bio e1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
a chromosome is best described as
a single piece of DNA
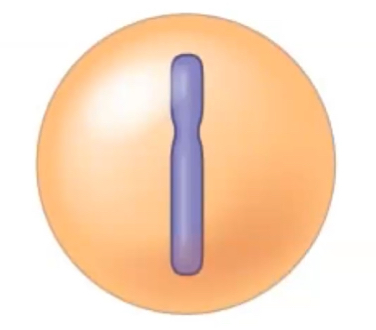
where is the DNA in this picture
the purple is DNA
a gene is
a zone on a chromosome
what is translation?
making a protein from RNA
what must be true for somethin to be part of your phenotype?
it must be able to be passed to offspring, it must be able to be inherited from parents

which of these are characters?
pea flower color
what are sister chromatids?
duplicated chromosomes held together

what is the first codon
GGT or GTA
what is true about homologous chromosomes?
the genes are the same
what can you see in a karyotype?
duplicated DNA, DNA, duplicated homologous chromosomes, sister chromatids
what can be different about homologous chromosomes?
the alleles can be different?
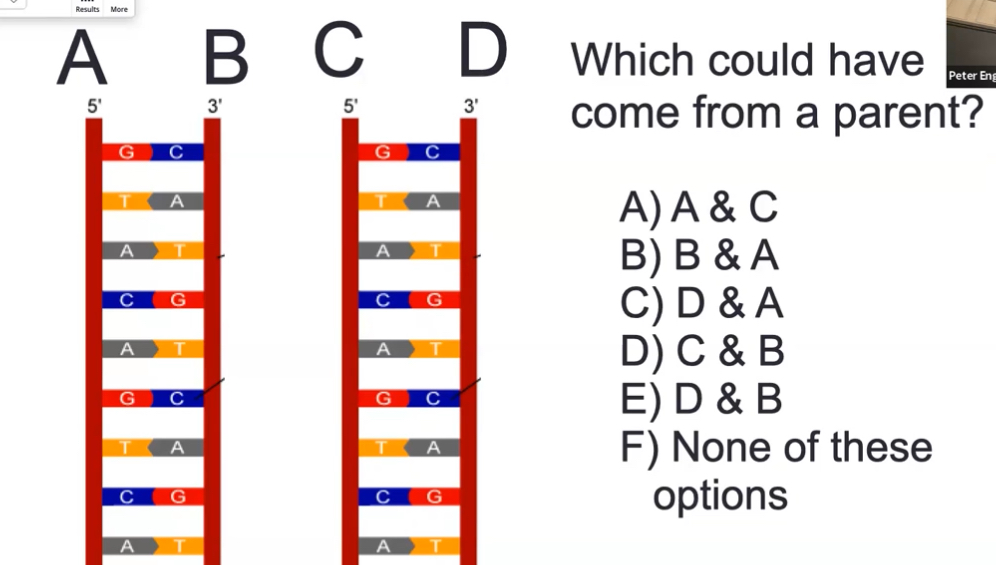
which could have come from a parent?
B and A
why do we need haploid gametes?
so offspring can be diploid?
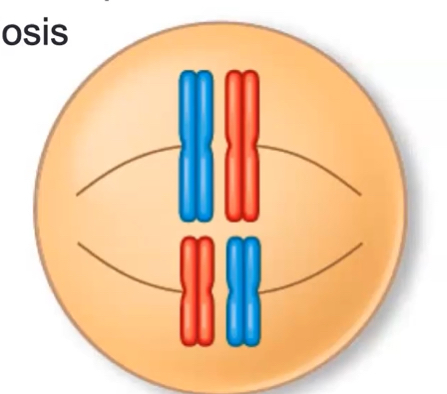
what does this cell show?
duplicated homologous chromosomes, sister chromatids, duplicated DNA
this will become how many chromosomes?
4
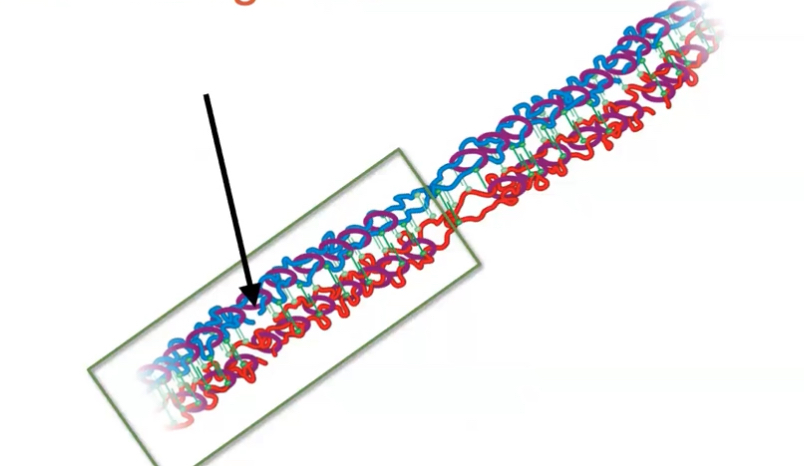
how many strands of DNA are broken in this view of crossing over?
4
crossing over results in
different sets of alleles compared to the beginning
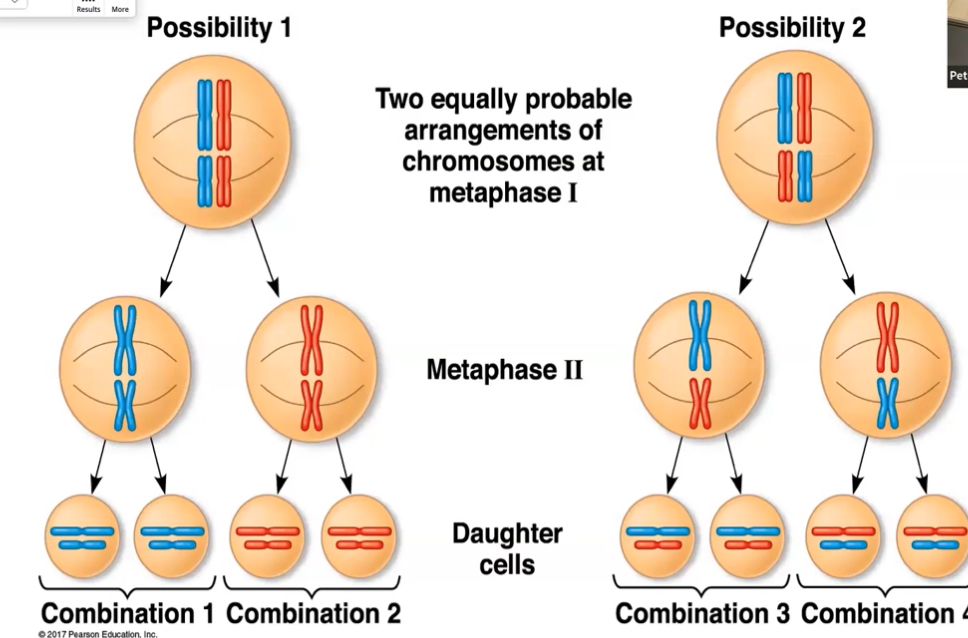
why is this image unrealistic and potentially misleading?
crossing over is not shown
what do you get from one parent?
one chromosome from each homologous pair, one of each gene, one allele per gene
dominant alleles ( or phenotypes) are
expressed in the heterozygote
which sequence of events is correct to make a protein?p
DNA-RNA-protein
genotype of a white flower plant
pp
why only one letter in each parent box in a monohybrid cross?
because offspring have two alleles
crossing over results in different sets of alleles compared to the beginning, what does “the beginning” look like?
a normal somatic cell
correct order of events for meiosis
DNA duplication - crossing over - independent asssortment
who mates with the P2 generation
the mate with each other
which generations show two phenotypes?
P1 and F2
what is true about the genes for Mendel’s seven characters
on different chromosomes
only two homologous chromosomes in an individual, could there be more than two alleles in the population?
no- only 2 homologous chromosomes
one gene, two different alleles, standard mendelian: how many genotypes and phenotypes
3, 2
the white flower plant phenotype is
homozygous
for pea shape, round is dominant and wrinkled is recessive, how is this expressed in letters:
R is round, r is wrinkled
how many GENES are depicted in a Punnett square?
1
why do offspring probability boxes have two letters?
parents each give one allele
for the peas: P1 generation has how many genotypes?
2
for peas: genotypes of P1 generation
both are homozygous
for peas: how many genotypes in F2 generation?
3
for peas: what would the P1 genotypes be
half RRYY and half rryy
for peas, F1 genotypes will be:
all RrYy
for peas, F1 phenotypes will be
all yellow, round
what do you get from each parent?
23 chromosomes, one chromosome, one gene, one allele
mendelian genetics: which represents 2 homozygous parents who have different alleles
PP *pp
what does “P” really represent?
the actual nucleotide code on one strand of the double-stranded DNA at a specific location
rule of independent assortment
is a physical thing that happens in meiosis
two genotypes for flower color in P1 generation
both are homozygous
what are proportions of offspring phenotypes when both parents are heterozygotes?
75 dom/25 rec
what would the P1 parents genotypes be? (dihybrid)
half RRYY and half rryy
two genes; how many diff phenotypes are possible in F2?
4
two genes; how many F2 boxes will result in offspring that are round
12
what level are we talking about when we say incomplete dominance/codominance
allele
Mendel started with 50/50 in P1, by F2 the proportion of alleles in the population was
50% one and 50% the other allele
why didn’t the proportion of alleles in a population change for Mendel?
because Mendel made all the decisions
one gene: if proportions of 2 alleles in a population could change? what are plausible options?
one allele could become 100%, one allele could become 0%, proportions could fluctuate forever
how likely is no heritable advantages in the actual world
zero likely
physically, what are different alleles of the same gene
different DNA sequences found at the same locus on homologous chromosomes
a gene is expressed using incomplete dom. and the two parents in P1 are homozygous for different alleles. How many phenotypes will be expressed in the F2 generation?
3
what is a mutation?
a change in the genotype
what differentiates founder effect from population bottleneck?
founder effect results in new sub population?
what is most likely the same about homologous chromosomes?
the genes and the loci
most swiss starlings produce 4 to 5 eggs in each clutch, starlings that produce fewer eggs or more eggs than this number have reduced fitness. What best describes this situation
natural selection, stabilizing selection
what are some possible outcomes of a single mutation in a gene
might not cause a phenotypic change, could cause a change in phenotype, must cause a change in genotype
what is fitness?
an idea about future offspring
A is 20% and a is 80% of alleles, what is the proprtion of AA genotypes in the population?
4%
why is whale anatomy different?
selection resulted in important changes to whale forelimb anatomy
if two unrelated species converge on the same answer:
characters would be analogous
species converge on “the same answer” to what?
problem related to survival, reproduction, fitness
the character of flight:
evolved independently several times
what is a zygote:
a single-cell fertilized egg
can bacteria have species?
yes but not using the biological species concept
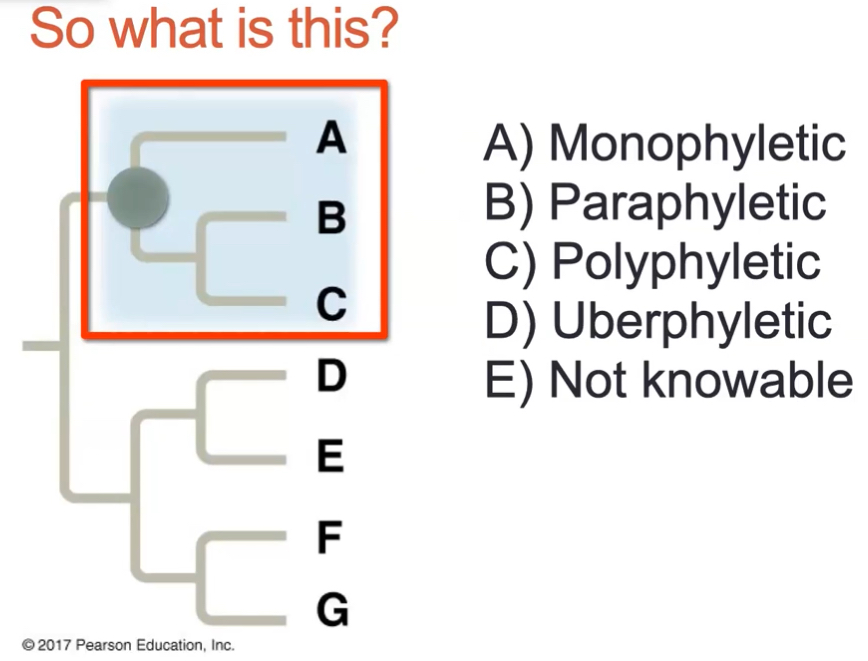
what kind of tree is this?
monophyletic