PSYCH100: Final
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
types of drug therapies
antipsychotics, antidepressants, antianxiety drugs
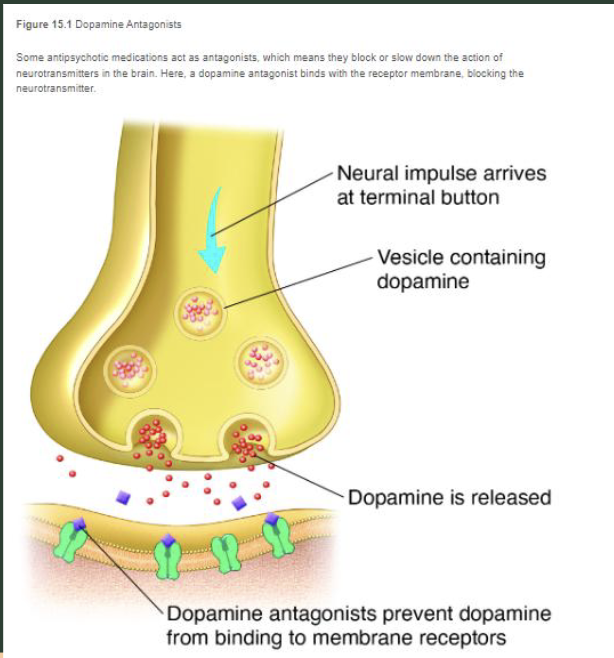
antipsychotics
use chlorpromazine, a dopamine antagonist that blocks receptors in the brain
treats schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, psychotic episodes
side effects: drowsiness, dizziness, weight gain, dry mouth, tardive dyskinesia=involuntary movements
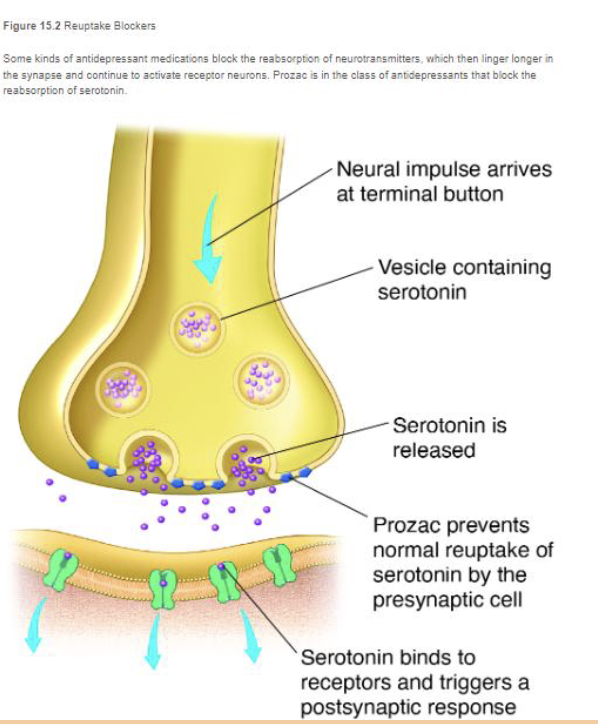
antidepressants
use tricylics, which increase the effect of serotonin and norepinephrine
EX: SSRIs (selective, serotonin, reuptake, inhibitors) - prozac, lexapro, paxil, zoloft block serotonin reuptake
antianxiety drugs
use benzodiazepines to treat anxiety
EX: xanax, valium
enhance GABAs (gamma-aminobutyric acid) which reduce neuron excitability
short term use
insight therapy
helps people gain knowledge about their inner thoughts + behavioral change
psychoanalysis techniques (sigmund freud)
free association: relax and discuss whatever comes to mind
dream analysis: desires of the unconscious
dreams: latent content: unconscious, manifest content: actual events
resistance: unconsciously motivated attempt to hinder therapy (inattentive, “forgetting” dreams, arguing)
transference: redirects feelings from people in their own life onto the therapist
psychodynamic therapy: a modern approach
cognitive therapy
changes maladaptive, conscious beliefs
“bad beliefs and interpretations cause bad symptoms”
rational-emotive therapy (cognitive, albert ellis)
challenge irrational beliefs through active and aggressive confrontations
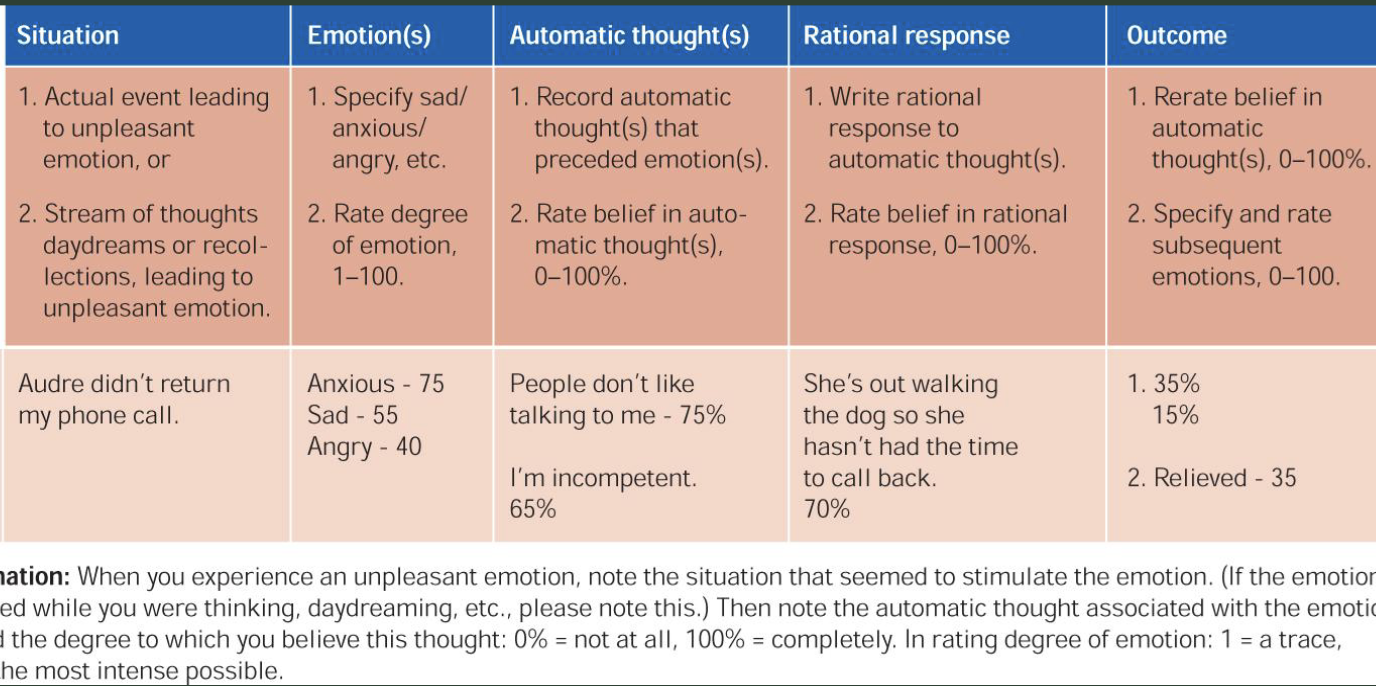
beck’s cognitive therapy (cognitive)
therapist acts as a “co-investigator” to help the client come to conclusions on their own
hw: record thoughts and create rational responses
humanistic therapy
insight of self-worth, humans can fix their own problems and control their own behaviors
client-centered therapy (humanistic, carl rogers)
client holds the key to health and happiness, therapy offers unconditional positive regard
behavioral therapy
counterconditioning: conditioned and unconditioned stimulus and responses
systematic desensitization: gradually exposing to fears to reduce fear
aversion therapy: associating unwanted behaviors with unpleasant stimuli
CBT: changing perceptions
types of therapy
individual therapy, group therapy (support groups, structured interventions, open or closed), couples therapy, family therapy
consciousness
awareness of one’s internal and external states
brain and mind are inseparable
attention
the internal processes used to set priorities for mental functioning
attention is selective bc the resources of the brain are limited
dichotic listening studies
focusing on one ear results in poor processing of the other ear
can also result in switching sentence fragments, bc we dont completely ignore everything (treisman)

cocktail party effect
ability to focus attention on a specific sound while ignoring background noise
automaticity
fast and effortless processing that requires little or no focused attention
practice creates automaticity (playing a piano piece w/ no sheet music)
if the mind wanders, there’s decreased performance, but increased creativity
attention disorders
visual neglect: ignoring some things that occur on one side of the body (usually left side), caused by damage to right parietal lobe of cerebral cortex
attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): difficulties in concentrating for long periods of time, strong genetic influence, diet too, low levels of dopamine, treatment: medication and behavioral therapy
subtypes: hyperactive-impulsive, inattentive, combined
circadian rhythms
biological activities that rise and fall in accordance with a 24 hour day
regulated by hypothalamus
light influence!
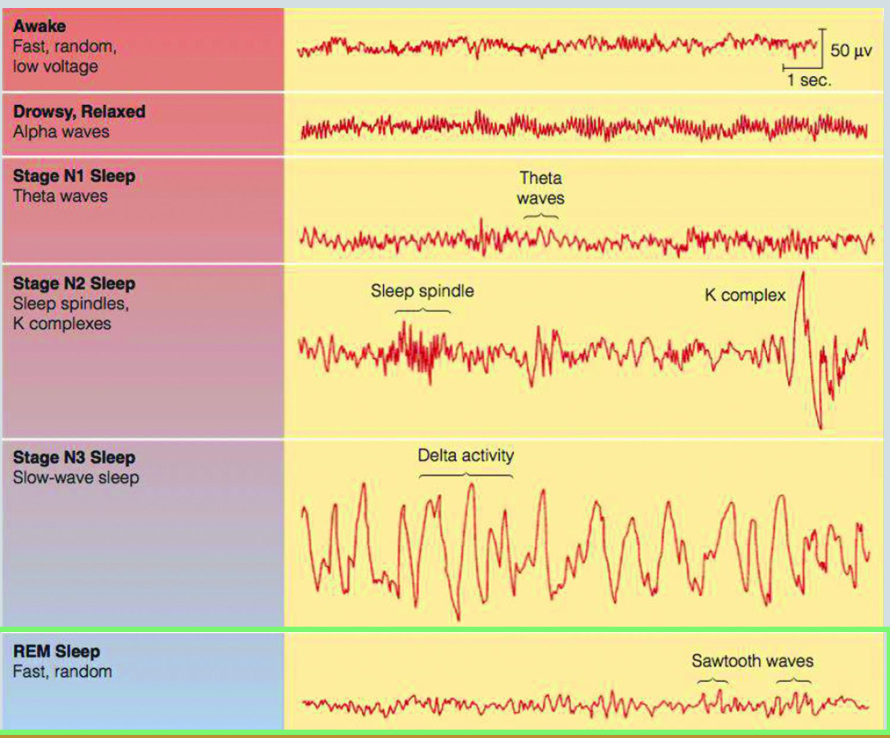
stages of sleep
alpha waves: relaxed state, slower/higher amplitude
N1-theta waves: drifting thoughts, irregular/lower amplitude
N2: sleep spindles-short bursts of brain activity and k complexes-triggered by external stimuli
N3-delta waves: synchronized, slow wave pattern “deep sleep”
rem (rapid eye movement): body is activated but fully asleep, heart rate increases and eyes move back and forth, dream time
sleep disorders
insomnia: difficulty falling or being asleep
hypersomnia: excessive sleepiness usually caused by sleep apnea
narcolepsy: extreme sleepiness entering rem directly sometimes
nightmares: frightening dreams during rem, can be related to mental health disorders and cause waking up
night terrors: waking up in panic, mainly in children during NON rem
sleep walking: gets up and wanders, mainly in children during NON rem
substance use disorder
drug that remains compulsive despite its negative consequences
drug tolerance
amount of drug increases to produce the same physical and behavioral effects
drug dependence
one experiences a physical and psychological need for continued use of a drug
withdrawal
physical reactions that occur when you stop using a drug
sweating, headache, vomiting, tremors
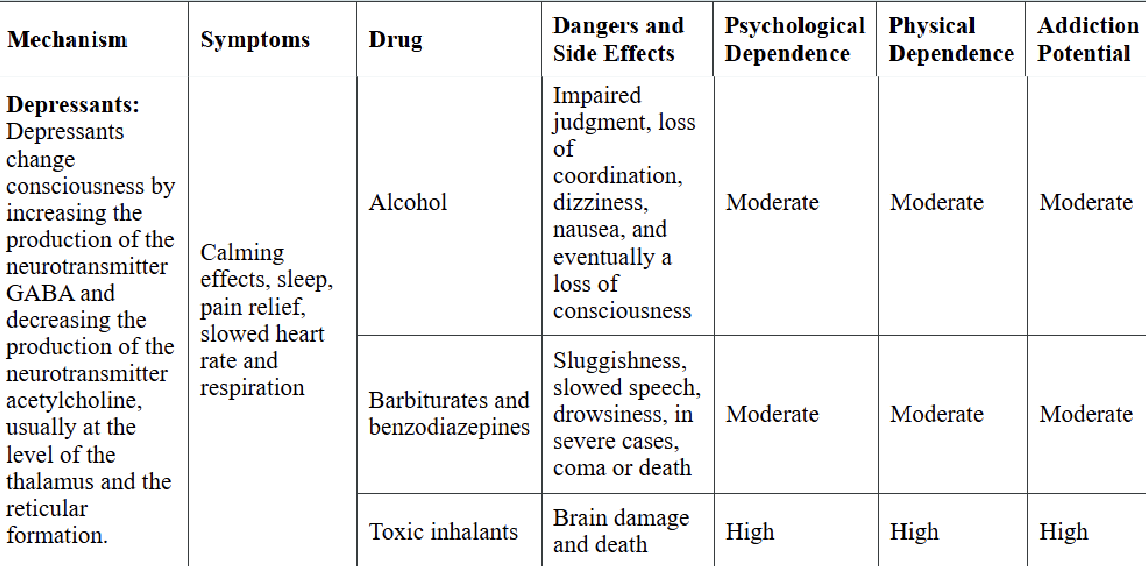
depressants
EX: alcohol, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, toxic inhalants
Mechanism: increasing GABA, decreasing acetylcholine
Side effects: calming effects, pain relief, slowed heart rate, and respiration
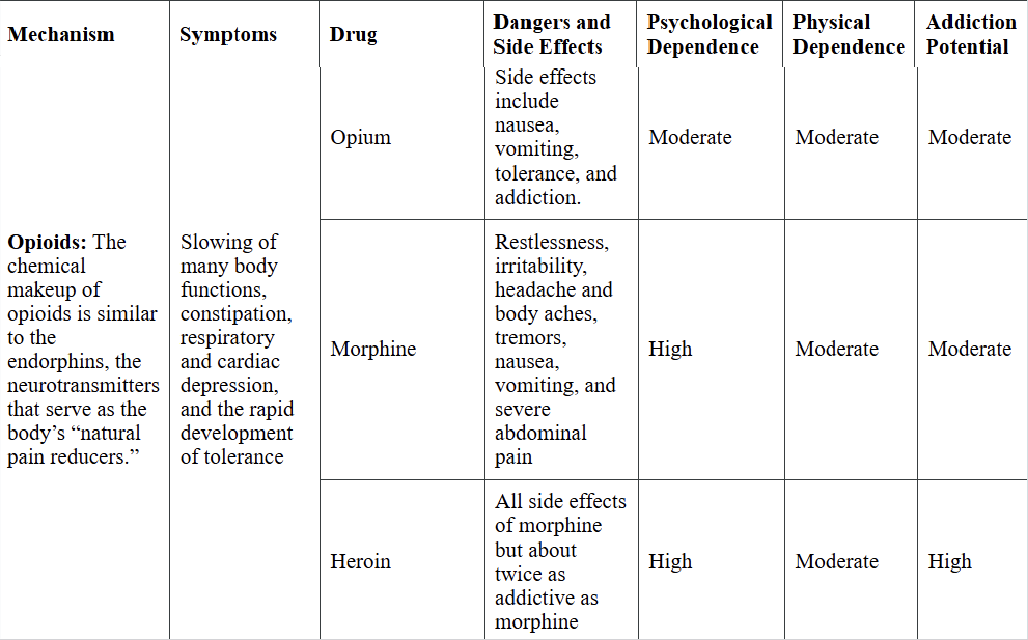
opiates
EX: opium, morphine, heroin
Mechanism: mimics endorphins
Side effects: slowing of many body functions, respiratory and cardiac depression, rapid development of tolerance
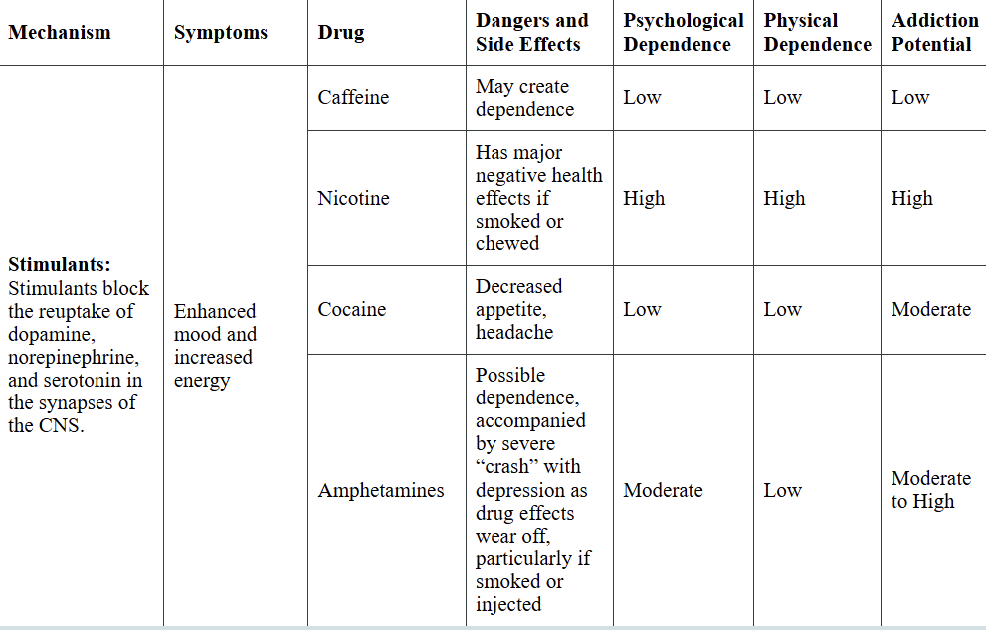
stimulants
EX: caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, amphetamines
Mechanism: block dopamine/norepinephrine/serotonin reuptake
Side effects: enhanced mood and increased energy
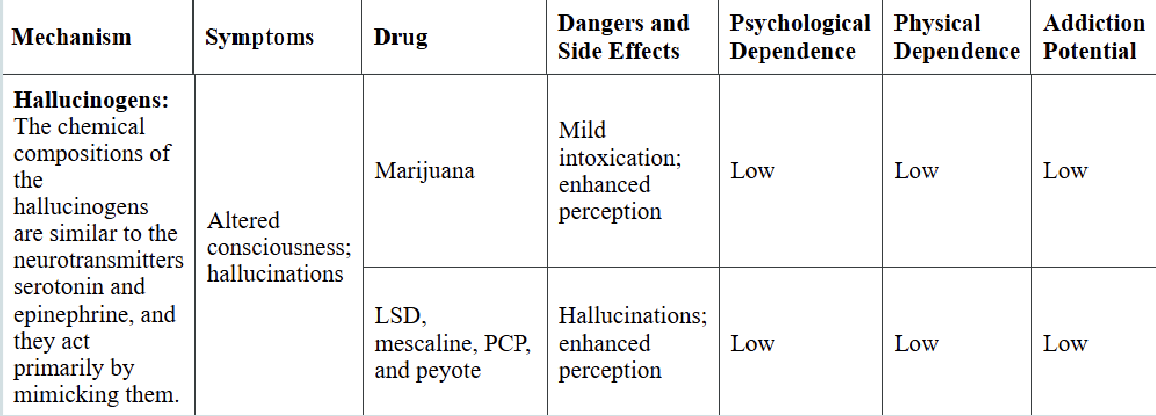
hallucinogens
EX: marijuana, LSD, psilocybin, mescaline, PCP, peyote
Mechanism: mimic serotonin and epinephrine
Side effects: altered consciousness, hallucinations
habituation vs sensitization
habituation: getting “used” to a repeated event so declines in responsiveness
sensitization: increased responsiveness to a repeated event
classical conditioning (ivan p. pavlov)
procedures used to find out how organisms learn about the signaling properties of events
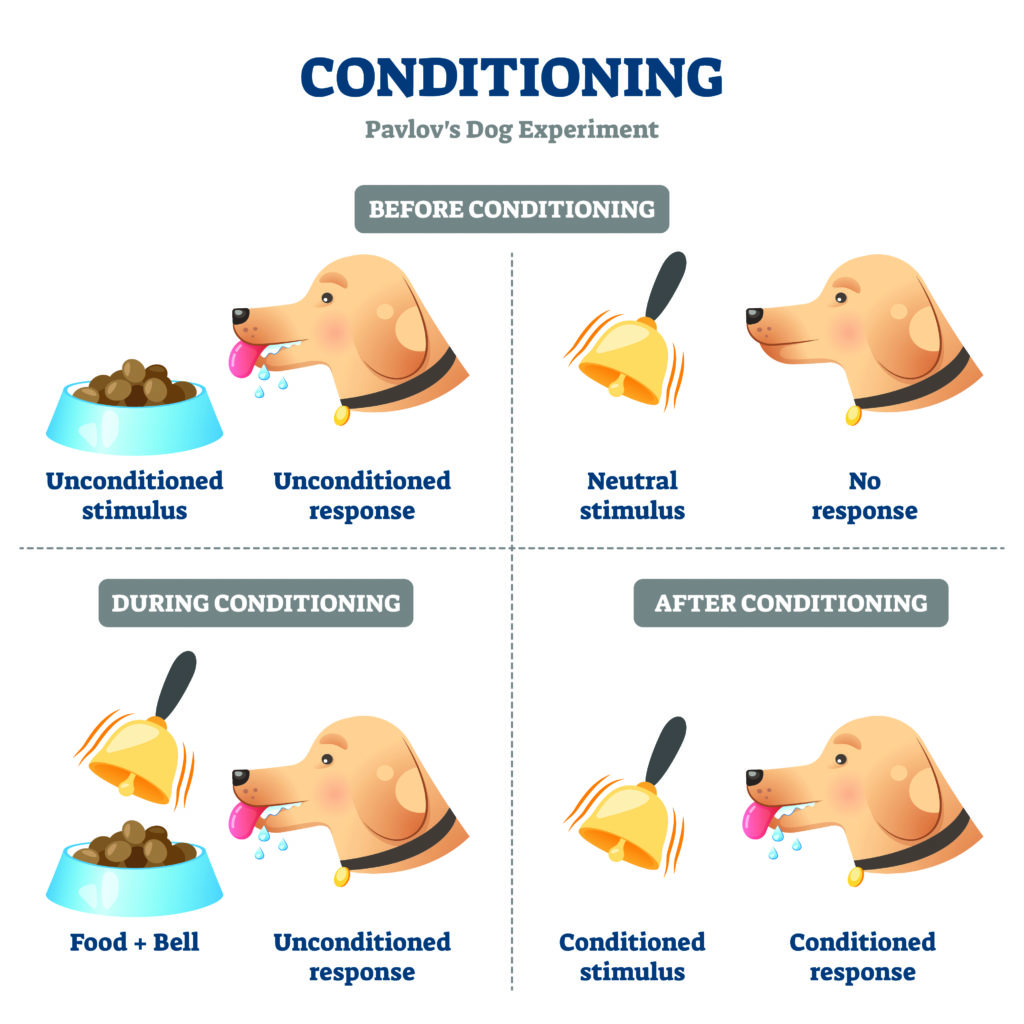
unconditioned stimulus vs. conditioned stimulus
unconditioned: observable responses w/ no prior training
conditioned: signal for the unconditioned stimulus
unconditioned response vs conditioned response
unconditioned: observable response w/ no prior training
conditioned: acquired response produced by the conditioned stimulus
rules of classical conditioning
conditioned stimulus should be presented first
unconditioned response should be presented quickly after conditioned stimulus
conditioned stimulus must provide new information about the unconditioned stimulus
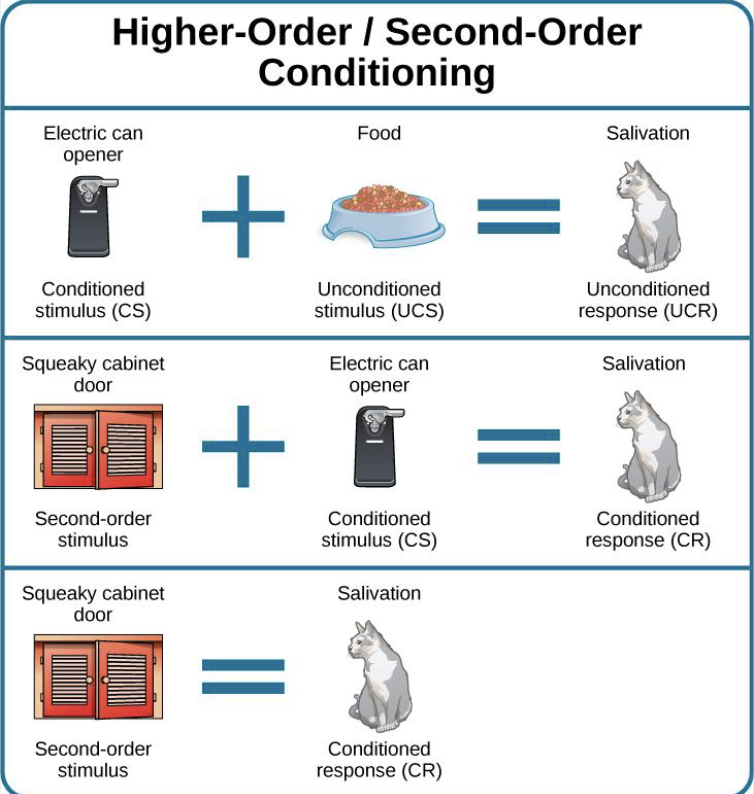
second-order/higher-order conditioning
needing two or more factors for a conditioned stimulus to create a conditioned response
Thorndike’s law of effect
behaviors that result in a positive outcome are more likely to be repeated while behaviors that result in a negative outcome are less likely to be repeated

operant conditioning
a procedure to study how organisms learn about the consequences of their own voluntary actions
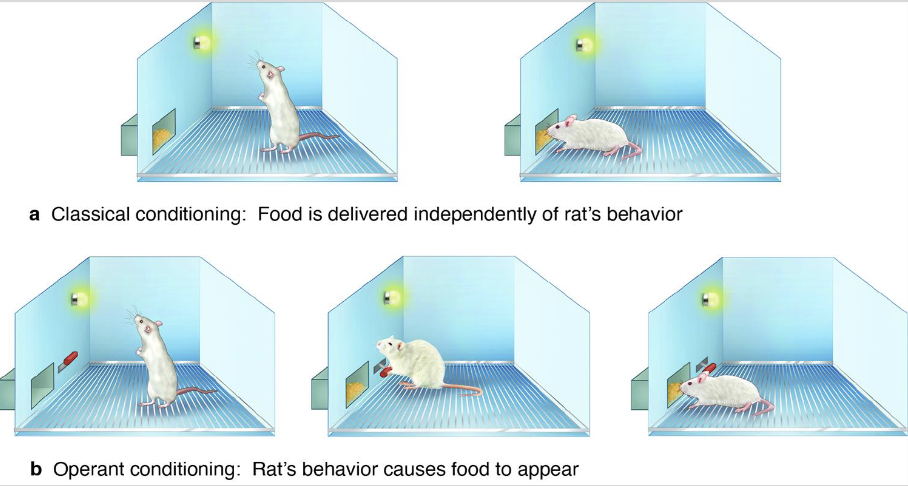
pos/neg reinforcement and punishment
positive: adding/giving/gaining something
negative: taking away
reinforcement: increase behavior
punishment: decrease behavior

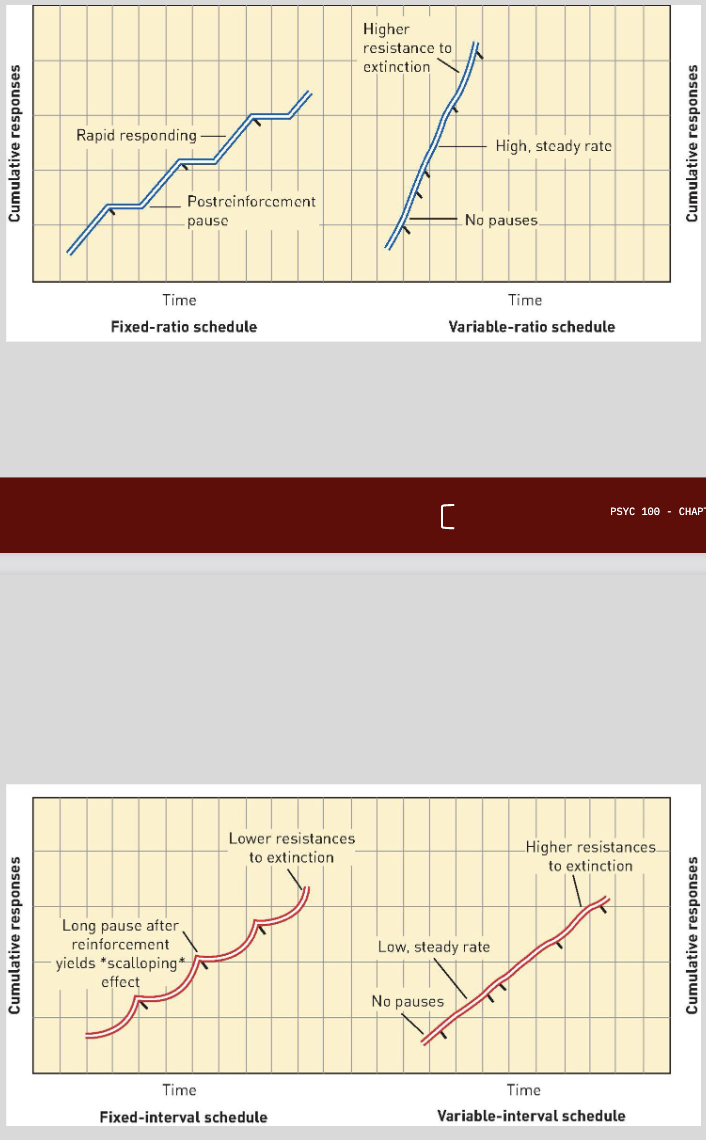
types of partial reinforcement
fixed-ratio: number of required responses is fixed (getting a bonus after selling x number of things)
variable-ratio: a varying number of responses are required (slot machine)
fixed-interval: reward is given for the first response after a set amount of time (getting paid every two weeks)
variable interval: reward is given for first response after a varied amount of time (fishing)
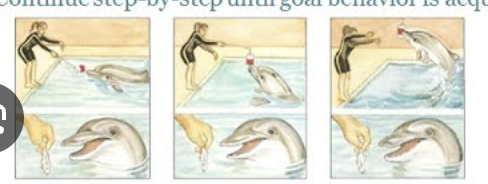
shaping
operant-conditioning that reinforces behaviors that are increasingly similar to desired behavior
observational learning
uses mirror neurons and you imitate a model (individual performing the behavior), especially if they have good qualities (Lebron)

modeling
learning from others
EX: bobo doll experiment

memory
the capacity to preserve and recover information
stages of memory processes (encoding, storage, retrieval)
encoding: forming memories
storage: storing memories
retrieval: recovering and translating memories into performance
sensory memory, how do we produce an exact replica of an environmental message
iconic: short lived image of a visual sensation
echoic: audio information as the brain processes sound
interference
short term memory is lost by interference of new information
chunking
arranging incoming information into meaningful or familiar patterns (te acu pse t)
long term memory
there are theoretically no limits to what we can remember (pi memorizing)
information must be encoded to later retrieve it
elaboration: actively relating new information to already stored long-term memory (u do this all the time in bio!!)
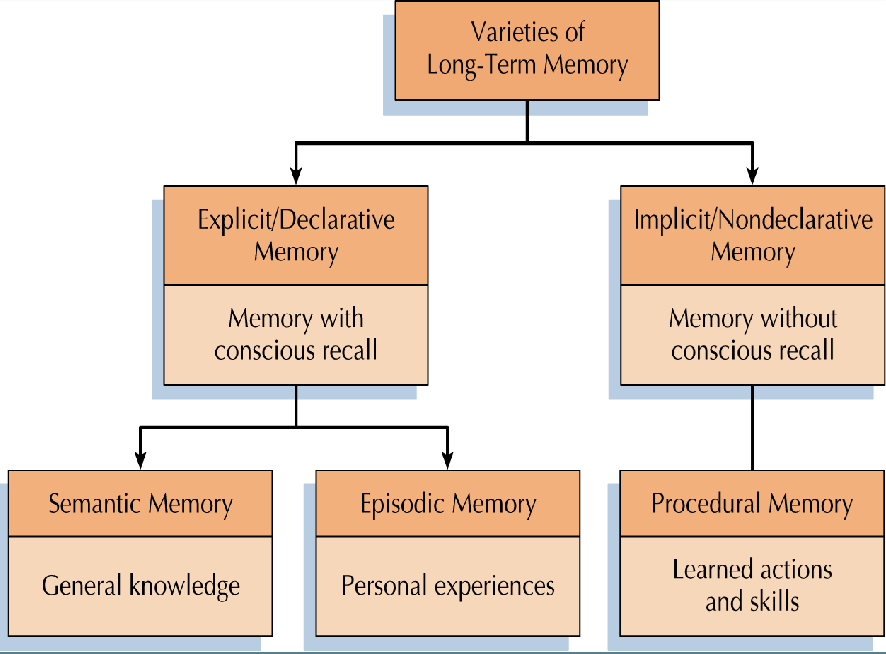
types of memory
episodic: events, personal
semantic: facts, knowledge about the world, not personal
procedural: how to do things (like riding a bike)
remembering without awareness (explicit vs implicit memory)
explicit memory: conscious remembering, hippocampus
implicit memory: unconscious remembering like our friends, neocortex+striatum
*both use retrieval cues
decay theory
memories fade over time
retroactive interference: new memories replace some recovery of old memories
proactive interference: old memories interferes with recovery of new memories
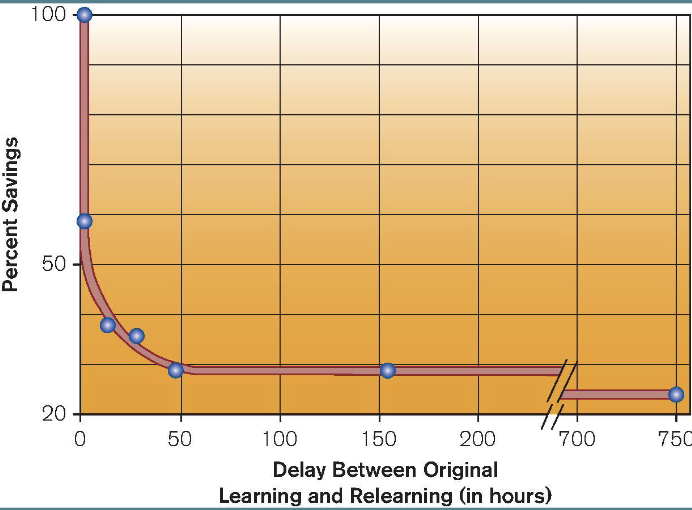
forgetting
inability to retrieve memory from long-term storage
occurs rapidly over first few days and then levels off
free vs. cued recall
free recall: recall without retrieval cues
cued recall: recall after receiving retrieval cues
amnesia
forgetting caused by physical problems in the brain like injury or disease
retrograde vs anterograde amnesia
retrograde: memory loss that occurred prior to the injury
anterograde: memory loss that occur after the injury; implicit memory is usually still in tact
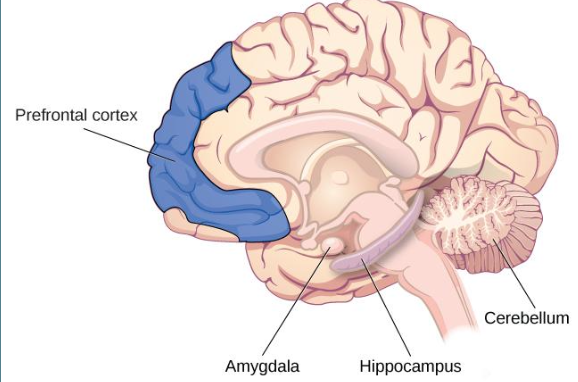
where are memories stored?
HIPPOCAMPUS!!
thinking
processes that underlie the mental manipulation of knowledge and ideas
cognition
all activities that underlie forms of thought
linguistic relativity hypothesis (how does language relate to thought?)
language influences how we think and how we perceive the world, but doesn’t completely determine thought
EX: masculine/feminine of an item
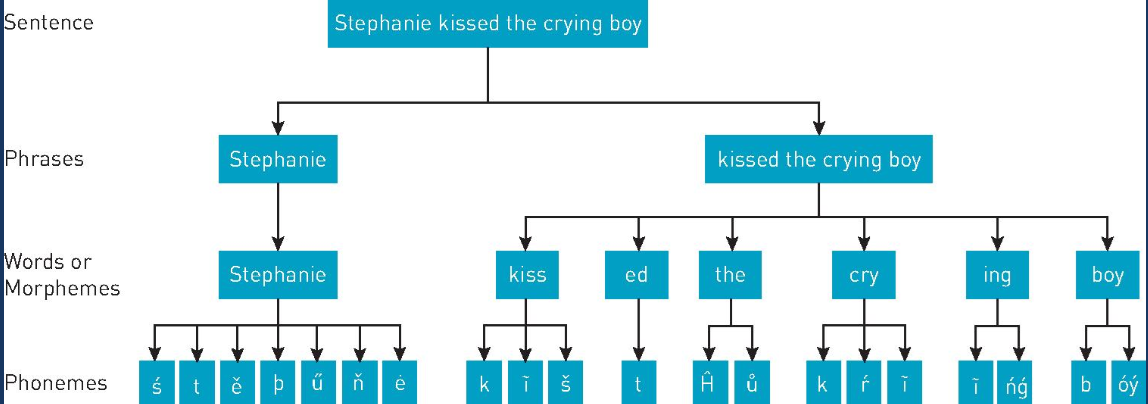
structure of language key words
grammar: rules that allow words to be combined in sentences
phonology: combining sounds to make words
syntax: combining words to make sentences
semantics: rules used to convey meaning
morphemes: smallest lang. units that have meaning, including suffixes and prefixes
phonemes: the basic sounds of speech
surface vs deep structure language
surface: literal order of words in a sentence
deep: underlying meaning of a sentence
language comprehension
ability to derive meaning from written oral language
factors: past knowledge, shared knowledge, anticipate words (top-down processing)
aphasia
difficulty coming up with (broca’s area) and comprehending language (wernicke’s area)
patterns of language development when growing up
1 month: cooing
4-6 months: babbling
1 yo: first word
2 yo: telegraphic speech “want milk”
3+ yo: full sentence
categories
a class of objects. can share defining features
family resemblance
core feature that all categorical members share
prototype vs category exemplar
prototype: the most representative
category: specific examples of category members that are stored in long-term memory
mental set
tendency to rely on past, successful problem solving strategies
heuristics
rules of thumb to solve problems but do not offer a gauranteed solution
confirmation bias
tendency to seek out information that confirms a priori decision or belief

availability heuristic
over reliance on easy to access information because it is recent, frequent or stands out
representativeness heuristic
mental shortcut used to make judgments about someone/something
EX: assuming people with tattoos are dangerous
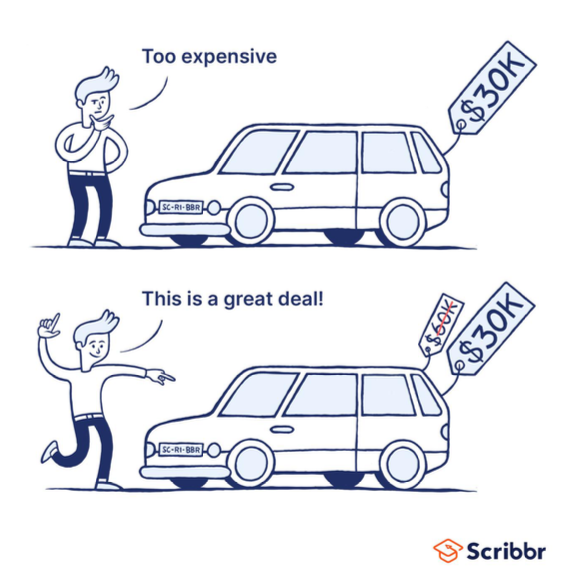
anchoring heuristic
rely heavily on the first piece of information encountered when making decisions or estimates. initial information=anchor
intelligence
an internal capacity that accounts for individual differences in mental performance, an ability that enables us to adapt to changing environments
theories of intelligence
psychometric: how people perform on standardized psychological tests (spearman)
hierarchal models of intelligence: 7 primary mental abilities (verbal, numbers, memory, reasoning, speed etc.) (thurstone)
fluid vs. crystalized: based on genetics vs acquired through experience (cattel & horn)
multiple intelligences: musical, body, logical, spatial, etc. and testing with case studies (gardner)
triarchic: analytical, creative, and practical (sternberg)
achievement tests
measure current level of knowledge; psych 100 exams
aptitude tests
measure ones ability to learn a subject
EX: SAT
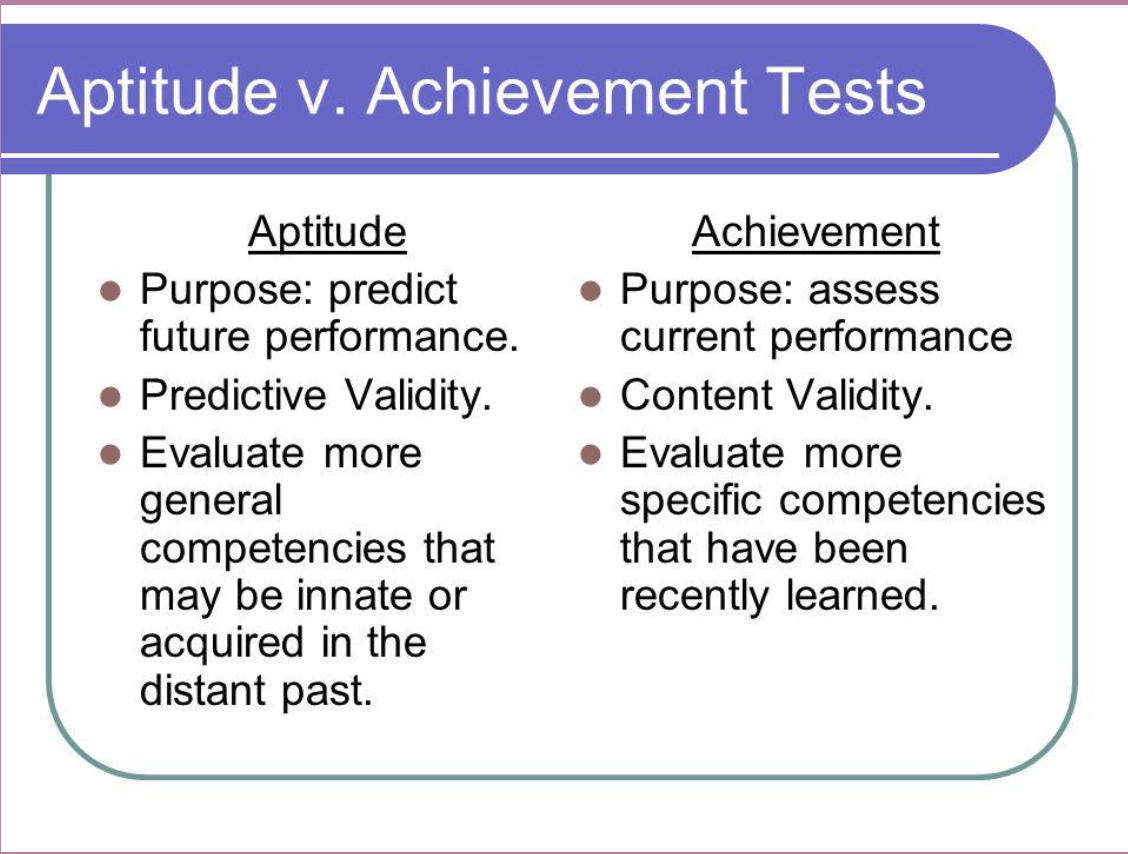
intelligence quotient (IQ)
iq=mental age/chronological age *100

deviation IQ
an intelligence score that shows your IQ on an age-based distribution of test scores
<70 score = intellectual disability (>130 is gifted)
must be diagnosed before 18
causes: down syndrome, lack of nutrition
savants
have tremendous ability in one domain
pros and cons of labeling individuals based on their IQ
pros: personalized education, identifying giftedness, targeted support
cons: stigma and bias, limited scope, self fulfilling prophecy, misuse, narrow focus
the flynn effect
iq on average is scoring higher per generation
motivation
set of factors that initiate and direct behavior, usually towards a goal
emotions
psychological events=>physiological reaction, expressive reaction, subject experience
instinct theory of motivation
motivation is driven by innate instincts but psychologists debate on this
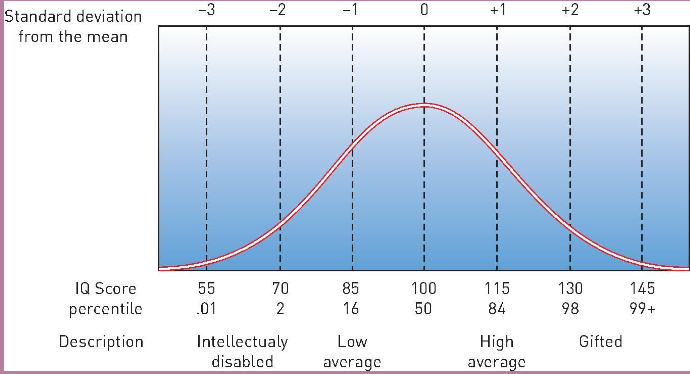
drive reduction theory of motivation
drive: internal state that arises in response to a need like homeostasis
incentive theory of motivation
external rewards like money and good grades have a pulling effect on behavior
achievement motivation: an internal need to succeed
more motivation = better retaining info, learning, seeking challenges
want to outperform = concerned about errors, miss learning opportunities
culture influences achievement (gender, society)
intrinsic motivation
goal directed behavior that is entirely self-motivated
introducing rewards can actually reduce the frequency of behavior bc it is an indirect way of being controlled
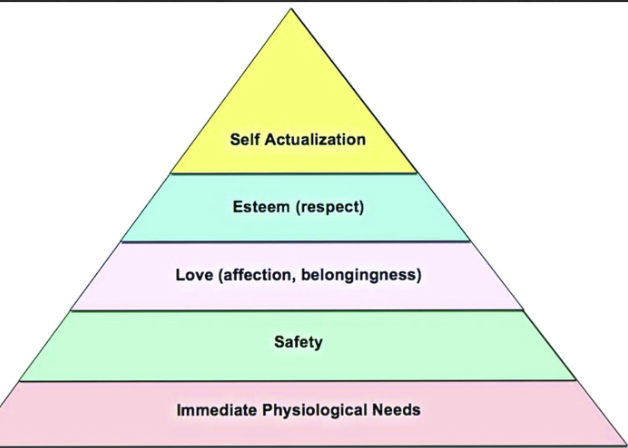
abraham maslow’s hierarchy of needs
human desire to elevate one’s self
cons: hard to define and measure, and why can’t we seek two needs at once
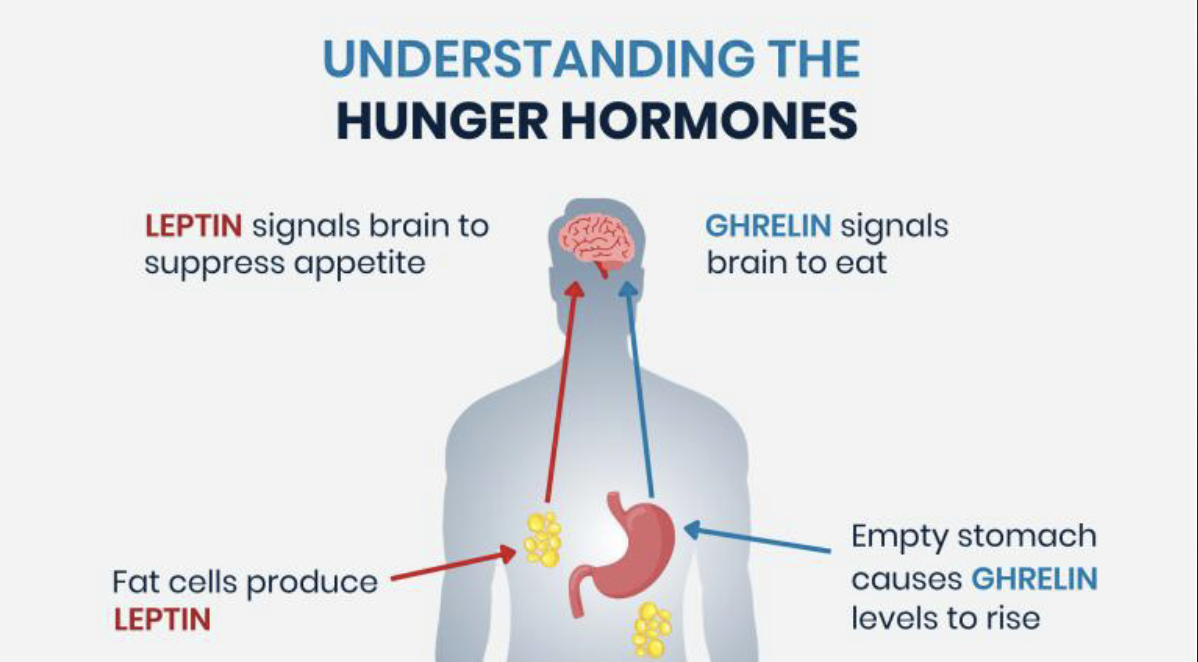
what controls hunger?
glucose: blood-sugar level
ghrelin: increases before eating and reduces after eating
satiation signals: reduce the desire to eat such as CCK cholecystokinin
leptin: high levels→obesity, low levels→less fat
insulin: from pancreas
body fat→cells become less responsive to insulin→high insulin→higher risk of type 2 diabetes
external factors: eating habits, culture, food cues
brain areas important for hunger
hypothalamus: sensitive to leptin and insulin, so if it is destroyed→overeat, stimulated→undereat
hindbrain: integrates info from body to hypothalamus, important for starting to eat
hippocampus: memory about food intake
factors behind body weight
genetic predisposition
set point: natural body weight that the body maintains
metabolic rate
obesity
prolonged exposure to high fat diets can change the brain and inflame brain structures that indicate fullness
factors: genetics, metabolic rate, set point, number of fat cells, eating habits, culture, stress, lack of access, eating disorders
eating disorders
anorexia nervosa: restricting food intake and fear of weight gain
bulimia nervosa: cycles of binge eating and purging
binge eating disorder: binge eating w/o purging
health problems:
ceasing of menstruation, low blood pressure, loss of bone density, gastrointestinal problems, organ failure, high mortality rates
intestinal damages, nutritional problems, tooth decay
obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular problems, sleep problems
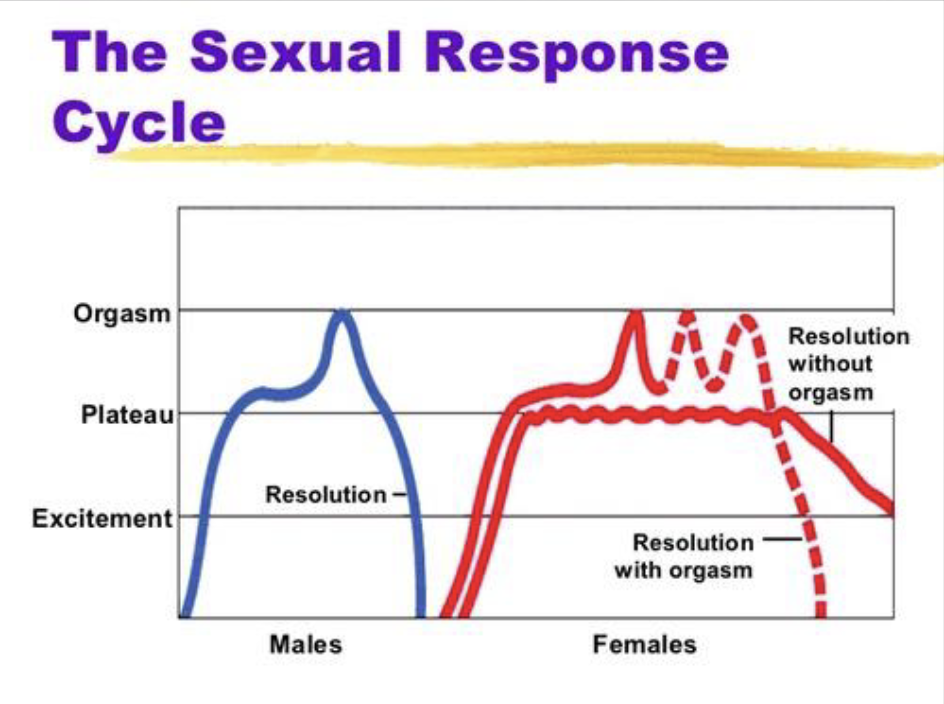
sexual response cycle
excitement: muscle tension, increased HR and BP, blood to genital organs
plateau: arousal increases (erection,vaginal lubrication)
orgasmic: rhythmic contractions, ejaculation
resolution: arousal returns and refractory period for men stops further arousal
sexual scripts/mate selection
learned processes that teach us what to do in our interactions with sexual partners
EX: differences between sex, financial stability for women
external factors influence sexual behavior
attraction stimulates sexual drive, physical touch, and body odor
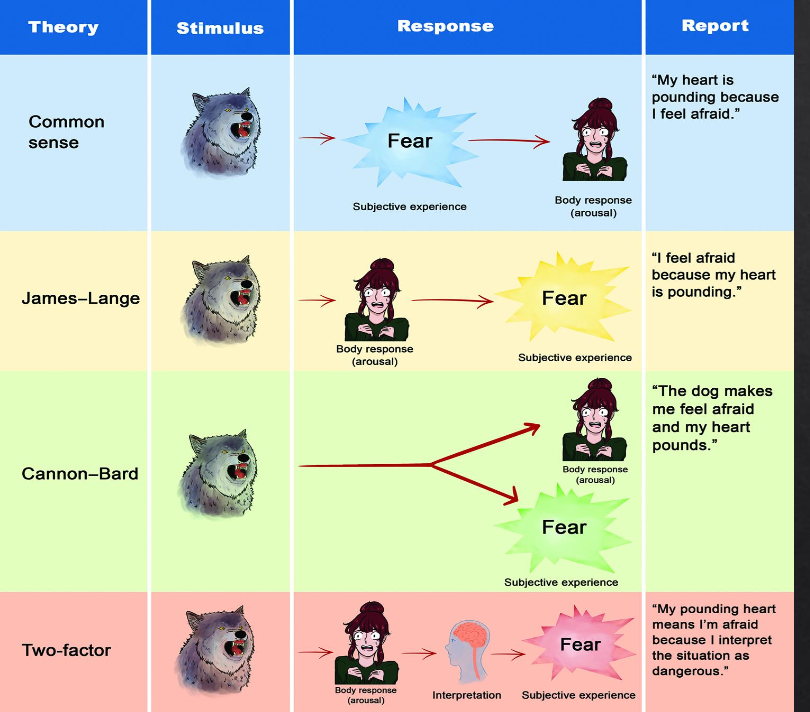
theories of emotions
common sense: perception of a stimulus elicits emotion and body arousal
james-lange: emotions arise from physiological arousal. heart pounding → fear
cannon-bard: physiological arousal and emotions occur simultaneously, yet independently. fear and heart happens at the same time
Schachter and Singer Two-factor theory: physical changes → labeling changes based on our understanding of the situation around us