Unit C: Biology - Parts of the Cell
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Nucleus
“The Control Centre”
The organelle that controls the functions of the cell
Contains genetic material (DNA or chromosomes)
Directs cellular activities
Parts: Chromatin & nucleolus
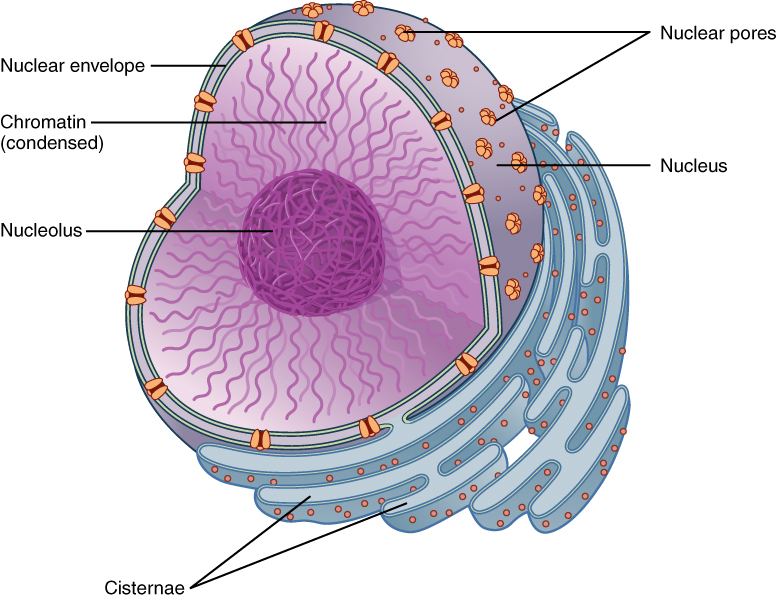
Nucleolus and Chromatin
Found inside the cells of the nucleus and region where ribosomes are produced
strands that contain genetic material
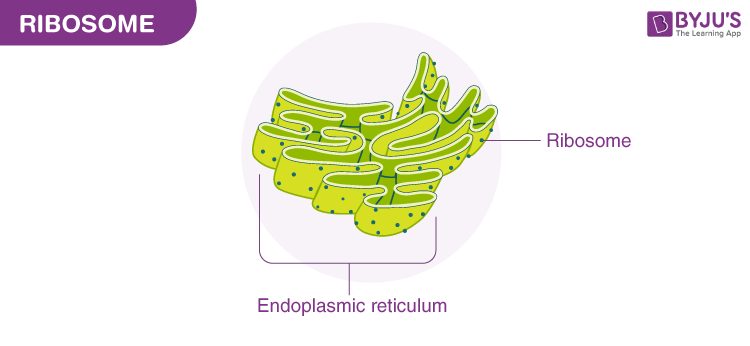
Ribosomes
“Workers of the assembly line”
Small granules that are the sites where amino acids are assembled into protein (protein synthesis)
may be attached to endoplasmic reticulum, or free floating in the cytoplasm
found in ALL cells (pro and eu)
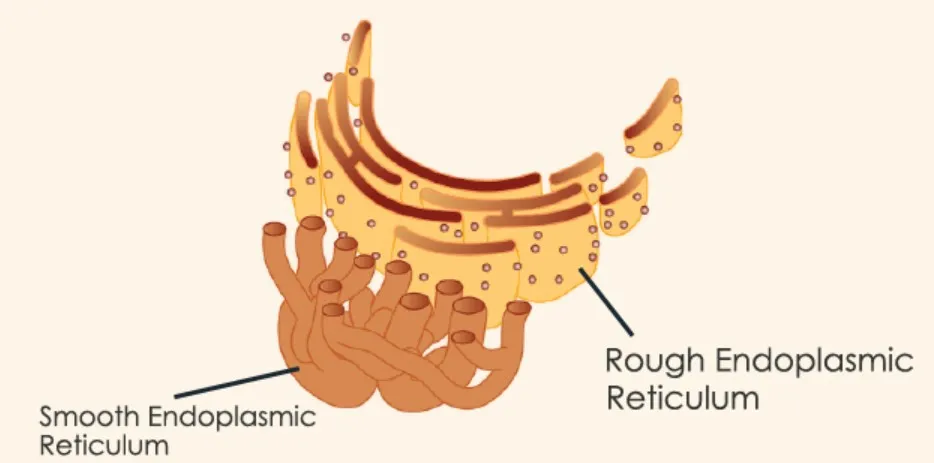
Endoplasmic Reticulum
“The Assembly Line”
Series of interconnected small tubes that branch from the nuclear envelope
Transportation of materials
Can be rough or smooth
Rough ER: is where ribosomes are attached to the E.R, is associated with protein synthesis (primary production line - makes toys)
Smooth ER: is associated with fat and oil production (NO RIBOSOMES)
accessory production line - makes toy decorations
Golgi Apparatus
“Packaging Plant”
flat disk shaped sacs involved in secretion
receives substances from the E.R.
and packages them for transport out of the cell (exocytosis)
Lysosomes are also produced here
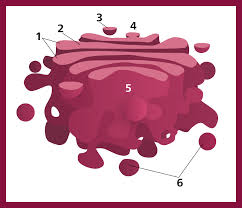
Lysosomes
“Recycling stations”
membrane bound sacs in which digestion occurs
defense against invading pathogens
destruction of damaged organelles
break done, clean up, and clean items in and around the factory
controlled digestion of certain tissues during development
Salvage any material that cell can use
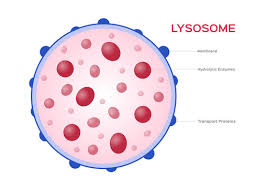
Mitochondria
“Powerhouse”
rod like structures where reactions occur to convert chemical energy in sugars into energy the cell can use (Cellular Respiration)
energy for muscle contractions, molecule synthesis, and transportation of molecules (active transport)
has 2 membranes (smooth outer, folded inner)
inner membrane have cristae (finger-like projections)
produces adenosine triphosphate = ATP (energy storage unit)
can reproduce in the cell if more energy is needed
C6H12C6 + 6O2 — 6CO2 + 6H2) + Energy (ATP)
Vacuole
“Storage warehouse”
Animal cells: membrane bound structures that store nutrients, products of secretion, and fats
Plant cells: the central vacuole contains water increasing tugor pressure
Vesicles
“transporter”
small membrane sacs pinched off of the cell membrane
store or transport materials in and out of the cell
Centrioles
Plays a role in cell division
Within the cytoplasm near the nucleus, in animal cells only
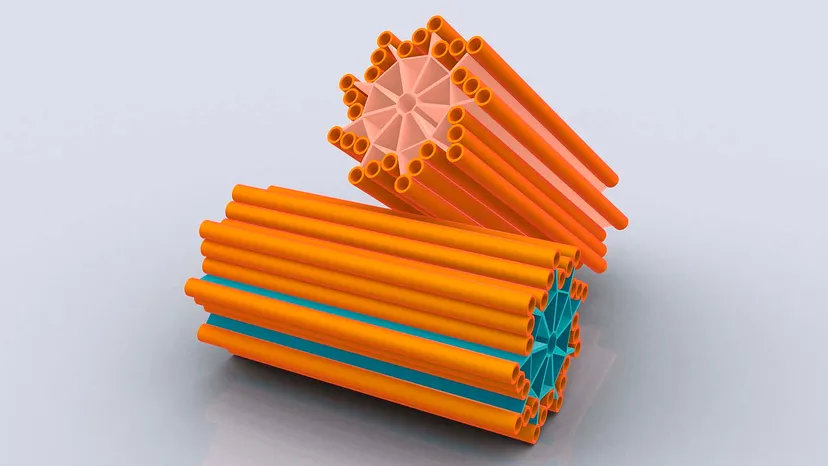
Cytoplasm
“The Safe Environment”
gel like substance inside the cell membrane contains the nutrients required to carry out the cell functions
organelles are suspended in the cytoplasm responsible for holding the components of the cell and protects them from damage
Cytoplasm is defined as the fluid-like part of the cell as well as the organelles. Cytosol refers to the fluid part only.
Cell wall
“Security gate” of the factory
A cell wall is defined as a rigid, external layer that is specifically designed to provide structural support and rigidity. It also keeps the interior components of the cell intact and safe from the external environment
Made of cellulose: a carbohydrate that we cannot digest - gives the plants their structure
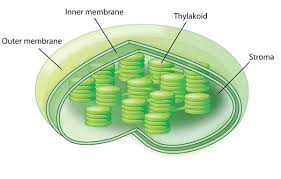
Chloroplasts
A chloroplast is an organelle within the cells of plants and certain algae that is the site of photosynthesis, which is the process by which energy from the Sun is converted into chemical energy for growth.
Green in color because of chlorophyll
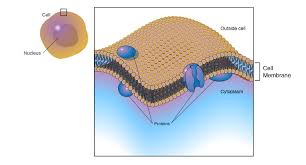
Cell Membrane (plasma)
“Front Doors” of the factory
Protective barrier for the cell - separates the inside of the cell (cytoplasm) from its environment
Allows transport of needed materials into the cell and waste materials out
Made of phospholipid bilayer
controls what enters and leaves - is semi and selectively permeable
A cell membrane does the same thing for plant and animal cells
in plant cells, it is to the inside of the cell wall
in animal cells, it is the outermost part of the cell