AQA A level Chemistry 3.3.3 Halogenoalkanes
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What is the general formula for haloalkanes? (1)
CnH2n+1X, where X is a halogen (F, Cl, Br, or I)
What are the three types of haloalkanes? (3)
Primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°)
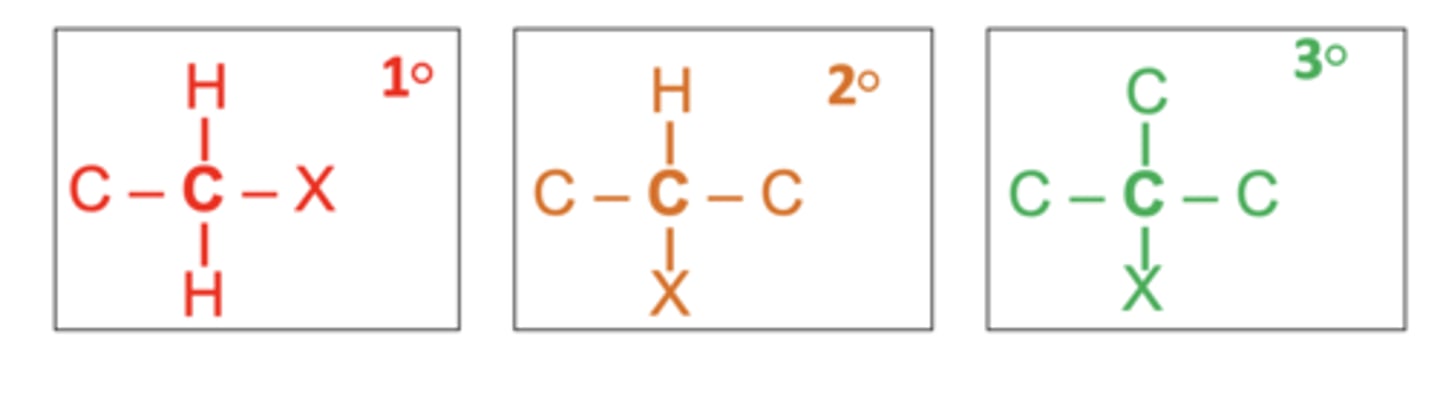
What happens during the formation of halogenoalkanes via free radical substitution? (2)
- Alkanes react with halogens in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light
- To form halogenoalkanes and hydrogen halides
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of methane with chlorine to form chloromethane. (1)
CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl.
In free radical substitution, what happens to the hydrogen atom in the alkane? (1)
It is replaced by a halogen atom
What condition is necessary for the free radical substitution reaction to occur? (1)
Ultraviolet (UV) light
What happens during the initiation stage of free radical substitution? (2)
- The X-X bond in halogen molecules is weaker than the C-H bond in alkanes and breaks first under ultraviolet light
- Forming two halogen radicals
Write the equation for the initiation stage of free radical substitution. (1)
X2 → 2X·
Write the equation for the first propagation stage of free radical substitution. (1)
CH4 + X· → ·CH3 + HX
Write the equation for the second propagation stage of free radical substitution. (1)
·CH3 + X2 → CH3X + X·
What happens during the termination stage of free radical substitution? (1)
Radicals combine to form stable molecules, ending the reaction
What are the three possible termination steps in free radical substitution? (3)

Write the initiation, propagation, and termination steps for the reaction of methane with bromine in the presence of UV light to form bromomethane. (3)

What are chlorofluorocarbons - CFCs (1)
Halogenoalkanes containing both chlorine and fluorine atoms but no hydrogen
How are chlorofluorocarbons used? (2)
- Short-chain CFCs are gases used in refrigerators.
- Longer chains are used for dry cleaning and as degreasing solvents
What happens to CFC gases in the atmosphere? (1)
CFC gases decompose in the atmosphere to give chlorine free radicals
Why is the ozone layer important? (2)
- The ozone layer absorbs harmful UV radiation
- Preventing DNA damage in skin cells and reducing the risk of skin cancer
How do chlorine radicals affect the ozone layer? (2)
- Chlorine radicals decompose ozone in the stratosphere
- Causing a hole in the ozone layer
Write the reaction for the breakdown of the C-Cl bond in the presence of UV radiation. (1)
C-Cl → Cl·
Write the reaction showing how Cl· decomposes ozone. (1)
Cl· + O3 → ClO· + O2
How is Cl· regenerated in the breakdown of ozone? (1)
ClO· + O3 → 2O2 + Cl·
What is the overall equation for ozone breakdown catalyzed by Cl·? (1)
2O3 → 3O2
Why is Cl· considered a catalyst in ozone breakdown? (2)
- Cl· is not destroyed and is regenerated during the reaction
- Enabling it to repeatedly catalyse the breakdown of ozone to oxygen
Why are the carbon-halogen bonds in halogenoalkanes polar? (2)
- The halogen atoms are electronegative, so the electrons in the C-X bond are attracted towards the halogen atom
- Giving it a slight negative charge (δ-) and leaving the carbon atom with a slight positive charge (δ+)
What type of species readily attacks the electron-deficient carbon atom in halogenoalkanes? (1)
Nucleophile
What happens to the C-X bond during nucleophilic substitution? (1)
The electrons in the C-X bond move onto the halogen atom, breaking the bond and releasing a halide ion
What is nucleophilic substitution? (2)
- It is a reaction where the halide ion is substituted for a nucleophile
- Involving the donation of a lone pair of electrons from the nucleophile to the carbon atom
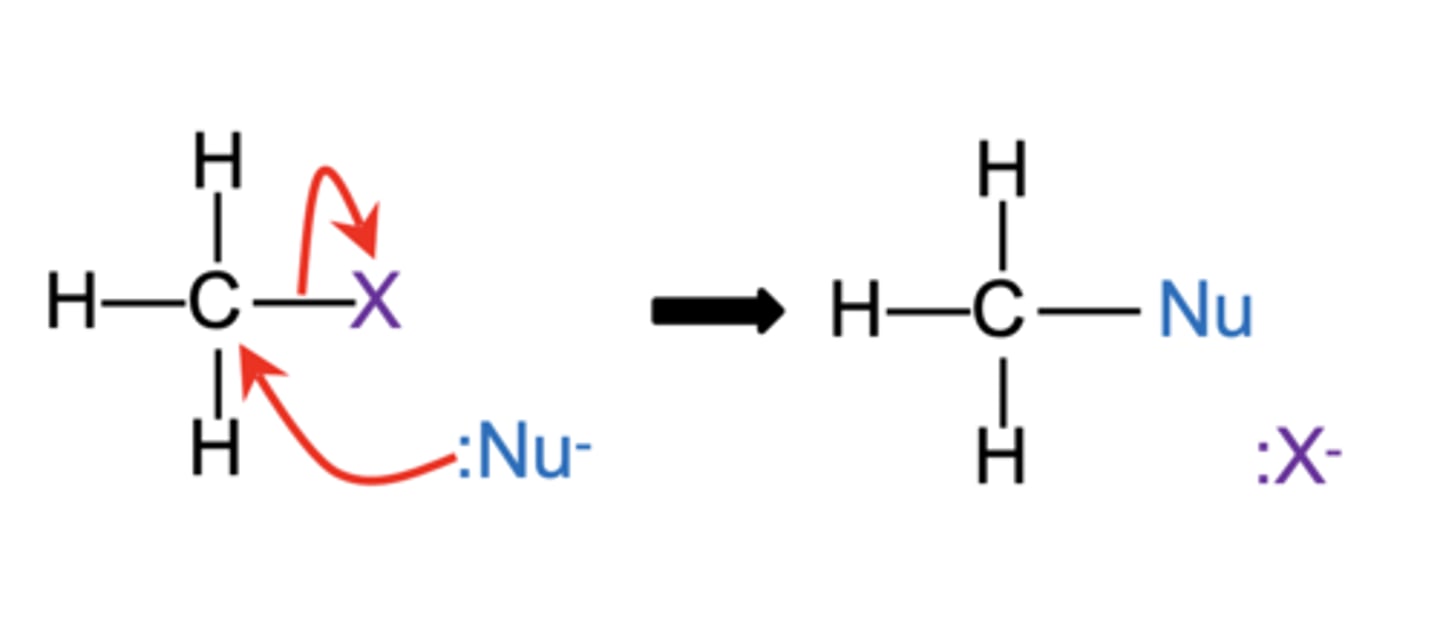
What are the three steps in the nucleophilic substitution mechanism? (3)
1. The lone pair on the nucleophile forms a covalent bond with the δ+ carbon atom.
2. The electrons in the C-X bond move onto the halogen atom, breaking the bond.
3. The halogen atom gains the electrons from the bond to form a halide ion
Draw the general mechanism for nucleophilic substitution. (1)
What happens to the strength of the C-X bond as we go down the group? (3)
- The C-X bond strength decreases as we go down the group
- Because the shared electrons are further from the halogen nucleus
- Making the bond weaker
Why is the C-F bond the strongest among carbon-halogen bonds? (2)
- Fluorine is the smallest halogen
- The shared electrons are strongly attracted to the fluorine nucleus
What does bond enthalpy suggest about the reactivity of carbon-halogen compounds? (2)
1. Bond enthalpy suggests that iodo-compounds with the weakest bonds are the most reactive
2. While fluoro-compounds with the strongest bonds are the least reactive
What trend does experimental data show about the reactivity of carbon-halogen bonds? (1)
Experimental data shows that reactivity increases as we go down the group
Arrange the following carbon-halogen bonds in order of decreasing bond enthalpy: C-F, C-Cl, C-Br, C-I. (1)
C-F > C-Cl > C-Br > C-I
What reagent and conditions are used for nucleophilic substitution of halogenoalkanes with hydroxide ions to form alcohols? (2)
- Reagent: Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) or potassium hydroxide (KOH).
- Conditions: Warm and aqueous
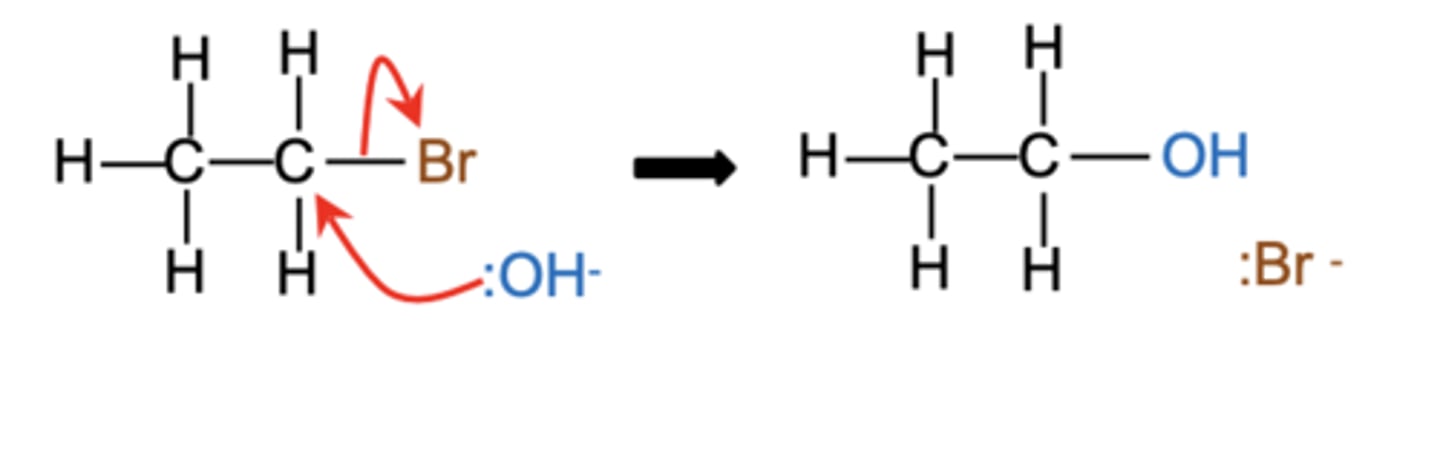
What product is formed when CH3CH2Br reacts with hydroxide ions (:OH⁻) in a nucleophilic substitution reaction? (1)
Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and bromide ion (:Br⁻)
What is the mechanism involved in the reaction of halogenoalkanes with hydroxide ions? (1)
Nucleophilic substitution
Draw the mechanism for the reaction of CH3CH2Br with hydroxide ions. (4)
What reagent and conditions are used for nucleophilic substitution of halogenoalkanes with cyanide ions to form nitriles? (2)
- Reagent: Potassium cyanide (KCN).
- Conditions: Warm with aqueous ethanol
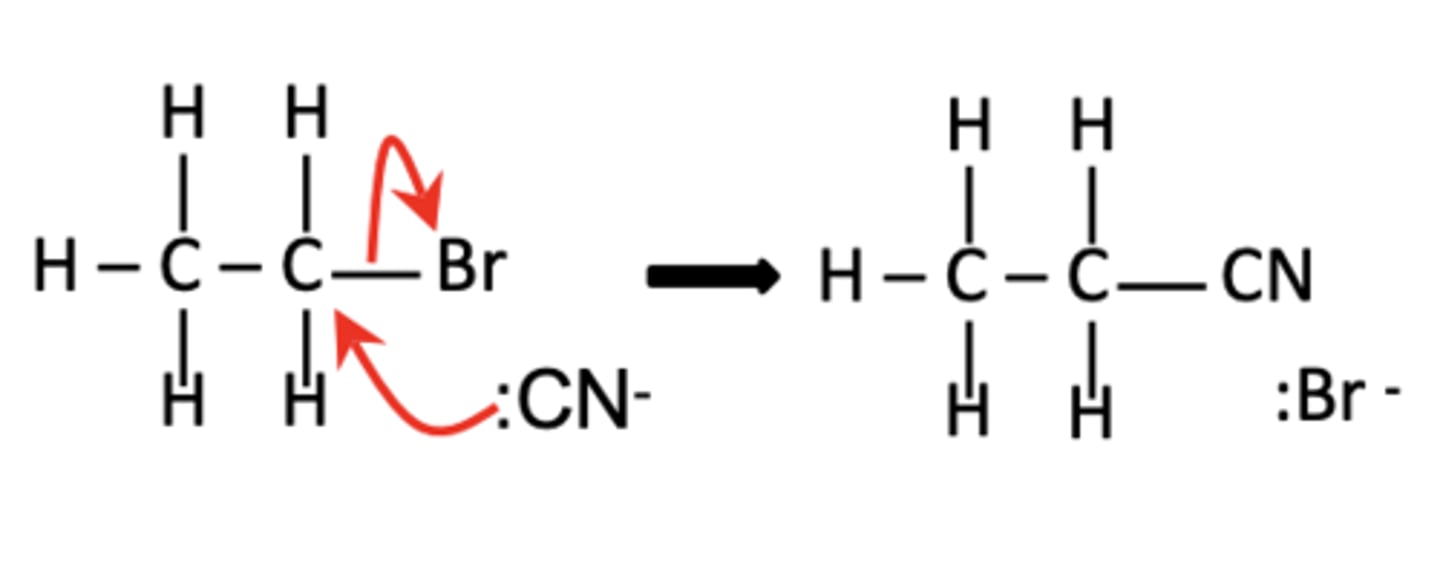
Write the full equation for the reaction of CH3CH2Br with cyanide ions. (1)
CH3CH2Br + HCN → CH3CH2CN + HBr.
Draw the mechanism for the reaction of CH3CH2Br with cyanide ions. (4)
What reagent and conditions are required for the reaction of halogenoalkanes with ammonia? (2)
- Reagent: Excess ammonia (NH3)
- Conditions: Sealed container, warmed
What is the nucleophile in the reaction of halogenoalkanes with ammonia? (1)
The nucleophile is ammonia (NH3)
Write the first step of the reaction of ethyl bromide (CH3CH2Br) with ammonia. (1)
CH3CH2Br + NH3 → CH3CH2NH2 + HBr
What is the overall equation for the reaction of ethyl bromide with excess ammonia? (1)
CH3CH2Br + 2NH3 → CH3CH2NH2 + NH4Br
Describe the mechanism for the nucleophilic substitution of halogenoalkanes with ammonia. (4)
1. The lone pair on the nitrogen of ammonia attacks the delta-positive carbon, forming a covalent bond.
2. The C-Br bond breaks heterolytically, forming Br-.
3, A proton from the attached NH3 is removed by another ammonia molecule,
4. Forming the amine and NH4+
Draw the general mechanism for the nucleophilic substitution of halogenoalkanes with ammonia. (4)
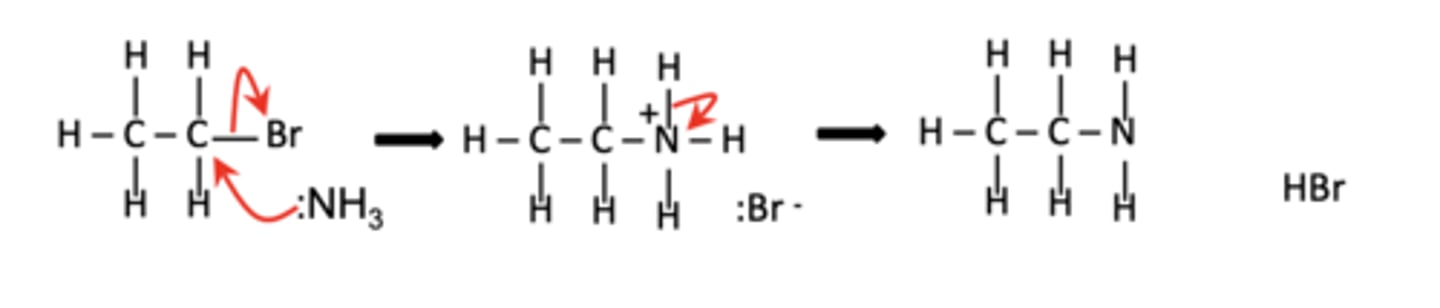
How does a primary amine react further with a halogenoalkane? (2)
- The primary amine acts as a nucleophile due to its lone pair on nitrogen
- Reacting with the halogenoalkane to form a secondary amine
Write the general equation for the formation of a secondary amine. (1)
RX + RNH2 → R2NH + HX
Draw the mechanism for forming a secondary amine from a primary amine and a halogenoalkane. (3)
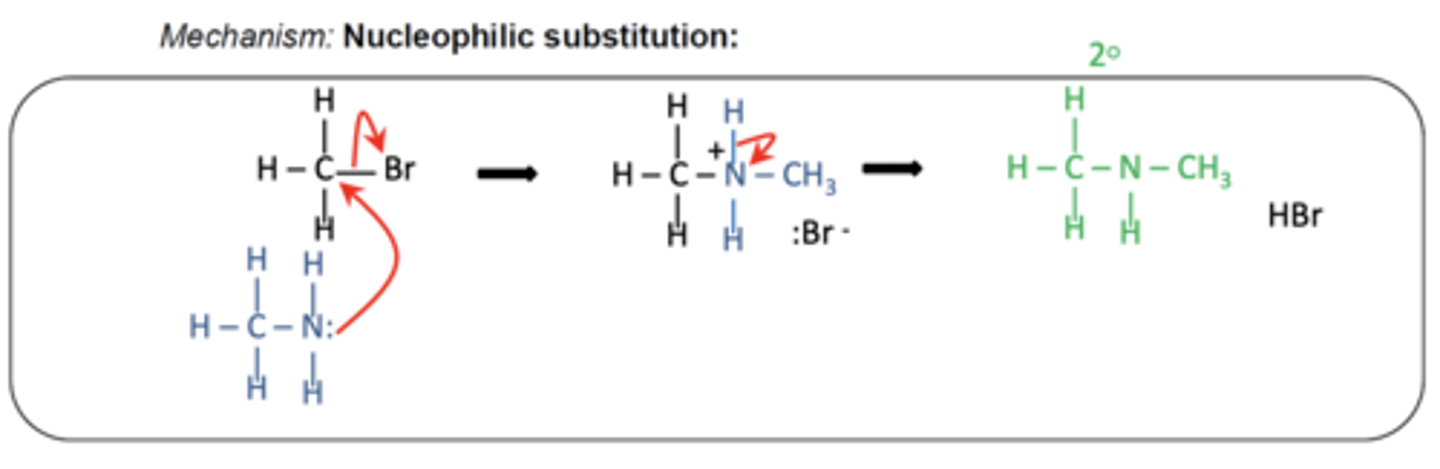
How is a tertiary amine formed from a secondary amine? (1)
- A secondary amine reacts with a halogenoalkane
- Via nucleophilic substitution to form a tertiary amine and a halide ion
Write the general equation for the formation of a tertiary amine from a secondary amine. (1)
RX + R2NH → R3N + HX
Draw the mechanism for forming a tertiary amine from a secondary amine and a halogenoalkane? (3)
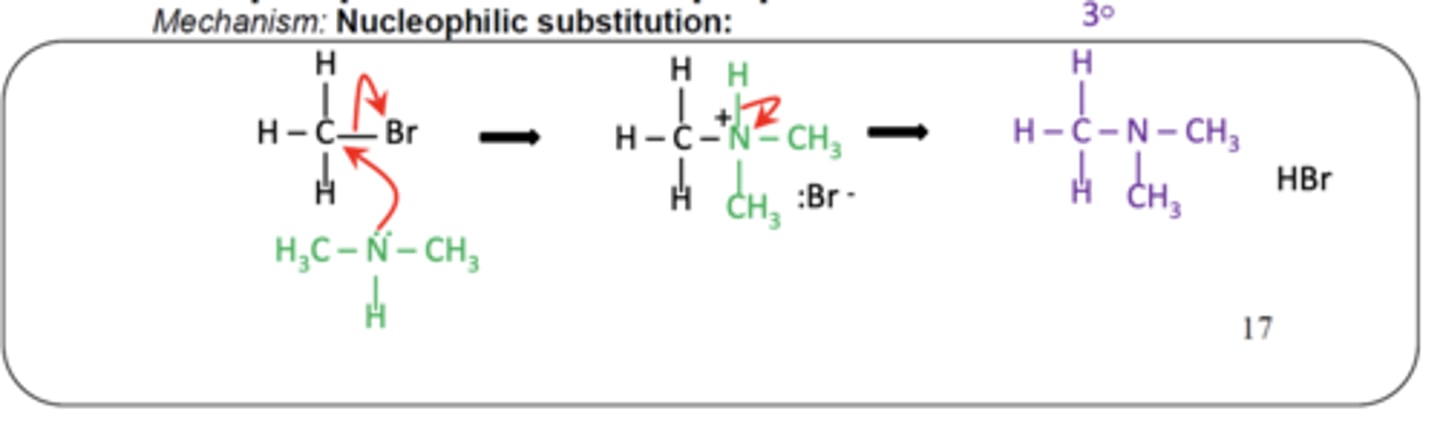
What is the product of the reaction between a tertiary amine and a halogenoalkane? (1)
A quaternary ammonium salt is formed
Write the general equation for the formation of a quaternary ammonium salt. (1)
RBr + R3N → [R4N]+ Br-
Draw the mechanism for forming a quaternary ammonium salt. (4)
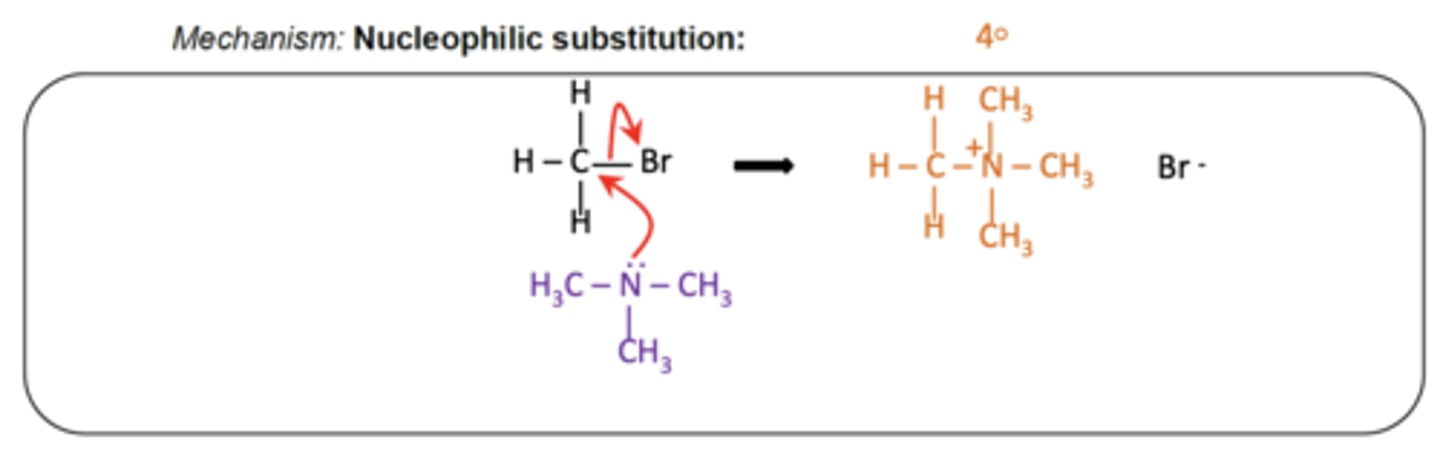
What results in a high yield of quaternary ammonium salt? (1)
Using a large excess of halogenoalkane
How can a better yield of primary amine be achieved? (1)
- By using a large excess of ammonia
- Which reduces further substitution
What is the reagent and condition for elimination reactions involving halogenoalkanes? (2)
- Reagent = NaOH;
- Conditions = Hot, in ethanol
Write the reaction of the elimination reaction with CH₃CHBrCH₃. (2)
CH₃CHBrCH₃ + :OH⁻ → CH₃CH=CH₂ + H₂O + :Br⁻
Explain the role of :OH⁻ in the elimination reaction with CH₃CHBrCH₃. (2)
- Acts as a base, removing a hydrogen atom from a carbon adjacent to the one bonded to the bromine.
- This leads to the formation of a double bond (alkene)
Draw the elimination mechanism for the reaction of CH₃CHBrCH₃ with :OH⁻ (4)
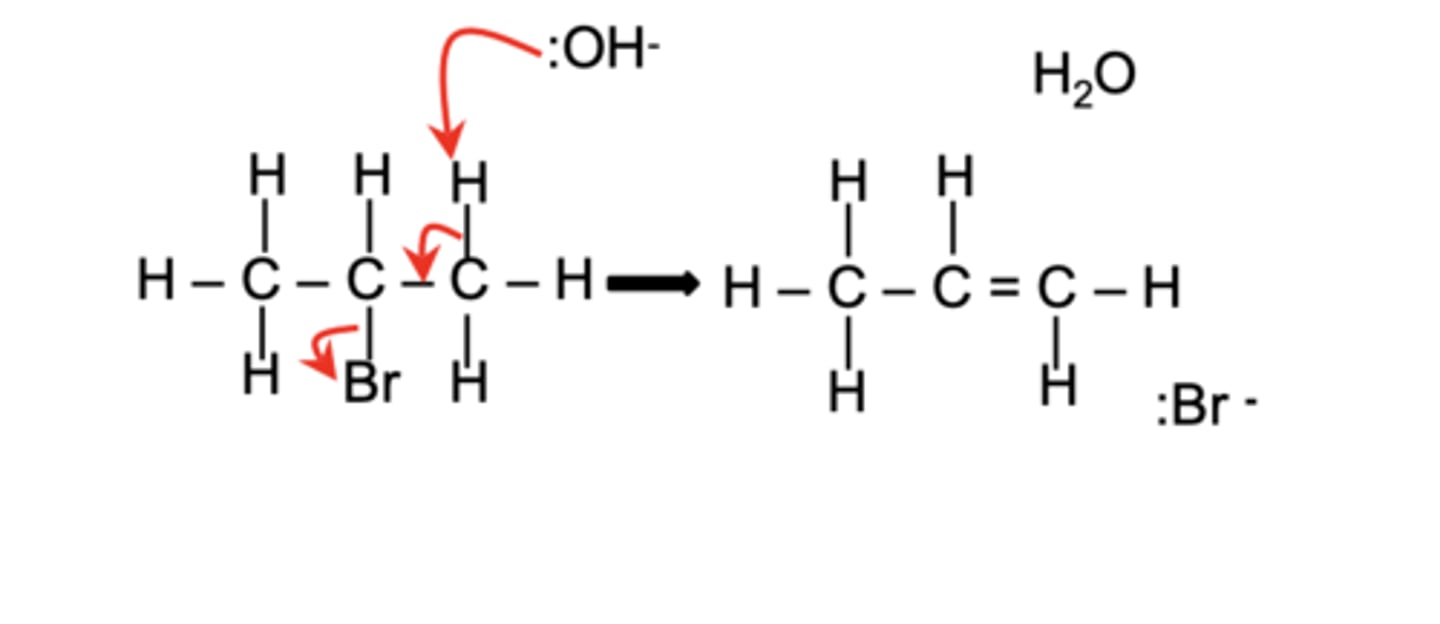
What types of isomers can form in the elimination reaction of CH₃CHBrCH₃? (2)
Both Z and E isomers of the alkene product can form due to geometrical isomerism.
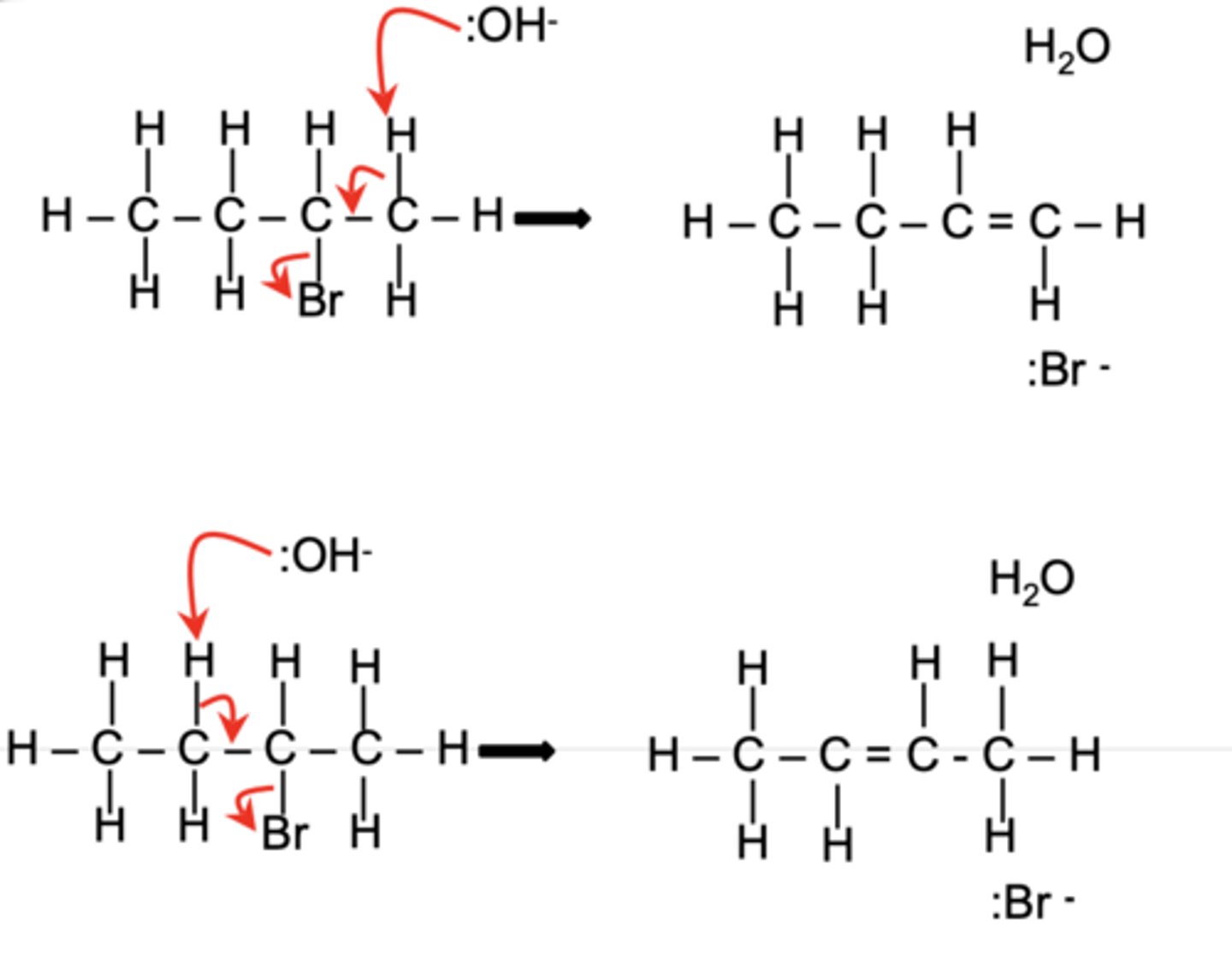
Draw the elimination mechanism of CH₃CH₂CHBrCH₃ with :OH⁻, showing the formation of both major and minor products. (6)
Bottom = major (as it is more stable)
Top = minor (as it is less stable)
How do primary halogenoalkanes (RCH₂X) influence the reaction? (1)
They favour substitution
How do secondary halogenoalkanes (R₂CHX) influence the reaction? (1)
They favour both substitution and elimination
How do tertiary halogenoalkanes (R₃CX) influence the reaction? (1)
They favour elimination
How does a stronger base affect substitution and elimination? (1)
Stronger bases increase the likelihood of elimination
What solution favours substitution? (1)
Aqueous solution favours substitution
What solution favours elimination? (1)
Ethanolic solution favours elimination
How does temperature affect substitution and elimination? (1)
Higher temperatures favour elimination