Unit 2: Cell Membrane Structure Vocabulary
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
Carbon Bonding
Carbon can form up to 4 (single or double) covalent bonds
Covalent bonds
Created by sharing electrons (strongest bond)
Six most common elements in life
Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous, sulfur (CHNOPS)
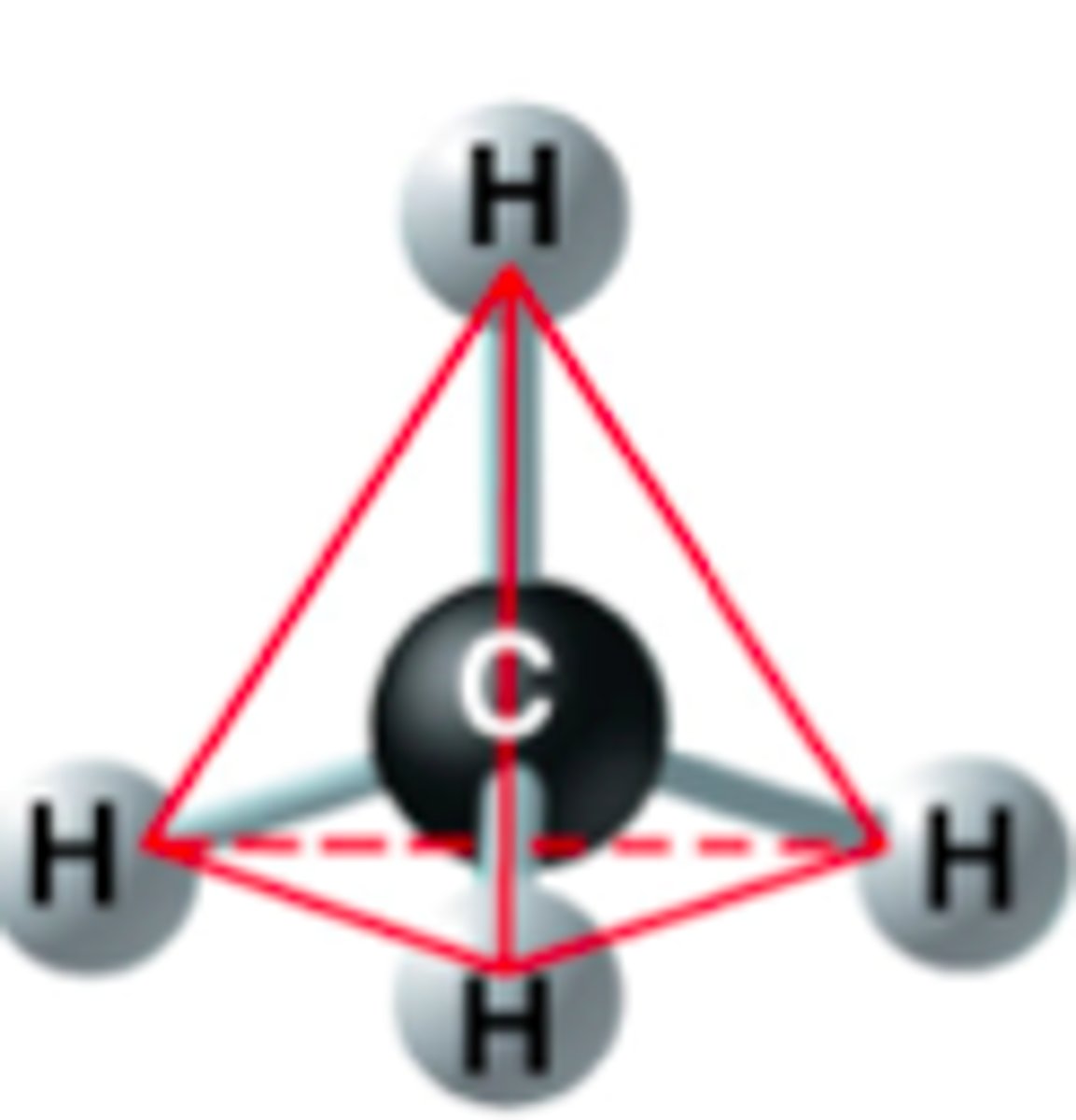
Tetrahedron
Shape that carbon takes on after making four single bonds
Metabolism
Sum of all chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Functions of metabolism (2)
Energy for cellular processes; synthesis and assimilation of new materials
Anabolism
Joining of simple molecules (monomers) to produce complex ones (polymers); condensation reaction; endergonic
Condensation
Removal of H20 to link bonds; water formed from OH (hydroxyl) from one monomer and H from another
Endergonic
Requires energy
Catabolism (digestion)
Breaking of complex molecules (polymers) to produce simple ones (monomers); hydrolysis; exergonic
Hydrolysis
Splitting of molecules by adding water
Exergonic
Releases energy
Carbohydrates
Monomer: Monosaccharide;
Polymer: Polysaccharide
Bond: Glycosidic
Glycosidic Bond
Covalent bond between two monosaccharides (C-O-C)
Carbohydrate Function
Short-term energy storage, structure
Glucose Characteristics
Soluble, chemically stable, yields energy when oxidized (lose electron)
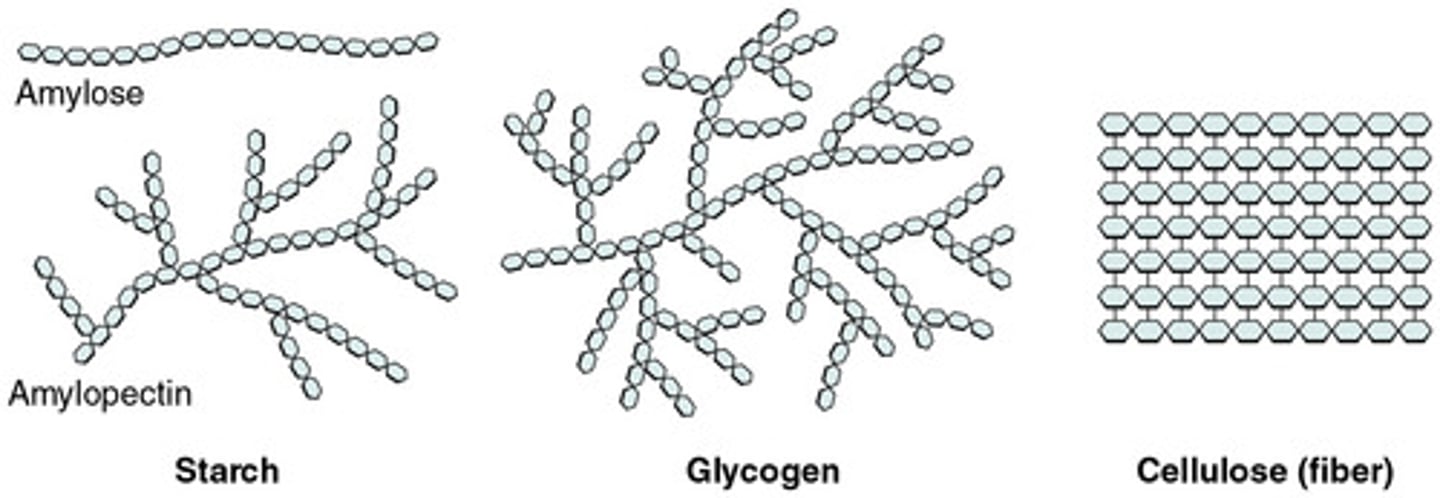
Starch
Plant energy storage made of alpha glucose (amylose or amylopectin)
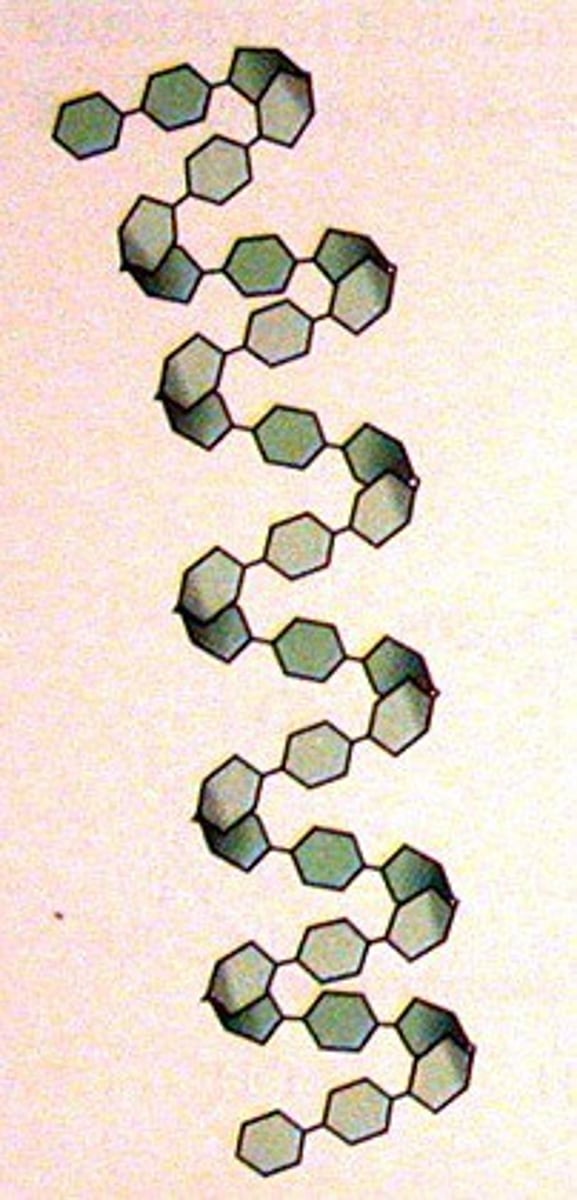
Amylose
Unbranched, helical (1-4 bonds), compact, more difficult to digest; type of starch
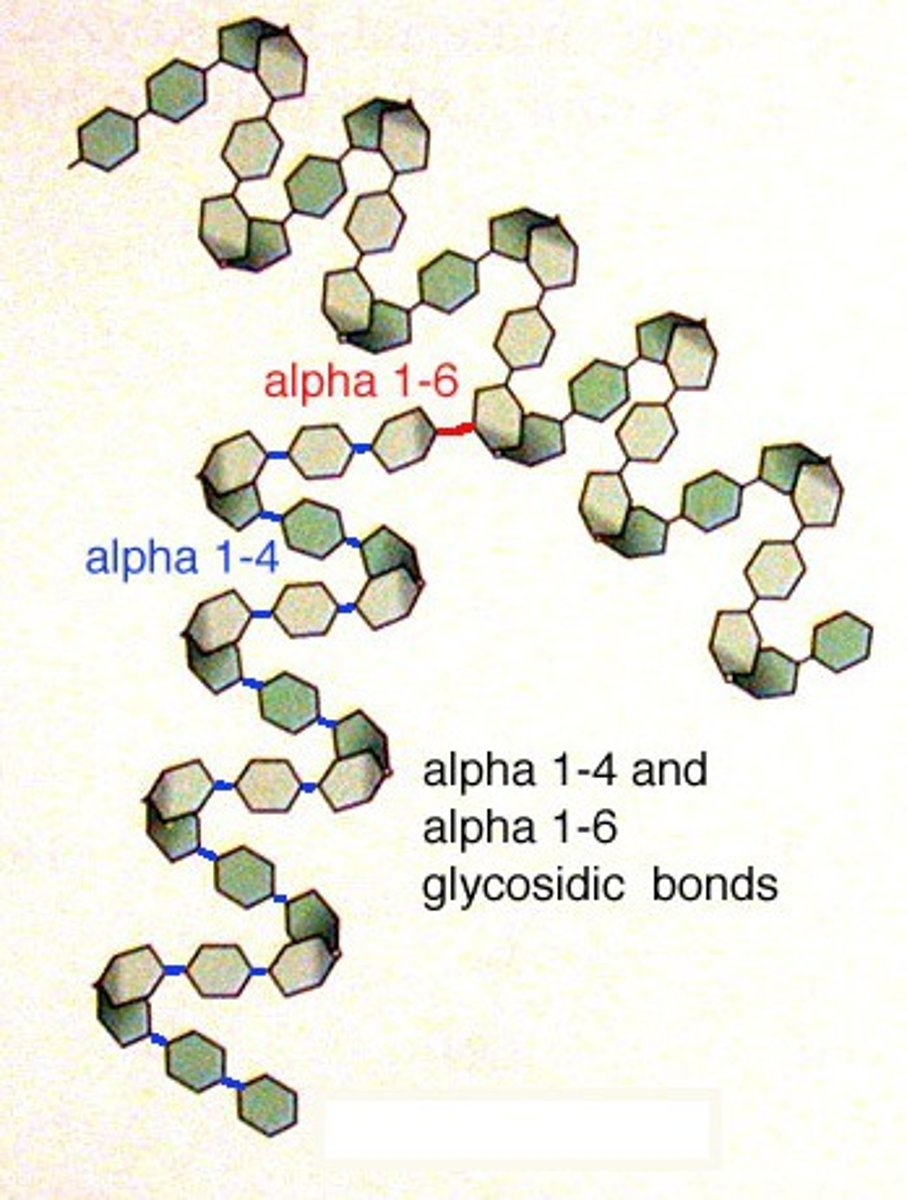
Amylopectin
Branched, 1-4 and 1-6 Bonds (1-6 bonds cause branching), easier to digest due to greater surface area; type of starch
Glycogen
Animal energy storage made of alpha glucose; unbranched (1-4) and branched (1-6); stored in liver in animals
Polysaccharide Characteristics
Large in size, but relatively compact due to coiling and branching; low solubility
Cellulose
Plant structure (cell wall) made of beta glucose; unbranched (1-4 bonds); indigestible for most (lack enzyme)
Alpha vs. Beta Glucose
structural isomers; position of hydroxyl on C1 is different
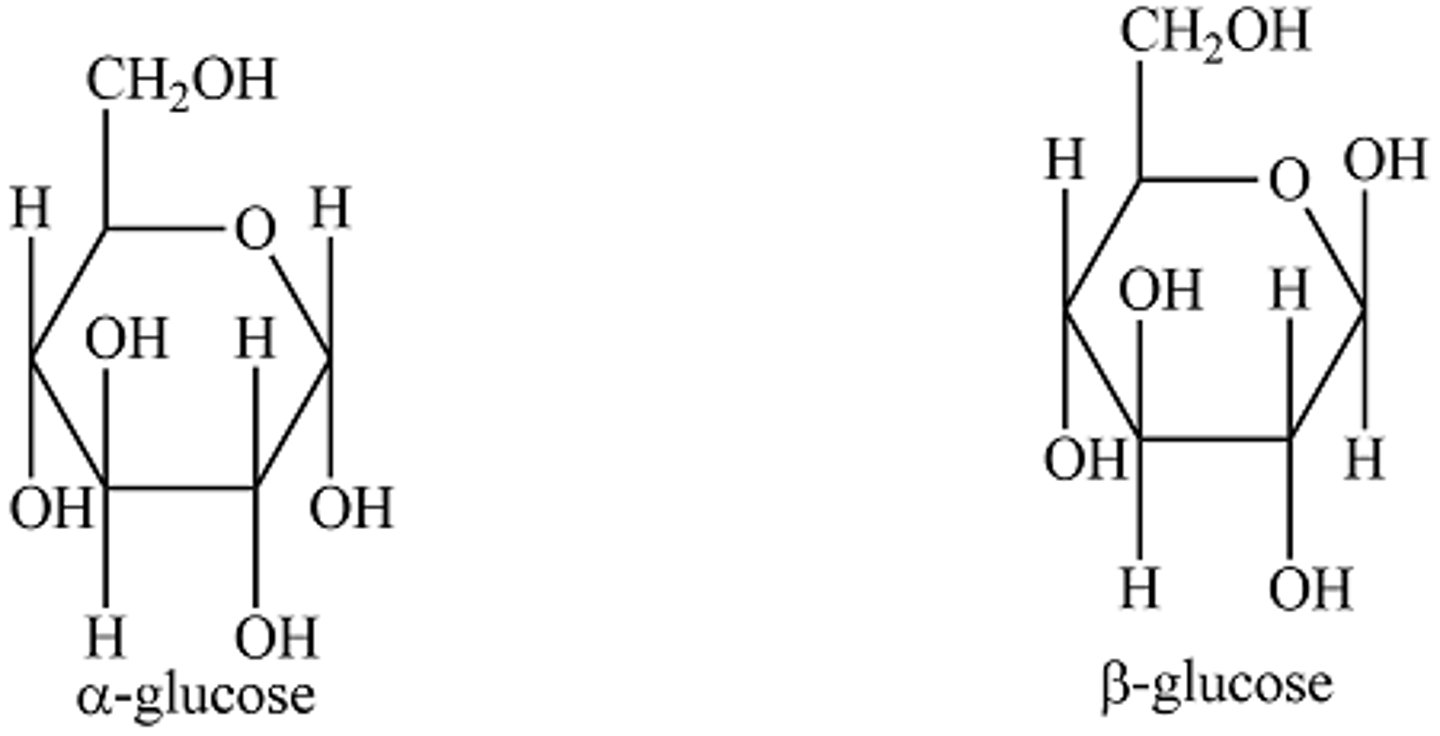
Beta-Glucose Bonding
Alternating OH groups allow additional hydrogen bonding; forms cross-link to provide tensile strength
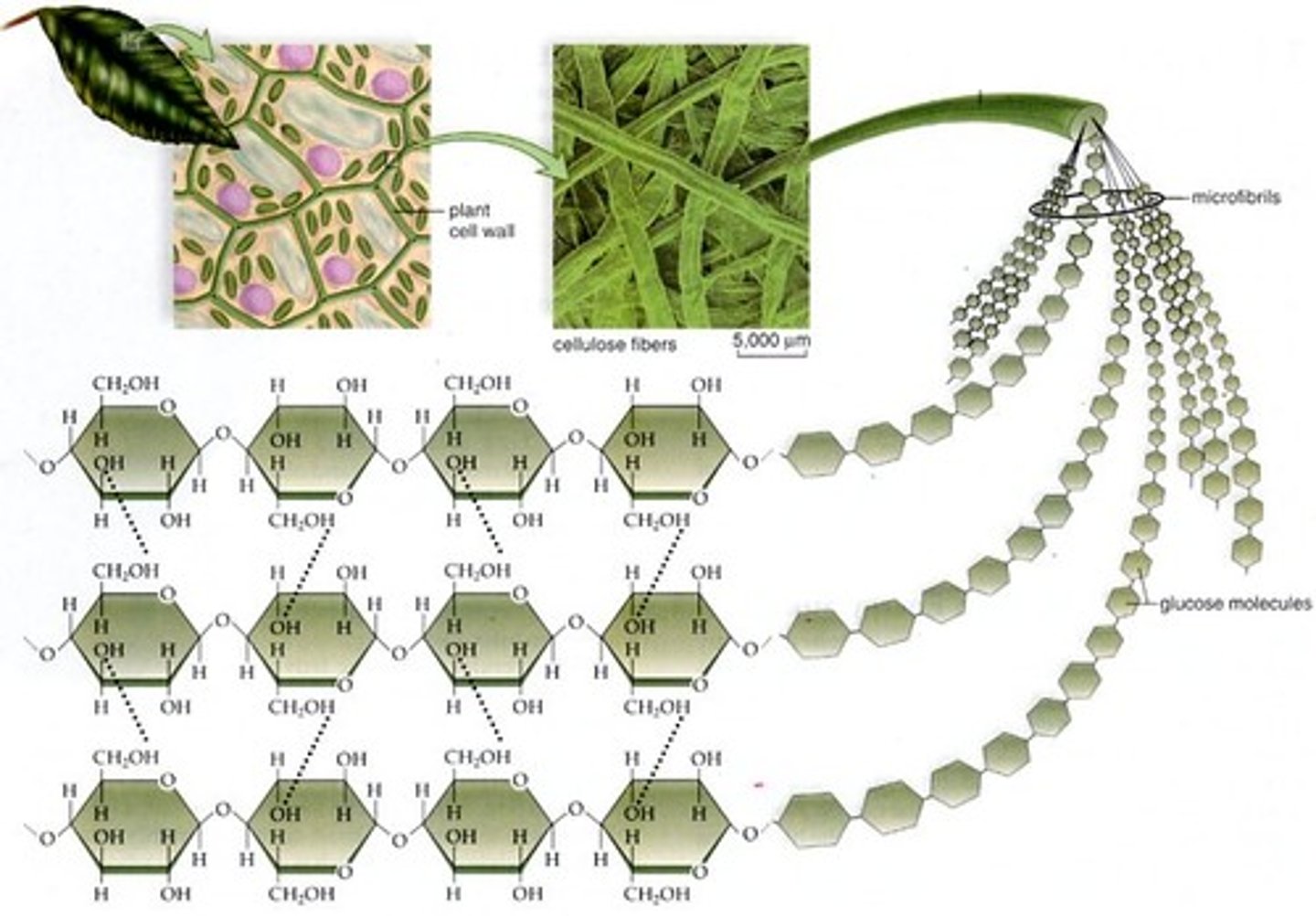
Images of Glucose Polymers
Glycoproteins
Polypeptides with oligosaccharides, found in plasma membranes; used for cell recognition & tissue formation
Oligosaccharides
Short chain of sugar (3-10)
ABO Glycoproteins
Red blood cells have glycoproteins that are used for identification purposes and affect transfusion
Lipids
Include fats, oils, waxes, and steroids;
Hydrophobic (or lipophilic), more attracted to nonpolar (not necessarily repelled by H2O)
DOES NOT CONSIST OF MONOMERS AND POLYMERS
Lipid Function
Long-term energy storage
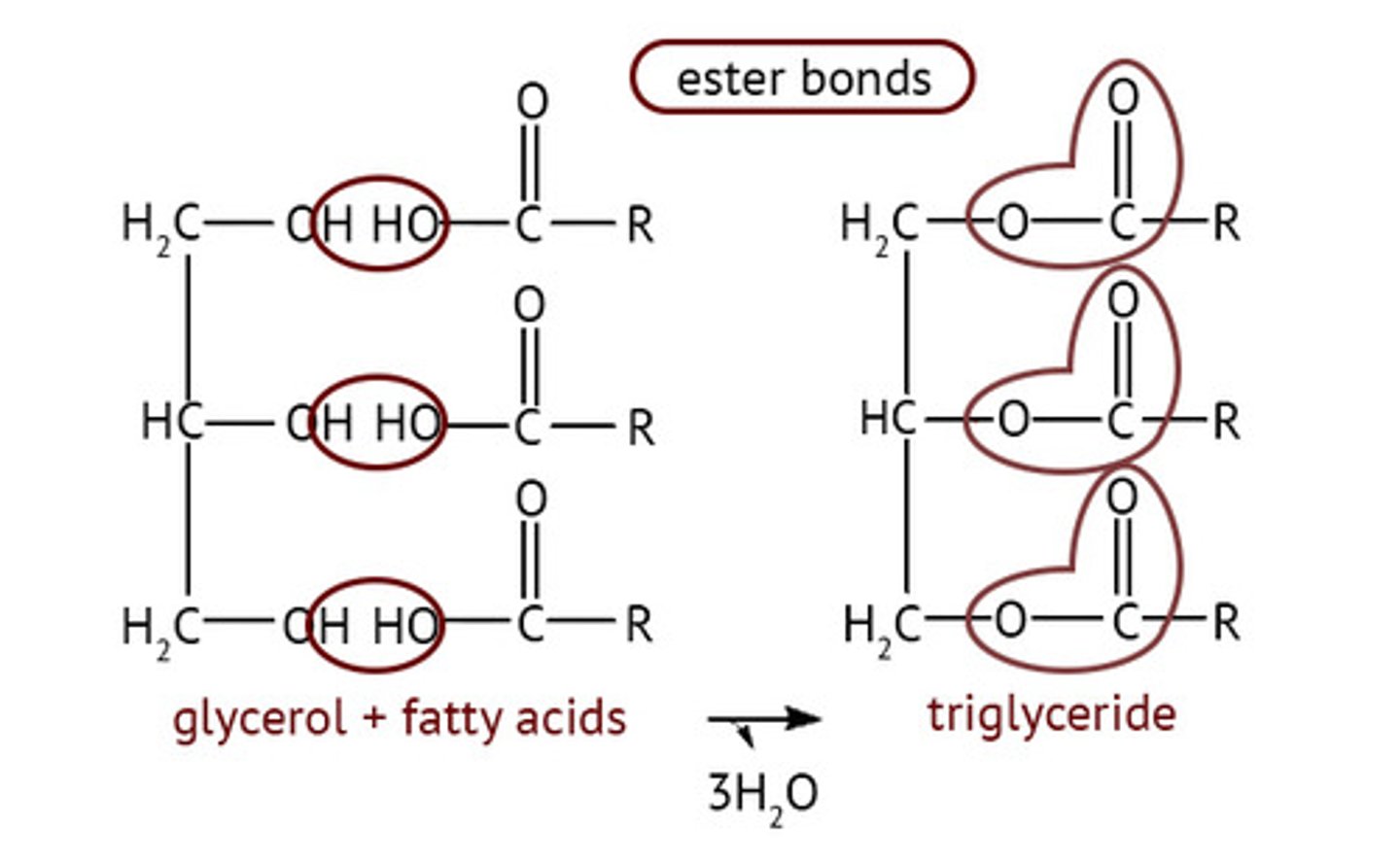
Triglycerides
One glycerol + three fatty acids form via ester bonds
Ester Bonds
Hydroxyl on glycerol loses H, carboxyl on fatty acid loses OH to form H2O; O-C=O
Phospholipids
Phosphate + two fatty acids; amphipathic
Lipophilic
Fat-loving, similar to hydrophobic
Fatty Acids Characteristics
Long hydrocarbons;
CH3 (methyl) at one end and COOH (carboxyl) on the other
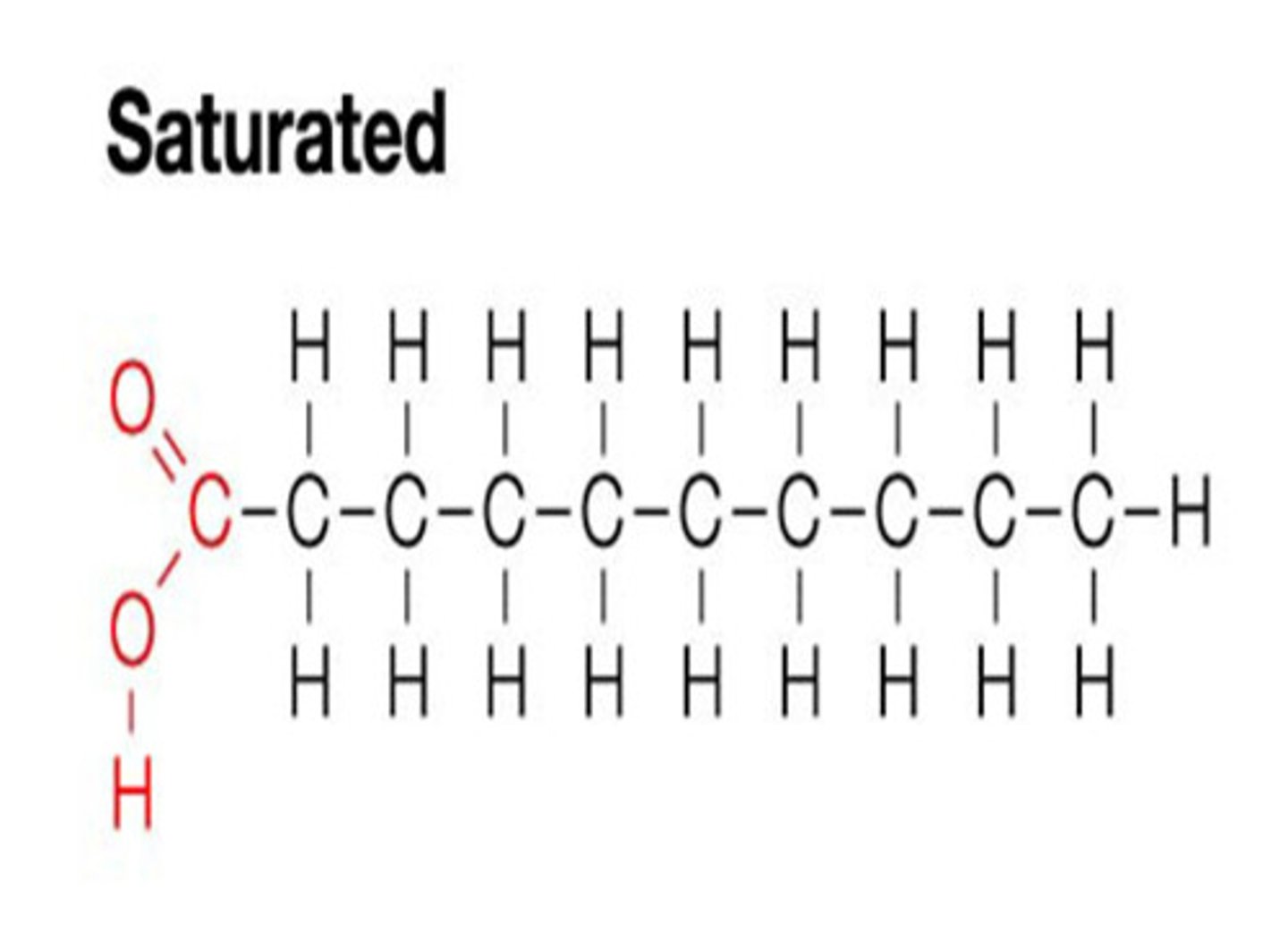
Saturated Fatty Acids
No double bonds, "saturated" with hydrogens;
Linear, come from animal sources;
High melting point - solid at room temperature
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Has double bonds, bent;
Come from plant sources;
Low melting point - liquid at room temp (typically)
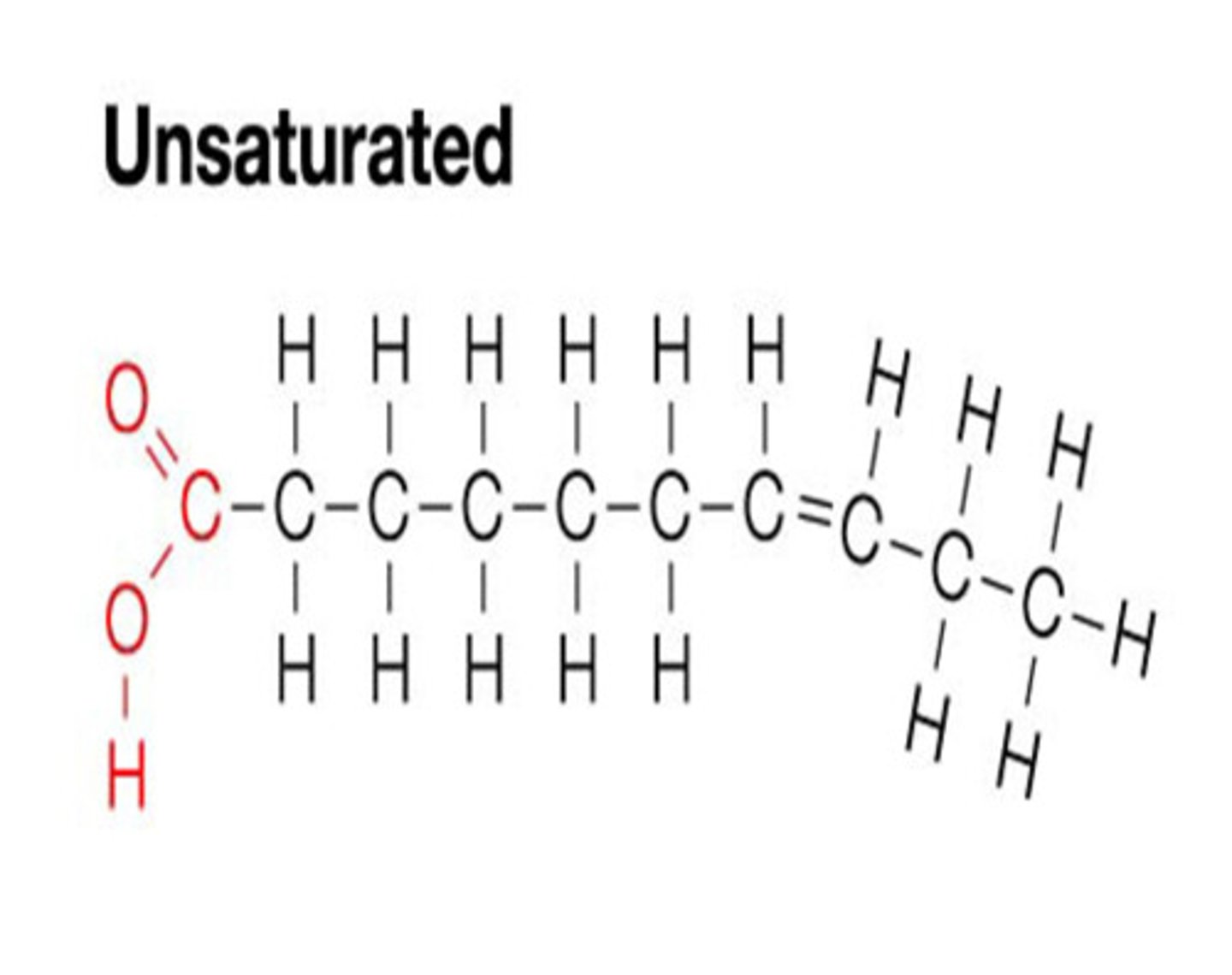
Monounsaturated/Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Mono = 1 double bond;
Poly = more than 1 double bond
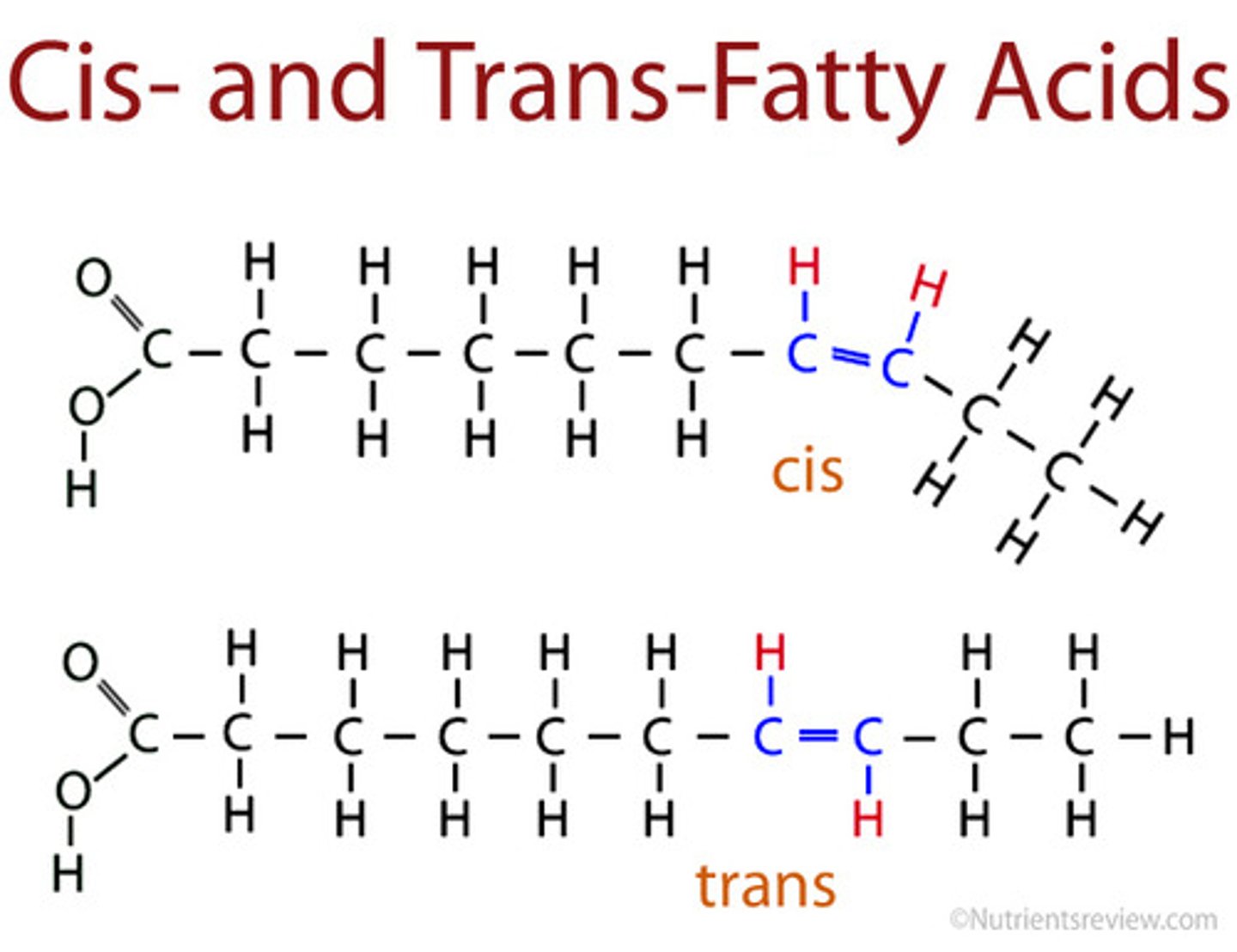
Cis Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Two H atoms adjacent to double bond are on same side, hydrogens repel one another, forming kinks
Trans Unsaturated Fatty Acid
Two H atoms adjacent to double bond are on opposite sides, produced in industrial process called hydrogenation (now banned);
Makes fats "spreadable" such as margarine;
Linear and solid at room temp, despite double bonds
Cis vs Trans Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Lipid Advantages over Carbohydrates (5)
Chemically stable, energy not lost over time;
Immiscible in H2O, no effect on osmotic pressure of cell;
Store 2x energy;
Poor heat conductors, used as thermal insulators such as blubber;
Act as shock absorbers
Proteins
Monomer: amino acid
Polymer: polypeptide
Bond: peptide
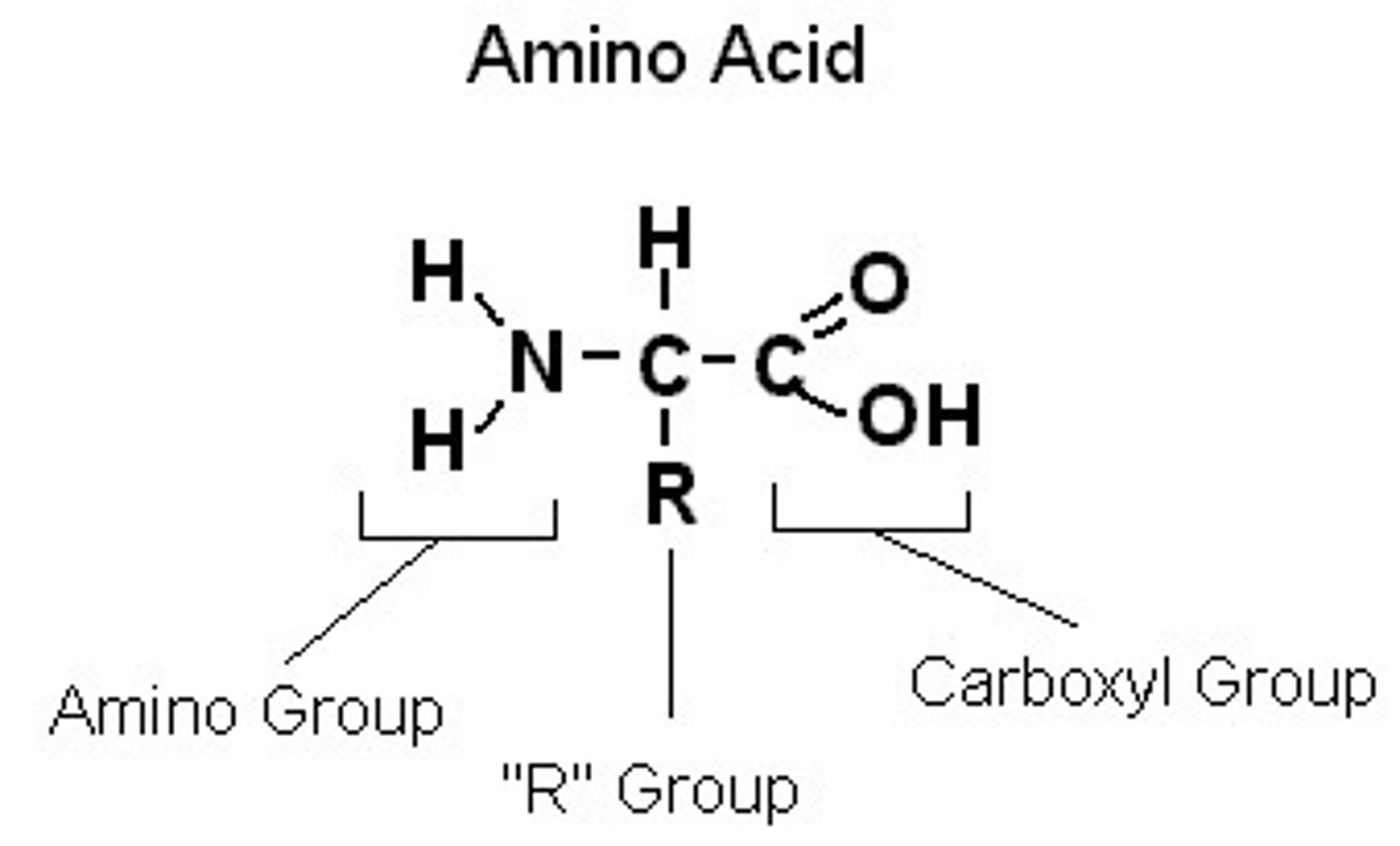
Amino Acid Structure (5)
alpha carbon;
NH2 (amino group), beginning;
COOH (carboxyl group), add to this end;
lone hydrogen;
R group (variable)
Amphiprotic
Molecule that has parts that can donate hydrogen and parts that can receive them (ex. amino acid)
R-Groups
Residue Group; define chemical characteristics of AAs by determining folds/bonding
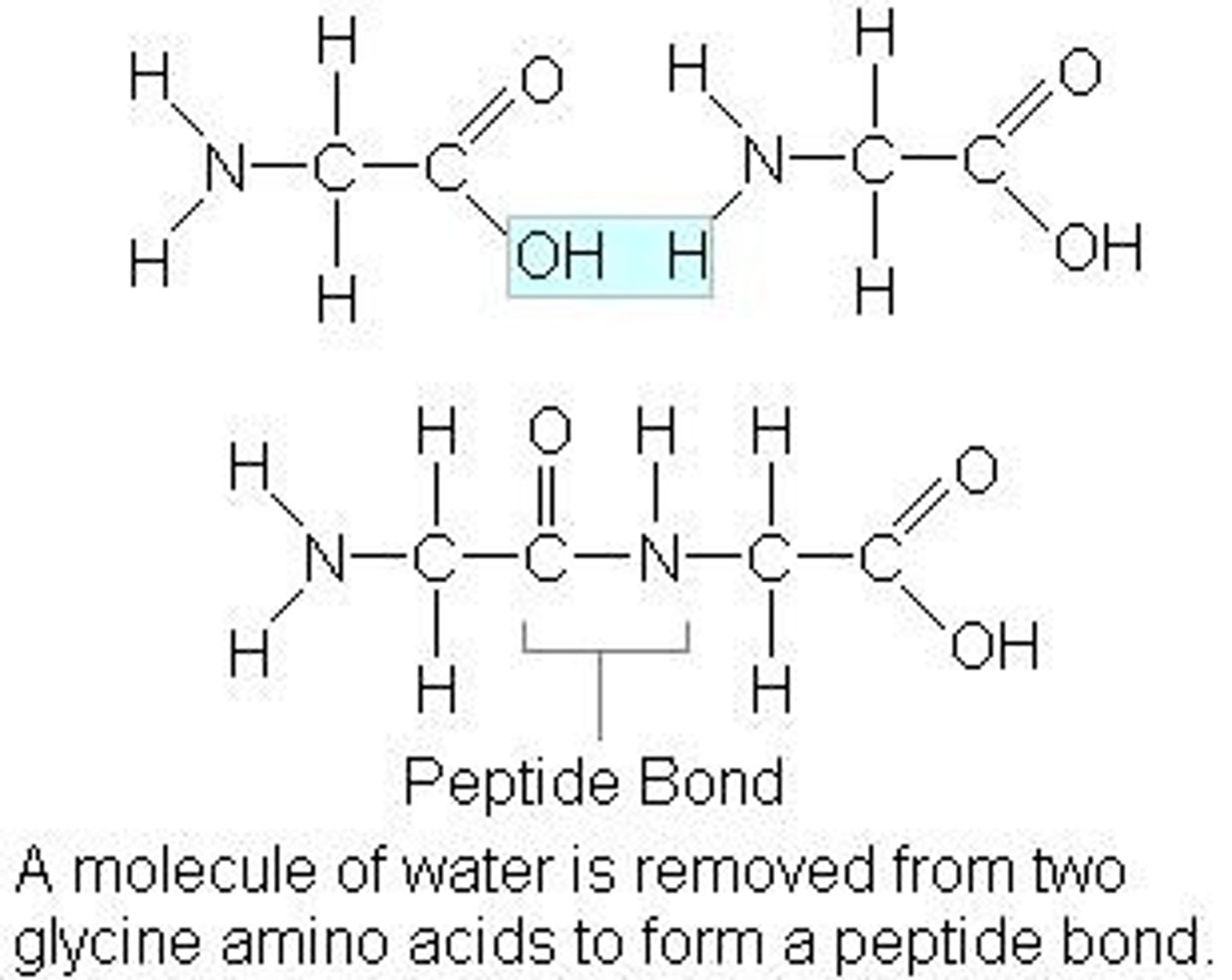
Synthesis of Polypeptides
Formed by condensation;
Forms peptide bond (C-N) and H2O;
*COOH always loses the OH, NH2 loses H*
Catalyzed by Ribosomes;
Polypeptide Directionality
N-terminus: NH2 end;
C-terminus: COOH end
Results in repeated sequence of N-C-C-N-C-C in backbone
Dipeptide Image
Essential AAs
Cannot be made in sufficient amounts by ORG, must be obtained through food
Non-Essential AAs
Can be made by the body via metabolic pathways
Proteome
Total amount of proteins that can be synthesized in the organism (> genome) due to splicing and modification
Primary Structure
Linear sequence of AAs, determined by DNA, formed via only peptide bonds btwn amino acids (covalent)
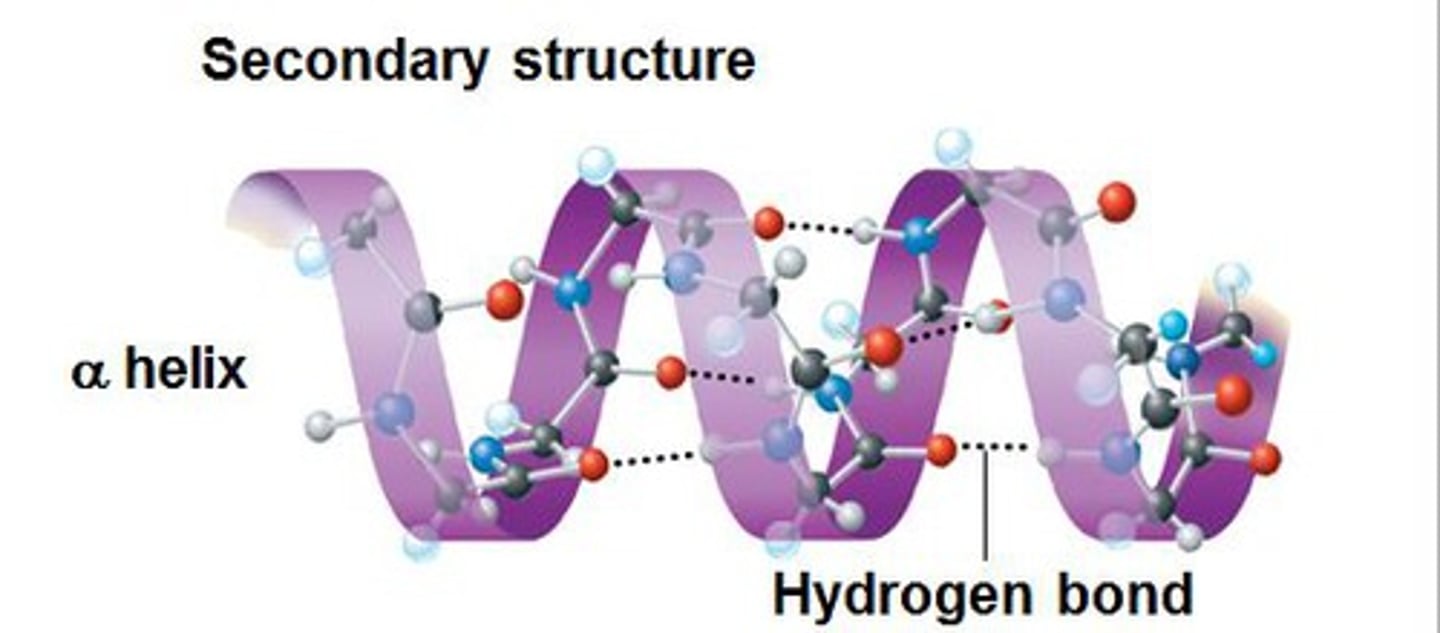
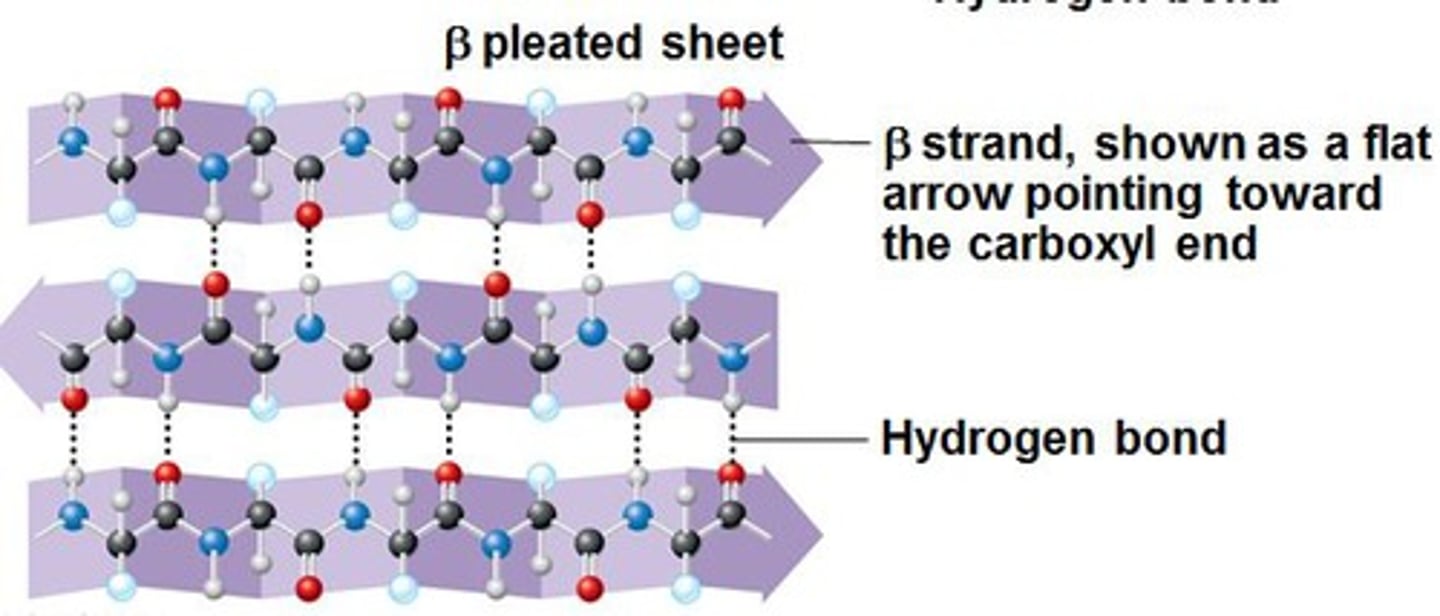
Secondary Structure
Exists as alpha helices & beta pleated sheets;
hydrogen bonds btwn carboxyl & amines groups of nearby AAs (not interaction btwn R-groups)
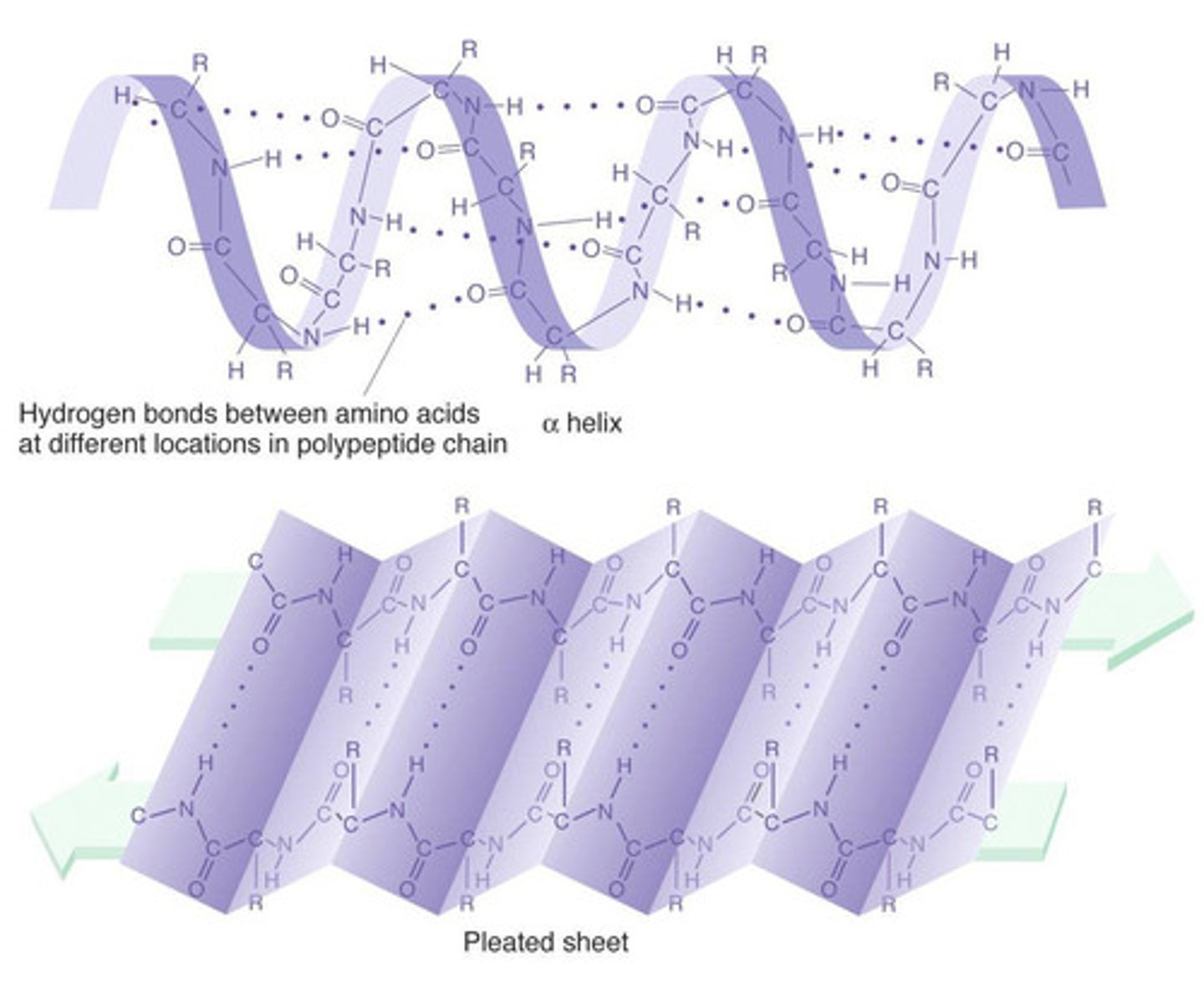
Alpha Helices
Spiral arrangement w/ h-bonds btwn adjacent turns
Beta-pleated sheets
Parallel strand arrangement w/ H-bonds btwn them
Tertiary Structure
Polypeptides 3D conformation, determined by R-groups
Bonds found in Tertiary Structure
Covalent:
-strongest, disulfide bridge (S-S); occurs btwn cysteins
Ionic:
-bonds formed btwn positively/negatively charged R-groups
Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrophobic Interaction
Chaperone Proteins
Proteins that help other proteins fold correctly
Quaternary Structure
Consists of more than 1 polypeptide chain, doesn't always happen
Types: non-conjugated and conjugated
Non-conjugated proteins
Only polypeptide chains; chains are bonded using all bonds found in tertiary structure interactions
Conjugated proteins
Contains one or more non-polypeptide subunits (prosthetic)
Ex. Hemoglobin, 4 polypeptides, each w/ prosthetic group
Prosthetic Group
Non-protein component of a conjugated protein (ex. heme group of hemoglobin)
Protein Form and Function
Structure = Function
DNA sequence, leads to specific AA sequence, leads to Unique r-group interaction, leads to 3D shape, leads to Function
Fibrous Proteins
Elongated polypeptides that lack folding found in secondary & tertiary structures (ex. collagen
Globular Proteins
Rounded by shape created via foldings, stabilized via r-group interactions (ex. insulin)
Cell Membrane
Bilayer of phospholipids that form a continuous barrier
Cell Membrane Function
Separates cell from environment & controls passage of particles
Phospholipid bilayer
Hydrophobic tails attracted to each other, hydrophilic heads H-bond with cytosolic (inside cell) and extracellular (outside cell) fluids
In aqueous environment, phospholipids spontaneously arrange into _________ (sphere)
Fluid-Mosaic Model
Fluid - phospholipids move freely laterally;
Mosaic - has embedded different types of proteins (like tiles in a mosaic)
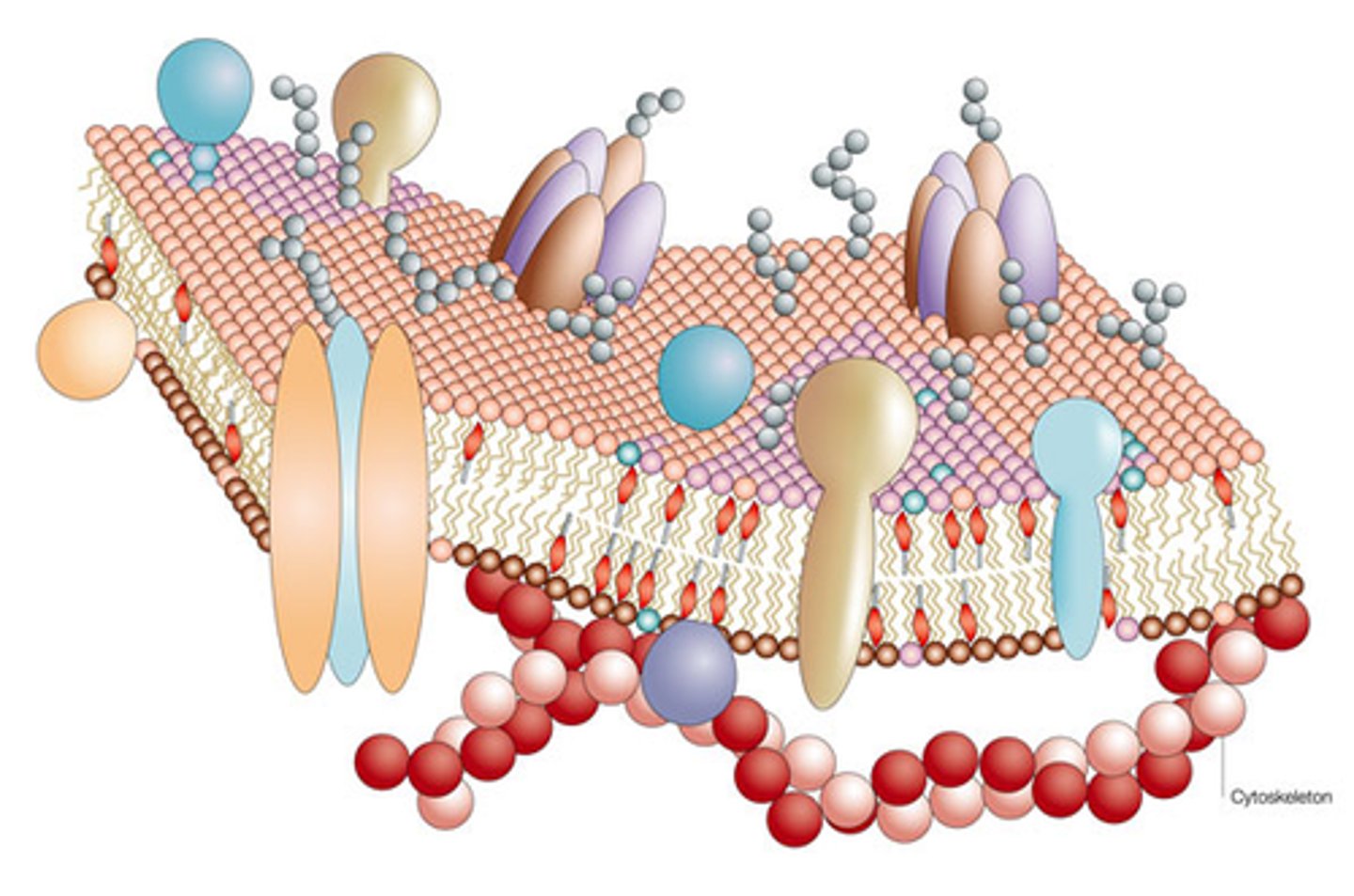
Fatty Acids in Cell Membrane
Sustained by hydrophobic interaction, drifts laterally but not transversely
Saturated fatty acids in membrane
Straight, packs tightly, increases density of membrane, decreases fluidity and permeability
Unsaturated fatty acids in membrane
Kinks, bent, packs loosely, decreases density, increases fluidity and permeability
*Ratio of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids are regulated, must be fluid but intact, must be permeable but not perforated*
Steroid
4 fused carbon rings, 3 cyclohexane rings, 1 cyclopentane ring
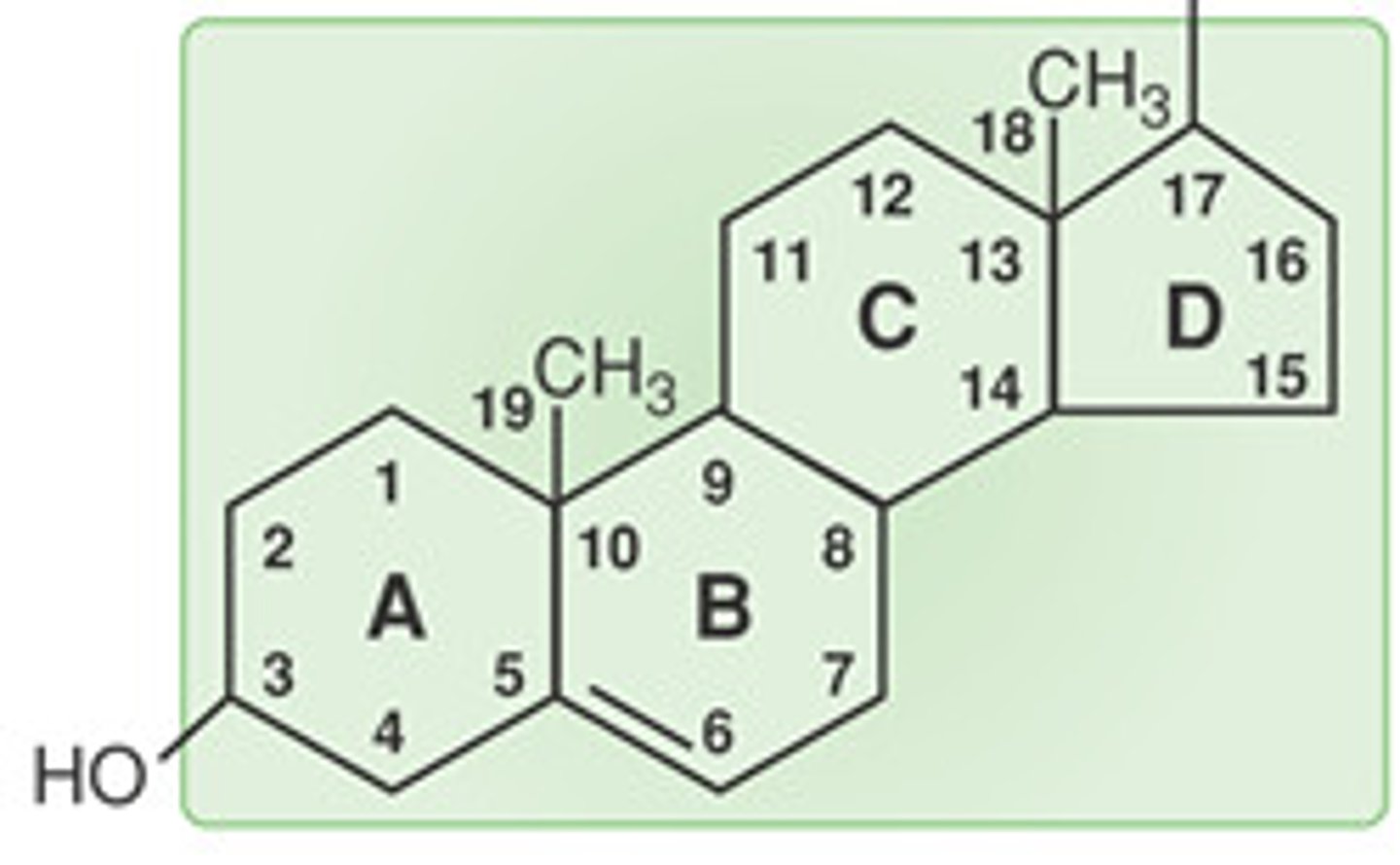
Cholesterol
Maintains membrane fluidity and stability in animal cells; located between saturated fatty acids to create gaps between phospholipids
Cholesterol Function
Controls membrane fluidity;
Buffers against temperature changes
in high temp - maintains impermeability
in low temp - stops crystallization;
Secures peripheral proteins
Glycoproteins and Glycolipids
Involved in Cell to cell recognition
Glycolipids
Lipid embedded in hydrophobic core w/ carbs projecting out (ex. antigen)
Glycocalyx
Used for cell adhesion & recognition;
formed w/ glycoproteins and glycolipids - carbohydrate-rich layer outside of membrane
Cell-adhesion Molecules (CAMs)
When same types of CAMs bind, leads to tissue; different types of CAMs or to extracellular matrix, leads to junction (usually more complex structure)
Semi-Permeable
Determined by size & polarity;
small or nonpolar will cross, large or polar will not;
different from selective, won't choose specific things to let cross like Cl- channels
Passive Transport
Particles are in continuous, random motion ******
move down their own [ ] gradient from high to low; no ATP; move towards equilibrium, once reached, no NET movement (but molecules keep moving)
Types of Passive Transport
simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion (w/ channels)
Simple Diffusion
Particles move directly through membrane (if permeable; from high to low [ ]; until equilibrium is reached
Factors that affect Diffusion
temperature, size of particle, steepness of gradient
Solvation
Combination of solvent and solute
Reason for Osmosis
Solutes in H2O can move, but cannot separate from H2O, therefore they restrict H2O movement.
Some solutes cannot cross the cell membrane, resulting in movement of water, rather than solutes
Osmosis
Passive movement of H2O across membrane from low solute [ ] to high solute [ ] until dynamic equilibrium is reached
Solutions w/ greater concentrations have more osmotically active solutes, therefore more intermolecular interactions w/ H2O
Dynamic Equilibrium
State where there is continuous movement of particles but no overall (net) change in concentration
Concentration (Osmolarity)
solute per volume of solution (mol DM^-3) or (mol/L)
Hypertonic
high concentration of solute, therefore water moves towards it; both cell or solution can be hypertonic
Hypotonic
low concentration of solute, therefore water moves away from it; both cell or solution can be hypotonic
Isotonic
Same solute concentration, therefore no net water movement - at dynamic equilibrium
Tonicity
Ability of solution to cause a cell to gain/lose water
Tonicity of Animal Cells
isotonic - *optimal;
hypertonic - cell shrivels (crenation)
hypotonic - cell lysis
Crenation
When a cell shrinks and shrivels;
originated from describing RBCs
Contractile Vacuoles
Used in freshwater unicellular organisms to remove incoming water, typically needed when in hypotonic solution (ex. freshwater paramecium)
Tonicity of Plant Cells
isotonic - cells are flaccid, plants wilt;
hypertonic - cells plamolyze, platns die;
hypotonic - cells are turgid, *optimal
Turgor Pressure
pressure that water exert against cell wall
Plasmolysis
cytoplasm shrivels and plasma membrane detaches from cell wall; occurs in hypertonic environment