unit three - metabolic functions
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Digestive System
The human digestive system is responsible for ingesting food, breaking it down into small molecules (nutrients), and eliminating indigestible residues as feces.
Digestion
Digestion is the process by which food and beverages are broken down into their smallest parts to be used by the body as an energy source and to nourish cells.
• Depending on the diet, we absorb between 90% and 97% of the food consumed.
Macronutrients
Nutrients required in large amounts, including carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids.
Micronutrients
Nutrients required in smaller amounts, including vitamins and minerals.
Stomach
A hollow organ that expands and is responsible for both mechanical and chemical digestion.
Chyme
The semi-fluid mass of partially digested food that is passed from the stomach to the small intestine.
Pancreas
A mixed secretion organ with both endocrine (insulin and glucagon) and exocrine functions (digestive enzymes and bicarbonate secretion).
Gallbladder
A small organ that stores bile produced by the liver until it is needed for digestion.
Absorption
The process by which nutrients are taken up by the intestinal mucosa into the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
Liver
The largest organ in the body responsible for over 500 vital functions including metabolism and detoxification.
Rectum
The final section of the large intestine that stores feces until elimination.
Defecation
The process of expelling feces from the body, triggered by rectal distension.
Gastrin
A hormone that stimulates acid secretion in the stomach.
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
A hormone that stimulates bile release from the gallbladder and enzyme secretion from the pancreas.
Peristalsis
The series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract.
Emulsification
The process by which bile salts break down large fat globules into smaller ones, aiding in fat digestion.
Functions of the Digestive System
1. Digestion:
• Macronutrients: Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids.
• Micronutrients: Vitamins, minerals.
• Liquids.
2. Physical Barrier: Protects against harmful substances.
3. Regulatory Functions: Maintains internal balance.
4. Metabolic Functions: Processes nutrients.
5. Immune Functions: Defense against pathogens.
Parts of the Digestive System
1. Mouth.
2. Oropharyngeal structures.
3. Esophagus.
4. Stomach.
5. Liver.
6. Gallbladder.
7. Pancreas.
8. Small intestine.
9. Large intestine.
10. Anus.
mouth
Functions:
• Chewing.
• Salivation.
• Initial digestion.
• Secretion from salivary glands:
• Saliva contains mucus (mucin).
• Salivary amylase: Ptyalin and amylase.
• pH: 6.9.
pharynx
• Passage for both food and air.
• Connects directly to the esophagus.
• Walls formed by constrictor muscles that push food toward the esophagus.
• The epiglottis, a mucosal fold, directs food into the esophagus and prevents it from entering the respiratory tract.
esophagus
• A 25 cm muscular tube.
• Flexible and dilatable.
• Connects the pharynx to the stomach, passing through the neck, thoracic cavity, and diaphragm.
• Contains two sphincters:
• Superior.
• Inferior (gastroesophageal or cardiac sphincter).
stomach
• A hollow organ that expands in size.
• Types of Digestion in the Stomach:
• Mechanical: Homogenizes food (bolus).
• Chemical: Secretes 2 liters/day of gastric juices, including hydrochloric acid, pepsin, mucin, water, and intrinsic factor.
• The bolus turns into chyme in the stomach.
Digestion Times:
• Solids: 2–3 hours.
• Liquids: 1–2 hours (except alcohol).
gastric emptying
• Influenced by food type:
• Liquids and solids.
• Carbohydrates, proteins, fiber.
• Low-calorie content empties first, followed by high-calorie content.
small intestine
Structure:
• Length: 7–8 meters.
• Diameter: 5 cm at the beginning, narrowing to 2.5 cm at the end.
Sections:
1. Duodenum (0.5 meters).
2. Jejunum (2–3 meters).
3. Ileum (3–4 meters).
Layers:
1. Mucosa: Contains intestinal villi to increase absorption.
2. Submucosa: Made of loose connective tissue.
3. Muscular Layer: Facilitates peristalsis.
small intestine secretions
1. Hormones.
2. Pancreatic juice.
3. Bile.
4. Brush border enzymes.
small intestine digestion
• Carbohydrates: Broken down into monosaccharides.
• Proteins: Broken down into peptides and amino acids.
• Lipids: Broken down into triglycerides, fatty acids, and monoglycerides.
small intestine absorption
Occurs in the intestinal mucosa, allowing nutrients to enter the bloodstream or lymphatic system.
large intestine
Structure:
1. Cecum: Contains the appendix.
2. Colon: Divided into ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid sections.
3. Rectum.
Layers:
1. Mucosa.
2. Submucosa.
3. Muscular layer.
Functions of the Large Intestine:
1. Absorption: Liquids and electrolytes.
2. Motor Function: Propels feces toward the rectum.
3. Synthesis: Produces vitamins B12 and K through bacterial fermentation.
liver
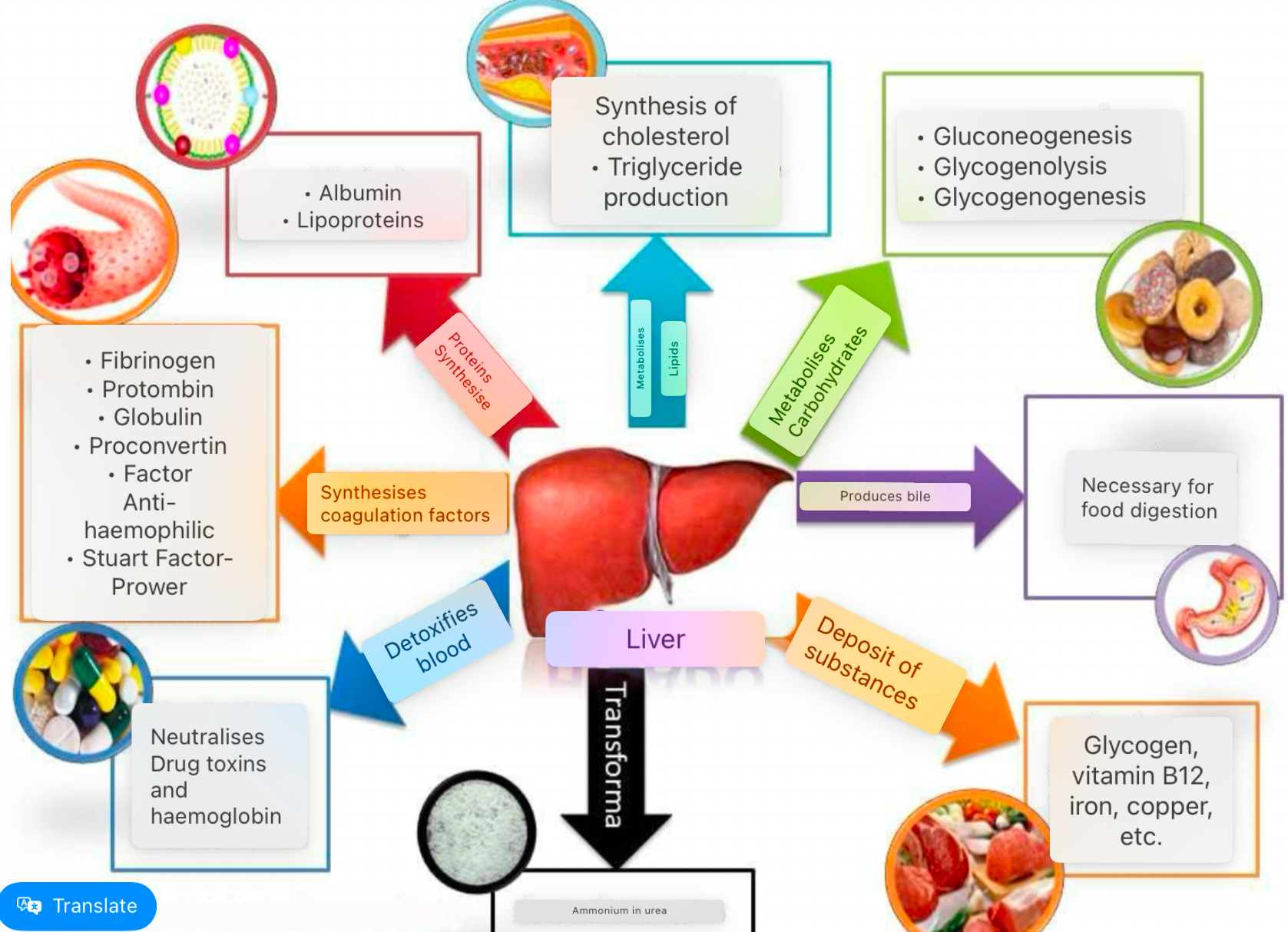
liver
Description:
• The largest organ in the body, weighing approximately 1420 grams.
• Composed of lobes and lobules, which serve as functional units.
• Responsible for over 500 vital functions.
Functions of the Liver:
1. Metabolic Functions:
• Processes carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, bile salts, and drugs.
• Supplies stored energy to other tissues during fasting periods.
2. Detoxification:
• Converts substances (e.g., alcohol, drugs, toxins) into more water-soluble forms for elimination through bile or urine.
3. Digestive Functions:
• Secretes bile, which is stored in the gallbladder and released into the intestine to aid in fat absorption.
gallbladder
• Acts as a bile reservoir, located beneath the liver.
• Holds approximately 50 mL of bile when full.
• Releases bile through the cystic duct, which joins the hepatic duct to form the common bile duct, emptying into the intestine.
pancreas
Mixed Secretion Organ:
1. Endocrine Function:
• Releases insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream.
• Purpose: Regulates blood glucose levels.
2. Digestive Function:
• Secretes pancreatic juice, composed of digestive enzymes and sodium bicarbonate.
• Purpose: Neutralizes stomach acidity.
key digestive organs
1. Mouth: Initial mechanical and enzymatic digestion.
2. Esophagus: Transports food to the stomach.
3. Stomach: Mechanical churning and chemical breakdown.
4. Small Intestine: Major site for digestion and nutrient absorption.
5. Large Intestine: Water and electrolyte absorption; waste compaction.
6. Liver: Metabolic hub and bile producer.
7. Gallbladder: Stores and releases bile.
8. Pancreas: Dual endocrine and exocrine functions supporting digestion and glucose regulation.
key hormones in digestion
1. Gastrin: Stimulates acid secretion in the stomach.
2. Secretin: Promotes bicarbonate secretion by the pancreas.
3. Cholecystokinin (CCK): Stimulates bile release from the gallbladder and enzyme secretion from the pancreas.
4. Ghrelin: Signals hunger to the brain.
5. Leptin: Regulates satiety by suppressing appetite.
secretions and origins
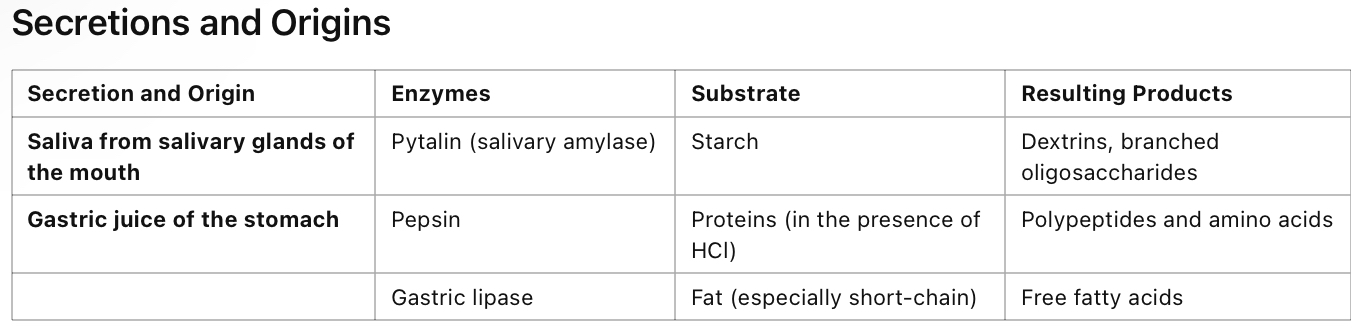
exocrine secretions of the pancreas
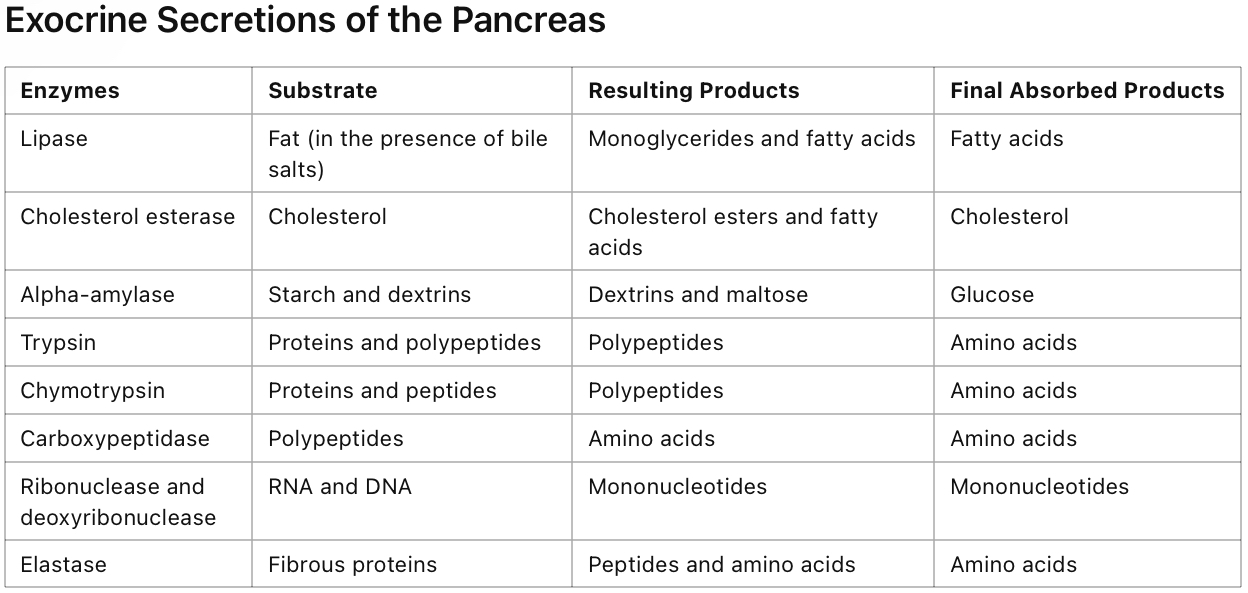
enzymes of the small intestine