Filtering
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
In what order must averaging and digital filtering be applied?
It doesn't really matter, as they are both linear operations. However, the files are smaller if averaging is done first
Why are digital filers beneficial?
they can increase SNR by lowering noise and remove unwanted frequencies from the data
What are potential drawbacks of digital filtering?
they can cause signal loss or distortion if they aren't used properly, changing the signal, resulting in temporal smearing, or "creating" a "signal" that doesn't really exist
Fourier's Theorem
states that nearly every wave can be expressed by superimposing single sinusoidal frequency waves
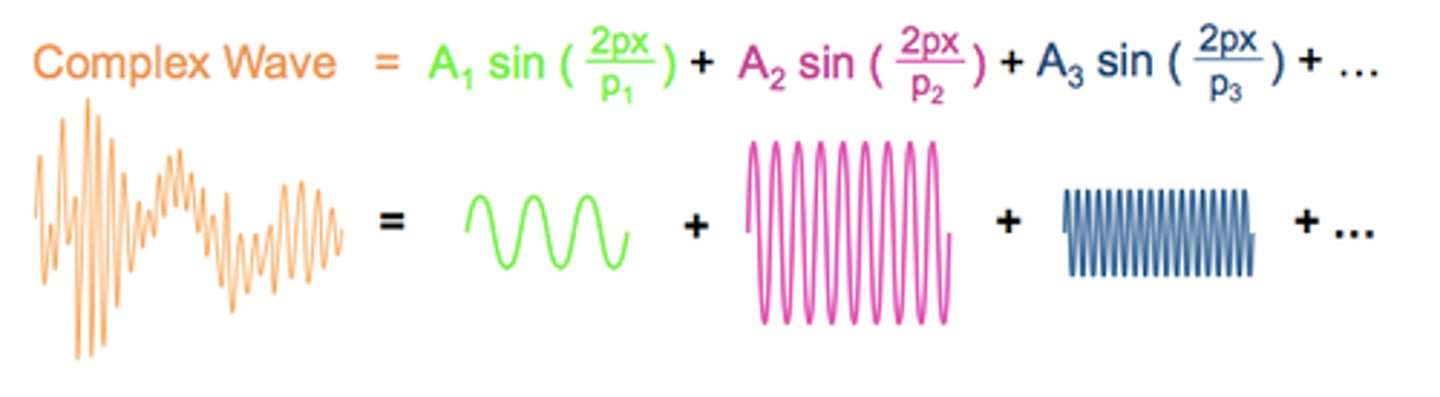
Fourier Synthesis
mathematical process of combining sine waves to create more complex periodic vibrations
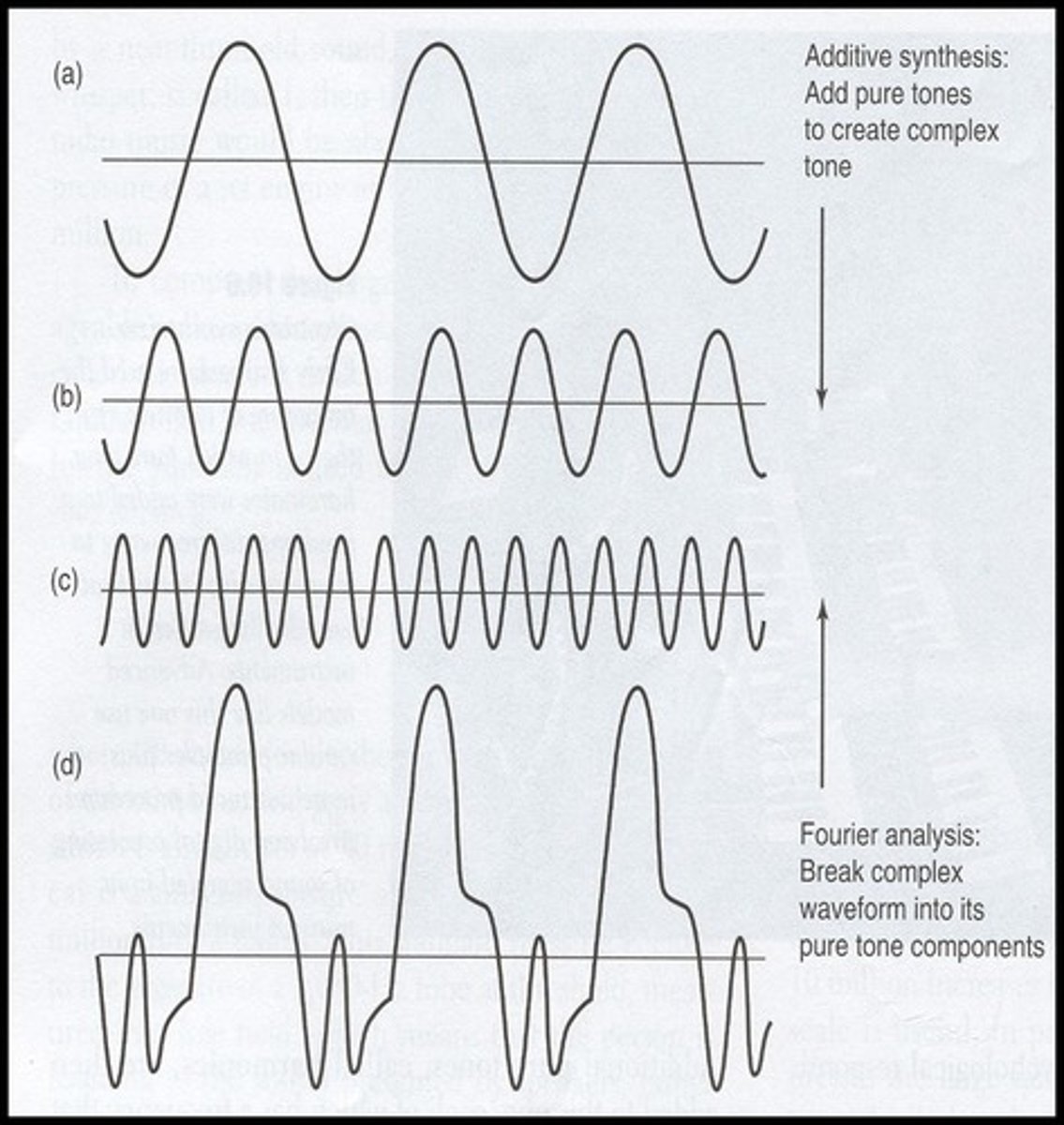
Fourier analysis
A mathematical procedure by which any signal can be separated into component sine waves at different frequencies. Combining these sine waves will reproduce the original signal.
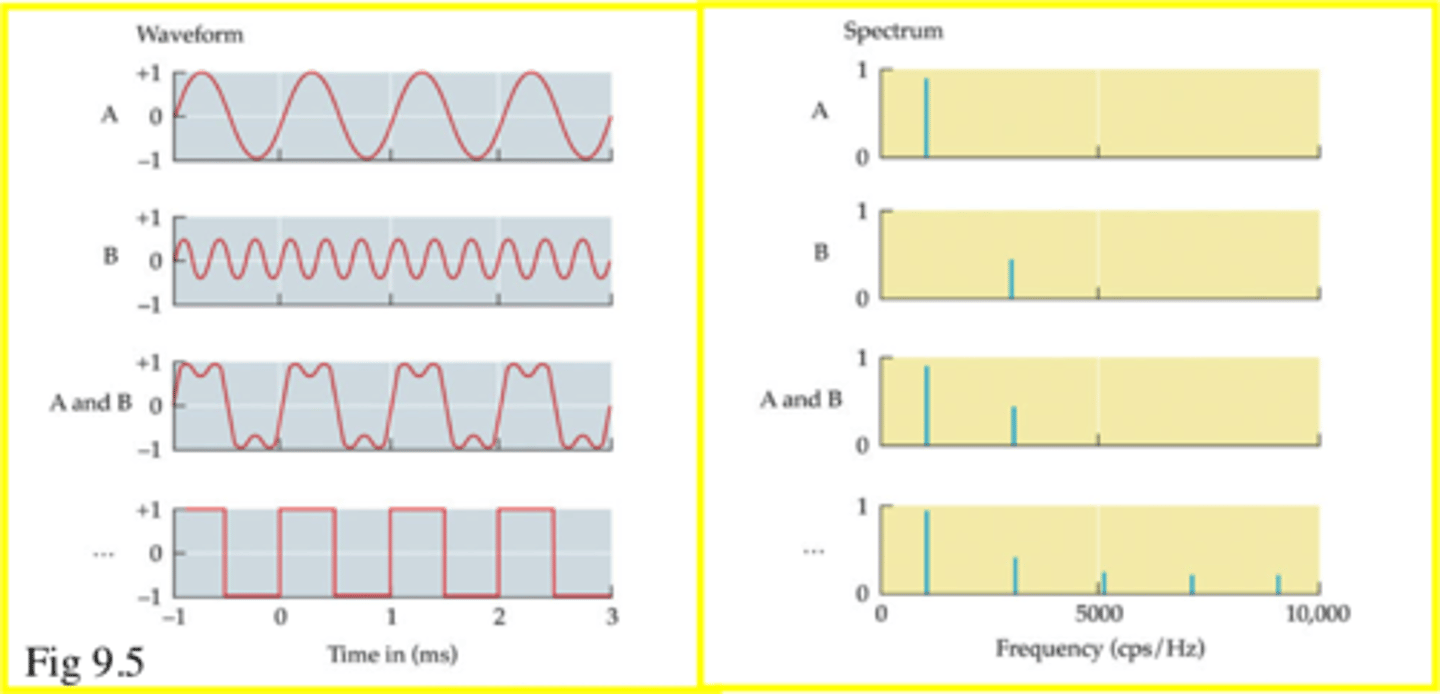
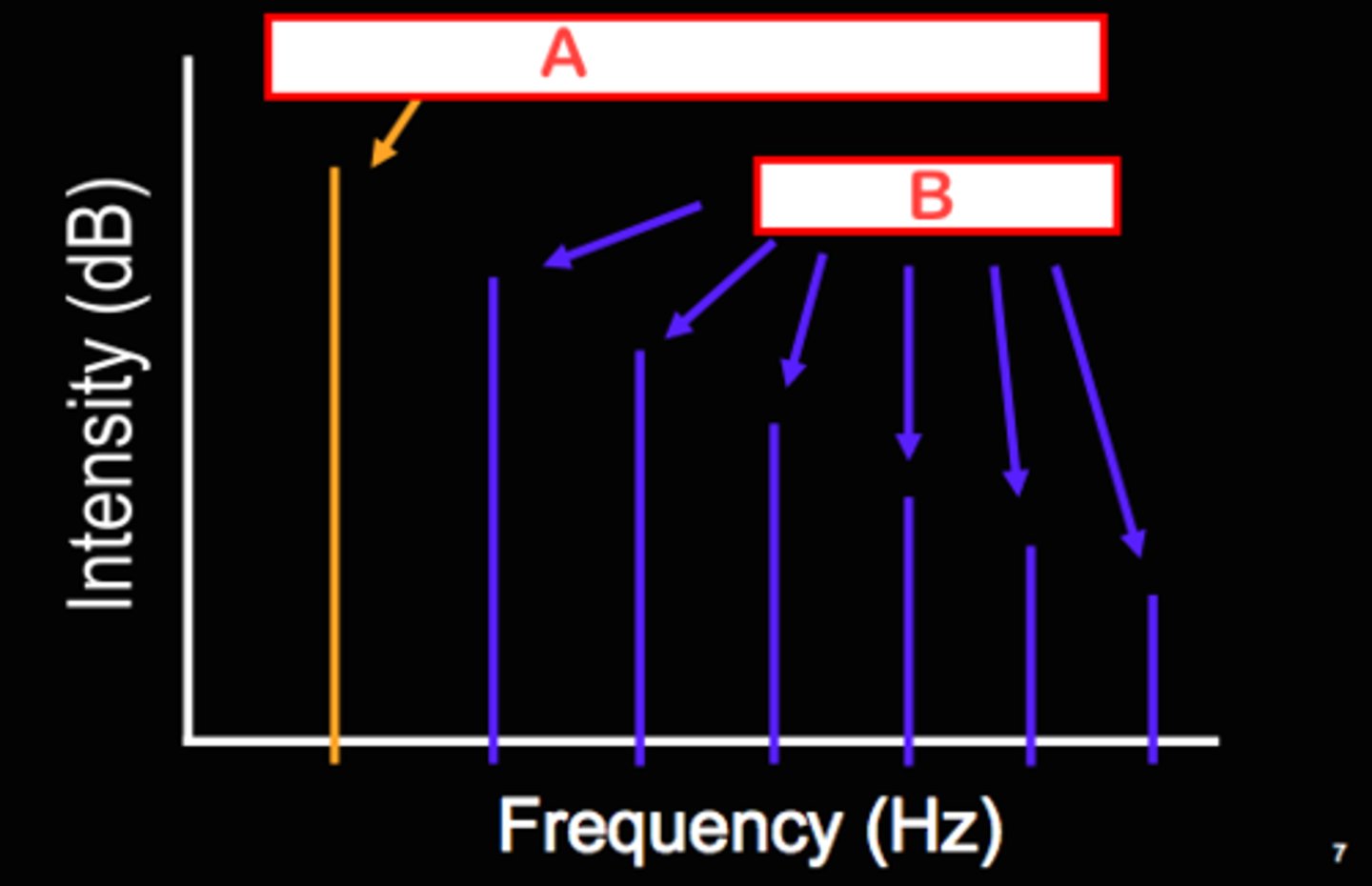
Frequency spectrum
a graph that shows the amplitudes of different frequencies present in a waveform
running average (boxcar filter)
an average consisting of a continuous window of averages of a certain number of data points

How does a waveform change when more points are added to a running average/boxcar filter?
it becomes more smooth as short fluxuations are eliminated, but temporal smearing also occurs and points at the end of the window are lost
Time frequency trade off
when frequencies are removed and waves are made more smooth and thus easier to analyze, timepoints at both ends of the window are also lost, resulting in temporal "smear" and loss of accuracy
What is a key difference between the points at which analog compared to digital filters can analyze?
digital filters can filter time using points before or after a given timepoint, while analog filters can only filter using points before a given timepoint
Pass band
the frequency region over which frequencies pass through the filter unchanged
stop band
the frequency region over which frequencies are attenuated
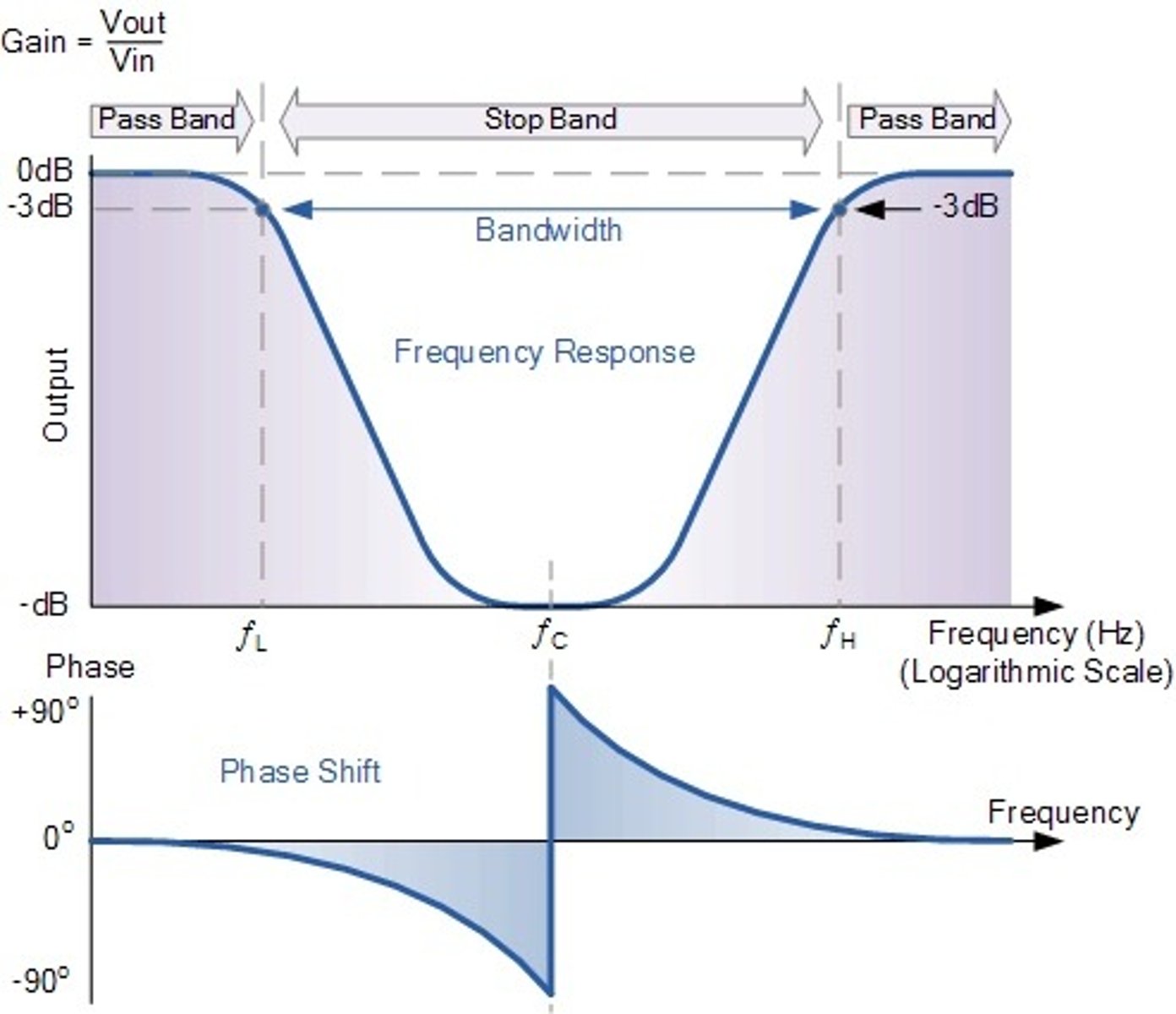
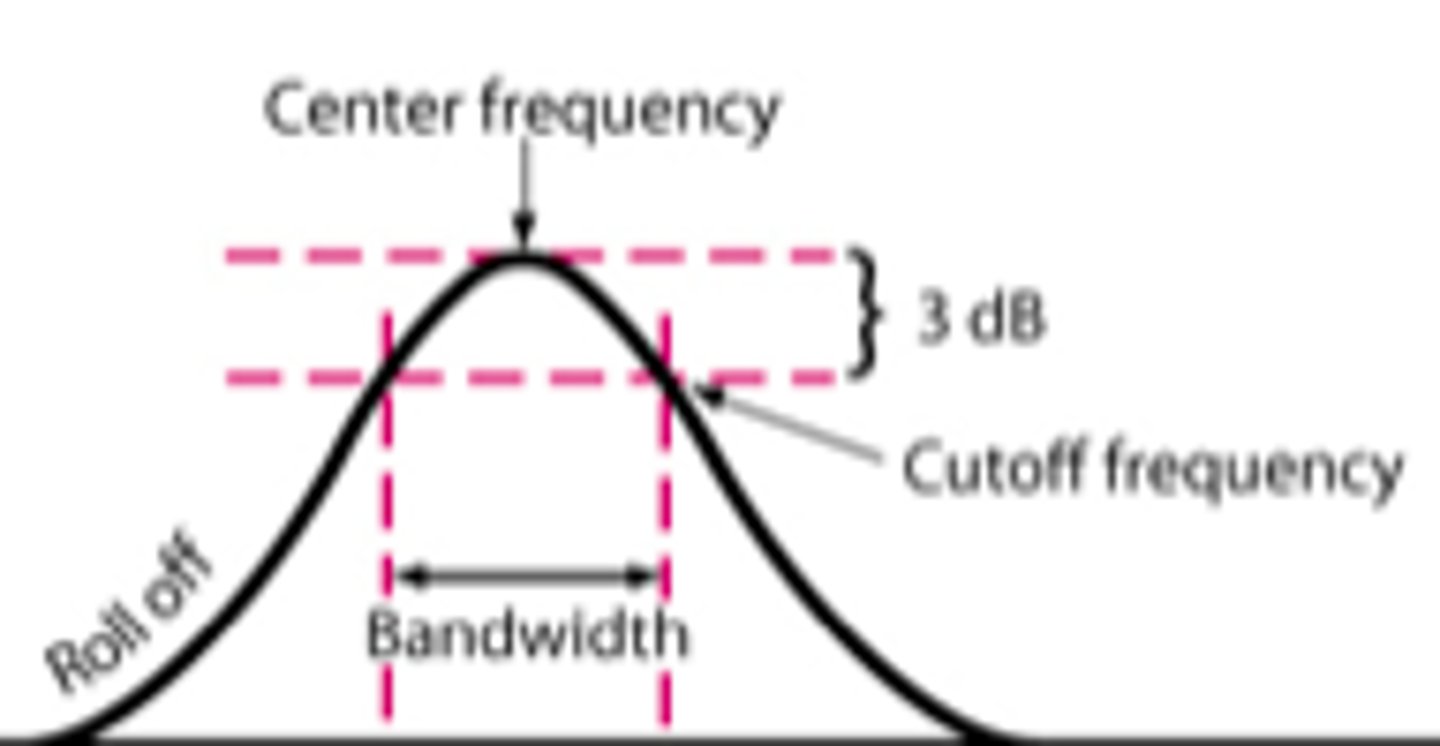
What is filter cutoff typically specified as?
the 50% amplitude cutoff, the frequency value at which 50% of a signal is passed (half amplitude or half power, -3dB)
cutoff slope
the steepness of the transition band of a filter
What are characteristics of a filter? (5)
1. analog or digital
2. low, high or band pass
3. cutoff frequency
4. cutoff slope
5. phase shifting vs zero phase (causal vs non-causal)
6 dB means...
50% drop in amplitude
3 dB means...
50% drop in power
Are high or low pass filters worse for signal distortion?
high pass, tend to have steeper transition bands
Butterworth Filter
Designed to have a gain which is maximally flat in the passband, have a capacitor, resistor, and inductor. Imitated by digital filters
Where is the cutoff for a filter normally put to prevent aliasing (analog low-pass filter)?
at 1/4 the Nyquist limit
What are guidelines for filtering? (3)
1. analog filtering should pass a broad range of frequencies to prevent phase shifting, but within the Nyquist limit
2. zero-phase (non-causal) filters only
3. only filter as much as needed