T6 PP PMT
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
forensics[1-14]I&I[
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
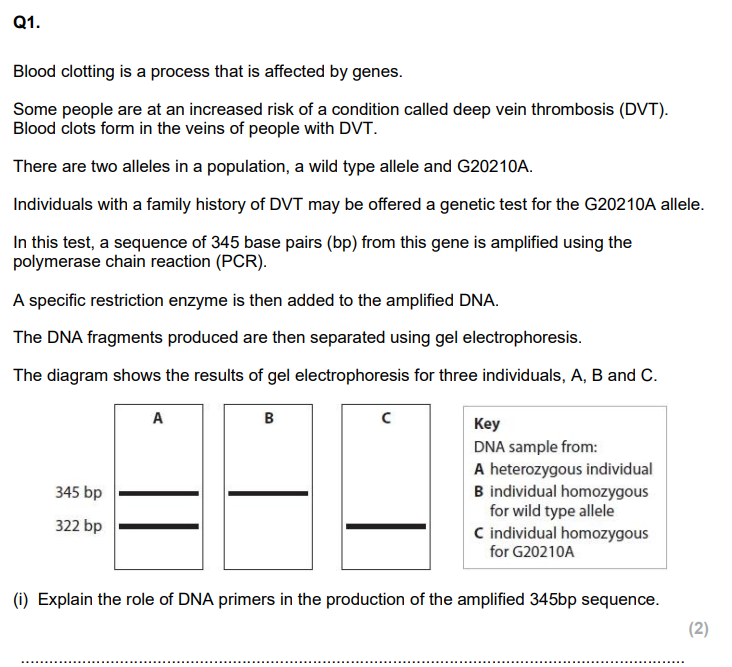
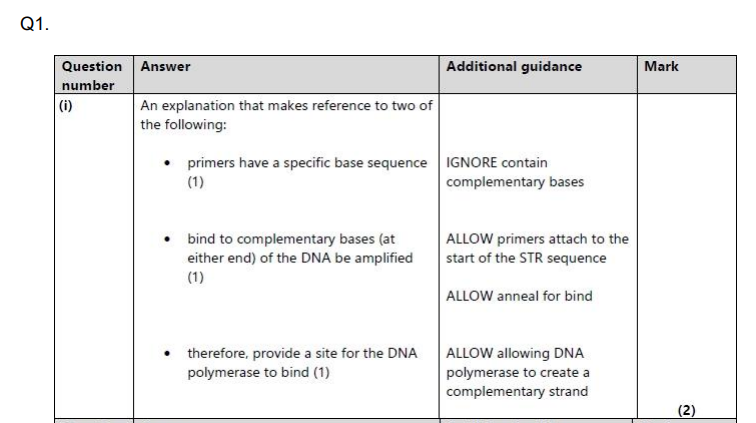
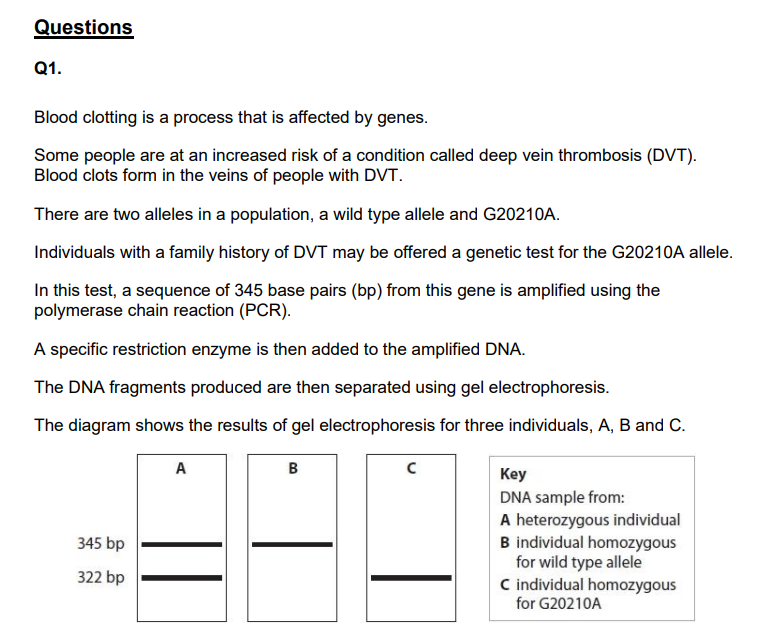
Explain why the amplified DNA fragments for the G20210A allele and the wild type allele are different. (3)

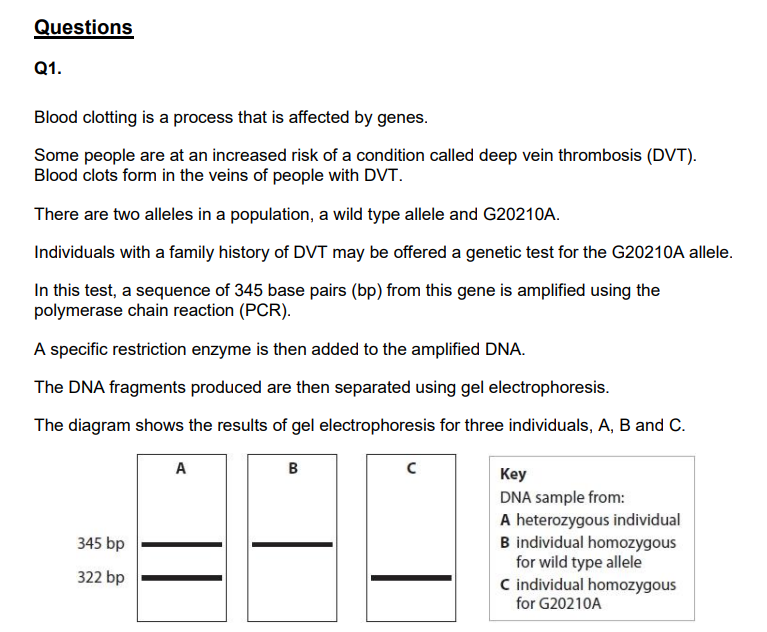
Devise an investigation to determine the optimum number of cycles for the polymerase chain reaction used to amplify the DNA for this test. (4)

Describe how DNA profiling could be carried out to show that these snakes are different species. (4)

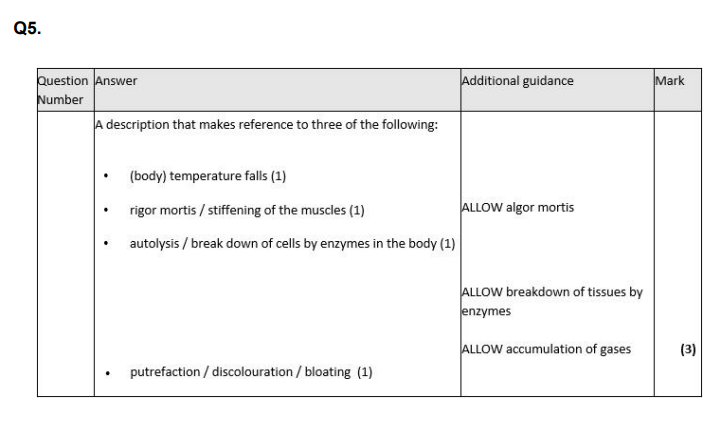
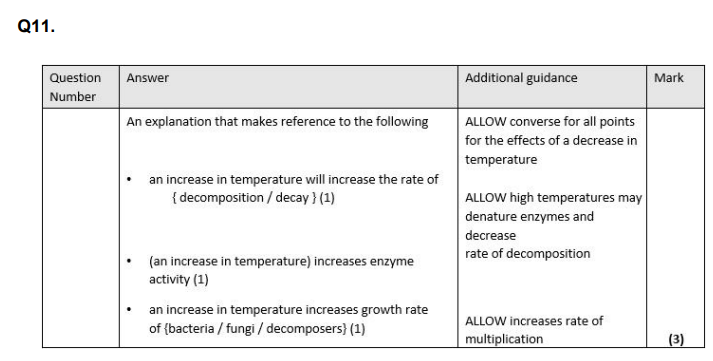
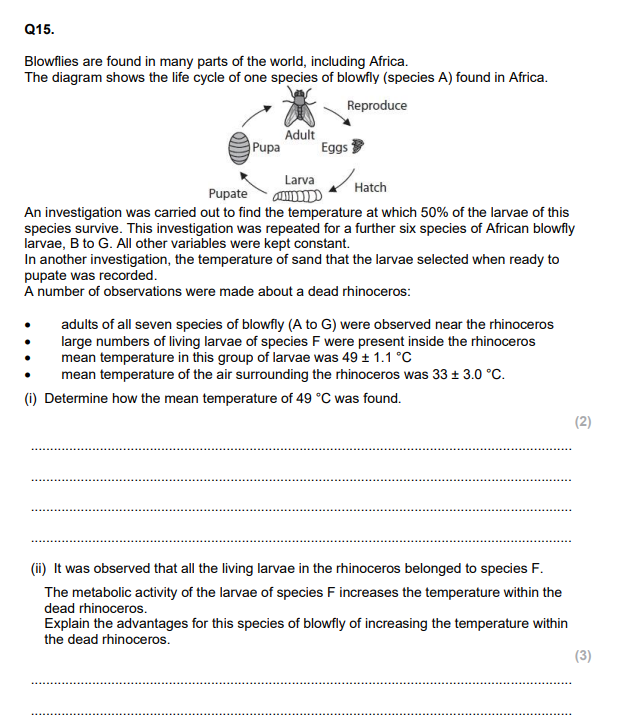
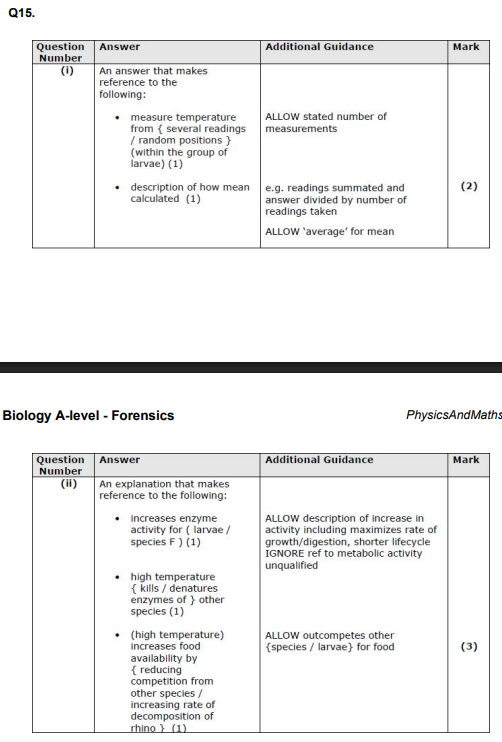
Explain the effect of temperature on the rate of growth of blowfly maggots. (3)
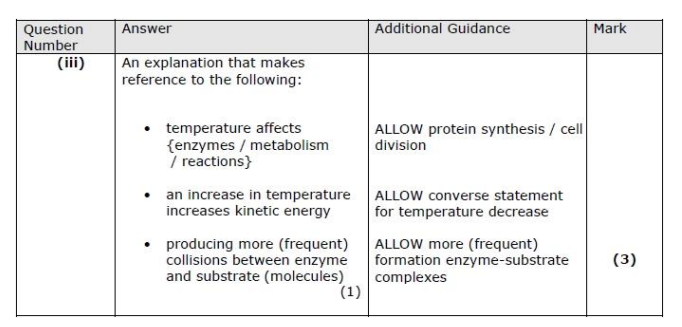
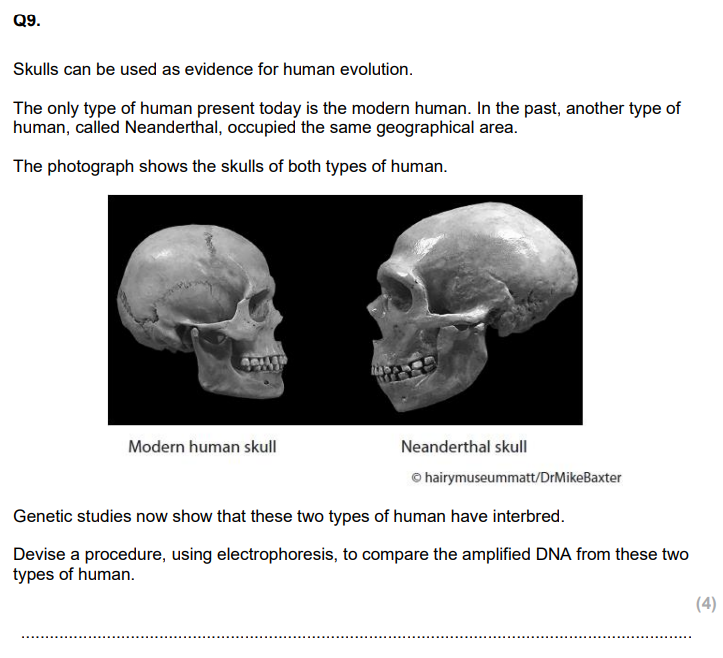
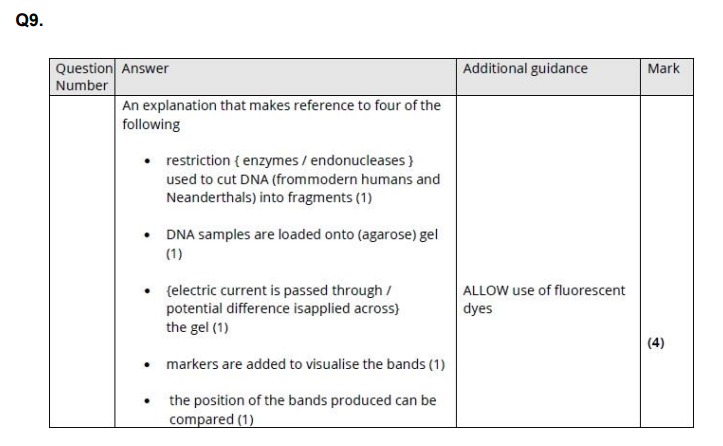

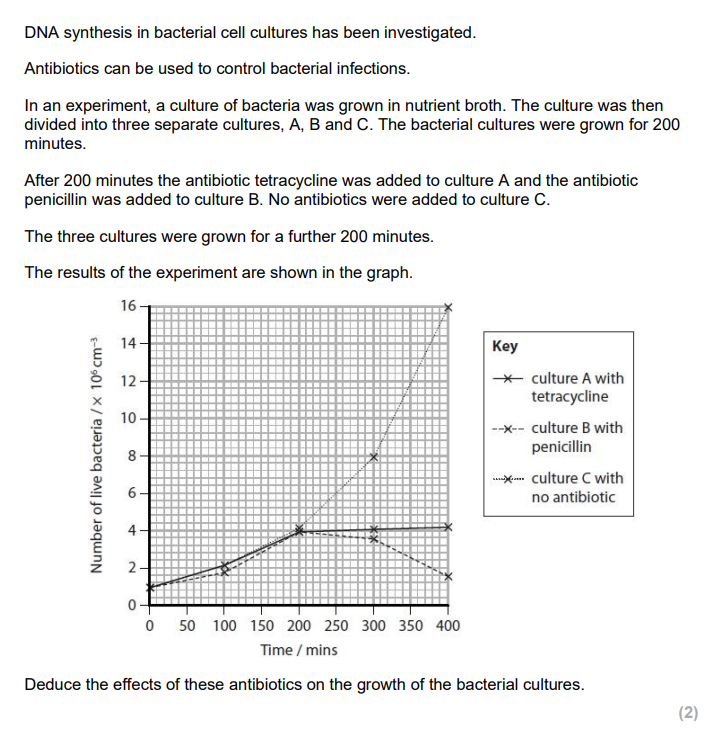
To determine if DNA from a black panther was present, DNA is first loaded into wells in an agarose gel placed in an electrophoresis tank with a buffer solution. A potential difference (voltage) is applied across the gel, causing the negatively charged DNA fragments to move toward the positive electrode. A DNA stain, such as ethidium bromide or methylene blue, is then used to visualise the bands. The sample is compared with known STRs (short tandem repeats) from a black panther. If the banding patterns or DNA profiles match, this indicates that DNA from a black panther was present.





Amplification factor=2^n
So after 20 cycles:
2^20=1,048,576

b
Hospitals have developed practices in response to the increase in hospital acquired infections. Describe the infection control practices hospitals have introduced. (3)

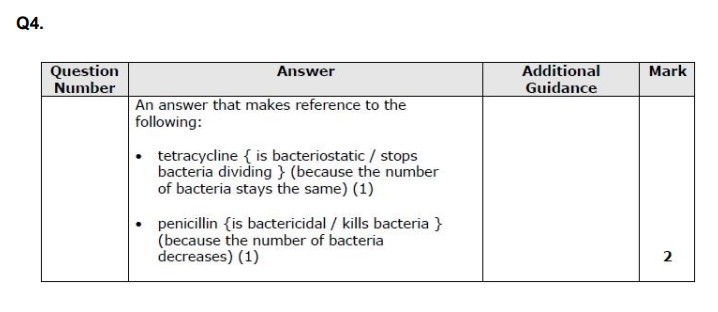
A newborn baby can respond to infections. Inflammation is a non-specific response to an infection. Explain how changes in the blood vessels result in the redness and swelling seen at the site of inflammation. (4)
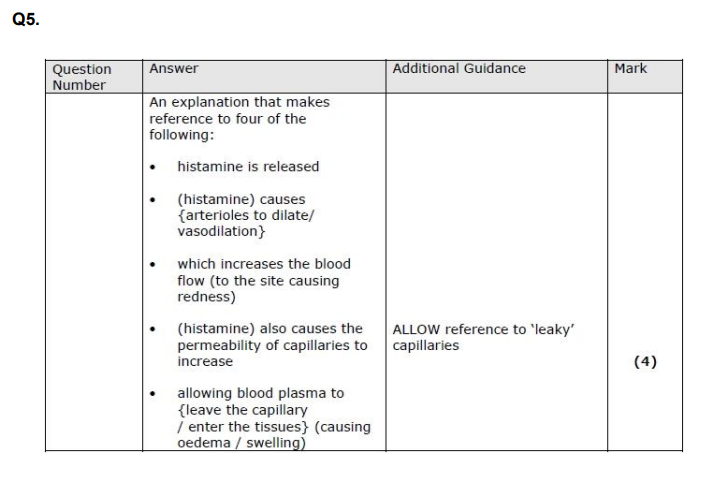

D
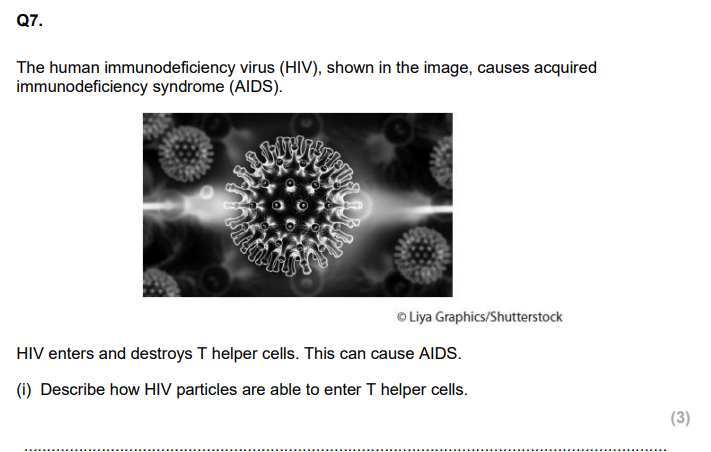
HIV is a retrovirus, which means it:
Contains RNA as its genetic material.
Carries the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which converts viral RNA into DNA once inside a host cell.
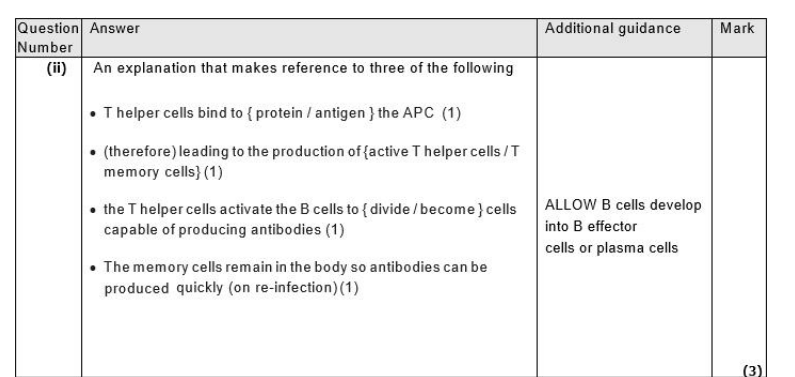
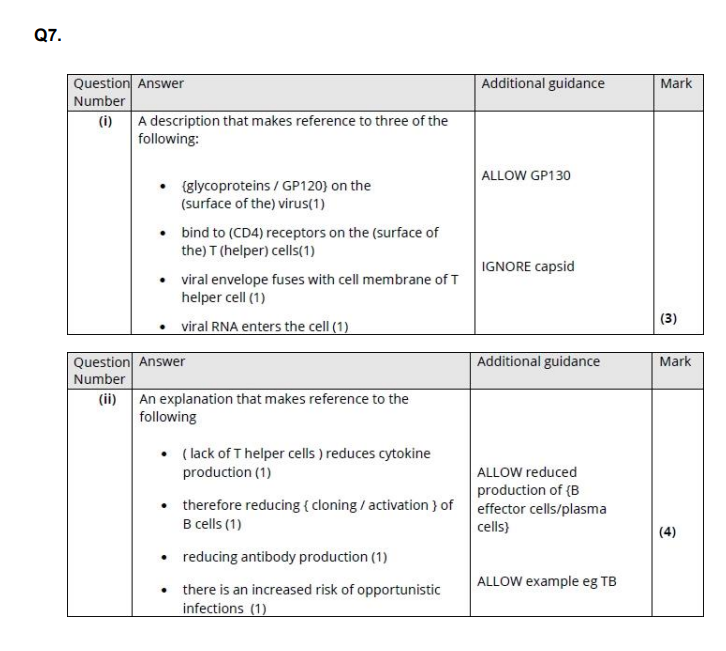
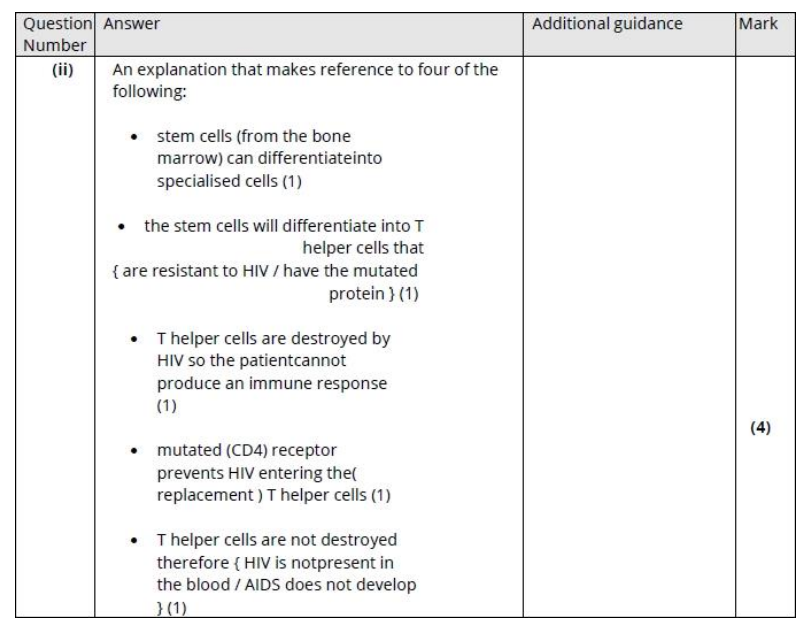
Explain why the destruction of T helper cells causes the symptoms of AIDS. (4)
A bacteriostatic antibiotic works by
preventing the multiplication of bacteria

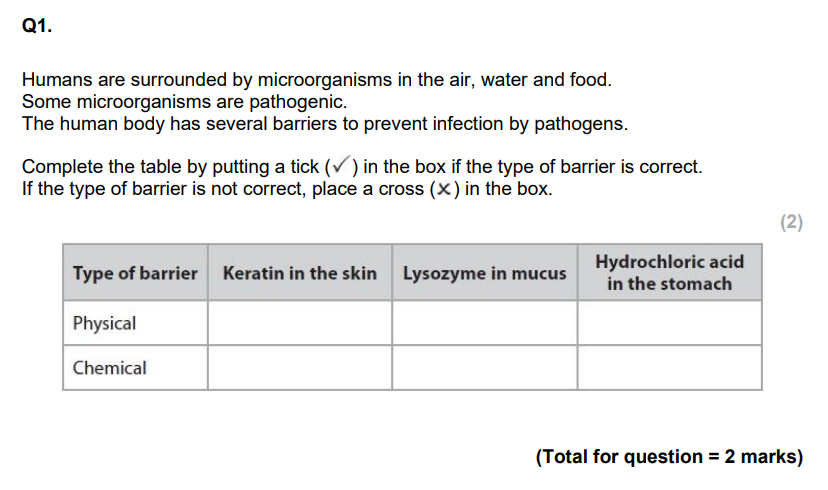
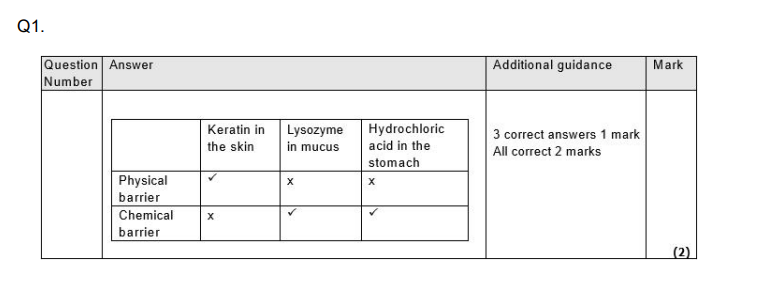
Explain why the presence of microorganisms on the skin and in the gut helps to prevent pathogenic organisms multiplying in the body. (3)

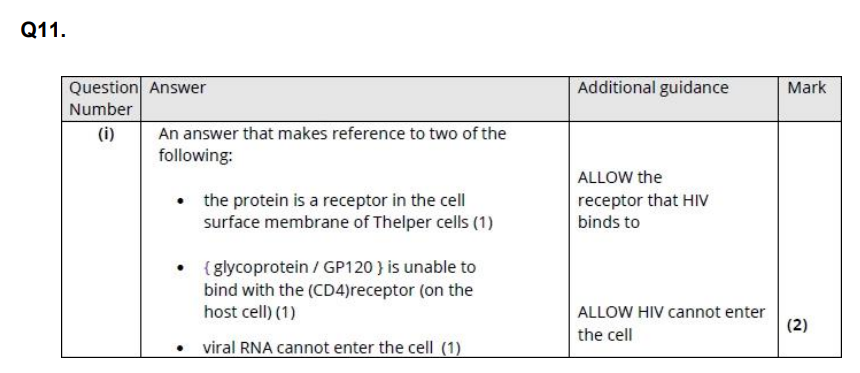
They have a mutation in a gene coding for a protein in the cell membrane. (i) Deduce why this mutation makes these people resistant to HIV infection. (2)








State what is meant by the term bacteriostatic antibiotic. (1)

Glycoproteins made in animal cells are released into the extracellular fluid by (1)
exocytosis
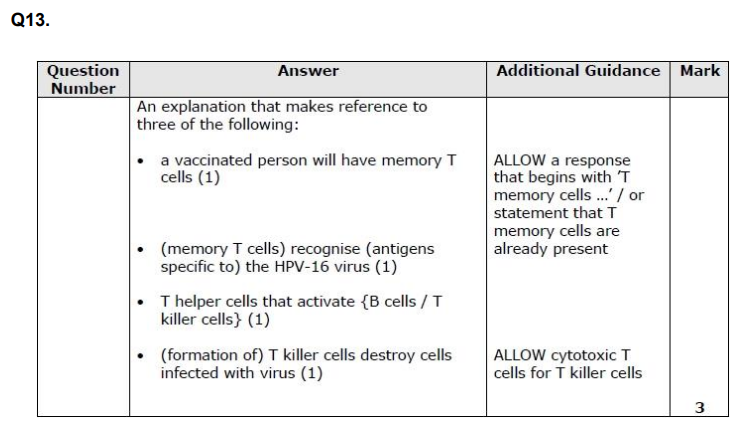
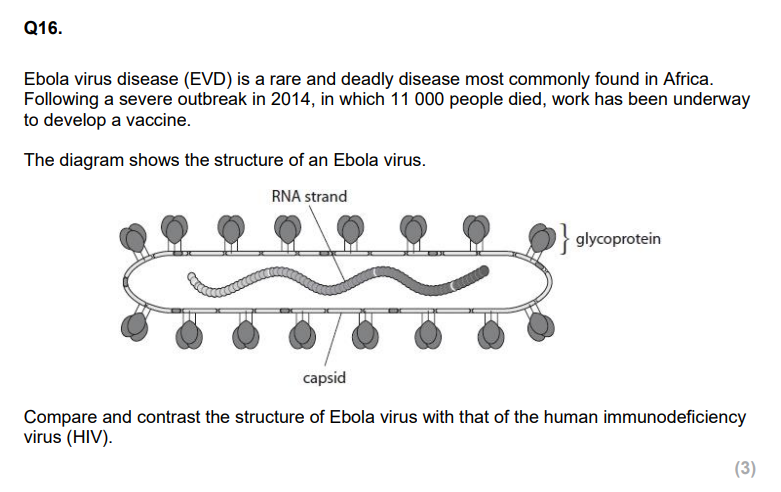
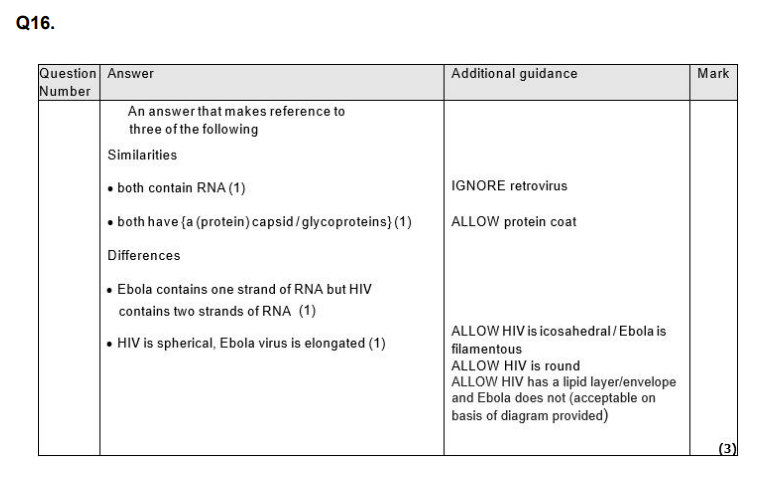
Explain the role of T cells in the immunity to the Ebola virus that develops following the use of this vaccine. (3)