Metals
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEC207 Materials Processing, metals section of the course
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
How does casting work?
molten metal
introduced into a mould cavity
solidification into the shape of the mould
finishing processes
how can heat transfer affect solidification?
most metals contract when solidifying
cooling too quickly can cause defects
What are the 3 types of casting? What are they good for?
sand casting - larger, one off objects
investment casting - small components
permanent mould casting - small, mass production
how do solid state deformation processes work?
they change the shape of the metal by plastic deformation using force
what is rolling?
the process of reducing the thickness (or cross section) by compressive forces applied by a set of rolls
why are backup rolls needed in a cluster mill?
to provide rigidity and prevent deflection
this is needed as the metals being rolled are at room temp. and so very strong
what unique thing does a steckel mill do? why is this good?
it pulls the metal whilst it is being rolled
this increases surface quality
and reduces energy requirements of the mill
what is the rolling force equation?
F - rolling load/force
X - friction factor
w - width of the material being rolled
R - radius of the rolls
ho - initial gauge thickness
hf - final gauge thickness
σflow - flow stress of the material
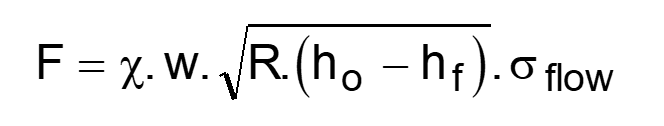
What should one do if the rolling load is greater than the capacity of the rolling mill?
get a better machine
raise the temperature in order to decrease the strength of metal
decrease the amount of rolling reduction per pass
What are 4 types of defects that can happen in rolling?
flatness
porosity
edges cracking
crocodile defect
How does extrusion work?
a round billet is placed into a chamber and forced through a die opening by a ram
it is normally carried out at elevated temperatures
what is the extrusion ratio equation?
R is the extrusion ratio
Ao is the initial cross sectional area of the billet
Af is the final cross sectional area of the extrusion
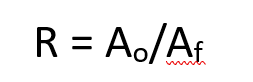
what is the extrusion pressure equation?
P is the extrusion pressure
σflow is the flow stress of the material
a and b are extrusion constants
R is extrusion ratio
Ln is the natural log
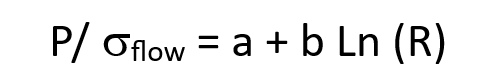
how does forging work?
heat the metal up that smack it into desired shape w
what is forgeability?
the capability of a metal to undergo deformation without severe surface cracking
what is the upsetting force equation?
σflow is the flow stress of the material
mu is the friction factor
r is the effective radius of the workpiece
h is the height of the workpiece
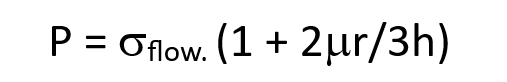
What is isothermal forging?
A type of forging where the dies are heated to the same temperature as the workpiece
It is good when you want more control over the mechanical properties though it is expensive
What is anistropy? How can it be resolved?
when the grains are aligned in the direction of deformation
change the direction of deformation every 90°
Why might powder metallurgy processes be used over traditional processing routes?
To avoid high scrap rate
Less steps
Alloys used are high cost and high performance
Can be difficult to machine
How does additive layer manufacturing work?
Layer upon layer addition of material to build up a final component
Advantages of ALM
near-net shape or net-shape
reduced buy-to-fly ratio
low amount of scrap
design iteration friendly - immense freedom of design
allows for complex geometries
What processes are used to turn metals into powders? Describe them.
Water and gas atomisation
The metal is melted then water/gas is blasted at it which turns it into a powder
Name and describe 2 types of ALM
Powder Bed - Laser beam is used to melt layers of powder. High risk of mess up.
Blown Powder - Powder is blown through nozzles and melted as it comes out
What are some issues with laser systems?
bog
Name an alternative to using a laser beam. Why?
electron beam
Disadvantages of ALM
certain powders are expensive to produce
high energy footprint in powder manufacture
still problems w mechanical properties and surface quality
some metal systems cannot easily be used
How does metal injection moulding work?
metal and binder mixed then granulated and put into injection mould
injection moulded into green compact that is around 65-70% dense
remove binder through heating to form brown compact
sintered to increase density then final product is virtually 100%
Name some considerations for MIM
quality of powder - fine and spherical is best
binder
injection
debinding - careful handling needed
sintering
What happens to the part’s volume due to sintering?
It decreases
Advantages and disadvantages of MIM
advs
good for very small parts
offers large flexibility on chemistry and geometry
lower energy footprint per part than casting
disadvs
carbon pickup
powders are expensive
high cost and energy footprint of powder involved
potential problems with mechanical properties because of porosity and poor surface finish
limitations on size and dimensions of component that can be built
Not all alloy systems suitable for MIM
How does hot isostatic pressing work?
Put powder in a paint can and squeeze it at high temperature to squeeze out all porosity
produces something fully dense
Name some considerations for HIP
capsule manufacture
design
HIP cycle
mould removal
Advantages and disadvantages of HIP
Advs
unparalleled shape complexity and surface quality
trusted process
only way to make some metal matrix composites
Disadvs
costly
complex
low volume
How does spark plasma sintering work?
Put powder in a mould and pulse a DC current through it for very short periods of time (10ms)
The spaces between particles get highly charges and pores close under high pressures
Name the different types of bonding
Primary - strong
ionic
covalent
metallic
Secondary - relatively weak
van der waals
hydrogen
Which 3 properties does bond energy affect?
melting temperature
elastic modulus (stiffness)
thermal expansion coefficient
how does bonding energy affect melting point?
higher bonding energy means higher melting point
what is thermal expansion?
when the temperature of an object increases and causes the amplitude to increase making the overall object to expand
how does bonding energy affect the coefficient of thermal expansion?
as bonding energy increases, the coefficient of thermal expansion decreases
what are the 3 main types of crystallographic structure?
face centred cubic (FCC)
body centred cubic (BCC)
hexagonal close packed (HCP)
Describe FCC
atoms touch each other along face diagonals
Describe HCP
hexagonal layers stacked on top of each other
Describe BCC
not a close packed structure
atoms on the edges of a middle one
touch on diagonals
why is atomic arrangement important?
determines microstructure and properties of a material
controls a large number of properties
similar behaviour is shown in materials with the same arrangement
can cause anisotropy
what is polymorphism?
when a material shows more than one crystal structure
what is allotropy?
when a change in structure is reversible
Describe iron’s polymorphism journey
low temp iron is BCC (alpha)
changes to FCC at 912°C (gamma)
reverts to BCC at 1394°C (delta)
upon cooling, the reverse occurs
How can one physically see iron’s structure changes?
a iron wire changes in length due to changes in density
as it changes from BCC to FCC, it undergoes a contraction as FCC is close packed while BCC is not. it expands suddenly when it gets to BCC again
What happens to Tin when it cools?
she be exploding because her structure changes which causes her volume to decrease by like 27%