Section 1 Lectures 1-3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry, Bonds, Acids, Bases, Polymerization, Proteins
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
1
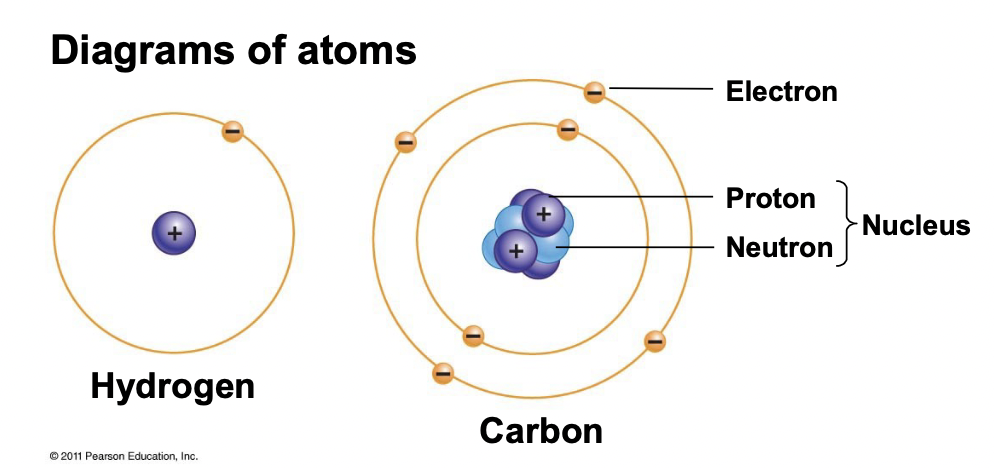
New cards
Atoms
Always have the same number of protons and neutrons, make up the nucleus.
2
New cards
What is the mass number and the atomic number? For mass # specify units.
Mass number = # protons + # neutrons, Unit is daltons (Da, D), kilodaltons (kD)
Atomic number = # protons
Atomic number = # protons
3
New cards
What are Isotopes?
Atoms with the same # of protons but a different number of neutrons. Often unstable (radioactive).
4
New cards
Molecules
Atoms linked together by covalent bonds.
5
New cards
Trends of elements in the same row or column, regarding electrons
Same row, all electrons in the same shell thus similar size
Same column, same # of valence electrons thus similar chemical properties
Same column, same # of valence electrons thus similar chemical properties
6
New cards
Covalent Bond
Made of 2 electrons (1 from each atom), they are shared between the atoms
7
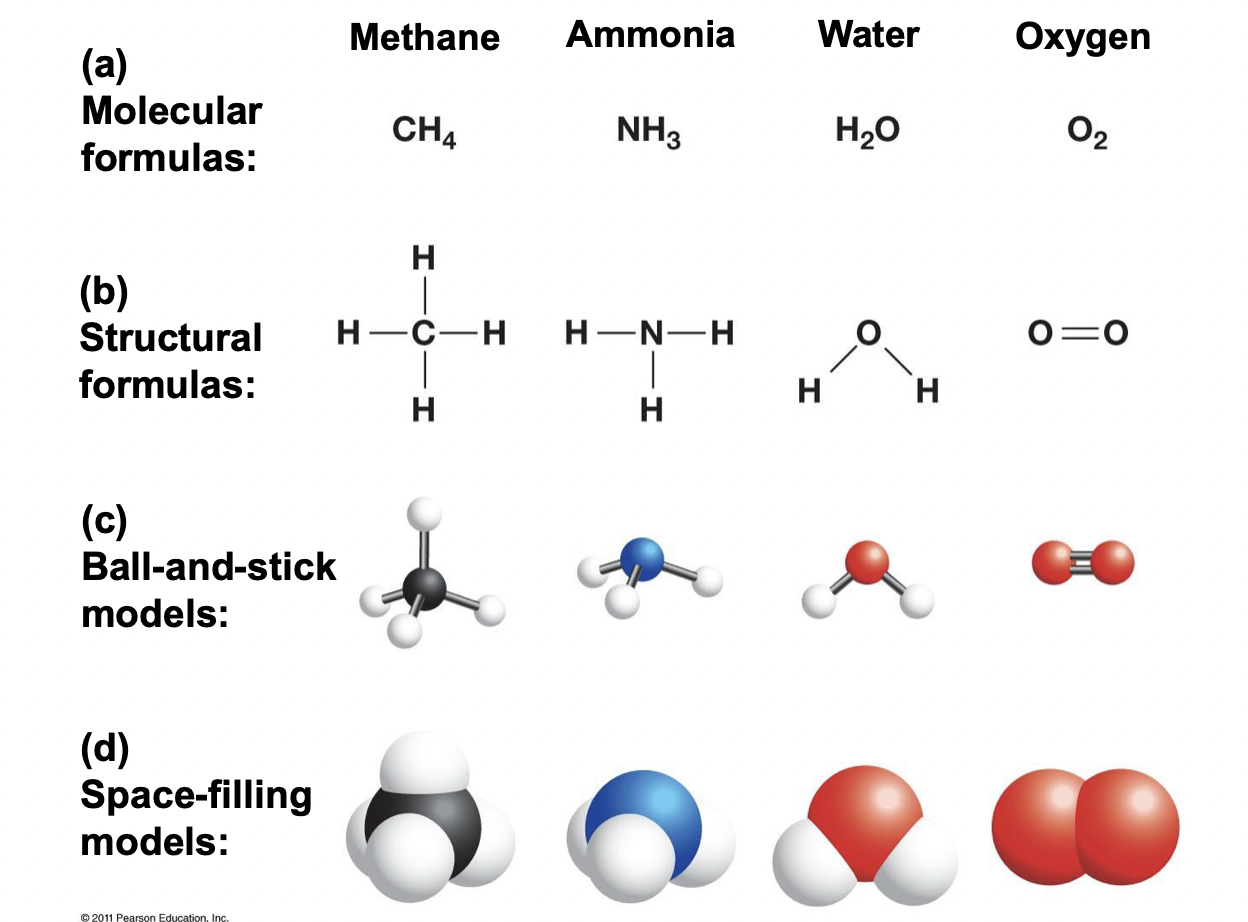
New cards
Difference Between Molecular Formula and Structural Formula
\
8
New cards
Electronegativity, What if atoms have the same # of shells?
How strongly electrons are attracted to the nucleus.
For elements with the same # of shells, those with more protons are more EN.
For elements with the same # of shells, those with more protons are more EN.
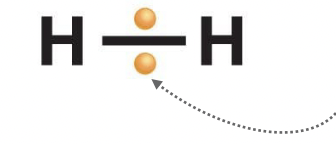
9
New cards
How are non-polar Covalent bonds drawn?
Electrons are shown to be superimposed on the bond to indicate they are halfway between the 2 atoms, shared equally.
10
New cards
Polar Covalent Bonds
Electrons are not shared equally, the atoms with a higher EN have a stronger pull and create partial charges. (Dipoles)
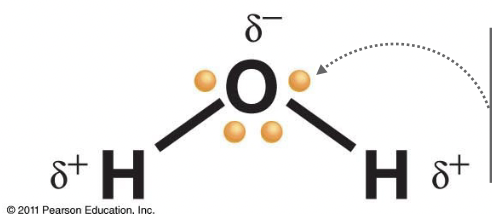
11
New cards
What 4 properties does water’s polarity cause?
1. Two forces cause water to make a meniscus
* Adhesion: water molecules adhere to the glass to resist the downward pull of cohesion
* Cohesion: water molecules at the surface experience a net downward pull from the H-Bonds in the water molecules below
2. High surface tension - i.e. light objects don’t fall through
3. In ice, molecules form a crystal lattice, but in liquid water there is no crystal lattice.
* This is why liquid water is more dense, and ice floats in water
4. Water moderates temperature since H-bond formation or disruption, buffers heat energy
12
New cards
Ionic Bond
The valence electrons of one atom is transferred completely to another, forming two ions, bonded/attracted by electrostatic attraction
13
New cards
Salts (Ionic)
Ionic compound composed of a cation and anion, resulting from an acid-base reaction.
Commonly formed between elements at the edges of the periodic table since the EN difference is large.
Commonly formed between elements at the edges of the periodic table since the EN difference is large.
14
New cards
Why does water facilitate reactions?
Water is a good solvent because polar molecules and ions dissolve easily in water due to its polarity.
15
New cards
Hydrophilic - Explain NaCl in Water
A substance that has a strong affinity for water, typically a polar molecule or ion.
For NaCl in water; Na+ is attracted to the negative O dipole, and the Cl- is attracted to the positive H dipole.
For NaCl in water; Na+ is attracted to the negative O dipole, and the Cl- is attracted to the positive H dipole.
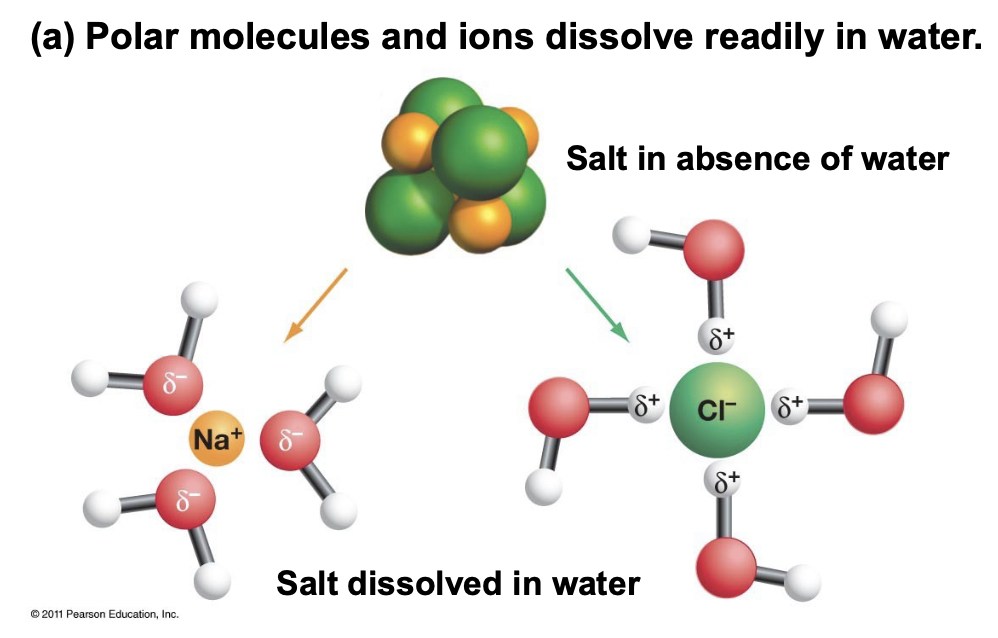
16
New cards
Hydrophobic - Why are molecules forced together?
Non-polar molecules that are introduced to water and do not dissolve.
They are forced together as it minimizes the disruption of the hydrogen bonding in the water. Van Der Waals forces also attract the non-polar molecules to each other.
They are forced together as it minimizes the disruption of the hydrogen bonding in the water. Van Der Waals forces also attract the non-polar molecules to each other.
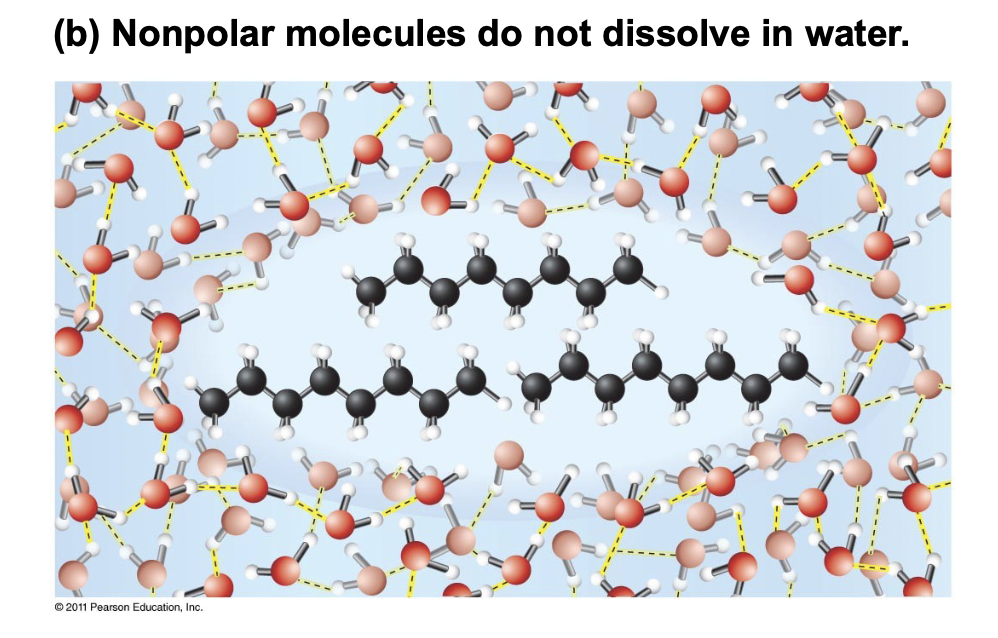
17
New cards
Bond Energy
The amount of energy needed to separate two bonded/interacting atoms under physiological conditions.
18
New cards
Hydrogen Bonds
Occur btw H and N, O, F. Attraction of opposite charges since there is a high EN difference.
19
New cards
Rank Covalent, Hydrogen, and Ionic Bonds, and Hydrophobic, and van der Waals interactions, in order of INCREASING strength. (In biological/physiological conditions)
Van Der Waals, Hydrophobic, Ionic = Hydrogen, Covalent
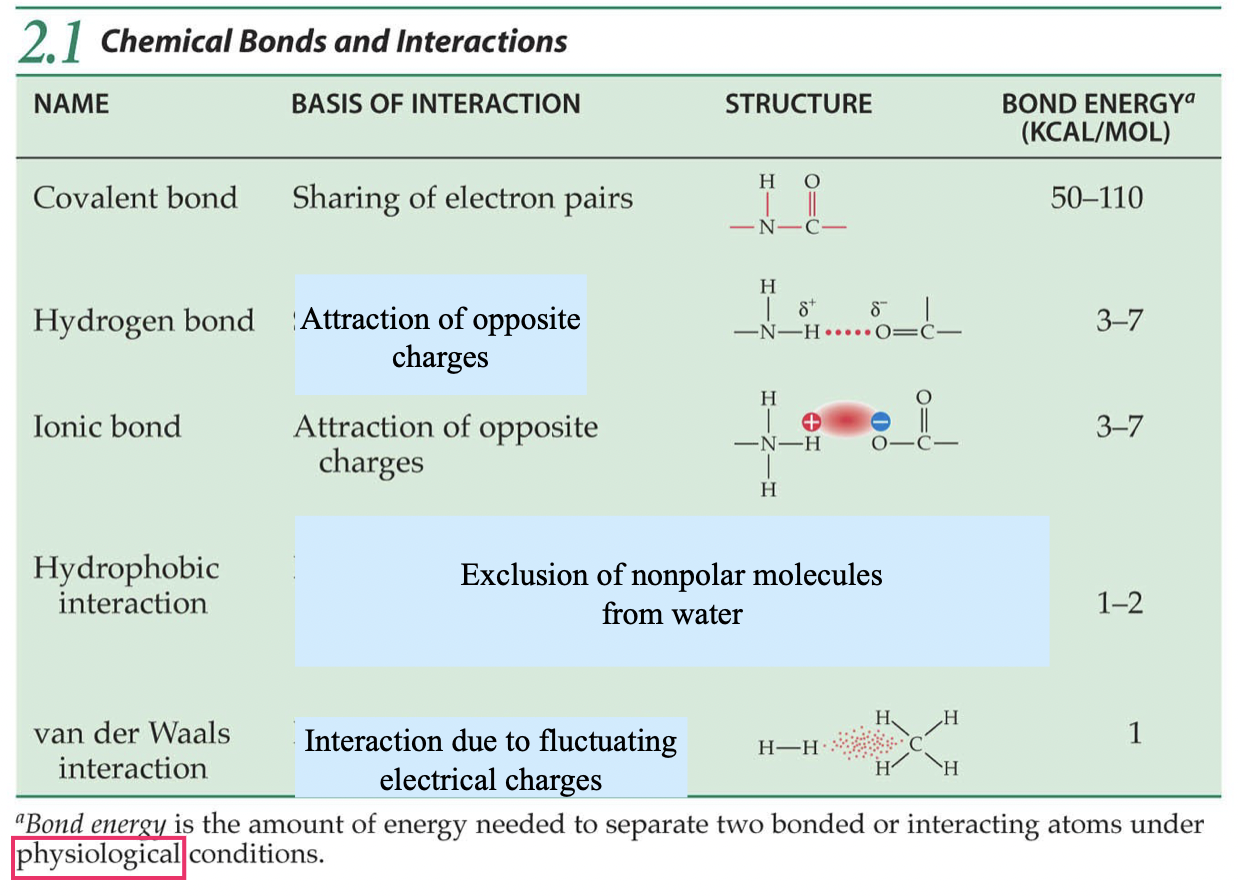
20
New cards
Explain the weakness of ionic bonds in biological settings.
Ionic bonds are within proteins and are relatively weak, ionic bonds in salt crystals are MUCH stronger.
21
New cards
Mole
Amount of a substance in grams whose weight is equal to its molecular weight. Ex. silver has an atomic weight of 107.8682 amu, so one mole of silver has a mass of 107.8682 grams.
22
New cards
Molar/Molarity
A 1M (molar) solution is one mole of a compound dissolved in water to make 1L.
23
New cards
Acids, give example
* Release/donate H+ ions in solution.
* Strong acids dissociate completely. (reaction is complete)
Ex. the carboxyl group (-COOH) functions as a weak acid because it dissociates partially and reversibly. The O is more EN and releases H+ to grab an electron pair.
* Strong acids dissociate completely. (reaction is complete)
Ex. the carboxyl group (-COOH) functions as a weak acid because it dissociates partially and reversibly. The O is more EN and releases H+ to grab an electron pair.
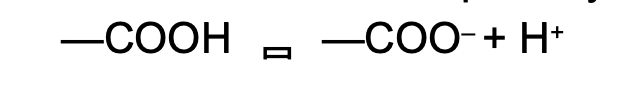
24
New cards
Bases, give example
* Accept H+ ions in solution, thus releasing OH-.
Ex. the amino group (-NH2) functions as a weak base because it partially and reversibly accepts H+. N is less EN so its free electron pair can accept H+.
Ex. the amino group (-NH2) functions as a weak base because it partially and reversibly accepts H+. N is less EN so its free electron pair can accept H+.
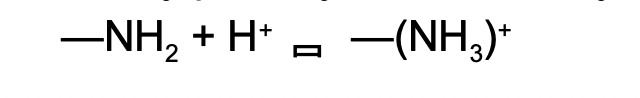
25
New cards
pH
pH is defined as the negative logarithm of the H+ concentration in moles/liter.
* High pH = basic
* Low pH = acidic
* High pH = basic
* Low pH = acidic
26
New cards
What are buffers? Relate to law of mass action
Make the overall solution resistant to pH change because they react with both added bases and acids.
Illustrate the law of mass action: Adding reactants accelerates the reaction forward, and removing products accelerates the reaction “backwards”.
Illustrate the law of mass action: Adding reactants accelerates the reaction forward, and removing products accelerates the reaction “backwards”.
27
New cards
What can be a buffer/how do they work?
* Need equal amounts of a weak acid and its conjugate base to reach the half-equivalence point (just means 50% of each at this point)
* Now, adding H+ or OH- will not change much as it pushes the reaction left or right
* Ex. Adding more H+ reacts withe acetate (CH3COO-) to form morn acetic acid, which removes the H+ in solution
* Then, adding OH- will react with H+ to form water, and the acid can dissociate adding more H+ back to solution, to balance everything out
* Now, adding H+ or OH- will not change much as it pushes the reaction left or right
* Ex. Adding more H+ reacts withe acetate (CH3COO-) to form morn acetic acid, which removes the H+ in solution
* Then, adding OH- will react with H+ to form water, and the acid can dissociate adding more H+ back to solution, to balance everything out
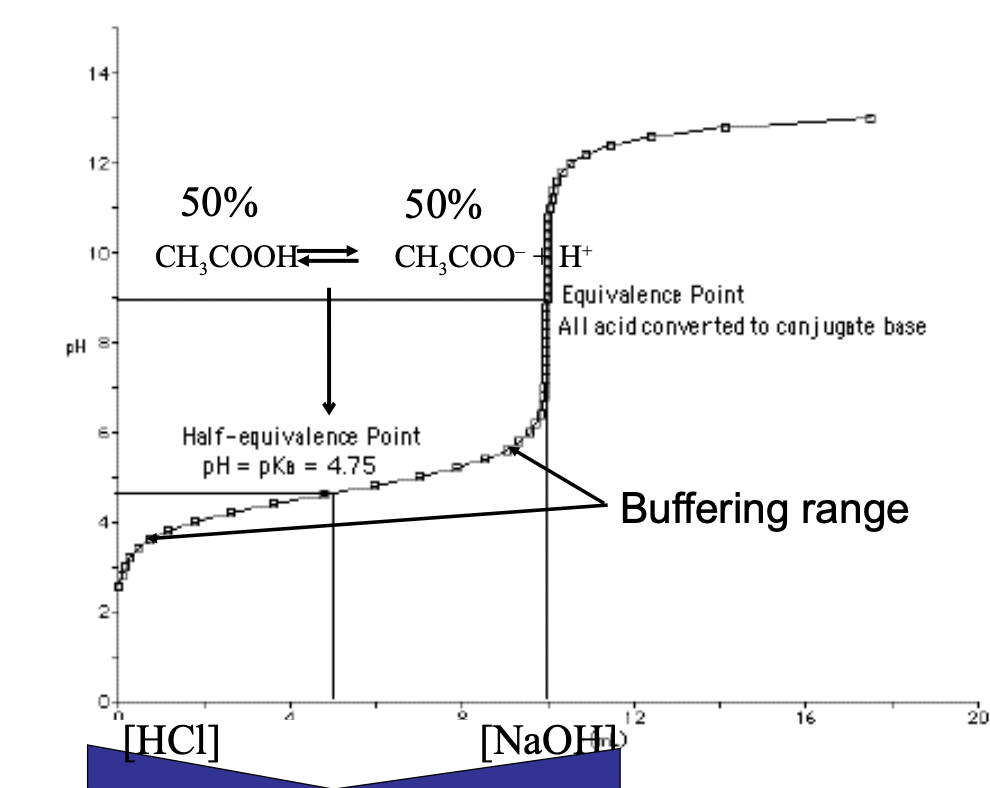
28
New cards
What is the equivalence point, and what happens after?
* Equivalence point: means that you have 100% of the base and all the acid is dissociated
* After this, only OH- ions alter the pH so the curve usually increases rapidly
* After this, only OH- ions alter the pH so the curve usually increases rapidly
29
New cards
Why are buffers important for our body? (How are they used)
Rapid pH change is bad for our body.
For ex., in our blood we want the intracellular solution of our cells to keep the pH constant and we use buffers to do so.
For ex., in our blood we want the intracellular solution of our cells to keep the pH constant and we use buffers to do so.
30
New cards
Carbon Backbone
Carbons linked in a linear molecule that is the basis for all molecules in our body.
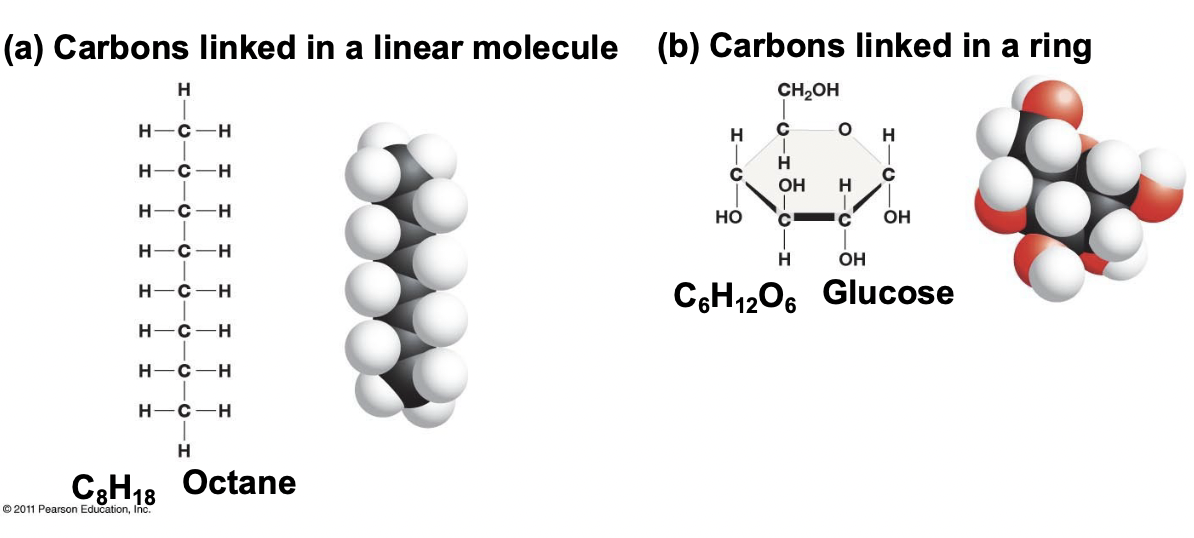
31
New cards
Hydroxyl Formula and Properties
* Highly polar
* Makes compounds more soluble through H-bonding with water
* Can act as a weak acid and drop a proton
* Makes compounds more soluble through H-bonding with water
* Can act as a weak acid and drop a proton
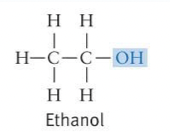
32
New cards
Phosphate Formula and Properties
* Breaking O-P bonds between multiple phosphate groups linked together releases large amounts of energy
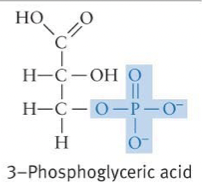
33
New cards
Sulfhydryl Formula and Properties
* When present in proteins, can form disulfide (S-S) bonds, contributing to protein structure
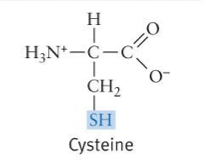
34
New cards
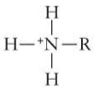
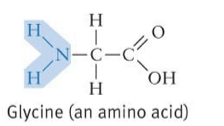
Amino/Amines Formula and Properties
* Acts as a base
* Tends to attract a proton to form: -RNH3+ complex
* Tends to attract a proton to form: -RNH3+ complex
35
New cards
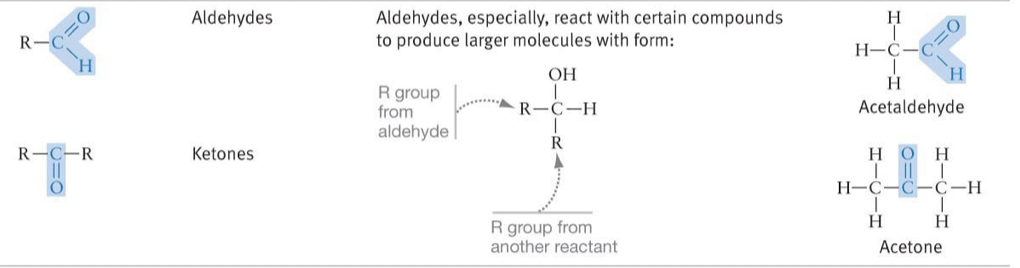
Carbonyl (
Aldehydes and Ketones
* React with certain compounds to produce larger molecules with the form:
* React with certain compounds to produce larger molecules with the form:
36
New cards
Carboxyl (Acid) Formula and Properties
* Acts as an acid
* Tends to lose a proton in solution to form:
* Tends to lose a proton in solution to form:

37
New cards
Macromolecules
* Proteins, nucleic acids (DNA & RNA), and carbohydrates
* They all can form large polymers
* They all can form large polymers
38
New cards
Biochemical Unity and Advantages
The idea that:
* Macromolecules are made the same way and present in all organisms
* Exist in roughly the same proportions in all organisms
Advantageous as it allows organisms to get biochemicals by eating other organisms.
* Macromolecules are made the same way and present in all organisms
* Exist in roughly the same proportions in all organisms
Advantageous as it allows organisms to get biochemicals by eating other organisms.
39
New cards
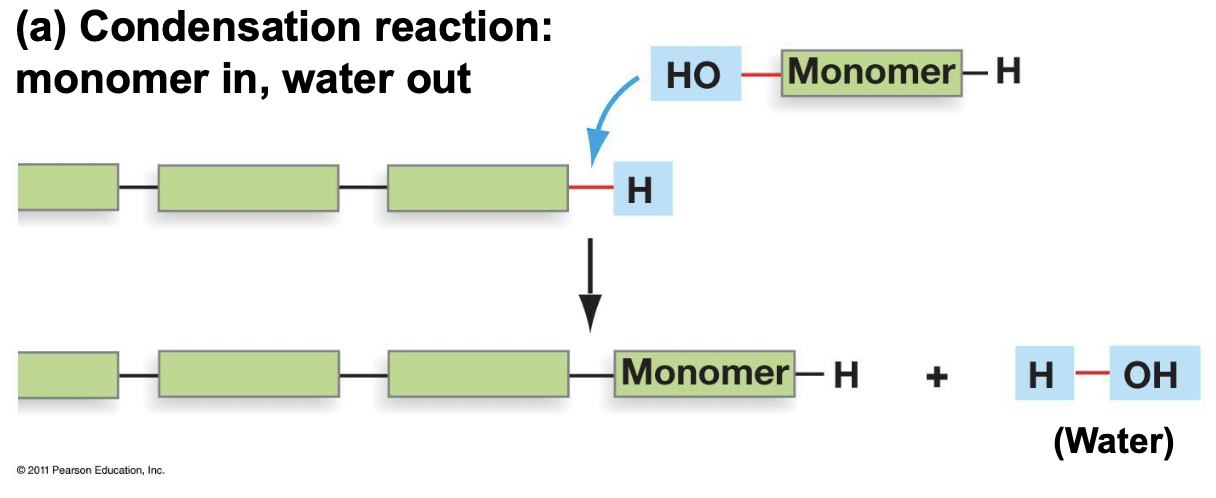
Polymerization and Examples
* Occurs through a condensation reaction (monomer in water out), anabolic (requires energy)
* Releases one water molecule with each monomer added, forming a covalent bond
* Ex. DNA replication, protein synthesis, making of starch
* Releases one water molecule with each monomer added, forming a covalent bond
* Ex. DNA replication, protein synthesis, making of starch
40
New cards
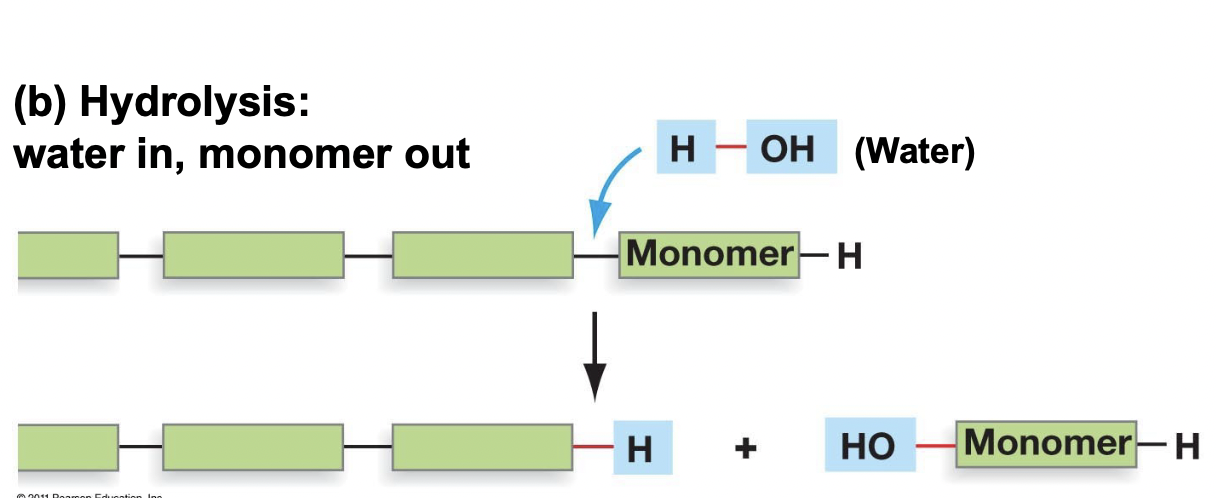
Depolymerization and Examples
* Occurs through a hydrolysis reaction (water in monomer out), catabolic (releases energy)
* With the help of one water molecule, the polymer releases one monomer
* Ex. digestion of food molecules for energy generation
* With the help of one water molecule, the polymer releases one monomer
* Ex. digestion of food molecules for energy generation
41
New cards
Bond Formation and Breaking (Biology)
In chemistry we think breaking bonds needs energy, forming them releases energy.
In biology we observe the ENTIRE reaction so we think that:
* ATP hydrolysis releases energy
* Covalent bond formation requires energy
\*\*\*BOTH ARE TRUE
In biology we observe the ENTIRE reaction so we think that:
* ATP hydrolysis releases energy
* Covalent bond formation requires energy
\*\*\*BOTH ARE TRUE
42
New cards
Proteins
* Do all the work in a cell (Ex. replicate DNA)
* Polymers made of amino acids (each monomer is 1 amino acid)
* Polymers made of amino acids (each monomer is 1 amino acid)
43
New cards
Protein Folding
* Crucial to the protein’s function
* Result of the sequence of amino acids
* Result of the sequence of amino acids
44
New cards
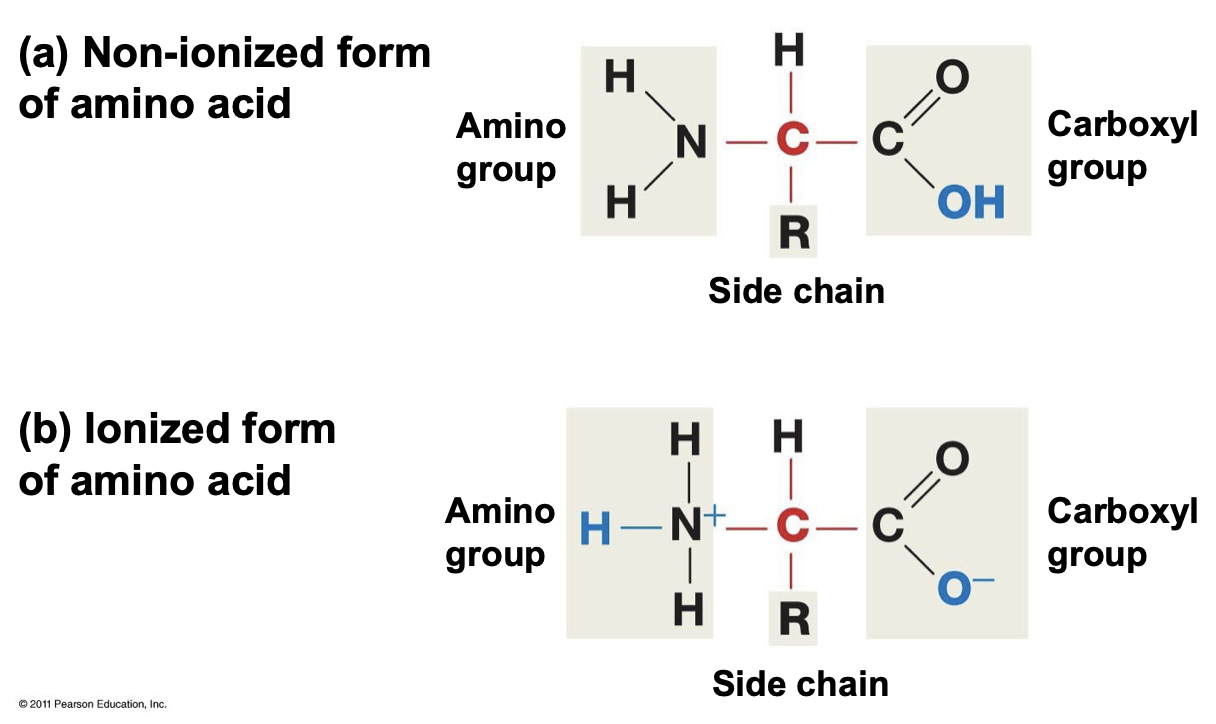
What do amino acids look like? (non-ionized and ionized)
* Both are made of an amino group, side chain, and carboxyl group.
* The ionized form has 3 H on the Nitrogen with a positive formal charge, and the OH group donates a proton, which occurs at a pH of 7.
* The non-ionized has 2 H on the Nitrogen.
* The backbone is everything other than the side chain.
* There are 20 amino acids
* The ionized form has 3 H on the Nitrogen with a positive formal charge, and the OH group donates a proton, which occurs at a pH of 7.
* The non-ionized has 2 H on the Nitrogen.
* The backbone is everything other than the side chain.
* There are 20 amino acids
45
New cards
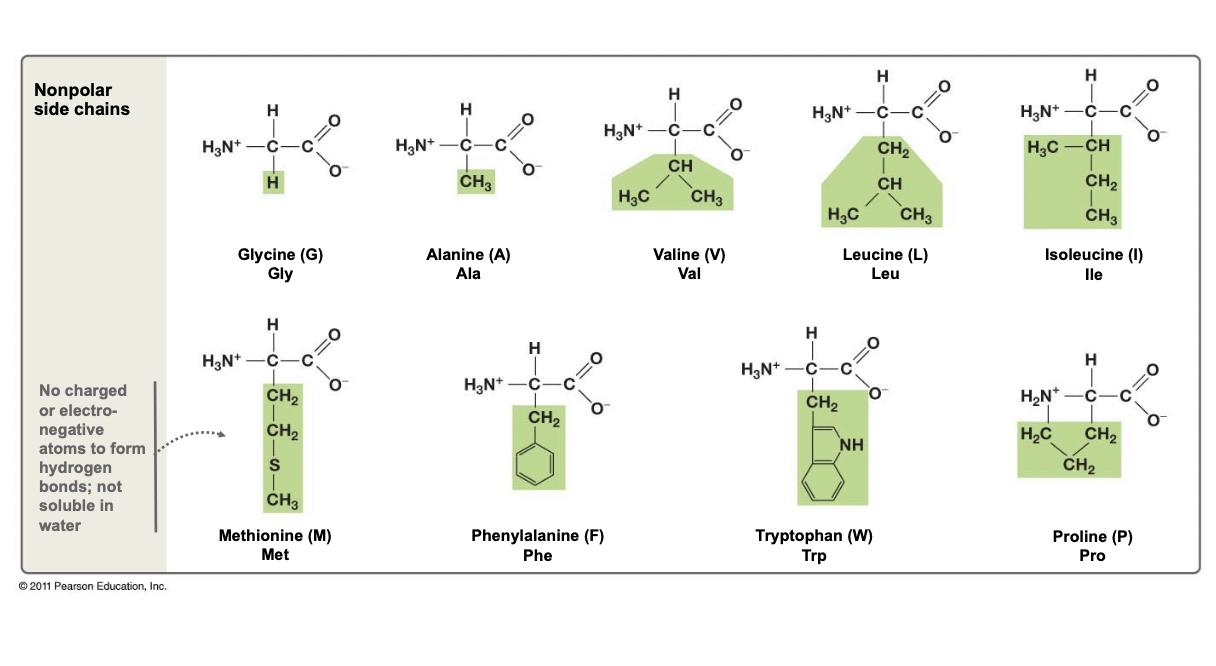
Non-Polar Side Chains
* Only have carbon and hydrogen atoms in their side chains
* Occasionally a N or S atom
* Chain is not charged
* No EN atoms to forms H-bonds, thus hydrophobic
* Occasionally a N or S atom
* Chain is not charged
* No EN atoms to forms H-bonds, thus hydrophobic
46
New cards
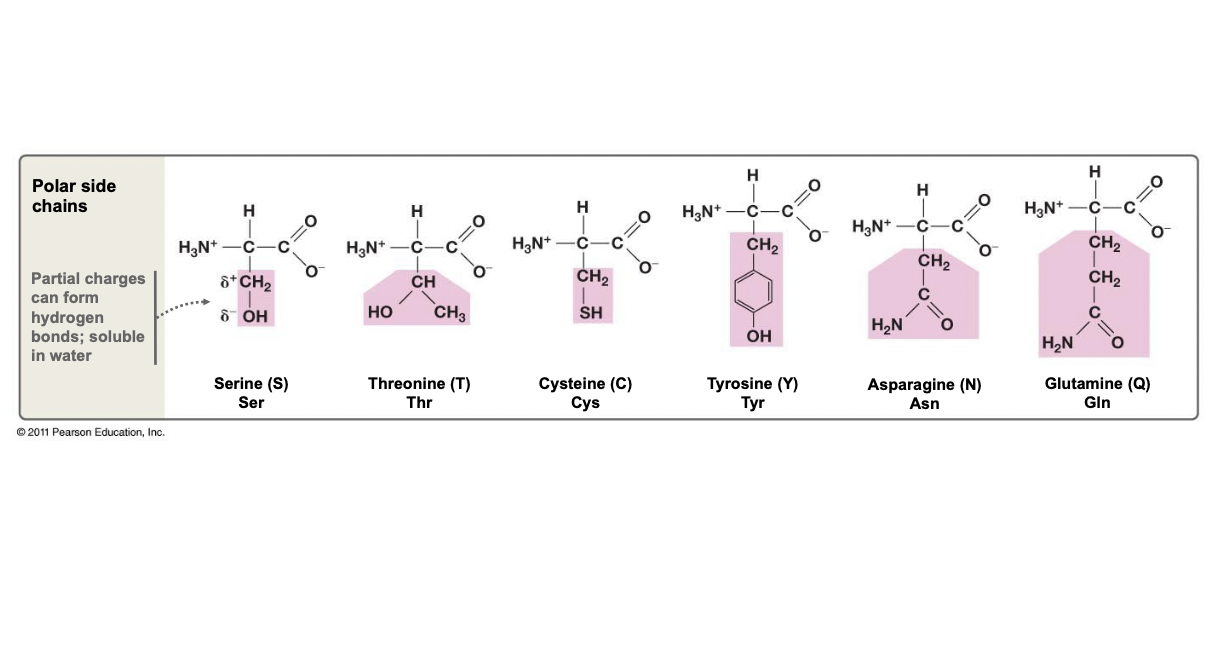
Polar Side Chains
* Can have a hydroxyl group, or the groups with partial charges
* H-bonds can be formed, thus hydrophilic
* H-bonds can be formed, thus hydrophilic
47
New cards
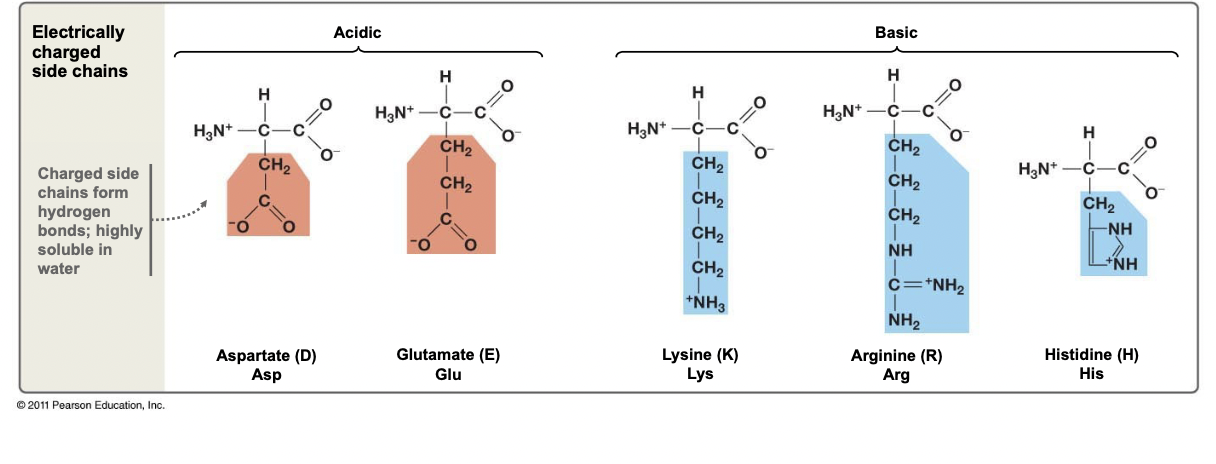
Electrically Charged Side Chains
* Has an atom with a formal charge
* Can form ionic bonds in the interior of proteins
* Forms H-bonds, thus very hydrophilic
* Can have acidic (-FC) or basic properties (+FC)
* Can form ionic bonds in the interior of proteins
* Forms H-bonds, thus very hydrophilic
* Can have acidic (-FC) or basic properties (+FC)
48
New cards
Peptide Bond Formation
* C on the carboxyl end of the first joins with the N on the ionized amino group of the added amino acid
* One water molecule is produced with each bond
* The electron sharing makes the peptide bond double-bond like
* Bond cannot rotate, would make a straight chain protein
* One water molecule is produced with each bond
* The electron sharing makes the peptide bond double-bond like
* Bond cannot rotate, would make a straight chain protein
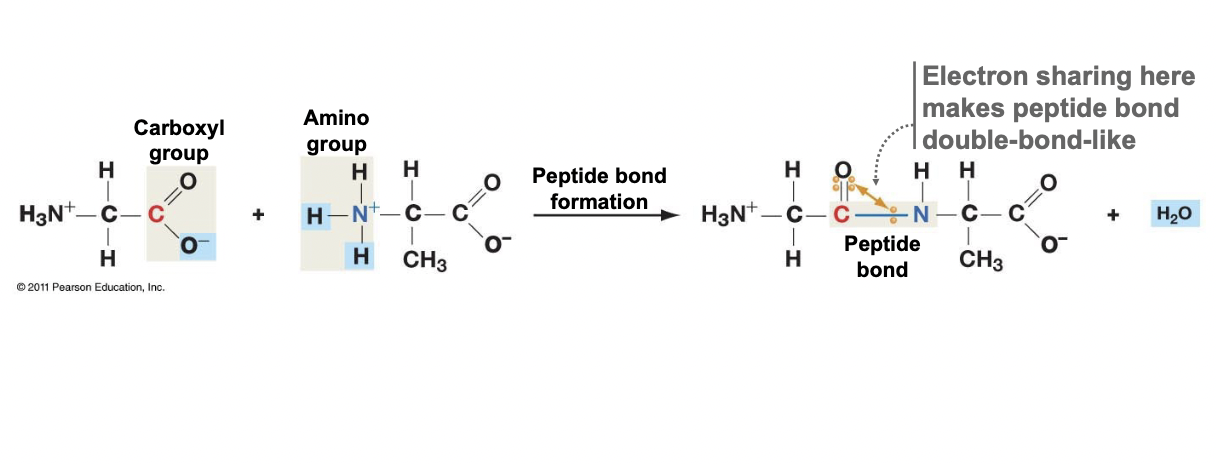
49
New cards
Polypeptide Chain
* Chain of amino acids joined by peptide bonds (protein)
* Always start with amino group or “N-terminus” and end with a carboxyl group “C-Terminus”
* Side chains dictate folding and function
* All start with methionine
* Always start with amino group or “N-terminus” and end with a carboxyl group “C-Terminus”
* Side chains dictate folding and function
* All start with methionine
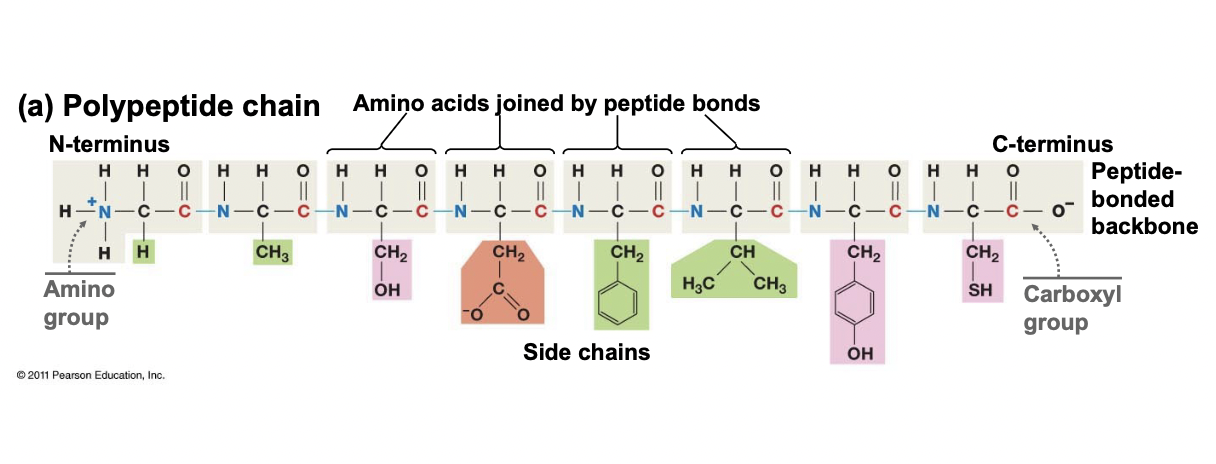
50
New cards
How are proteins created and fold? (1st and 2nd structure)
1) Ribosome makes unfolded polypeptide (primary structure)
2) H-bonds form between peptide chains with C=O oxygen and N-H nitrogen (secondary structure), alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
2) H-bonds form between peptide chains with C=O oxygen and N-H nitrogen (secondary structure), alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
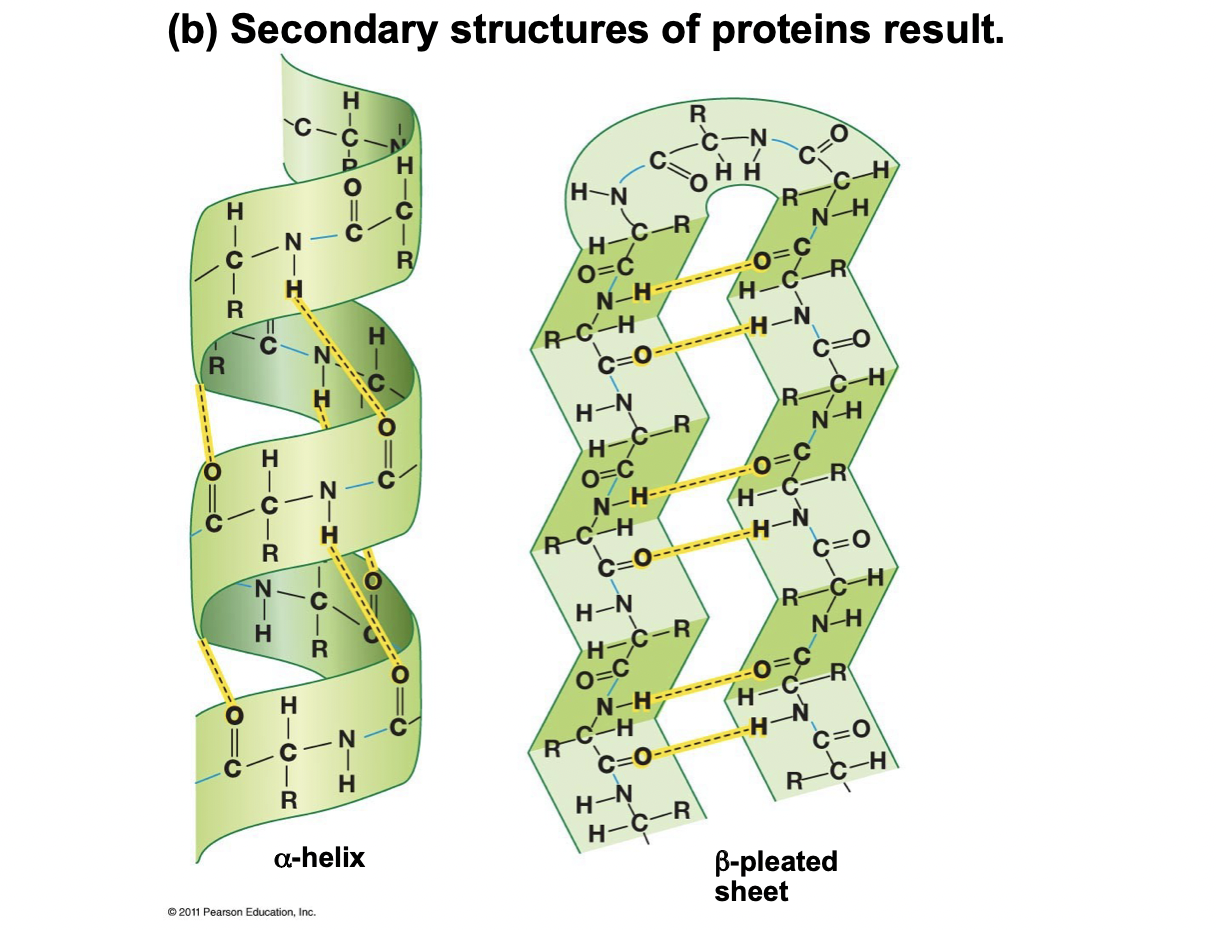
51
New cards
Alpha Helix
* A very stable straight rod
* Occurs due to a H-O bond of every fourth amino acid
* One “turn” of the helix is 3.6 amino acids
* Side chains not yet involved, they point outwards, away from helix
* Occurs due to a H-O bond of every fourth amino acid
* One “turn” of the helix is 3.6 amino acids
* Side chains not yet involved, they point outwards, away from helix
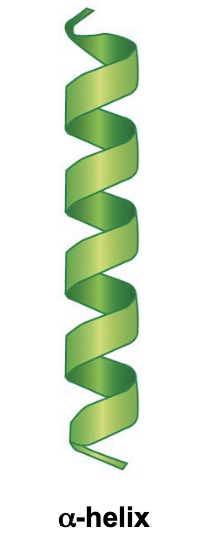
52
New cards
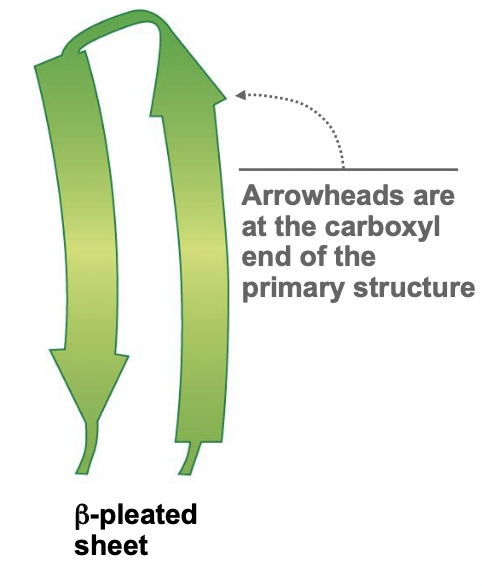
Beta Pleated Sheet
* H-Bonds are formed across in the plane of the paper
* Very stable
* Arrowheads on its ribbon diagram are the carboxyl end (C-terminus)
* Side chains point away from the plane, up or down
* Very stable
* Arrowheads on its ribbon diagram are the carboxyl end (C-terminus)
* Side chains point away from the plane, up or down
53
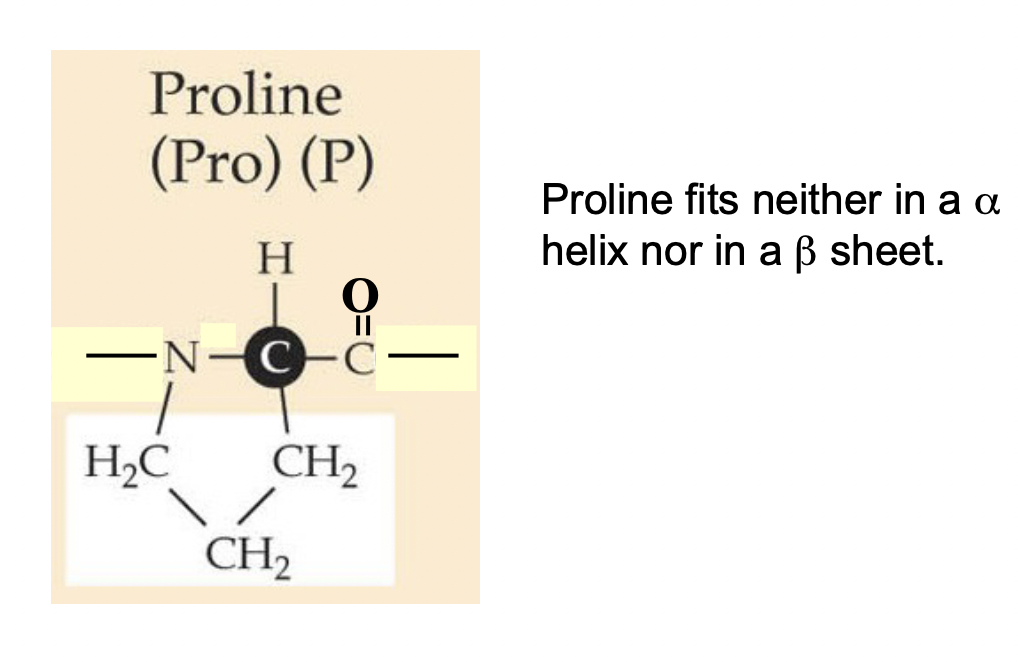
New cards
Proline (Pro) (P)
* Never occurs in an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
* The side chain forms a ring structure by bonding to its “own” N
* No H-bond can form between N and H, so no secondary structures can form
* The N-C bond is in a ring so it cannot rotate and it causes a kink in the peptide
* The side chain forms a ring structure by bonding to its “own” N
* No H-bond can form between N and H, so no secondary structures can form
* The N-C bond is in a ring so it cannot rotate and it causes a kink in the peptide