Roman D2L Quiz
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
What is obsequium?
The relationship between slave owner and his/her former slave.
What are latifundia?
large farms owned by wealthy Romans
Slaves had conubium.
False
When did large numbers of slaves start to come to Rome?
During the 4th century BCE when Roman began expanding.
What is the Latin term for "slaves"?
servi
What happened to the slaves who were part of the revolt with Spartacus?
They were crucified along the Via Appia.
These magistrates managed finances:
Quaestors
The magister equitum assisted the:
Dictator
The bundle of rods surrounding an axe that were carried by men who followed a consul when he was on official business were called:
fasces
Curule magistrates" are:
Consuls, Dictator, Tribune of the Plebs, Quaestors, Praetors
The interrex was the equivalent to the dictator.
False
These magistrates served as back-up for the consuls and had judicial duties.
Praetors
Which office held imperium?
praetor, quaestor, consul
A consul wore a special toga called the:
toga praetexta
Who was the first Christian emperor?
Constantine
Who was Rome's first emperor?
Augustus
After the fall of the monarchy, Rome divided power between two:
Consuls
Sicily was Rome's first overseas province.
True
Augustus took the title:
princeps ("leading man"
he traditional date of Rome's foundation is
753 BCE
Octavian, Lepidus, and Antony were part of the Second Triumvirate.
True
What is damnatio memoriae?
The removal of one's image and name from public monuments.
The year after Neo's reign is referred to as the Year of the
Four Emperors
Which part of the Punic Wars is also called the Hannibalic War?
Second
What is this building called?
Flavian Amphitheatre
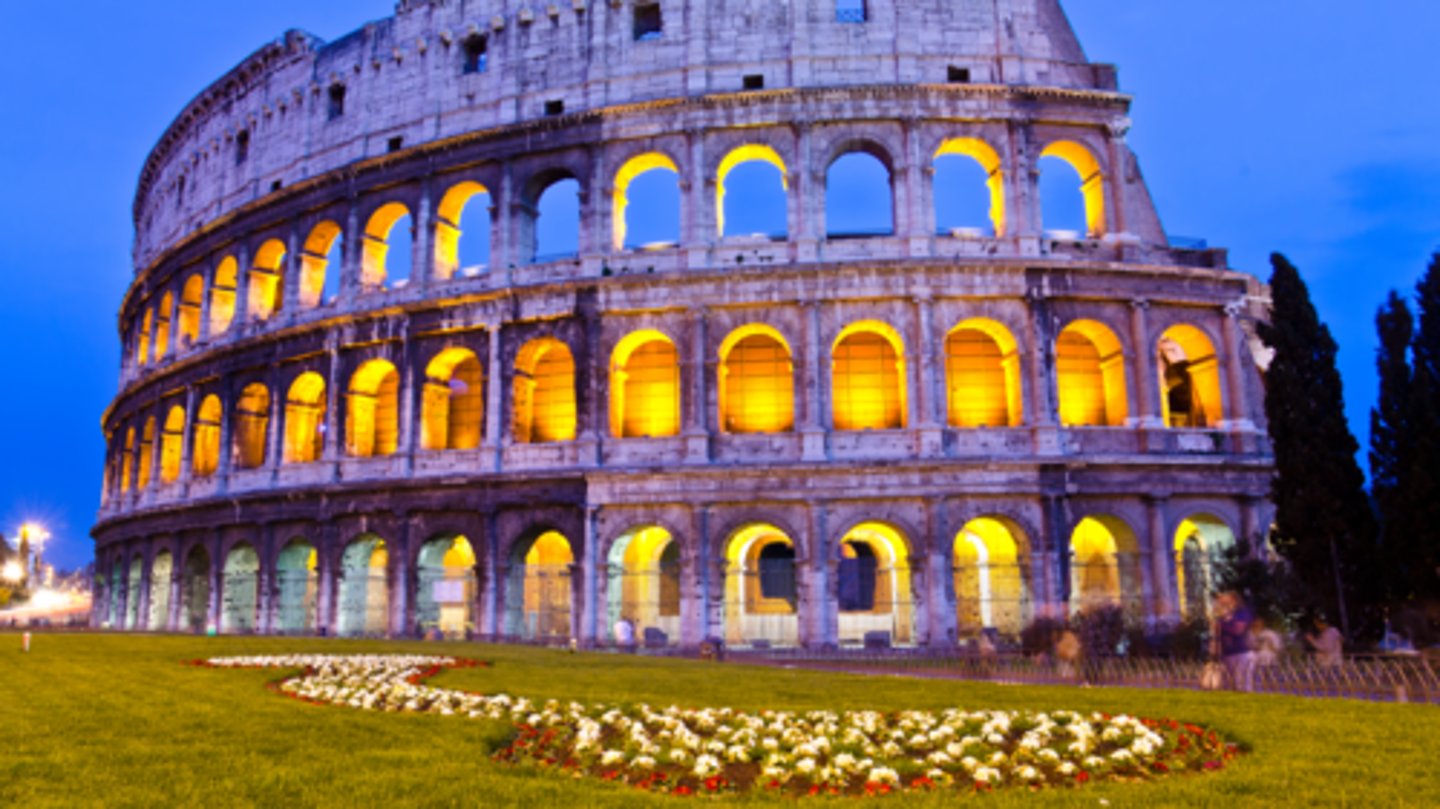

Who took control of Rome by marching on the city, becoming dictator, proscribing his fellow citizens, and then retired?
Sulla
Mark Antony and Cleopatra were defeated at the Battle of Philippi in 42 BCE.
False
The Punic Wars were a series of conflicts between Rome and:
Carthage
Who crossed the Rubicon River with his legions and initiated civil war?
Caesar
Nero
Julio-Claudian
Lucius Verus
Nerva-Antonine
Commodus
Nerva-Antonine
Claudius
Julio-Claudian
Titus
Flavian
Geta
Severan
Dynasties in the correct chronological order.
Julio-Claudian, Flavian, Nerva-Antonine, Severan
Correct 'cursus honorum' order:
Quaestor, Aedile, Tribune of the Plebs [if plebeian], Praetor, Consul
The term "class" has two connotations: economic class and:
social sophistication
Why do modern Roman historians prefer to use the terms "elite" and "non-elite"?
Because they're not too precise and generally lack judgement.
Romulus divided the original population of Rome into two groups:
atricians (patres or "fathers") and plebeians (the remainder of the population.)
Who would be the one who demoted you from your class if necessary?
Censor
Families of patricians monopolized priesthoods and magistracies and provided the cavalry of the Roman army during the early Republic.
True
What is a plebiscita?
a legal recommendation
"civis Romanus sum!" means:
"I am a Roman citizen!"
Julio-Claudian emperors in the correct chronological order
Augustus, Tiberius, Caligula, Claudius, Nero
Who or what is an aurgia?
charioteer
What is the Latin word for public games put on as civic celebrations?
Ludi
Gladiators fought in the _____ the performance area in the amphitheatre:
Arena
What were the venationes?
wild beast hunts
What were the munera?
Private productions of entertainment, like gladiatorial contests
Gladiators typically fought to the death.
False
Which Roman magistrates were responsible for the public games?
Aediles
Where in Rome would you most likely go to see chariot racing?
Circus Maximus
What is the typical program of events by the early imperial period?
Wild beast hunts, Executions, Gladiators
An owner or manager of a gladiatorial troupe was called a
Lanista
Hephaestus
Vulcan
Athena
Minerva
Hermes
Mercury
Hera
Juno
Aphrodite
Venus
What is the Latin term for marriage between two people with the legal right to marry?
Conubium
The Latin word domus refers to only the physical house.
False
The Latin term for "sexual misconduct" was
stuprum
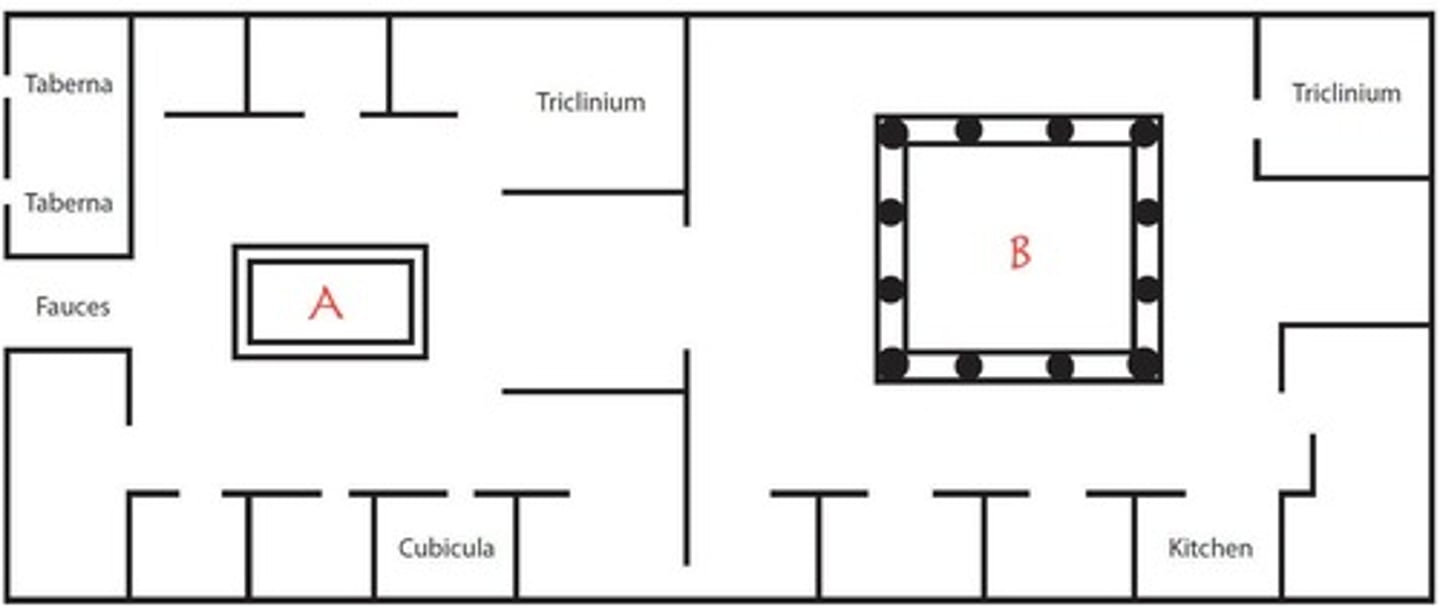
Choose a label for A in the floor plan:
impluvium
Oral sex was looked upon favourably in Roman antiquity, at least by elite authors.
False
The Romans had similar views on male homosexual relationships as the Greeks.
False
Freedpersons continued to have connections to their original household.
False
Housing in ancient Rome was rather simple and straight forward.
False
What was a triclinium?
Dining Room
In order for a couple to be able to marry legally, which of the following conditions had to be met?
They had to be Roman citizens, They were not too closely related, They hadn't been married previously, They had to be the minimum age for marriage.
The shrine to ancestral deities in the Roman home was called the:
Lararium
What is the Latin term for "manliness" or "courage" which was traditionally associated with the male ideal in Rome?
Virtus
The ancient Romans participated in pederasty just as the ancient Greeks did.
False
The paterfamilias had the right to decided whether a child born in his household was exposed or not.
True
What occupation could Roman women enter?
Midwife, Business owner, Priestess
Who was responsible for inspecting the entrails of the animal sacrificial victim?
haruspex
Who was part of the Capitoline Triad?
Augustus, Minerva, Jupiter, Venus, Roma, Mars, Juno
State religion was a significant expense for Rome.
True
Religion across the Roman empire was homogeneous.
False
Epitaphs were usually dedicated to the Di _____ the spirits or gods of the dead.
Manes
It is easy to separate the Roman government from Roman religion.
False
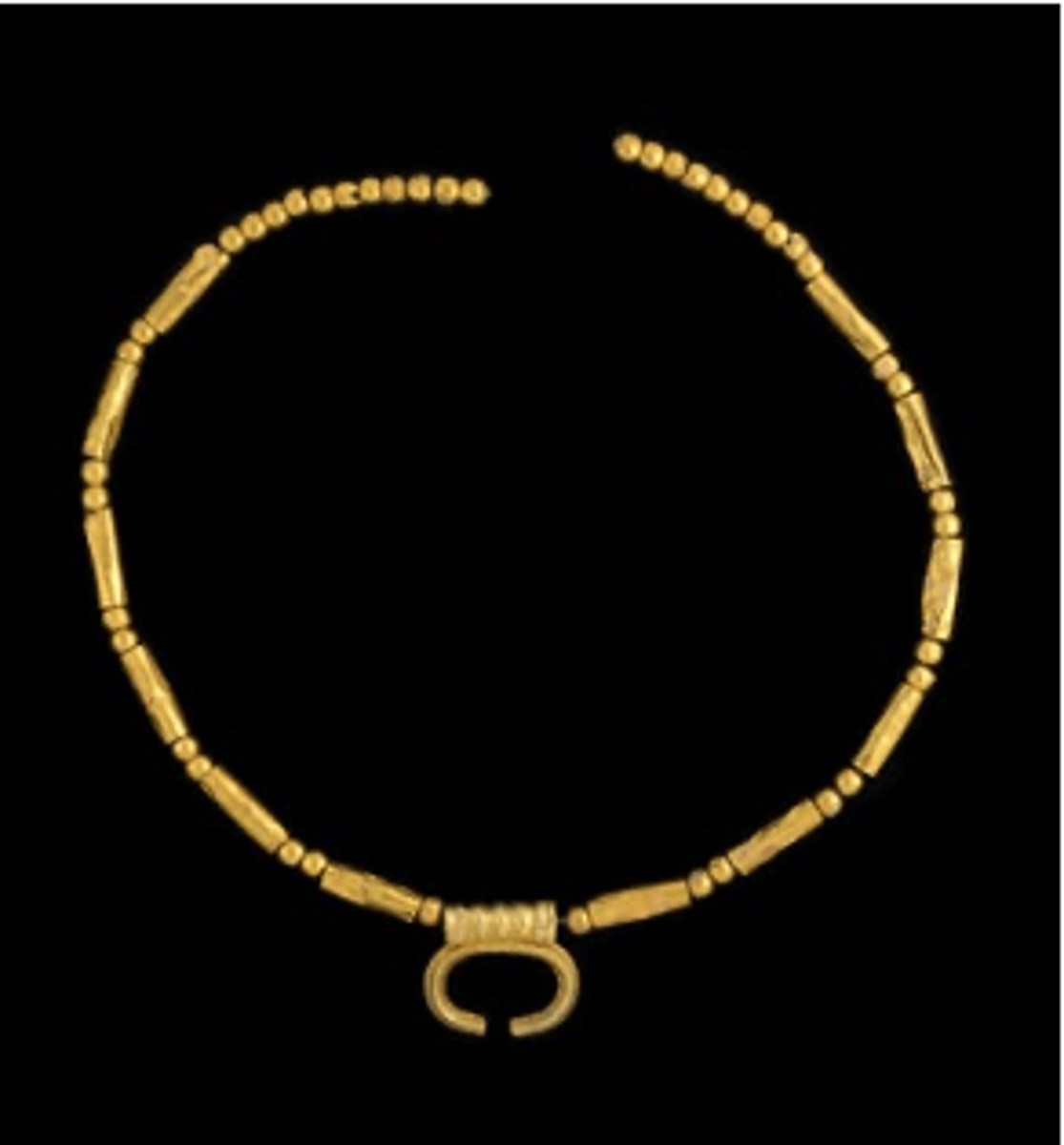
What is this?
lunula

One of the most important priestly offices of Rome was the __________ and was famously held by Julius Caesar in 63 BCE.
Pontifex Maximus
There were several types of auspicia.
True
Almost every aspect of Roman life was intertwined with religion.
True
Rome had a college of _______ who were in charge of various aspects of Roman state religion.
pontifices
Anybody had the right to consult or interpret the will of the gods in ancient Rome.
False