Cancer and Anti-cancer drugs
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What are two ways of treating cancer?
surgery, other cancers respond better to drugs
What are drugs used for cancer called?
chemotherapy
What are the commonly used cancer therapeutic drugs? (5)
alkylating agents
antimetabolites
topoisomerase inhibitors
vinca alkaloids and taxanes
What are alkylating agents?
They react with the proteins that bond together to form the double helix structure of DNA, by adding an alkyl group to some or all of the proteins
this therefore prevents the proteins from linking up, causes the breakage of the DNA strand and eventually the death of the cell
What are antimetabolites?
they induce cell death during the s phase of cell growth when incorporated into RNA and DNA or inhibit enzymes needed for nucleic acid production
What cancers are antimetabolites used for? (5)
breast, pancreatic, ovarian, GI, leukaemia
What do Topoisomerase inhibitors do?
chemical compounds that block the action of topoisomerase 1 and 2
these are enzymes that control the changes in DNA structure by catalysing the breaking and re-joining of phosphodiester backbone of DNA strands during normal cell cycle
they attack enzymes that help cancer cells divide and grow
What cancers are topoisomerase inhibitors used in? (4)
some leukaemia, cancer of the lungs, ovaries, intestines
What are vinca alkaloids?
class of cell cycle specific cytotoxic drugs that work by inhibiting the ability of cancer cells to divide by acting upon tubulin to prevent it from forming into microtubules which is a necessary component for cellular division in the mitotic phase of the cell cycle
the cell remain in metaphase
by binding to tubulin it cannot polymerise to form microtubules
What are vinca alkaloids used to treat?
germ cell tumours, (non) Hodgkin lymphoma, breast, lung, choriocarcinoma, neuroblastoma
What are taxanes?
inhibit the mitotic spindle by binding to the microtubules and preventing their depolymerisation, thus inhibiting mitosis and inducing apoptosis
affect the mitotic phase
like the opposite of the vinca alkaloids as they prevent the di-assembly of the mitotic spindles
Which stages of the cell cycle do each of these cancer drugs affect?
Taxanes - mitotic phase , vinca alkaloids - mitotic phase , topoisomerases - normal cell cycle, antimetabolites - s phase,
What are some treatments for oral cancer SCC?
surgery followed by reconstruction
radiotherapy
chemotherapy
targeted molecular therapy
immunotherapy
What are common side effects of SCC chemotherapy?
Dry mouth, decrease and thickening of saliva, nerve damage and pain, infection, tooth decay increased, loss or change in taste, mouth sores (oral mucositis), bone disease
what does radio therapy include?
X - rays
What are common side effects of SCC radiotherapy?
Fibrosis - growth of fibrous tissue in the mucous membranes, and in the muscle area that receives the radiation
tooth decay and gum disease]
bad breath
breakdown of tissues and bones in the area that receives the radiation
bronchiectasis - permanent enlargement of parts of the airways
What is expected of the general dentist?

Name 4 specialists and their roles?

What are types of cancer genes (2)
oncogenes, tumour suppressor genes
What are oncogenes?
Gain function or increased function associated with cancer
What are tumour suppressor genes?
loss of function or reduced function associated with cancer
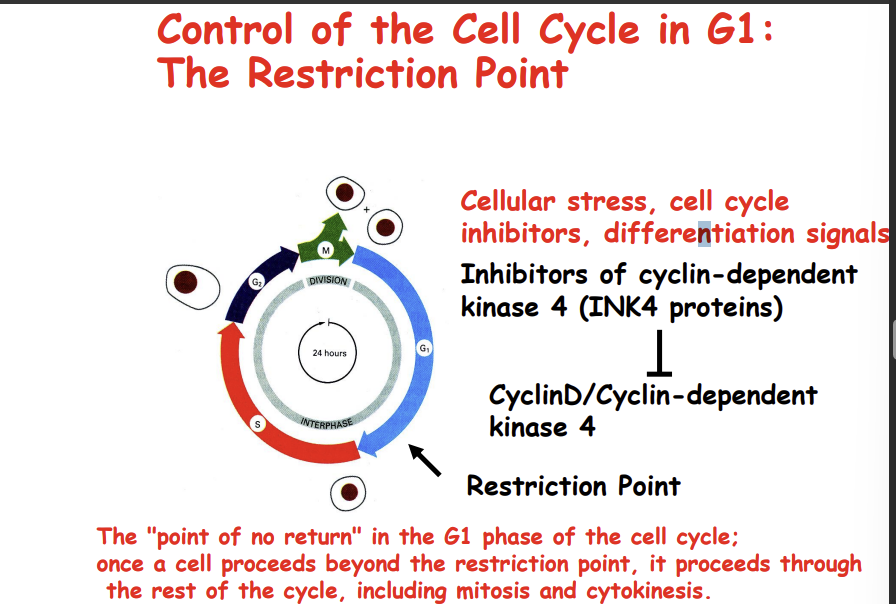
When would the inhibitors of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (INK4 proteins) work?
under cellular stress, cell cycle inhibition and differentiation signals
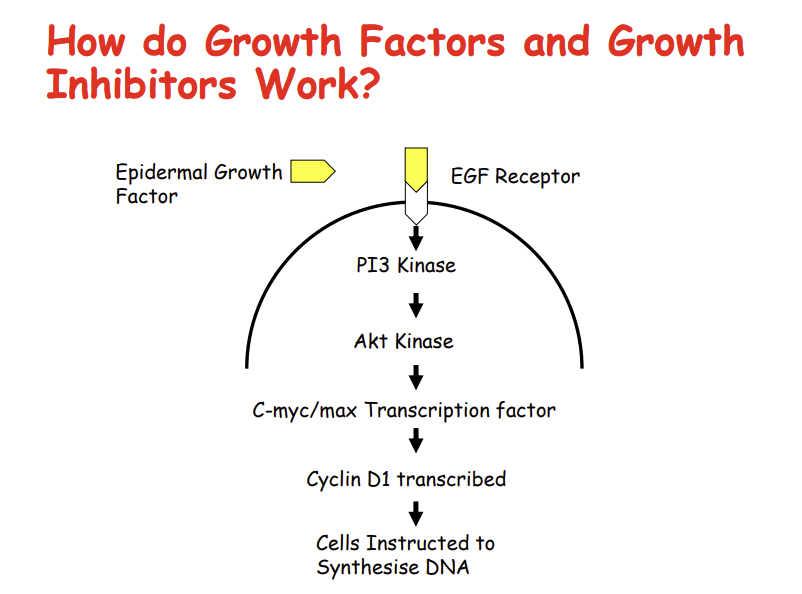
How can Epidermal growth factors have an effect otther than ras?
when it binds to its ligand it can activate PI3 kinase, (phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase), which activates AKt kinase which then activates a different transcription factor complex
c-myc and max, activates cyclin D1 and cells instructed to synthesis DNA
Why does the existence of more than one pathway for cell division a problem?
A problem in cancer as many different pathways must be inhibited
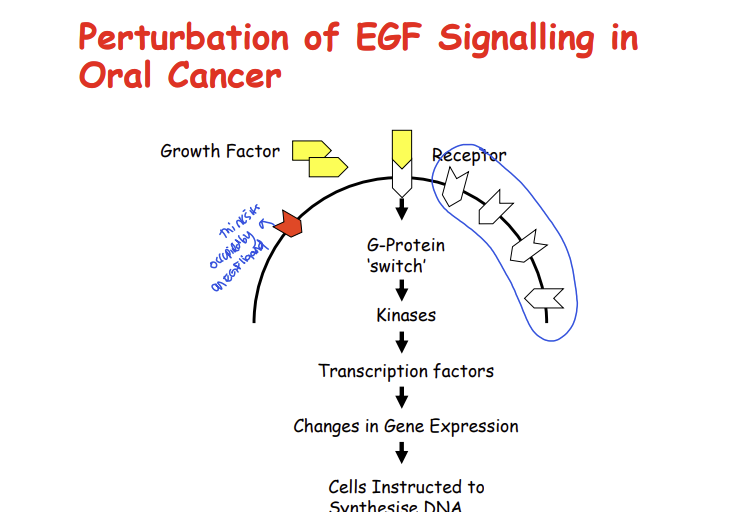
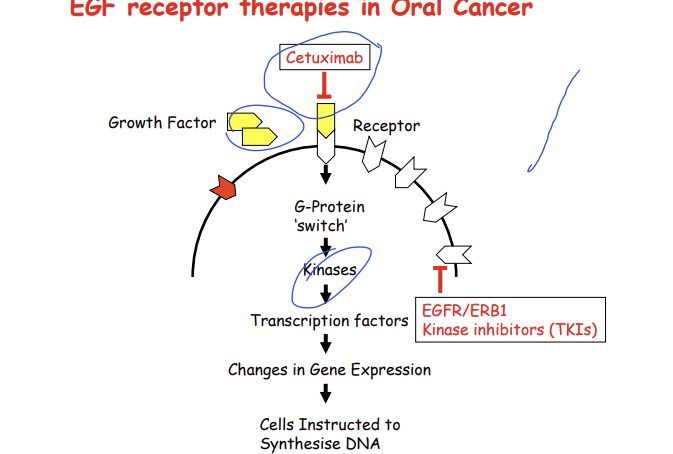
Describe EGF signalling in oral cancer
an increased number of EGF receptors, increased signalling through G proteins switches such as ras, PI3, causing more DNA synthesis
What can HPV do?
inhibit the inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinase
What can be targeted to treat oral cancer?
EGF receptor pathway
What are 2 ways you can target EGF receptors for cancers caused by EGFR upregulation?
tyrosine kinase inhibitors
Monoclonal antibodies
What do tyrosine kinase inhibitors do and give 2 examples?
bind to the tyrosine kinase domain in the EGFR and stop the activity of EGFR
epidermal growth factor
erlotinib and gefitinib
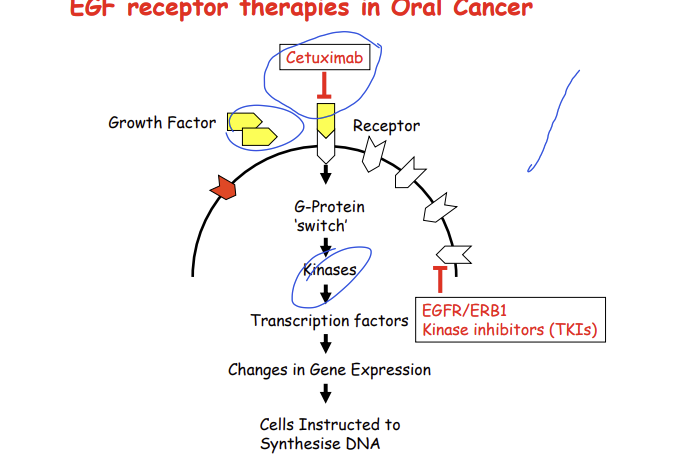
What do monoclonal antibodies do and give an example?
these bind to the extracellular component of the EGFR and prevent EGF from binding to its own receptor preventing cell division
cetuximab
What happened in the de-escalation trials in HPV-positive tonsil cancers?
