OCR Biology A-level - Cell Division
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Interphase
The stage in which normal growth and working take place
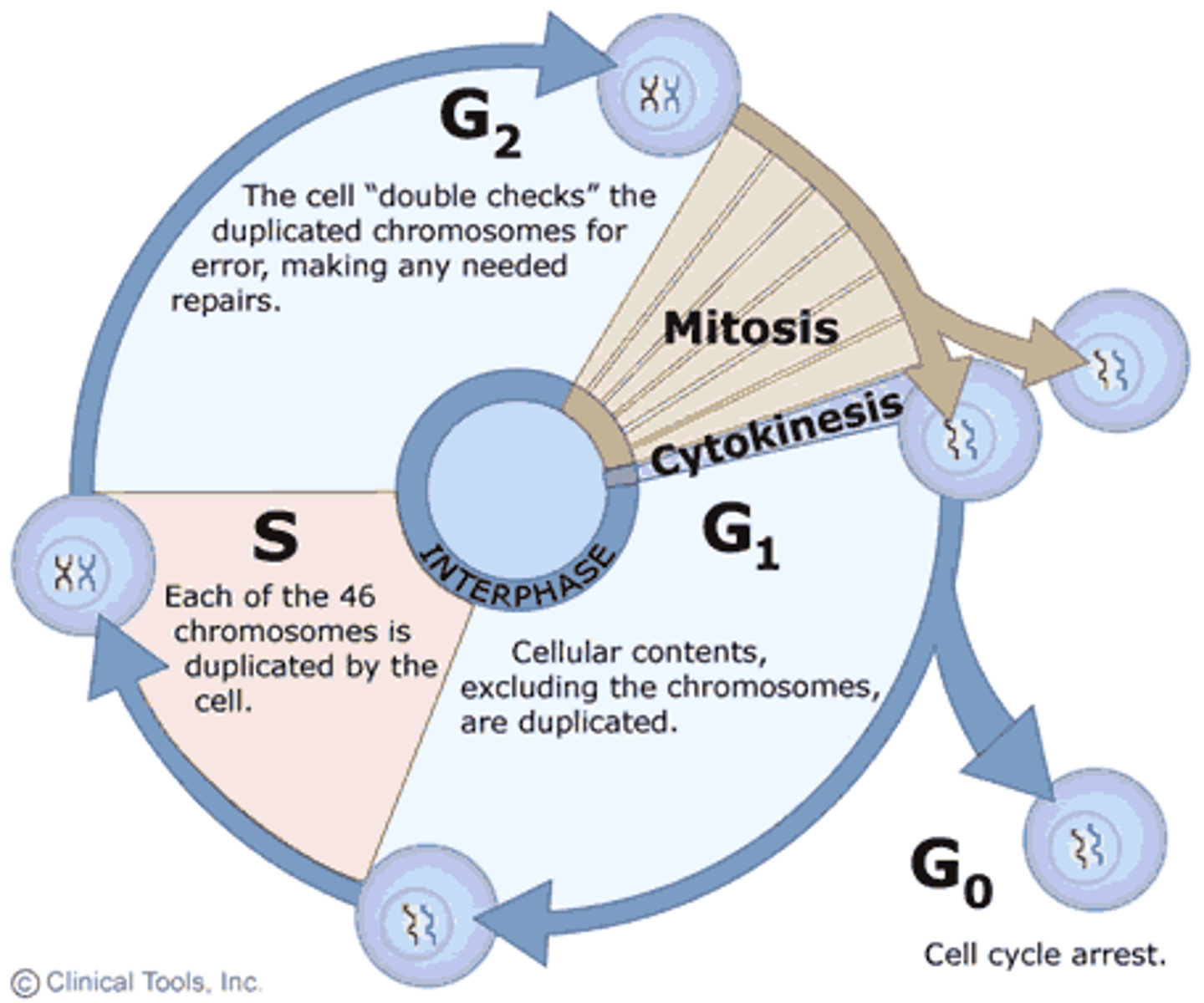
During interphase
DNA replicated + checked. Protein synthesis in the cytoplasm. Mitochondria grow + divide )in plant and algal cells). Chloroplasts grow + divide. Normal metabolic processes occur
Stages of interphase
G1 = 1st growth = proteins are synthesised, organelles replicate = cell increases in size.
S = synthesis = DNA replicates
G2 = 2nd growth = cell grows more, energy stores increase, duplicated DNA is checked for errors
Mitotic phase
The period of cell division
Stages of cell division
1. Mitosis 2. Cytokinesis
Mitosis
The nucleus divides
Cytokinesis
The cytoplasm divides and two cells are produced
G 0
The phase when the cell leaves the cycle, either temporarily or permanently.
Why might a cell leave a cycle (temporarily or permanently)
Differentiation, damaged DNA = cell arrest (G0), get older = more cells
Differentiation
A cell that becomes specialised to carry out a particular function is no longer able to divide. It will carry out the function indefinitely and not enter the cell cycle
How is the cell cycle controlled?
Checkpoints = monitor and verify whether each stage has been accurately completed before the cell goes in to the next phase.G1, G2 and metaphase checkpoints
Why are checkpoints important. 3 reasons.
Ensure cell divides when it's grown into the right size.
Replicated DNA is error free
Chromo see ones are in the correct position in mitosis
What are the requirements needed to be meet in the G1 checkpoint
Cell size
Nutrients
Growth factors
DNA Damage
G1 checkpoint. What's next.
After the G1 phase, before the S phase.
If the requirements are met then the checkpoint triggers the DNA replication, if not it enters resting state
What are the requirements needed to be meet in the G2 checkpoint
Cell size
DNA replication/DNA amage
G2 checkpoint
At the end of G2 phase, before the mitotic phase. DNA is checked. If it passes the cell initiates the molecular process that signifies the beginning of mitosis
What does mitosis produce?
The nuclear division, producing two, genetically identical daughter cells = exact copy of the parents DNA and same number of chromosomes.
What is the metaphase checkpoint
checks that chromosomes are attached to spindle and are alligned
What is mitosis
division of the nucleus
How many cells are produced. Are they genetically identical to parent cells
2. Yes they're genetically identical
When is mitosis used?
In multicellular organisms. Growth, replacement and repair of tissue. Also necessary for asexual reproduction
How do prokaryotic cells reproduce without a nucleus
Binary fission
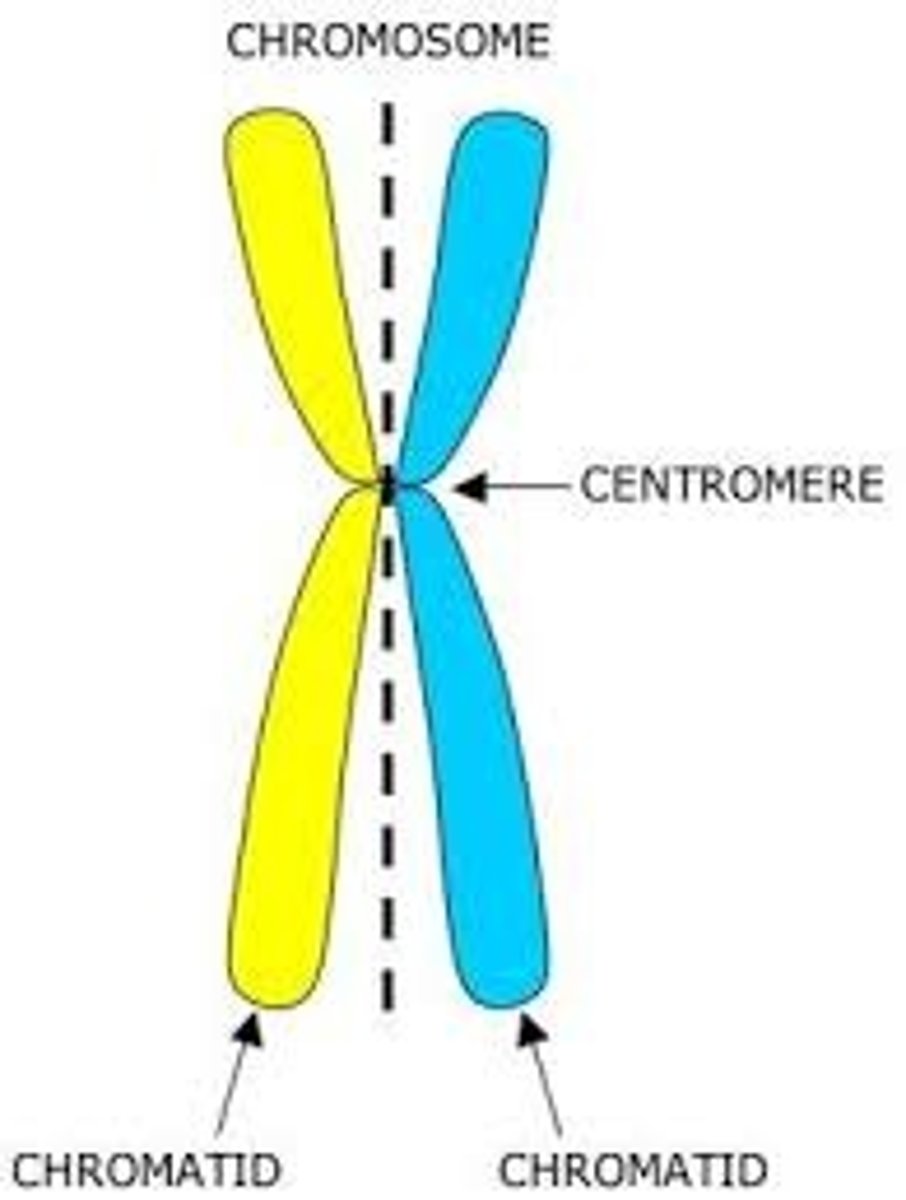
Chromosomes
Structures of condensed and coiled DNA in the form of chromatin.
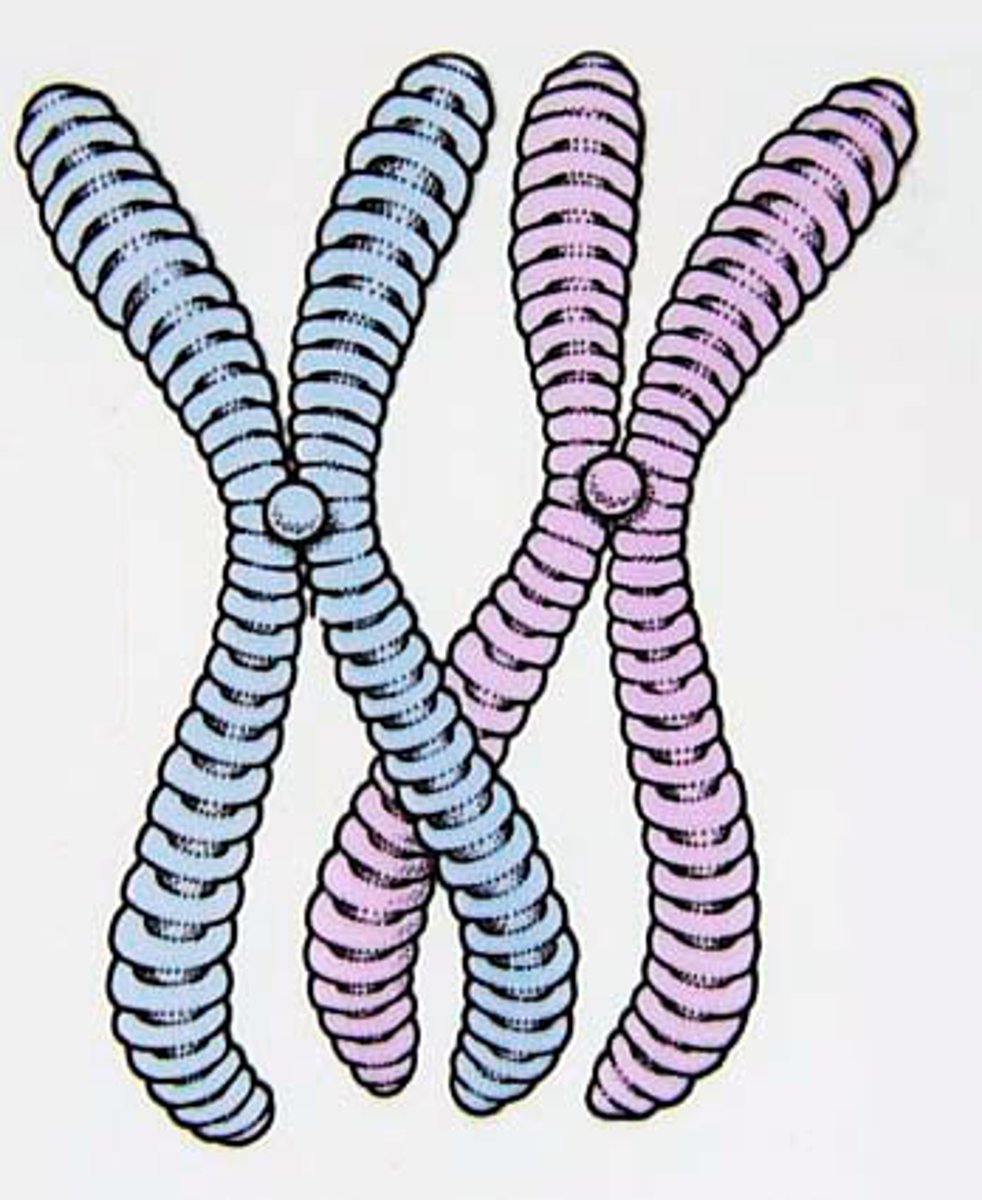
Chromatids
Two identical copies of DNA held together at the centromere
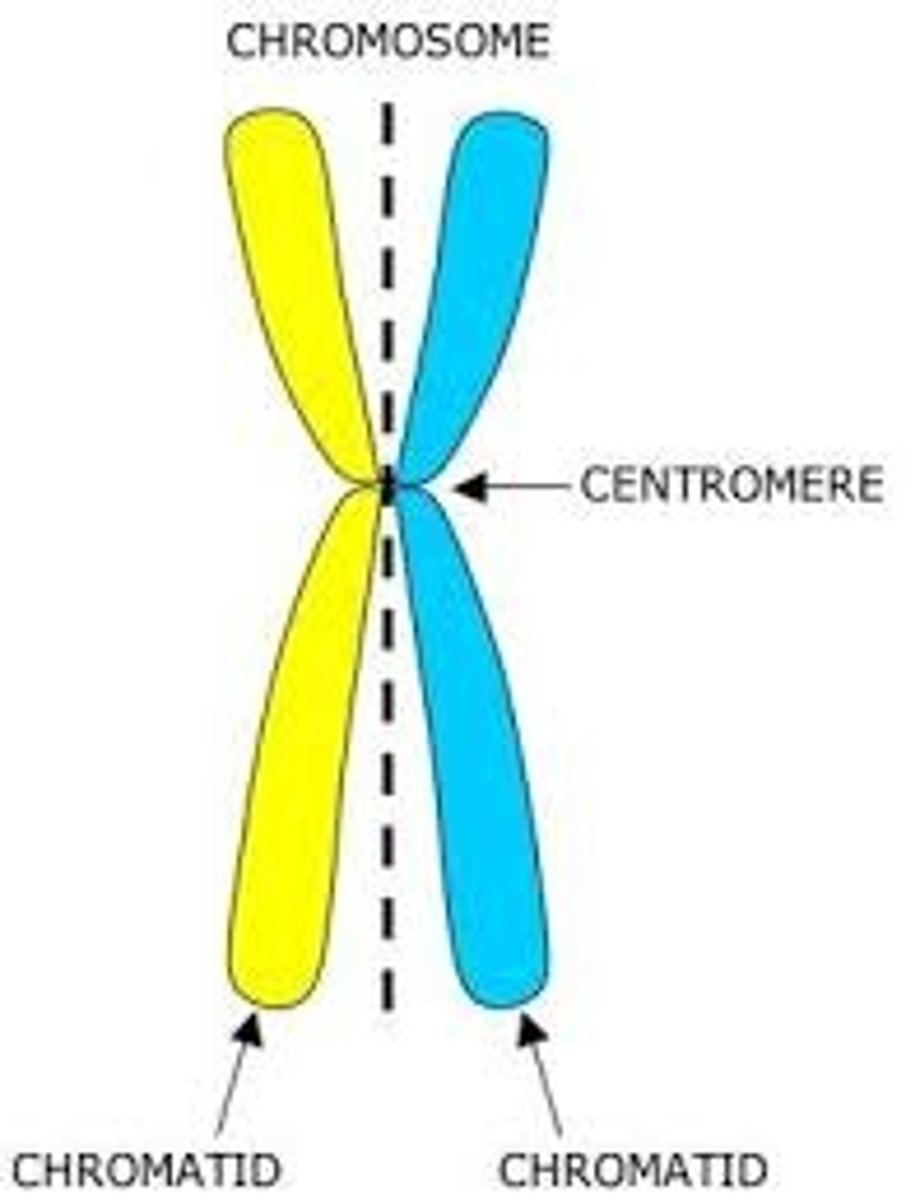
Centromere
A region where two chromatids are held together
Chromatin
Uncondensed DNA in a complex with histones
Stages of mitosis
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Prophase
Chromatin fibres start to coil and condense --> chromosomes. Nucleolus disappears. Nuclear envelope begins to break down.
Protein microtubules form spindle fibres = link poles = move chromosomes into correct place before division.
Centrioles migrate to poles.
Spindle fibres attach to specific areas on centromeres = start to move the chromosomes to the centre of the cell.
Nuclear envelope has disappeared

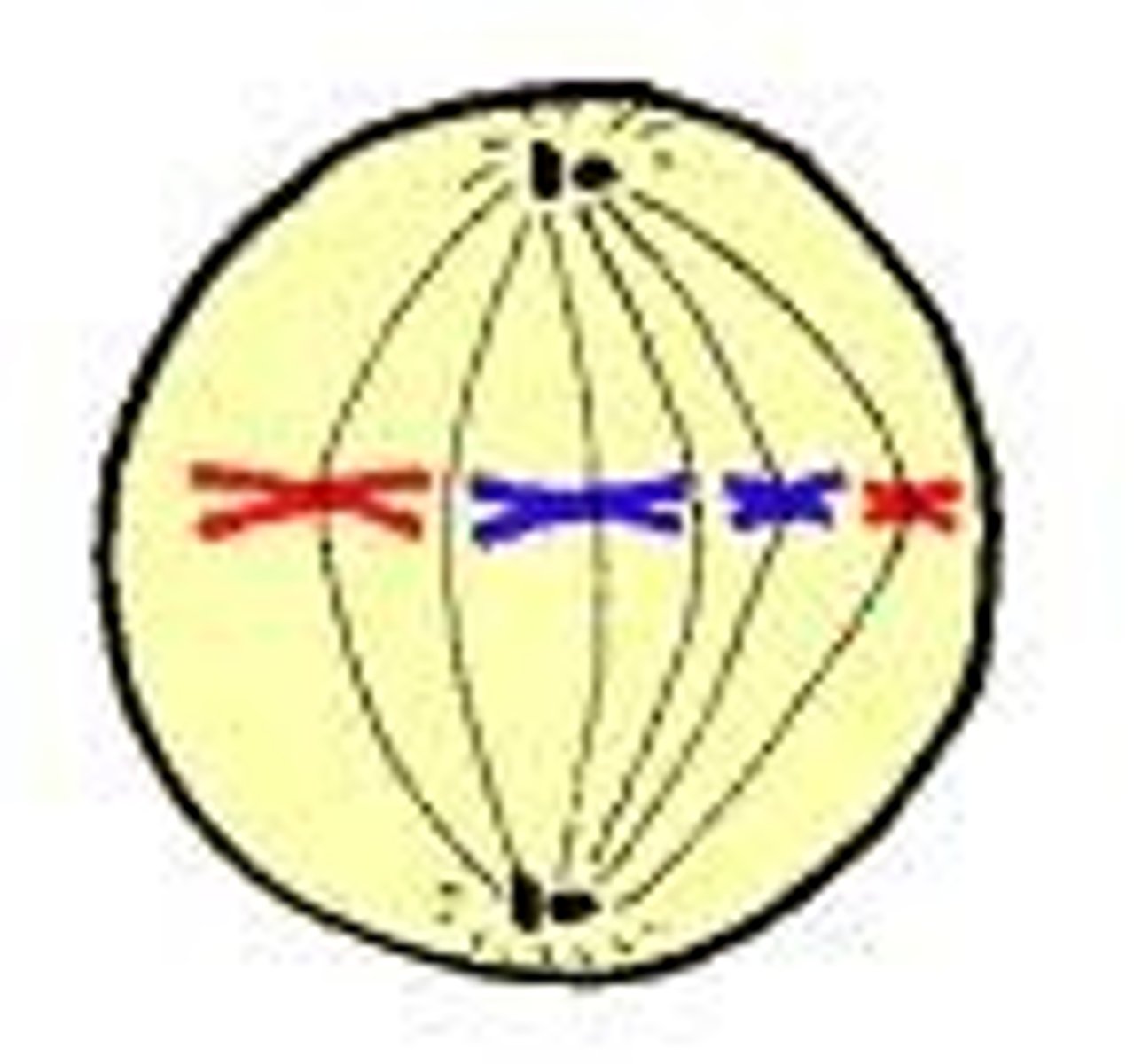
Metaphase
Chromosomes moved by spindle fibres = form plane in centre of cell (metaphase plate)
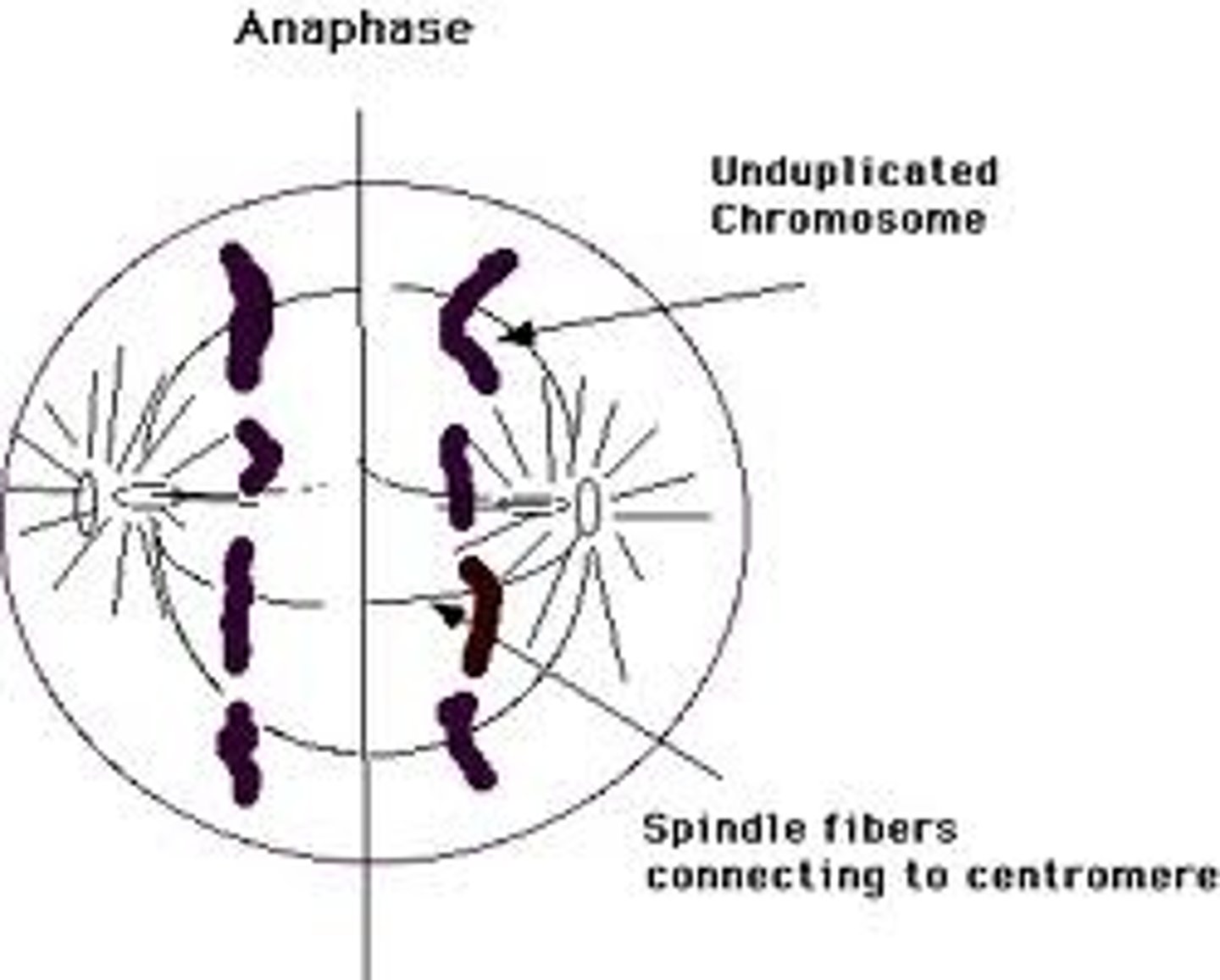
Anaphase
Centromeres in each chromosome divide and are pulled to poles. 'V' shape chromatids. Dragged through liquid cystol
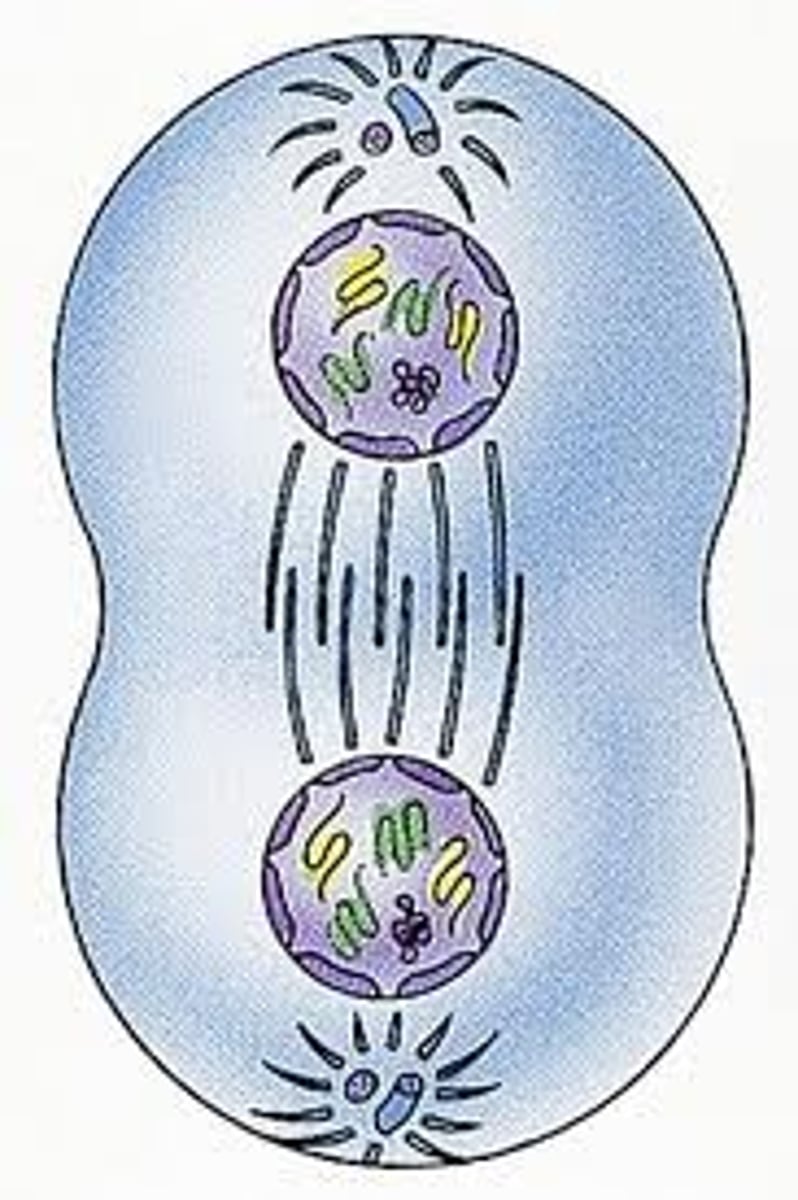
Telophase
Chromatids have reached poles and are now called chromosomes. Nuclear envelope reforms around the groups of chromosomes at each end. Chromosomes start to uncoil and nucleolus is formed. Cell division/cytokinesis begins
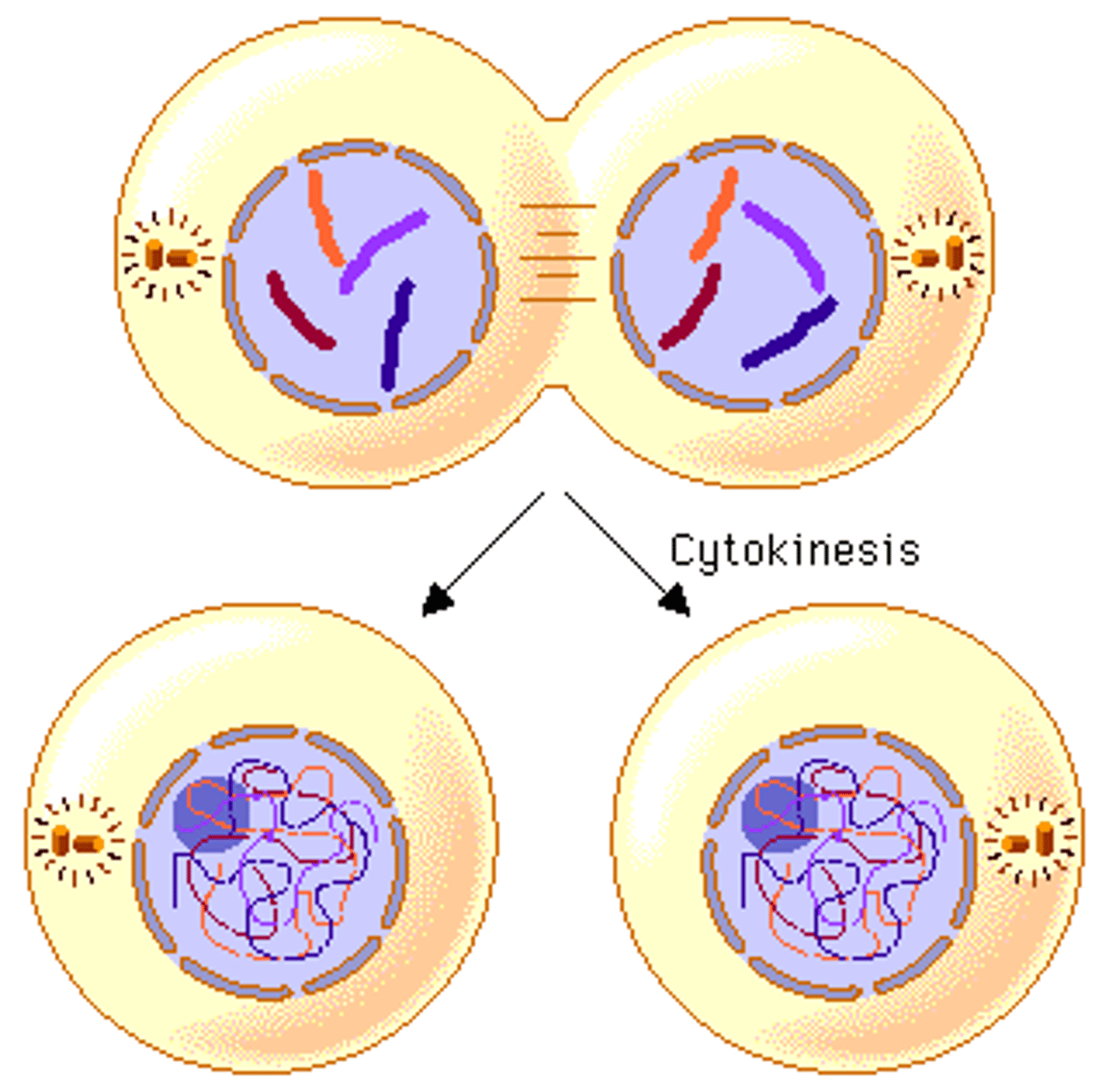
Cytokinesis in animal cells
A cleavage furrow forms in each side of the cell. The membrane is pulled in by the cytoskeleton until it is close enough to fuse = forming 2 cells
Cytokinesis in plant cells
Vesicles from the Golgi begin to assemble in the same place as the metaphase plate. The vesicles fuse with each other and the membrane, dividing into 2 cells. New sections of cell wall then form and the cell spilts
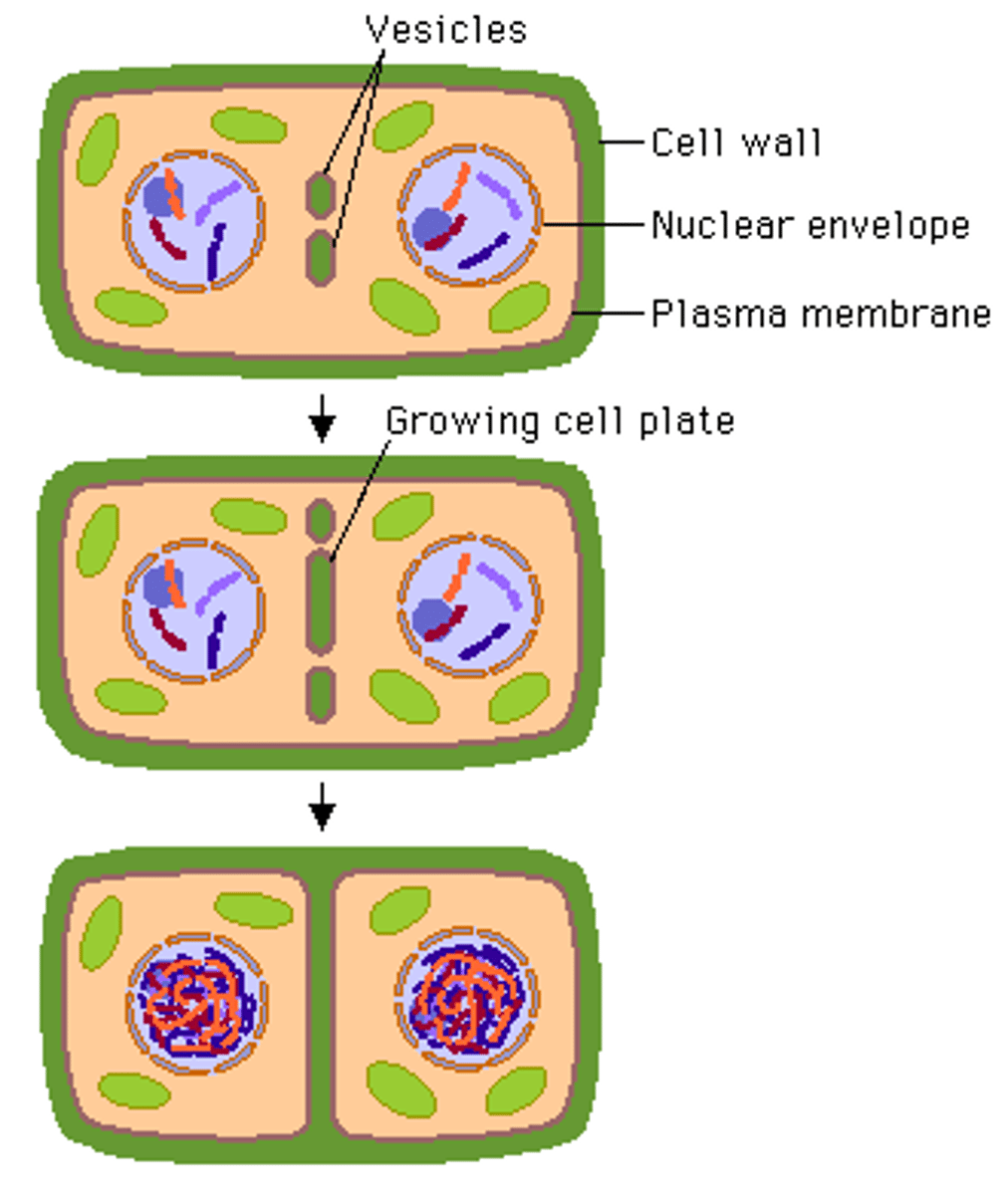
Why do plants cells not form a cleavage furrow
Have cell walls
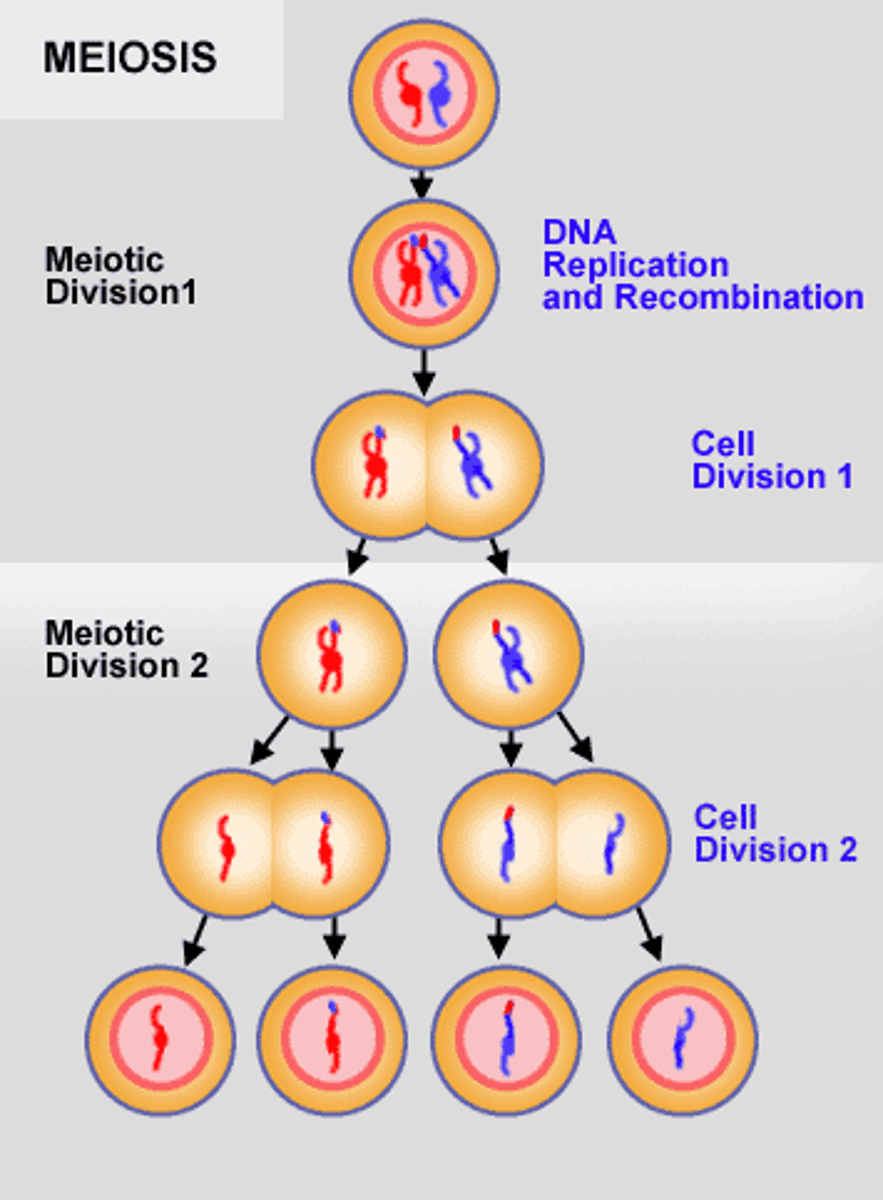
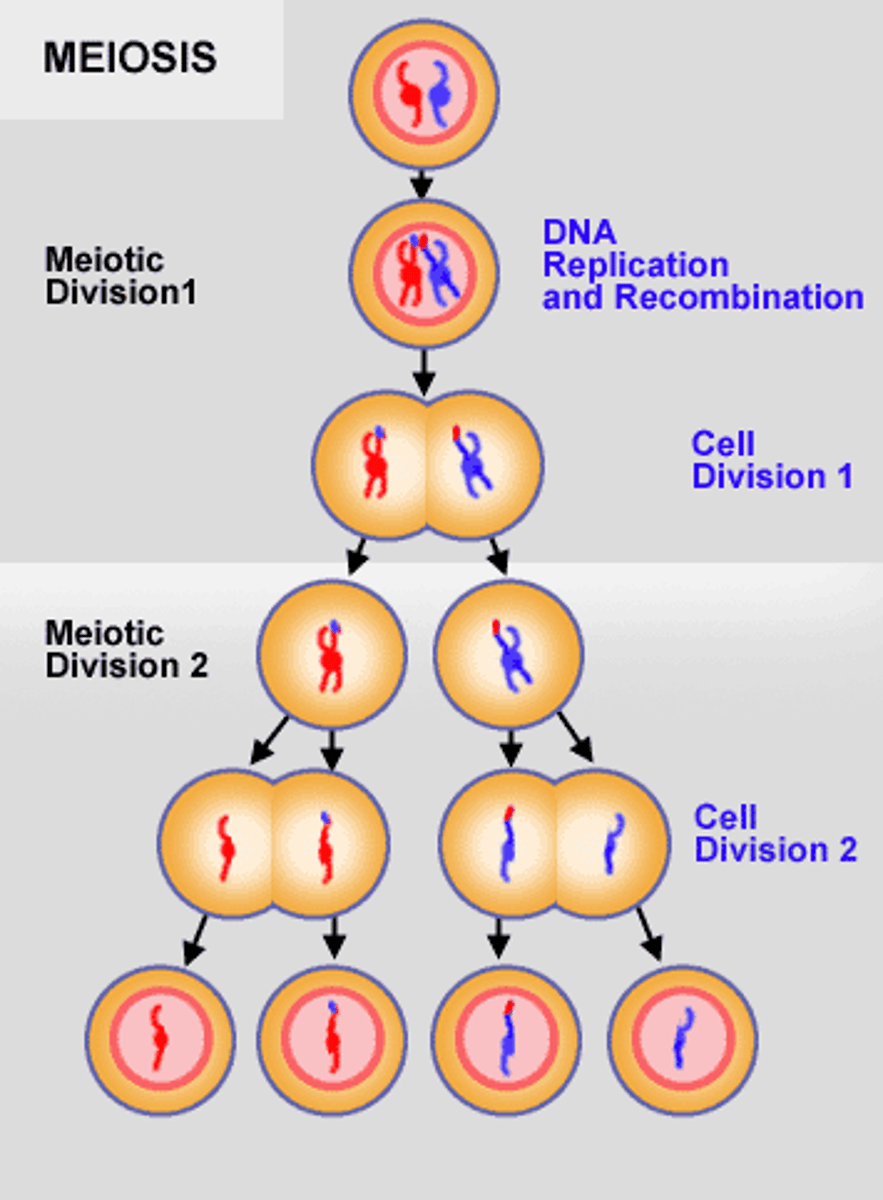
Meiosis
A form of cell division where the nucleus divides twice, resulting in half the number of chromosomes and producing 4 haploid cells from one diploid cell.
Gametes
Haploid sex cells produced by meiosis in organisms that reproduce sexually
Zygote
The initial diploid cell formed when 2 gametes are joined by the means of sexual reproduction (fertilised egg)
Haploid
Half the number of normal chromosome number; one chromosome of each type
What is produced during meiosis?
4 daughter cells - the gametes - that contain half the number of chromosomes of the parent
Homologous chromosomes
Matching pair of chromosomes, one from each parent
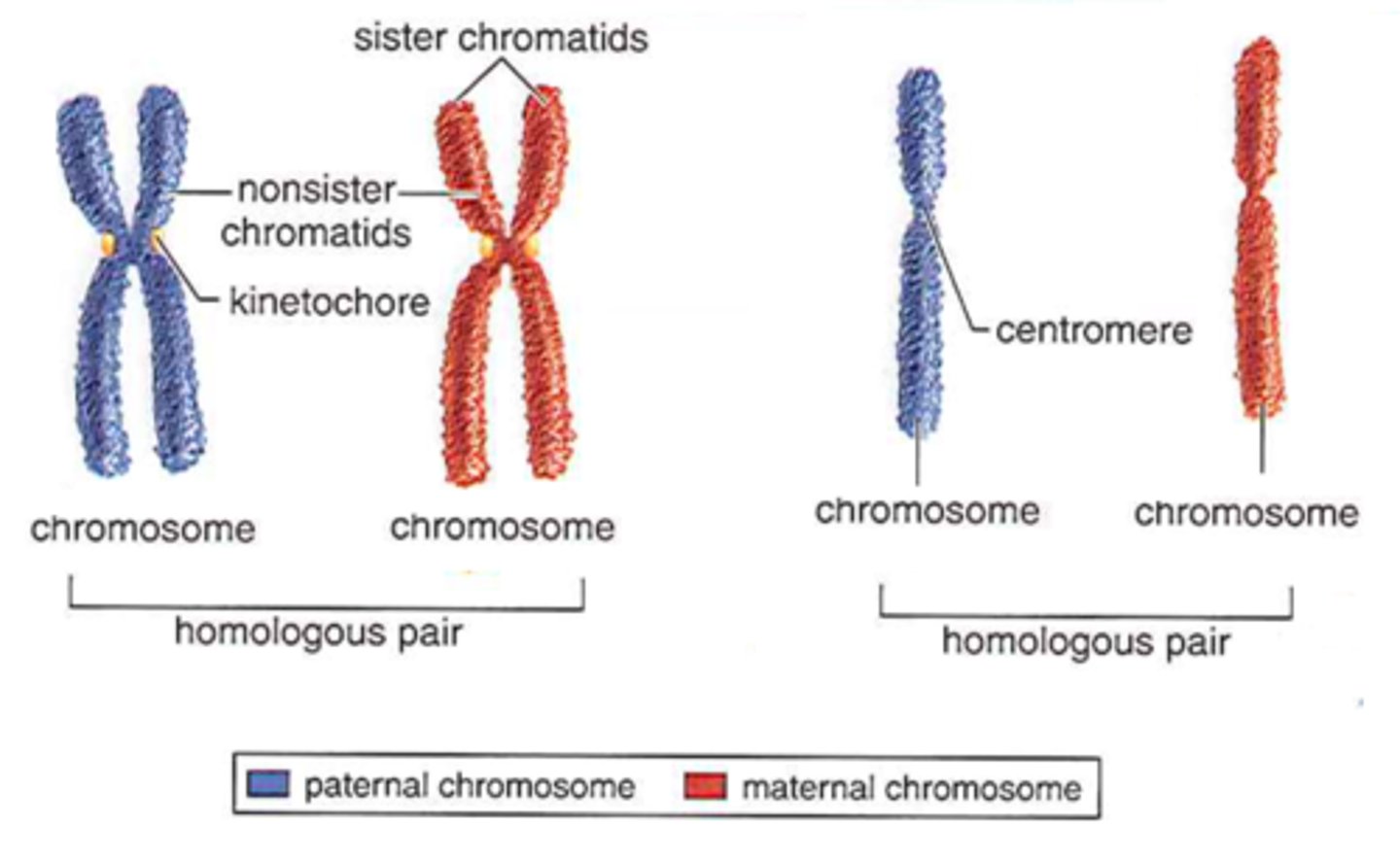
Alleles
Different versions of the same gene
Stages of meiosis
Meiosis 1 = Prophase 1, Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, Telophase 1
Meiosis 11 = Prophase 11, Metaphase 11, Anaphase 11, Telophase 11
Meiosis 1
The first division, the reduction division. The pairs of homologous chromosomes are separated into 2 cells. Each cell only contain one full set of genes instead of 2 = haploid
Meiosis 11
The second division (similar to mitosis), pairs of chromosomes in each daughter cell are separate, forming 2 more cells. 4 haploid cells are produced in total.
Prophase 1 (Meiosis 1)
Chromosomes condense, nuclear envelope disintegrates, nucleolus disappears and spindle formation begins, as in prophase of mitosis.
Difference = homologous chromosomes pair up --> bivalents. Chromatids entangle = crossing over.
Sections of DNA break off and re-join - sometimes resulting in the exchange of DNA. Exchange forms recombinant chromatids, with genes being exchanged between chromatids. Genetic variation occurs from the new combination of alleles = not identical
Metaphase 1
Homologous pairs assemble along the metaphase plate independently and randomly = genetic variation
What happens to homologous chromosomes during Anaphase 1?
Homologous chromosomes are pulled to opposite poles.
What is the state of sister chromatids during Anaphase 1?
Sister chromatids remain joined to each other.
What occurs during crossover in Anaphase 1?
Sister chromatids become entangled, break off, and rejoin at chiasmata.
What is the result of DNA swapping during Anaphase 1?
Genetic variation.
Telophase 1
Chromosomes assemble at each pole, nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes uncoil.
Cell undergoes cytokinesis and divides in two = haploid.
Genetic variation
A variety of different combinations of alleles in a population.
Independent assortment
The arrangement of each homologous chromosome pair in metaphase 1 and 2 of meiosis is independent of each other and results in genetic variation
Crossing over
Sections of DNA which become entangled, breaks and re-joins during prophase 1 of meiosis = genetic variation
Prophase 11
The chromosomes, which still consist of two chromatids, condense and become visible again. Nuclear envelope breaks down and spindles formation begins.
Metaphase 11
Individual chromosomes assemble on the metaphase plate.
Due to crossing over, the chromatids are not identical, there is independent assortment and more genetic variation is produced.
Anaphase 11
Results in the chromatids of the individual chromosomes being pulled to opposite poles after division of the centromere
Telophase 11
Chromatids assemble at the poles. The chromosomes uncoil and form chromatin again. Nuclear envelope reforms and the nucleolus becomes visible.
Cytokinesis results in the division of cells forming 4 daughter cells. Cells are haploid because of the reduction division. They will be genetically different from each other and the parent cell due to crossing over and independent assortment
What are stem cells
unspecialized cells from which differentiated cells develop
Erythrocytes function, structure and adaptations
Flattened biconcave shape which increases sa:vol.
NO nuclei/organelles= increases space available for haemoglobin .
Flexible= squeez through narrow capillaries
Neutrophils function, structure and adaptations
Multi-lobed nucleus= easy for them to squeez through small gaps to get to site of infection.
Granular cytoplasm= lysosomes containing enzymes to attack pathogens
Squamous epithelium function, structure and adaptations
Thin due to flat cells and is 1 cell thick. Aids rapid diffusion of oxygen into the blood. Lines alveoli
Palisade cells function, structure and adaptations
Present in mesophil, contain chloroplast to absorb light for photosynthesis. Thin cell walls increasing rate of diffusion for CO2. Large vacuole maintain turgor pressure. Chloroplast move to absorb more light.
Root hair cells function, structure and adaptations
Present on surface of roots at growing tips. Increase SA of cell (hairs). Maximises H20 and minerals from soil.
Cartilage function, structure and adaptations
Connective tissue, contains elastin and callogen. Firm and flexible. Composed of chondrocyte cells embedded in an extracellular matrix. Prevention of ends of bones from rubbing
What's an organ
A group of different tissues that work together to perform a certain function.
What's an organ system?
A group of organs working together to perform a particular function
What is the epidermis of a plant tissue
Cover plant surfaces. Single layer of closely packed cells. Covered by waxy, waterproof cuticle= reduce loss of h2o. Stoma present in epidermis. Allows 2 gases and water in and out.
What are is xylems structure and function
Vascular tissue transporting water and mineral ions. Vessel elements= elongated dead cells. Walls strengthened by waterproof material called lignin provide structural support
What is phloems structure and function
Vascular tissue transporting ssucrose assimilates from from leaves and stems. Has ST cells seperated by seive plates