km
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Thomas Young
examined one light source sent through two openings
observed constructive and destructive interference patterns
LIGHT IS A WAVE
Wavelength
(lambda) is the distance between identical points on successive waves. (m or nm) (1m = 1 x 10^9nm)
Frequency
(n) is the number of waves that pass through a particular point in 1 second (Hz = 1 cycle/s).
Electromagnetic radiation
lambda x v = c
lambda = wavelength
v = frequency
c = speed of light = 3.00 × 10^8 m/s
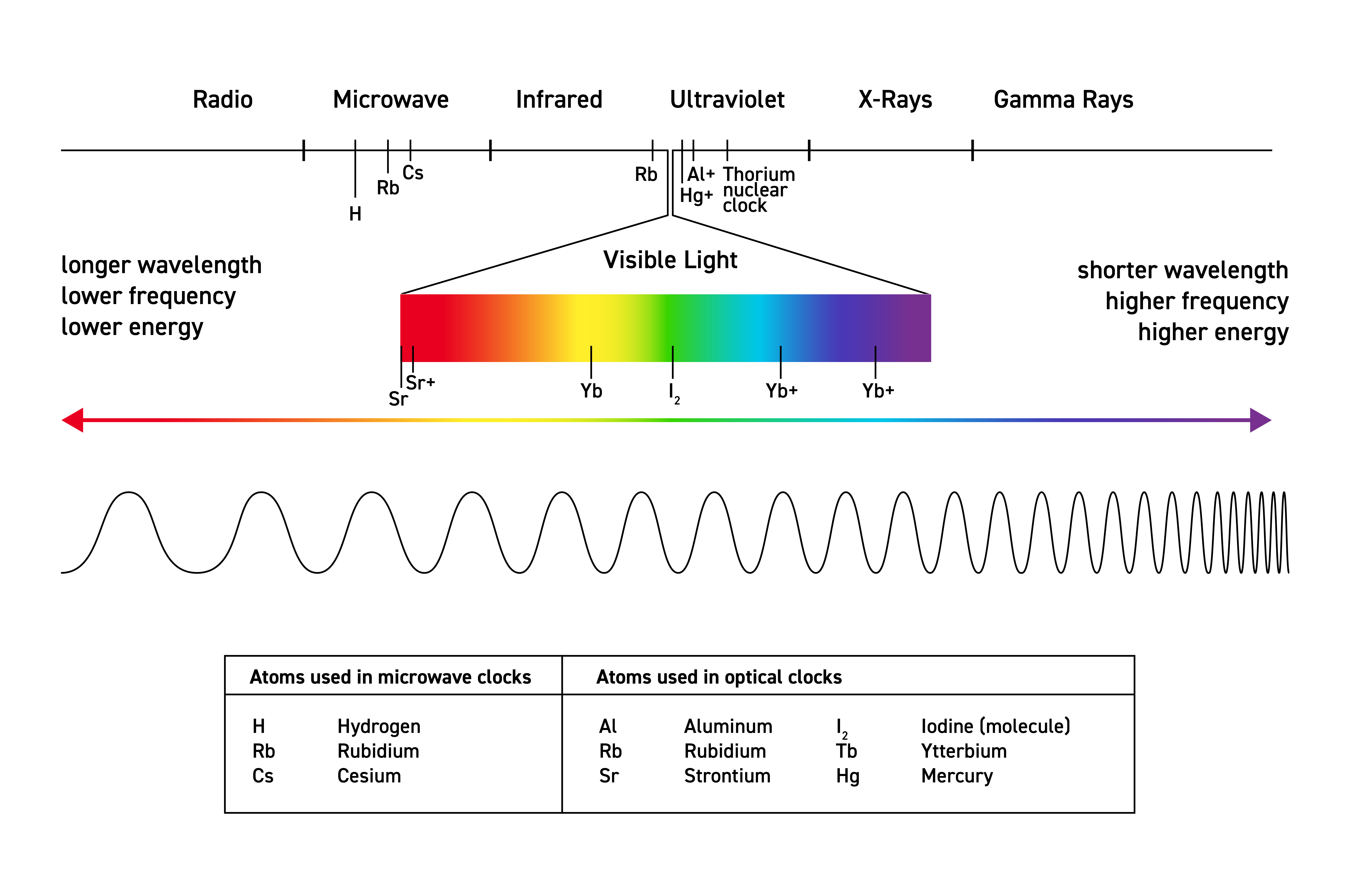
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Red Martians Invade Venus Using X-ray Guns
Visible Light: 400 nm - 700 nm
Planck
Heated Solids Problem
Solids emit electromagnetic radiation over a wide range of wavelengths when solids are heated. Radiant energy emitted by an object at a certain temperature corresponds to their wavelength and frequency
Energy(light) is emitted or absorbed in discrete units(quantum)
E = h x v
E: energy of a photon of light (J)
h = Planck’s constant = 6.63 × 10^-34 Jxs
v = frequency of light (1/s)
Einstein
Photoelectric Effect(1905)
Light has both wave and particle nature
Photon is a “particle” of light
hv = KE + W
hv = energy of the photons of light hitting metal
W = work function
KE = energy of ejected electron
Relationship between frequency and wavelength
Inversely proportional
Relationship between frequency and energy
Directly proportional
Hz in a GHZ
10^9
nm in a m
1 × 10^9
Bohrs Model of the Atom
Have quantized energy values(n=1, n=2, n=3…)
Able to jump to higher orbitals when they absorb enough energy
When electrons move towards nucleus, light is emitted and the energy is dependent on the energy difference
Energy of jump
En = -Rh (1/n²)
E = - Rh (1/nf² - 1/2i²)
n = 1,2,3, …
Rh (Rydberg constant) = 2.18 × 10^-18 J
Ion
An atom/group of atoms that has a net positive or negative charge due to the loss or gain of electrons
Shell*
Area around the nucleus where electrons reside (n)
Orbital
Specific area in the shell when the electrons reside
Valence electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell
Octet Rule
To be “happy” atoms want 8 valence electrons – LOW
ENERGY (**Exception – the first shell only wants 2 electrons)
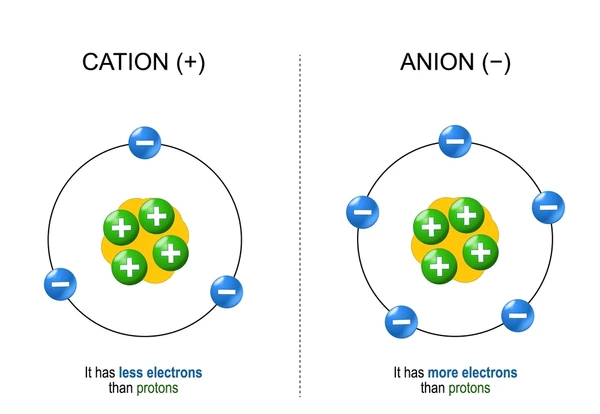
Cation
Ion with a positive charge
Neutral atom loses one or more electrons
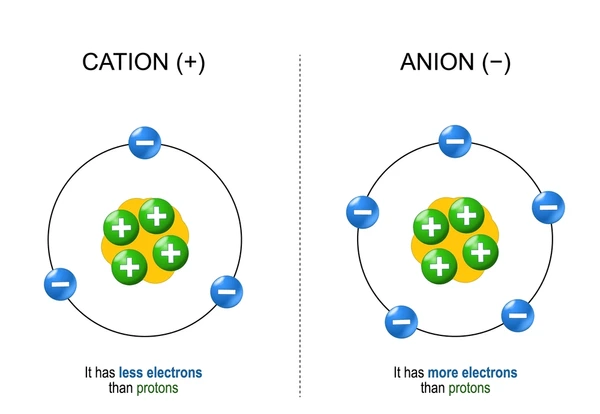
Anion
Ion with a negative charge
Neutral atom gains one or more electrons
ide
Work function
How strong/tight electron is bound to the metal
Emission Spectra
Charging gas in a tube which separates light into different components with a prism
J in a Kj
1000J
Shortcoming of Bohr
Didn’t account for emission spectra of atoms that have more than one electron
Conflict with wavelike properties
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Impossible to know the momentum p (m x v) and the position of a particle with certainty
Schrodinger
Equation describes particle and wave nature of the e-
Hydrogen atom
Wave function(psy):
Energy of e- with a given psy
psy ² = probability of finding electron in a volume of space
Electron density
Probability that an electron will be found in a particular region of an atom
Atomic orbital
Probability of locating an electron in space
Principal quantum number n
Distance of electron from the nucleus and average energy
n = 1, 2, 3, 4, …
Angular momentum quantum number /
Shape of the atomic orbital
Orbitals
l = 0
l = 1
l = 2
l = 3
Magnetic Quantum Number ml
Orientation of the orbital in space
Spin quantum number ms
ms = -1/2 or +1/2
Pauli exclusion principle
No two electrons in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers
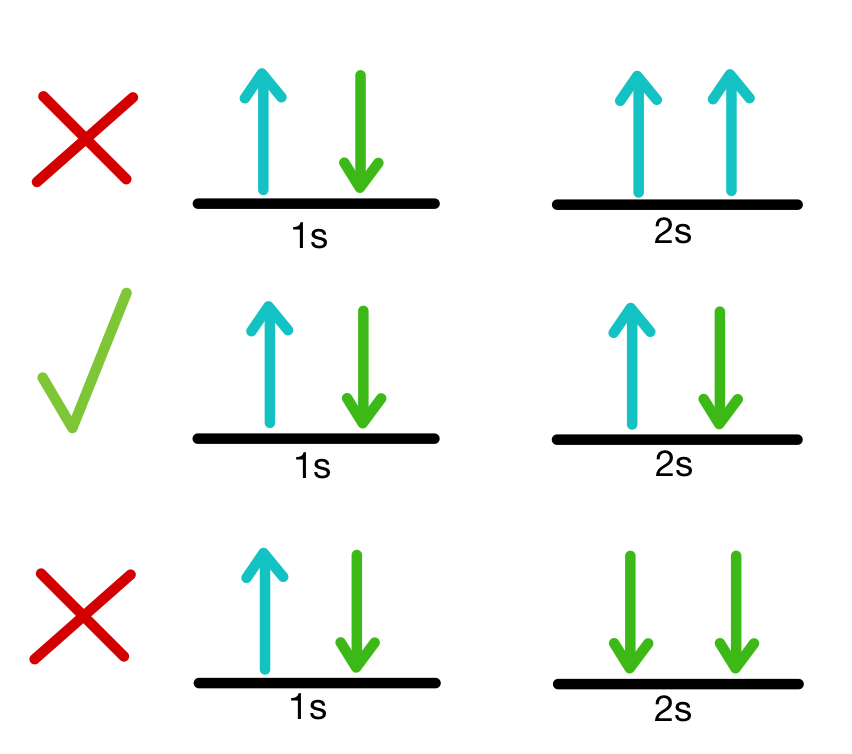
Hunds Rule
The most stable arrangement of electrons in subshells is the one with the greatest number of parallel spins
Aufbaus Principle
When in the ground state, electrons must fill orbitals from the lowest energy to the highest energy
Shell
Electrons with the same value of n
Subshell
Electrons with the same values of n and l
Orbital
Electrons with the same values of n, l, and ml
Total orbitals
n²
Total electrons
2n²
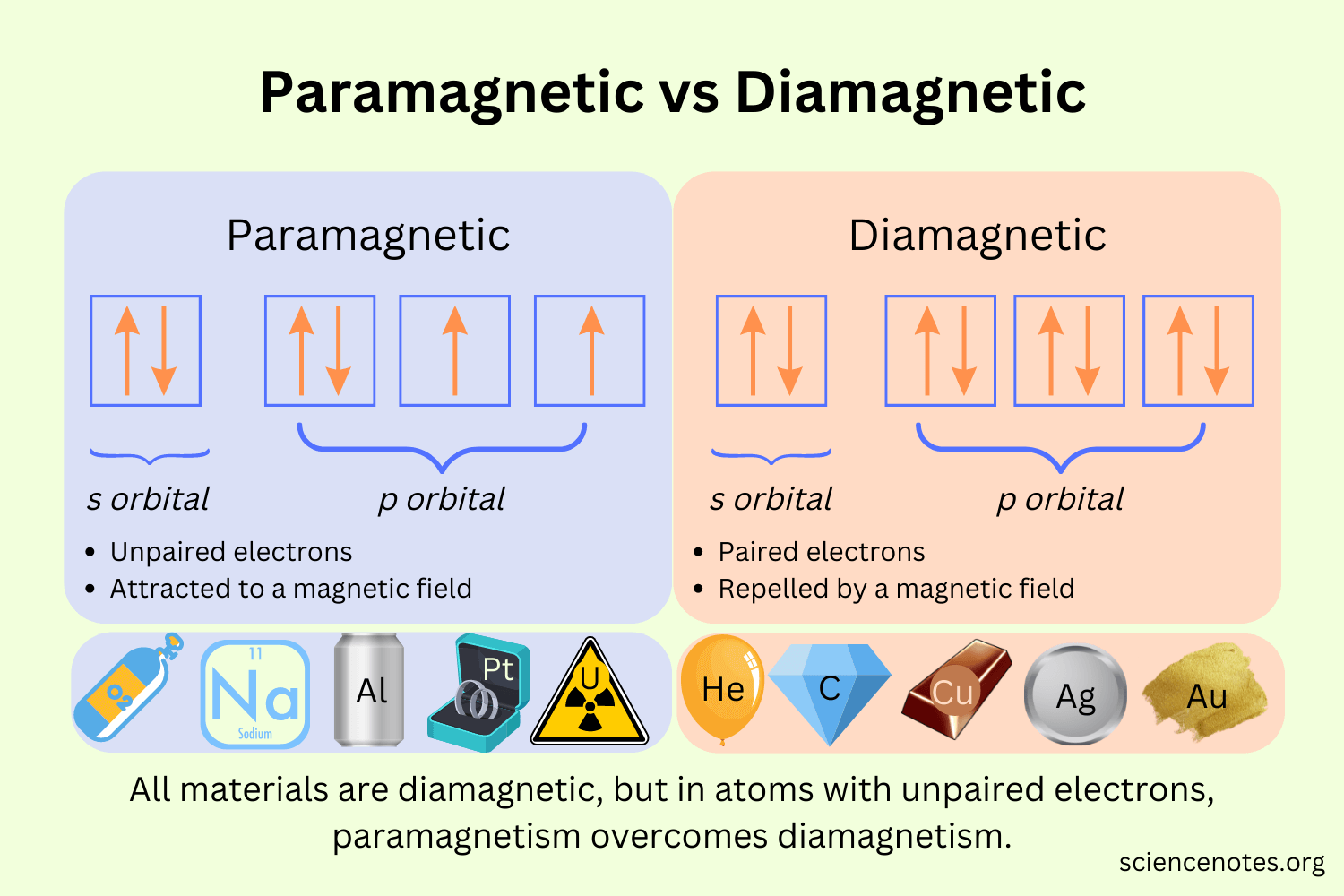
Paramagnetic
When there are unpaired electrons that are attracted to external magnetic fields
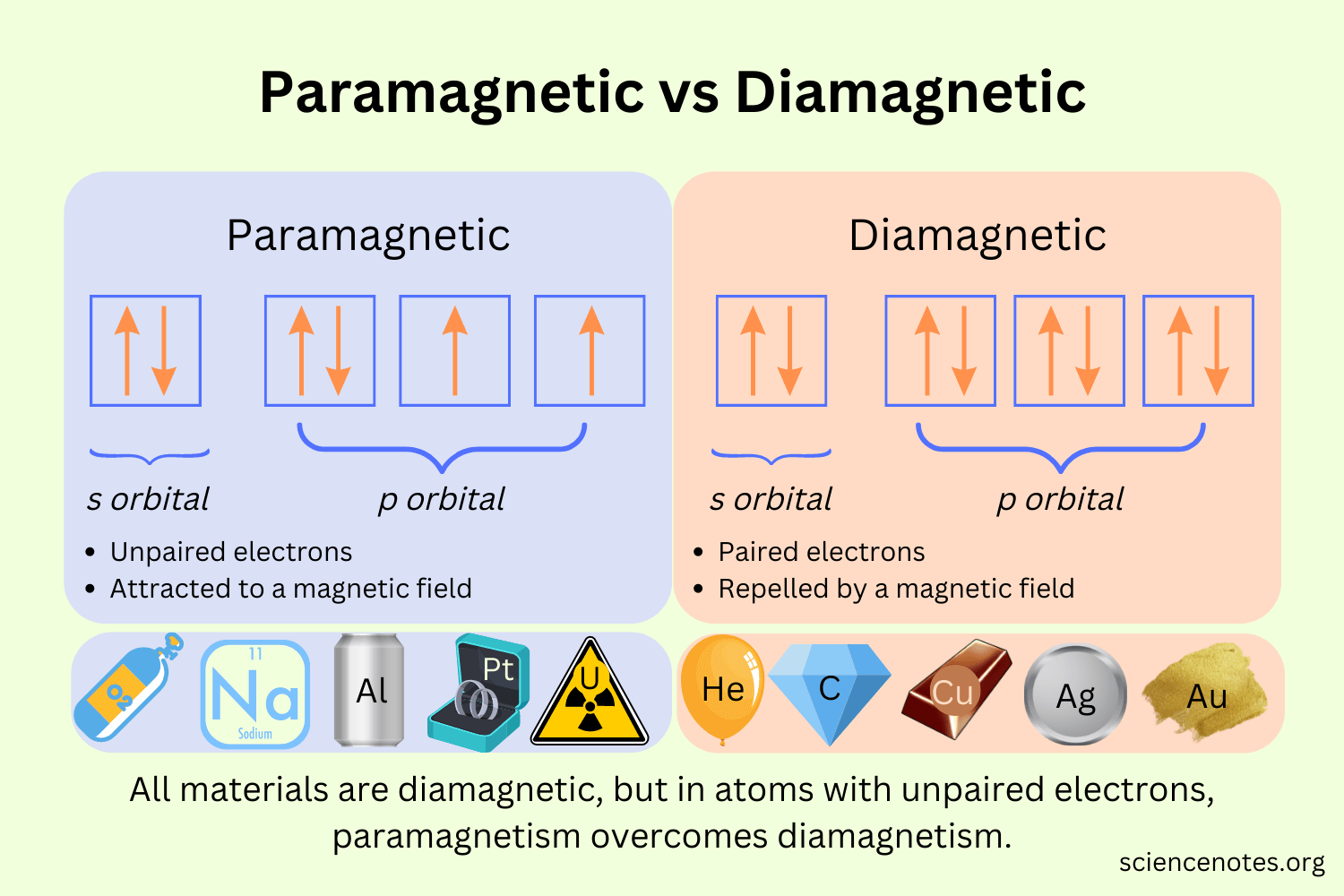
Diamagnetic
When electrons are paired
Isoelectronic
Have the same number of electrons and the same ground-state electron configuration
Constructive
Crest to crest - > Constructive Interference
Destructive
Crest to trough → Destructive Interference