States of Matter in Pharmacy: Properties, Phase Diagrams, and Gas Laws
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
What are the four states of matter discussed in the lecture?
Gas, Liquids, Crystalline Solids, Mesophase (liquid crystalline state or supercritical fluids)
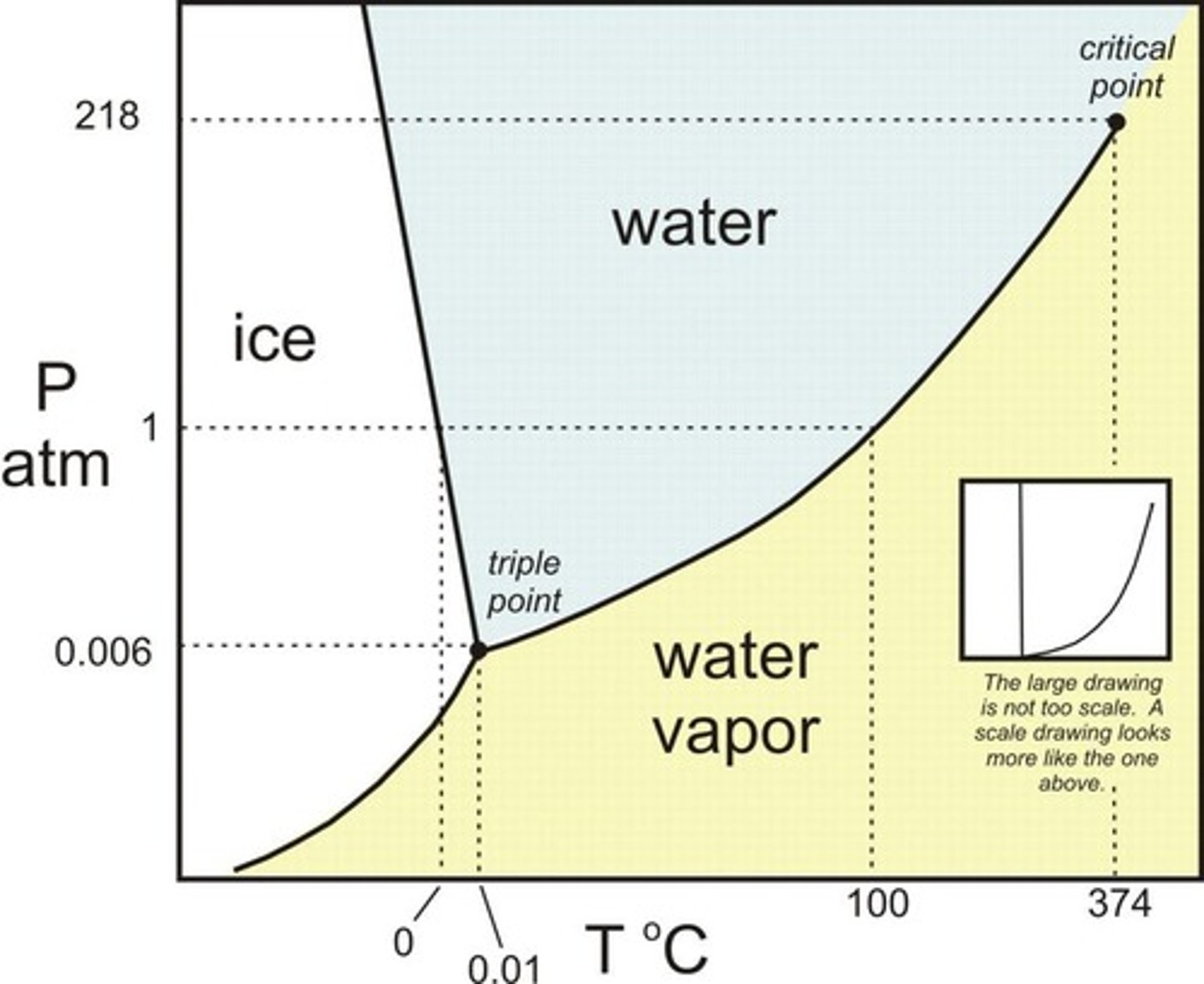
What is a phase diagram?
Graphs that relate pressure and temperature to the state of matter, visually representing the existence and extent of solid and liquid phases in mixtures.
What does Gibb's Phase Rule determine?
The relationship for the least number of intensive variables that can be changed without altering the equilibrium state of the system.
What is the formula for Gibb's Phase Rule?
F = C - P + X, where F is Degrees of Freedom, C is the number of components, P is the number of phases, and X is the number of independent variables.
What is the significance of Degrees of Freedom (F) in a condensed system?
F = C - P + 1, indicating that no pressure is involved and the vapor phase is ignored.
What is the significance of Degrees of Freedom (F) in a non-condensed system?
F = C - P + 2, indicating that pressure is considered and involves gas.
What is the Molar Heat of Fusion (ΔHfusion)?
The heat lost or gained in the conversion involving solid and liquid by 1 mole of substance.
What are the phase transitions associated with Molar Heat of Fusion?
S → L (melting/fusion) and L → S (freezing/congealing).
What is the Molar Heat of Vaporization (ΔHvaporization)?
The heat required for the conversion involving liquid and gas by 1 mole of liquid substance.
What are the phase transitions associated with Molar Heat of Vaporization?
L → G (vaporization) and G → L (condensation).
What is the Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases?
A theory that explains the behavior of gases in terms of particles in constant motion.
What is the importance of Raoult's Law in the properties of liquid state?
Raoult's Law relates the vapor pressure of a solvent to the mole fraction of the solvent in a solution.
How do crystalline and amorphous solids differ?
Crystalline solids have a well-defined geometric structure, while amorphous solids lack a long-range order.
What is polymorphism in the context of drug formulation?
The ability of a substance to exist in more than one form or crystal structure.
What is Le Chatelier's Principle?
A principle stating that if a system at equilibrium is disturbed, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the disturbance.
What is the significance of liquid crystalline states in pharmacy?
Liquid crystalline states have unique properties that can enhance drug formulation and delivery.
What is the role of temperature in phase transitions?
Temperature influences the energy of particles, affecting their state and the phase transitions between solid, liquid, and gas.
What are independent variables in the context of phase equilibria?
Variables that do not depend on the amount of matter present in the phases.
What is the difference between a one-component system and a multi-component system?
A one-component system consists of a single substance, while a multi-component system involves two or more substances.
What are the applications of phase diagrams in pharmacy?
Phase diagrams are used to understand the stability and behavior of drug formulations under different conditions.
What is the importance of understanding gas laws in pharmacy?
Gas laws help in predicting the behavior of gases in various pharmaceutical applications, including drug delivery systems.
What is the significance of solving problems involving liquid states of matter?
Understanding liquid states is crucial for drug formulation, stability, and delivery mechanisms.
What is the formula for the phase rule in a condensed system?
F = C - P + 1
What is the formula for the phase rule in a noncondensed system?
F = C - P + 2
What does F represent in the phase rule?
Degrees of freedom in a system.
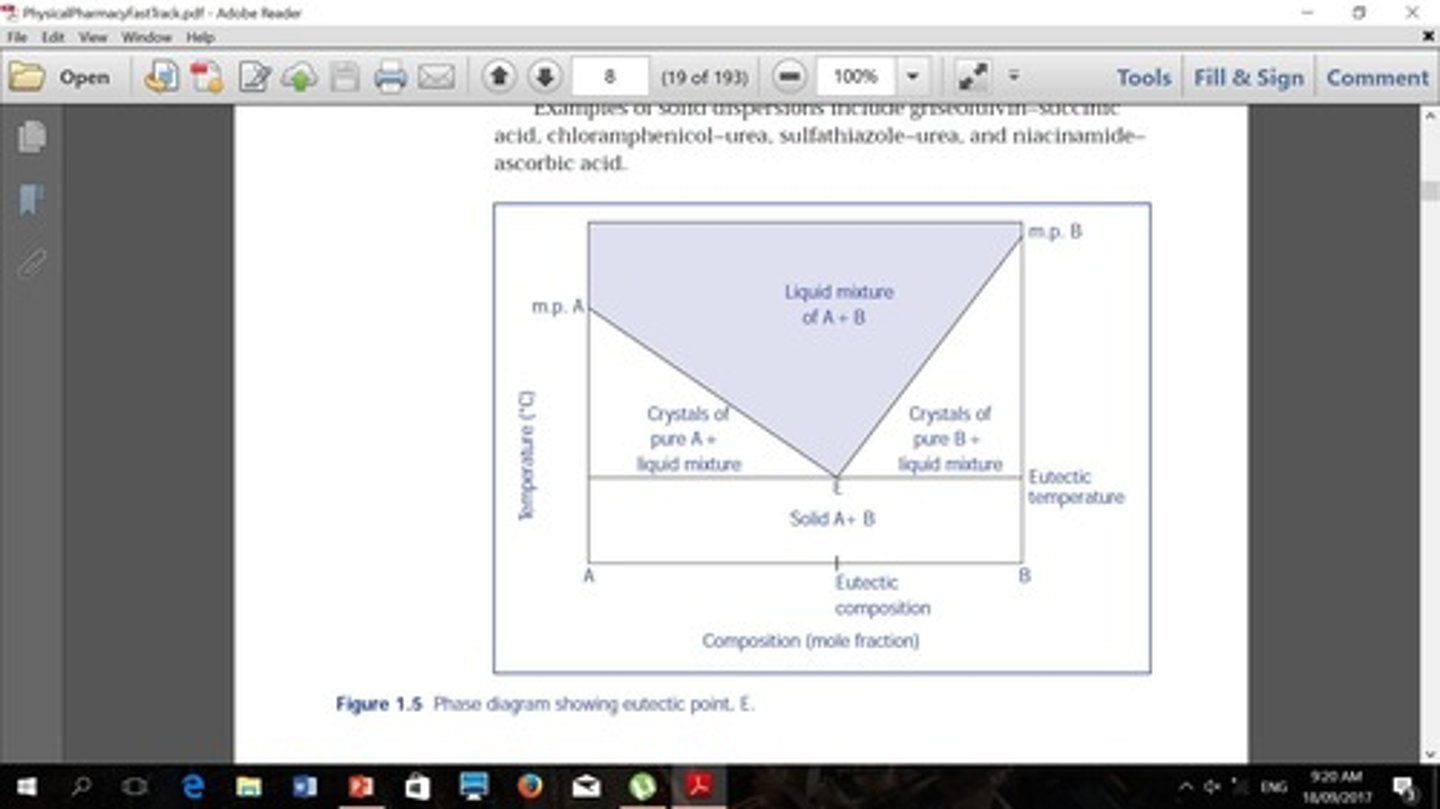
What is the significance of the eutectic point in a two-component system?
It indicates the lowest melting point of a mixture of components.
What are the basic properties of gases?
Pressure (P), Volume (V), Temperature (T), and moles (n).
What is Boyle's Law?
At constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume.
What is Charles' Law?
At constant pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature in Kelvin.
What is Avogadro's Law?
At constant temperature and pressure, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles of gas.
What is Gay-Lussac's Law?
At constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature in Kelvin.
What is the Combined Gas Law?
It combines Boyle's, Charles', and Avogadro's laws into one equation: (P1V1)/T1 = (P2V2)/T2.
What is the pressure exerted by a gas measured in mmHg?
It originates from measurements using a barometer and is also called Torr.
What is the relationship between mmHg and atm?
1 atm = 760 mmHg.
What is the SI unit for pressure?
Pascal (Pa), where 1 Pa = 1 N/m².
What is the average air pressure at sea level in Pascals?
101,325 Pa.
What is the conversion of 1 atm to psi?
1 atm = 14.7 psi.
What is the significance of phase diagrams?
They are valuable for interpreting interactions between components, purity, melting point depression, and formation of solid solutions.
What is the pressure of a balloon compressed from 10.0 L to 1.00 L at an initial pressure of 5.00 atm?
Using Boyle's Law, the final pressure is 50.0 atm.
What is EMLA?
A eutectic mixture of 2.5% lidocaine and 2.5% prilocaine in an oil-in-water emulsion cream, used as a topical anesthetic.
What is the importance of determining the eutectic point?
It helps in understanding melting point depression and the formation of mixtures.
What is the definition of a condensed system in the context of the phase rule?
A system where vapor phase is ignored, considering only liquid and solid phases.
What is the definition of a noncondensed system in the context of the phase rule?
A system that includes gas and considers pressure.
What happens to the degrees of freedom (F) at the eutectic point?
F is typically low, indicating limited variability in conditions.
What is the Ideal Gas Law equation?
PV = nRT
What is the average kinetic energy of gas particles proportional to?
The absolute temperature of the gas.
What is the volume of one mole of an ideal gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP)?
22.4 L.
How do you calculate the density of a gas?
Density (ρ) = PMW / RT
What is the density of oxygen gas at STP?
1.43 g/L.
How do you find the amount of gas in moles in a 10.0-L vessel at 1 atm and 0.00°C?
Use the Ideal Gas Law: n = PV / RT.
What is the molar mass of a gas if a sample has a mass of 5.60 g, volume of 2.00 L, temperature of 100.00°C, and pressure of 3.00 atm?
Calculate using the Ideal Gas Law to find n, then use molar mass = mass / n.
What is the molecular weight of ethyl alcohol if 0.30 g occupies 200 mL at 1 atm and 100°C?
Use the Ideal Gas Law to find n, then calculate molecular weight = mass / n.
What is the pressure exerted by a single component in a mixture of gases called?
Partial pressure (Pn).
What are the main components of dry air?
Nitrogen (78%), Oxygen (21%), Argon (0.9%), Carbon Dioxide (0.05%), Other Gases (0.06%).
What happens to the volume of a gas when it is cooled and compressed?
The volume decreases.
If a balloon's volume changes from 4.00 L to 22.0 L, how do you find the moles of hydrogen needed to be added?
Use the Ideal Gas Law and the initial and final conditions to solve for the change in moles.
What is the volume of nitric oxide gas at 0°C and 70 mmHg if it occupies 30.0 mL at 20°C and 740 mmHg?
Use the combined gas law to find the new volume.
What is the relationship between gas pressure and the volume of gas according to the Kinetic Molecular Theory?
Gas pressure is due to collisions of gas molecules with the walls of the container.
What is the molar volume of a gas at STP?
22.4 L.
What is the formula for calculating the density of a gas at STP?
Density (ρ) = mass / volume.
What is the significance of the average kinetic energy in gases?
It determines the temperature and behavior of the gas.
What is the effect of temperature on the volume of a gas?
Increasing temperature generally increases the volume of a gas if pressure is constant.
What does it mean for gas molecules to exhibit perfect elasticity?
There is no net loss of speed or energy after collisions.
How does the volume of a gas change with pressure at constant temperature?
Volume decreases as pressure increases (Boyle's Law).
What is the molar mass of helium gas?
4 g/mol.
What is the density of sulfur hexafluoride at 1.00 atm and 300.00°C?
Calculate using the formula ρ = PMW / RT.
How is the partial pressure of a gas in a mixture calculated?
The partial pressure of a gas (P_a) is calculated using P_a = (n_aRT)/V, where n_a is the number of moles of gas a.
What is the relationship between total pressure and partial pressures in a gas mixture?
P_total = P_a + P_b + P_c, where P_a, P_b, and P_c are the partial pressures of the individual gases.
How do you calculate the mole fraction of a gas in a mixture?
Mole fraction (X_a) is calculated as X_a = n_a / n_total, where n_a is the number of moles of gas a and n_total is the total number of moles.
What is Raoult's Law?
Raoult's Law states that the partial vapor pressure of a solvent in a solution is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction in the solution.
How do you find the partial pressure of xenon in a gas mixture?
PXe = P_total - (P_He + P_Kr), where P_total is the total pressure and P_He and P_Kr are the partial pressures of helium and krypton.
Given a total pressure of 5.00 atm and partial pressures of helium and krypton, how do you calculate the moles of xenon?
Use PXe = P_total - (P_He + P_Kr) to find PXe, then use the ideal gas equation to find n_Xe = (P_Xe * V) / (RT).
What is the molecular weight of a gas if 0.104 grams occupies 48.7 mL at STP?
Molecular weight can be calculated using the ideal gas law and the given mass and volume.
How do you calculate the pressure of a gas in a container?
Use the ideal gas law: P = (nRT)/V, where n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, T is temperature, and V is volume.
What volume of O2 is required to produce 0.500 mole of SO3 at STP?
Use stoichiometry based on the balanced reaction to find the volume of O2 needed.
What is the van der Waals equation?
The van der Waals equation accounts for the non-ideal behavior of gases: [P + a(n/V)^2](V - nb) = nRT.
What do the constants a and b in the van der Waals equation represent?
The constant a accounts for intermolecular forces, while b accounts for the volume occupied by gas molecules.
What is the root mean square velocity formula?
The root mean square velocity (u_rms) is calculated as u_rms = sqrt(3RT/M), where M is the molar mass in kg/mol.
How do you calculate the root mean square velocity of nitrogen at 50.00°C?
Convert temperature to Kelvin, then use u_rms = sqrt(3RT/M) with R = 8.314 J/(mol·K) and M = 0.028 kg/mol.
What is the stoichiometry for the synthesis of ethanol from ethylene?
C2H4(g) + H2O(l) → CH3CH2OH(l), with a 1:1 mole ratio.
How many moles of ethylene are needed to synthesize 10.0 g of ethanol?
Calculate moles of ethanol (10.0 g / 46.07 g/mol) and use the 1:1 mole ratio to find moles of ethylene.
What volume of ethylene gas is required to synthesize 10.0 g of ethanol at STP?
The volume of ethylene gas required is 4.86 L.
What assumptions are made in the ideal gas law?
Ideal gas law assumes no intermolecular forces and that gas molecules occupy no volume.
What conditions lead to non-ideal gas behavior?
Non-ideal behavior is more pronounced at high pressures and low temperatures.
How do you calculate the pressure of a gas using the ideal gas equation?
Rearrange the ideal gas equation to solve for pressure: P = (nRT)/V.
What is the significance of STP in gas calculations?
STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure) is defined as 0°C (273.15 K) and 1 atm, used as a reference point for gas behavior.
What is the root mean square velocity of a gas?
It is a measure of the average velocity of gas particles, influenced by molecular weight.
How does the mean free path of a gas change with pressure?
The mean free path increases with decreasing pressure.
What is the mean free path of a nitrogen molecule with a diameter of 300 pm?
93 nm.
What is diffusion in the context of gases?
Diffusion is the process by which gas particles spread out in response to a concentration gradient.
How does molecular weight affect the rate of diffusion?
Lighter particles diffuse faster than heavier ones.
What is effusion?
Effusion is the process by which gas particles escape from a container into a vacuum through a small hole.
How does molecular weight affect the rate of effusion?
Lighter particles effuse faster than heavier ones.
If an unknown gas effuses at a rate 4.00 times that of oxygen, how can its molar mass be calculated?
Using Graham's law of effusion, the molar mass of the unknown gas can be calculated based on the effusion rates.
What is the critical temperature of a gas?
The critical temperature is the temperature above which a liquid can no longer exist, regardless of pressure.
What is the critical pressure of a gas?
The critical pressure is the pressure required to liquefy a gas at its critical temperature.
What happens to the pressure required to liquefy a gas as it is cooled below its critical temperature?
The further a gas is cooled below its critical temperature, the less pressure is required to liquefy it.
What is the Joule-Thomson effect?
It describes the cooling effect that occurs when a gas expands adiabatically, doing work at the expense of its own heat energy.
What is equilibrium vapor pressure?
It is the pressure of the saturated vapor above the liquid.
What is the Clausius-Clapeyron equation used for?
It is used to compute the vapor pressure of a substance at different temperatures.