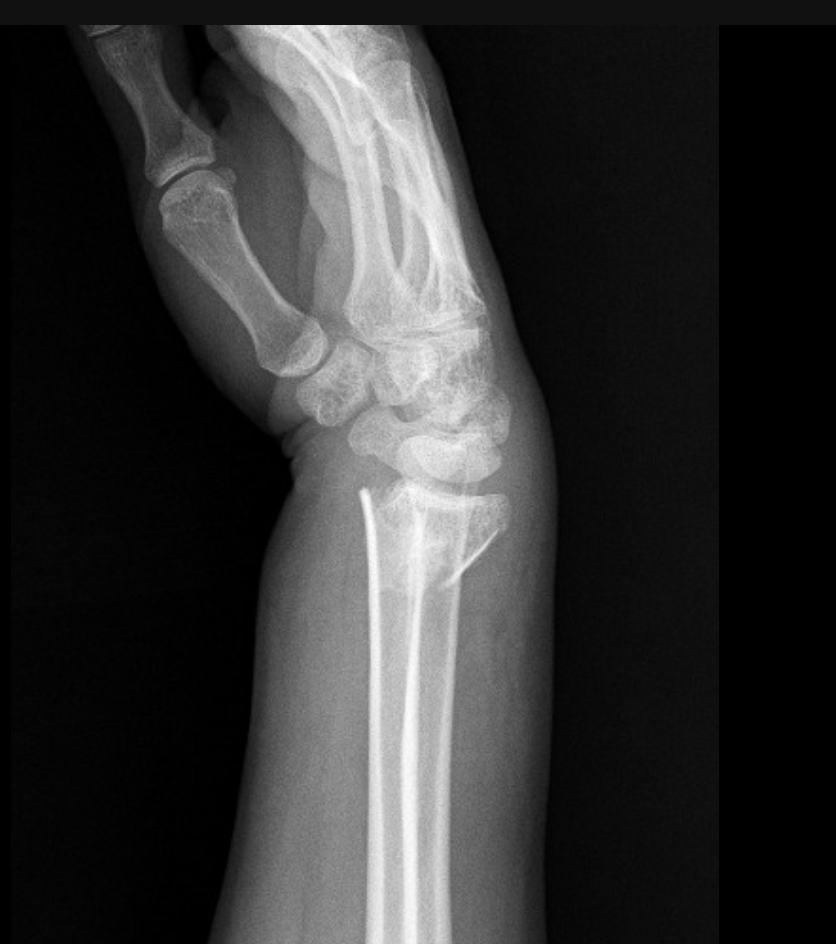
Colles fracture
A transverse distal radius fracture DORSALLY displaces and extra-articular - dinner fork deformity
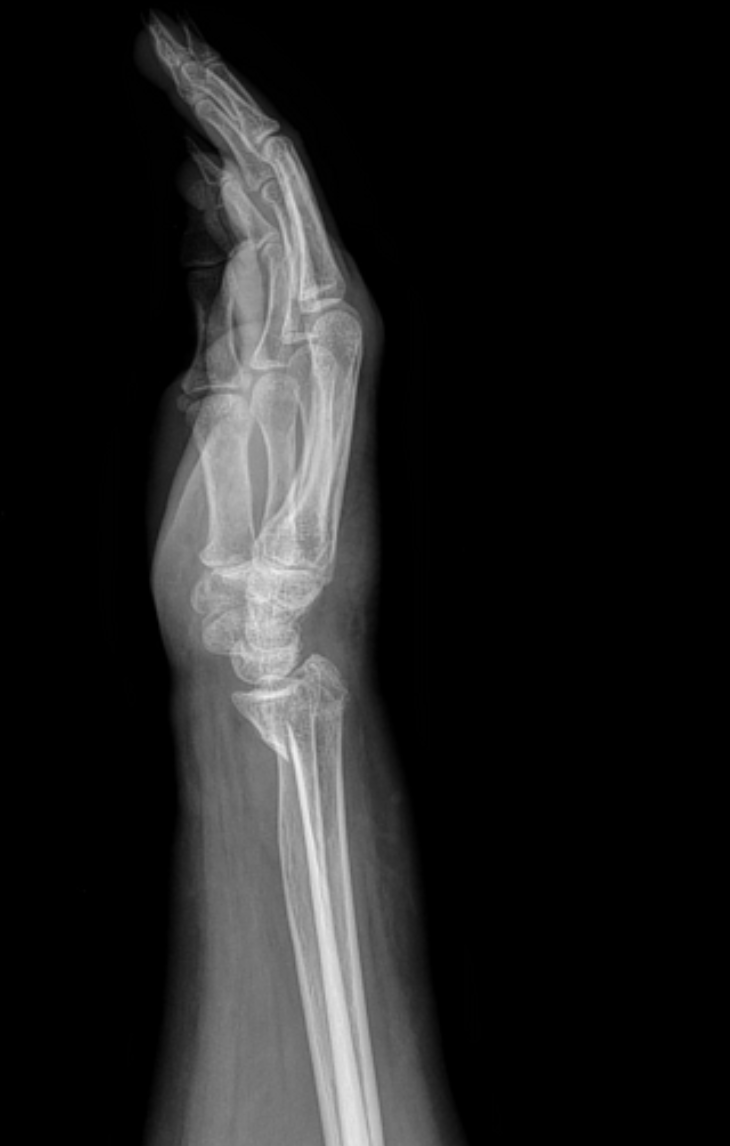
Smith’s fracture
A transverse distal radius fracture VOLARLY displaces and extra-articular
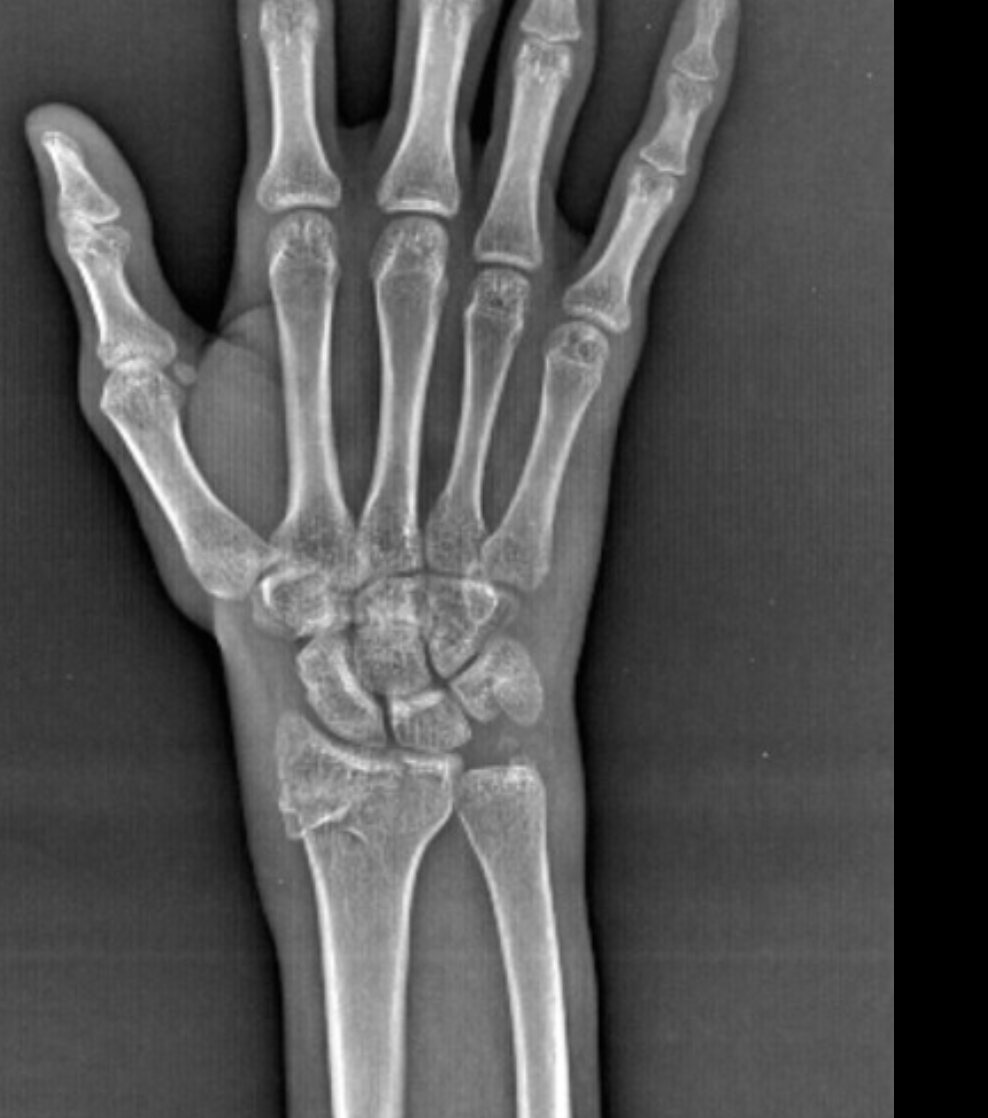
Barton’s fracture
A fracture-dislocation of the radiocarpal joint that is intra-articular and can be displaced dorsally or volarly
Chauffer’s Fracture
Fracture of the radial styloid
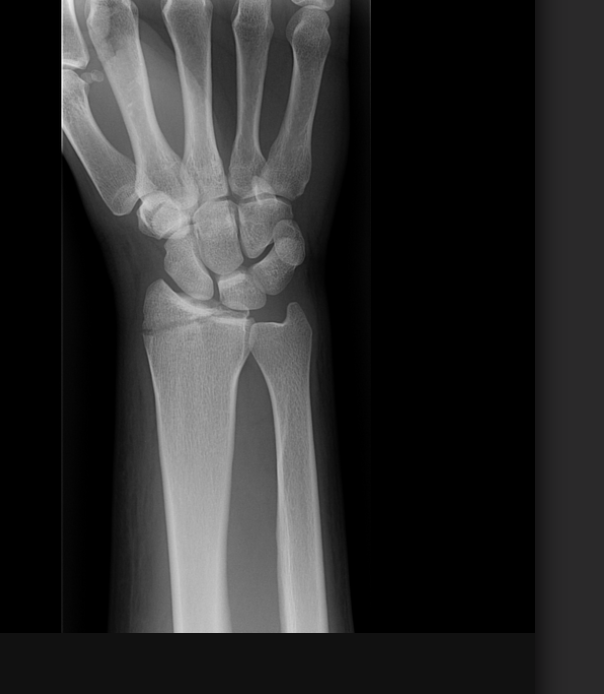
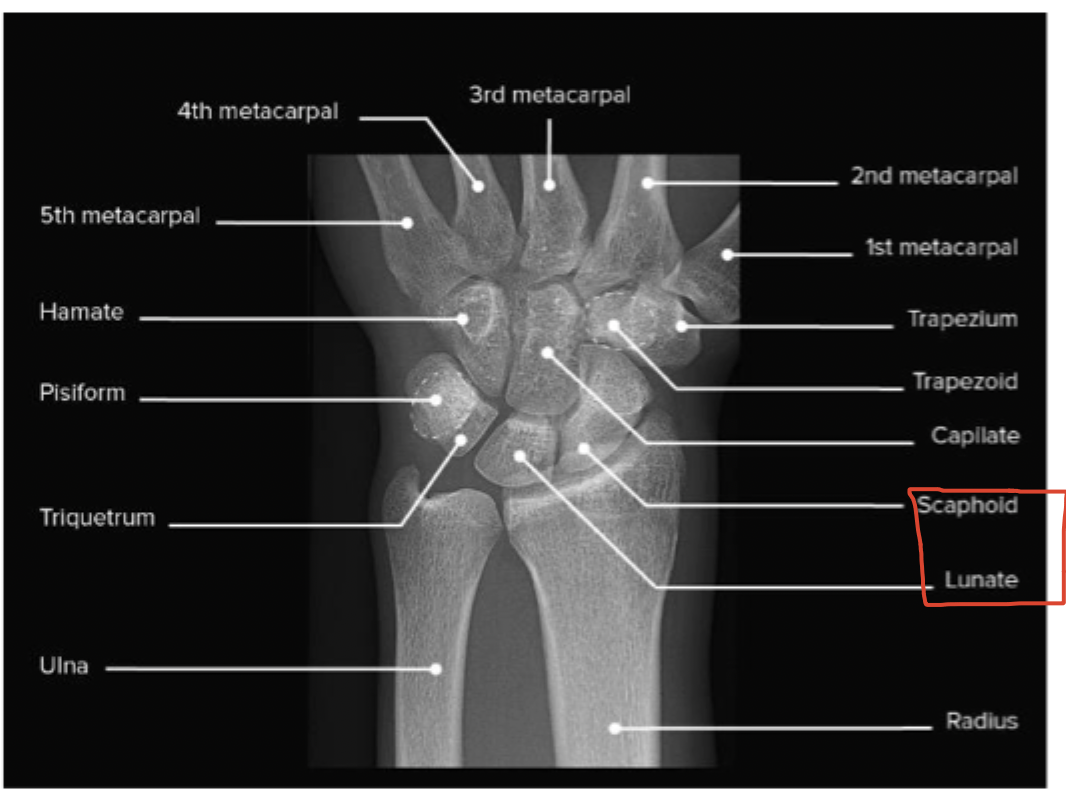
Scaphoid bone fracture
The most common carpal bone fracture that is a result of a FOOSH and leads to pain in the anatomical snuff box dorsally and scaphoid tubercle volarly
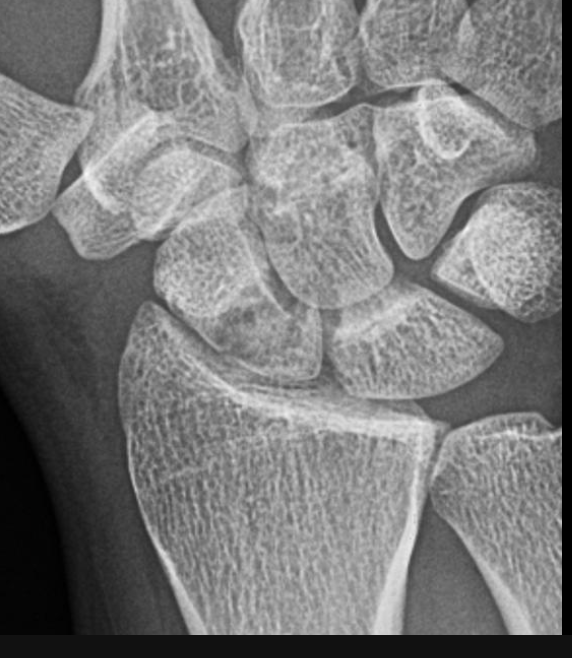
High incidence of avascular necrosis (palmar carpal branch is at risk) and nonunion
Quicks of a scaphoid bone fracture
Even with normal xray if they have pain in snuff box give them a thumb spica splint, re-xray in 2 weeks, MRI most sensitive, CT scan is best for pre-op
Treatment plan for scaphoid bone fracture
Waist (65%), Proximal 1/3 (25%), distal third (10%)
Locations of scaphoid bone fractures
6 weeks in long arm thumb spica cast → 6 weeks of short arm thumb spica cast → removable thumb spica splint for 4-6 weeks
Non-operative management of scaphoid fractures
screw placement (return to work sooner), high rate of AVN and non-union
Operative management for scaphoid fractures
increases incidence on wrist arthritis and instability of joint
IF AVN or non-union occurs for a scaphoid fracture what does this mean for our patient?