Biochem Lab Final
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
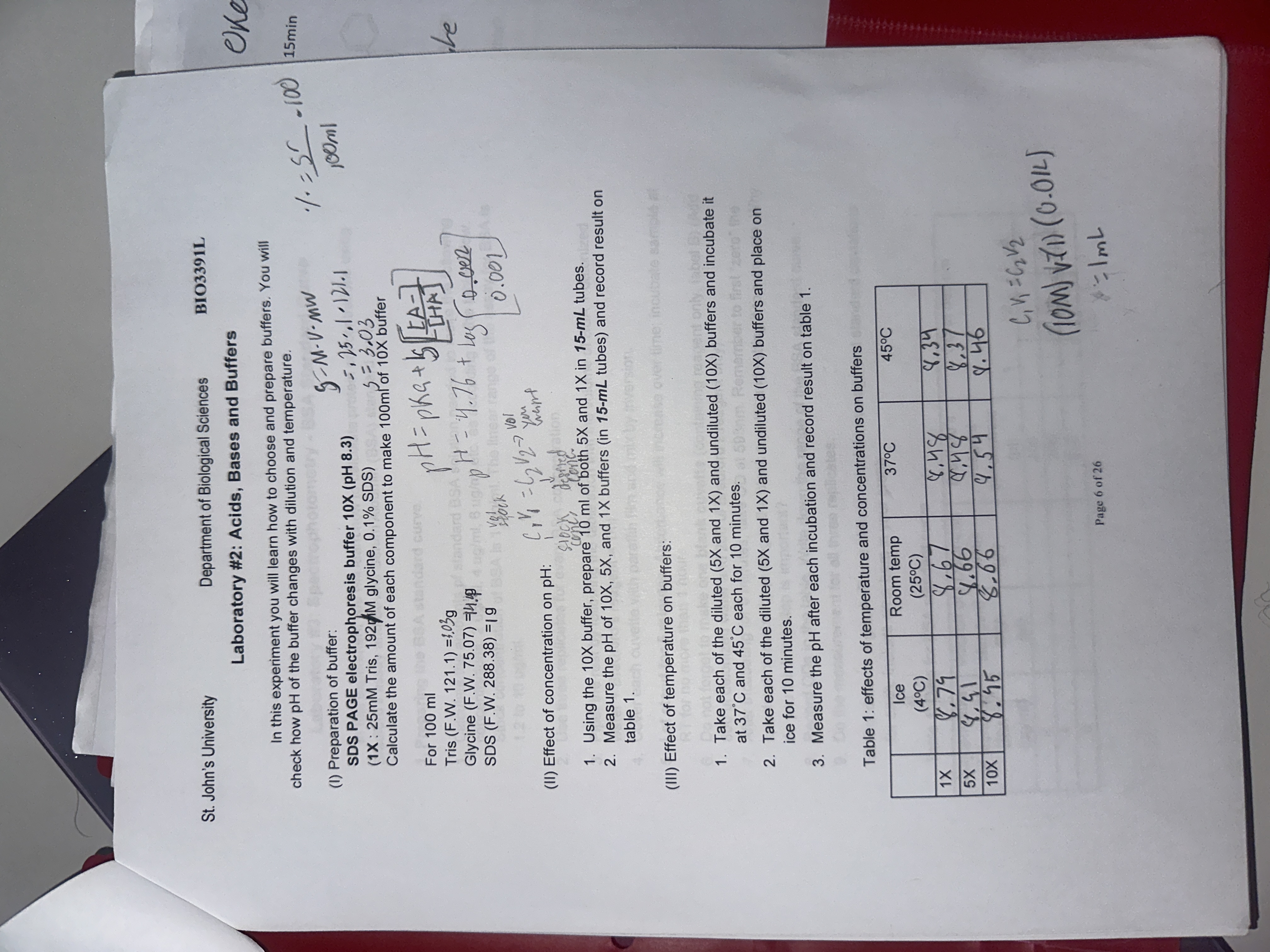
Metric System
Set of standard units defined to measure length, weight, capacity (volume) It is based on the decimal system as it includes numbers in powers of 10.
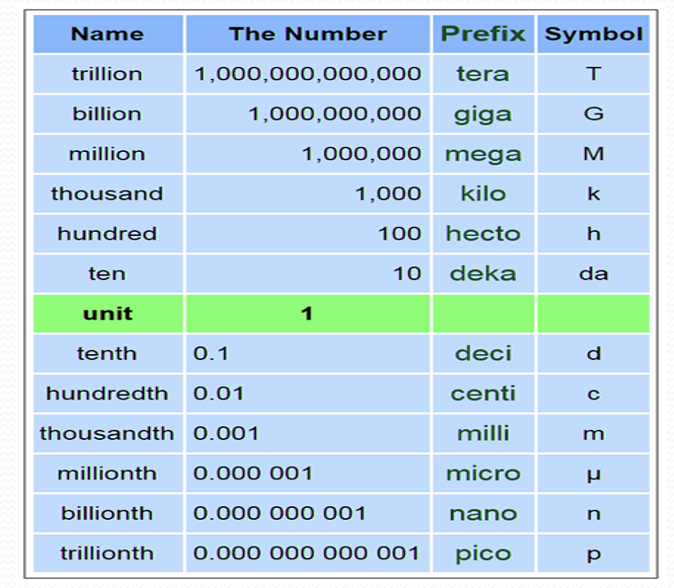
Metric Units
1Liter (L) | 1000 milli liter (mL) |
1 mL | 1000 micro-liter (µL) |
1Gram(g) | 1000 milli grams (mg) |
1 mg | 1000 micro-grams |
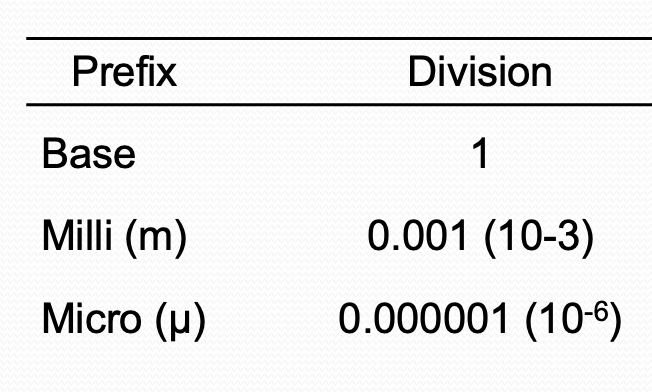
Metric Conversion
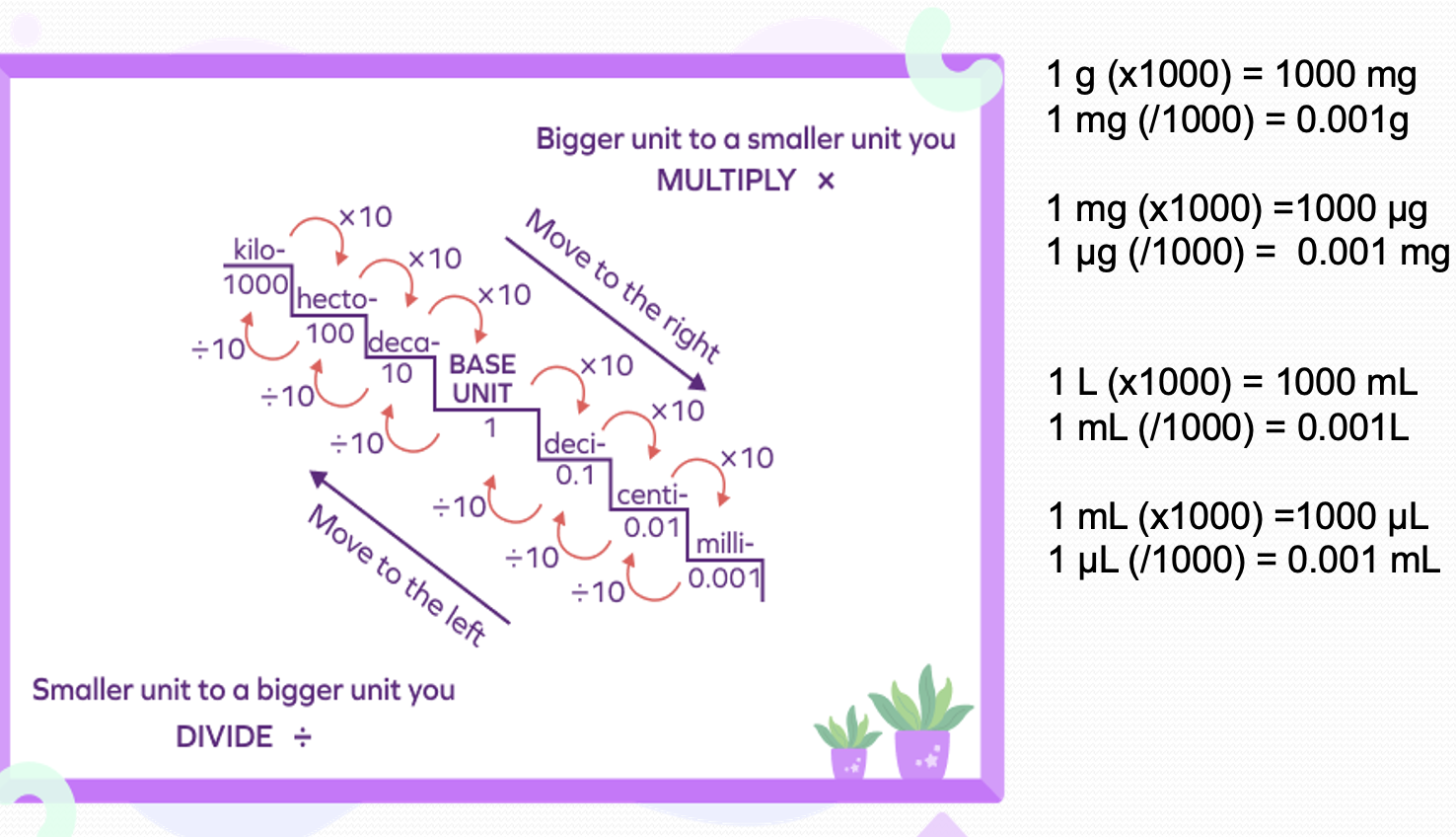
Solution
A homogeneous mixture (components are uniformly distributed) composed of two or more substances
Solute
A substance dissolved in another substance
Solvent
A substance that dissolves a solute
Concentration
A measure of the amount of solute that has been dissolved in a specified amount of solvent or solution
Lab 1 Calculations
Solute(gr) = M.W.(Molecular Weight) M(Molar) * V(Liter)
Molarity (M) = Moles of solute/Liters of solution
Molarity = Mass of the solute/(Molar mass of the solute)(Vol. of soln. in liters)
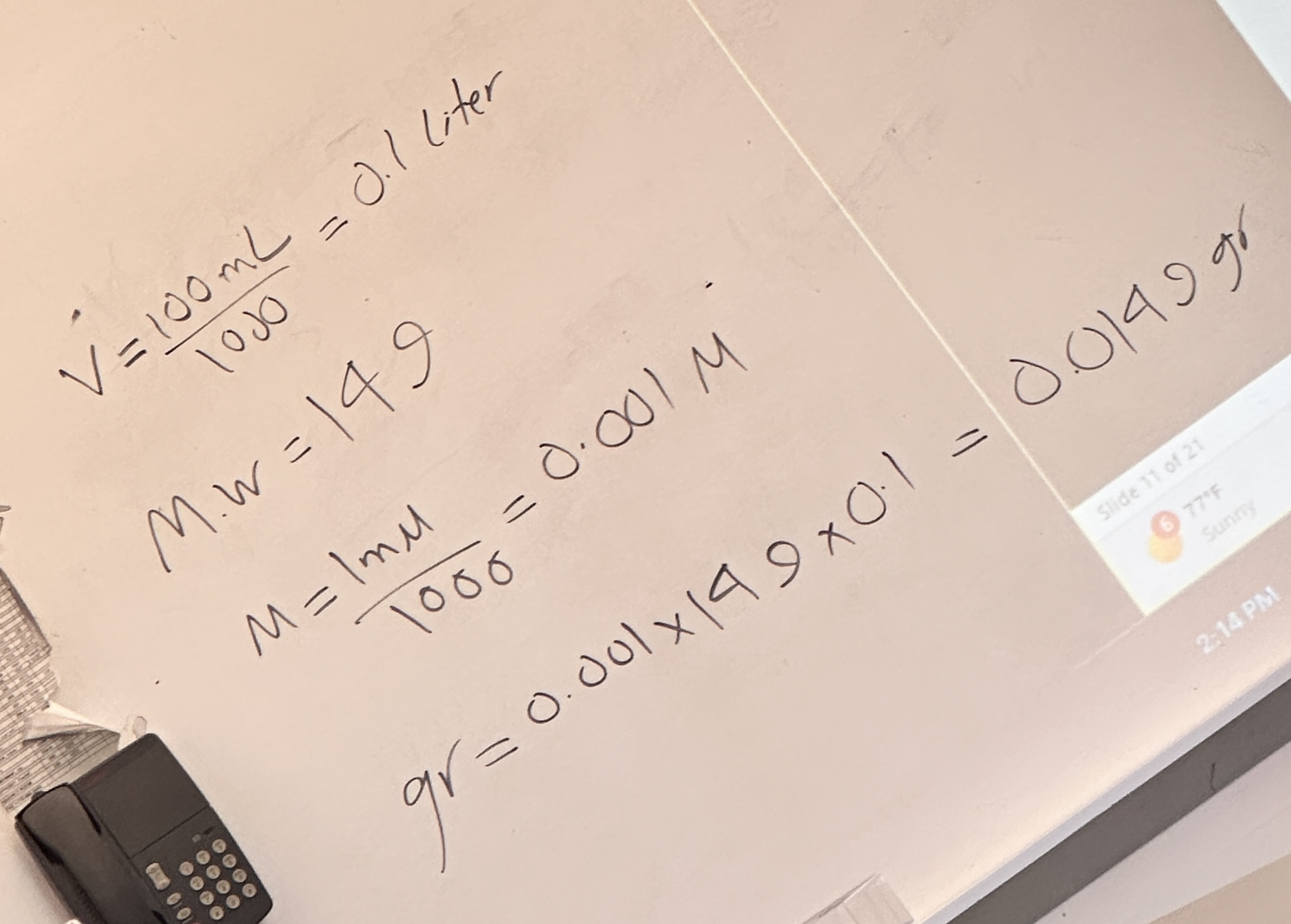
Molarity
A measure of how much of a substance is dissolved in a solution
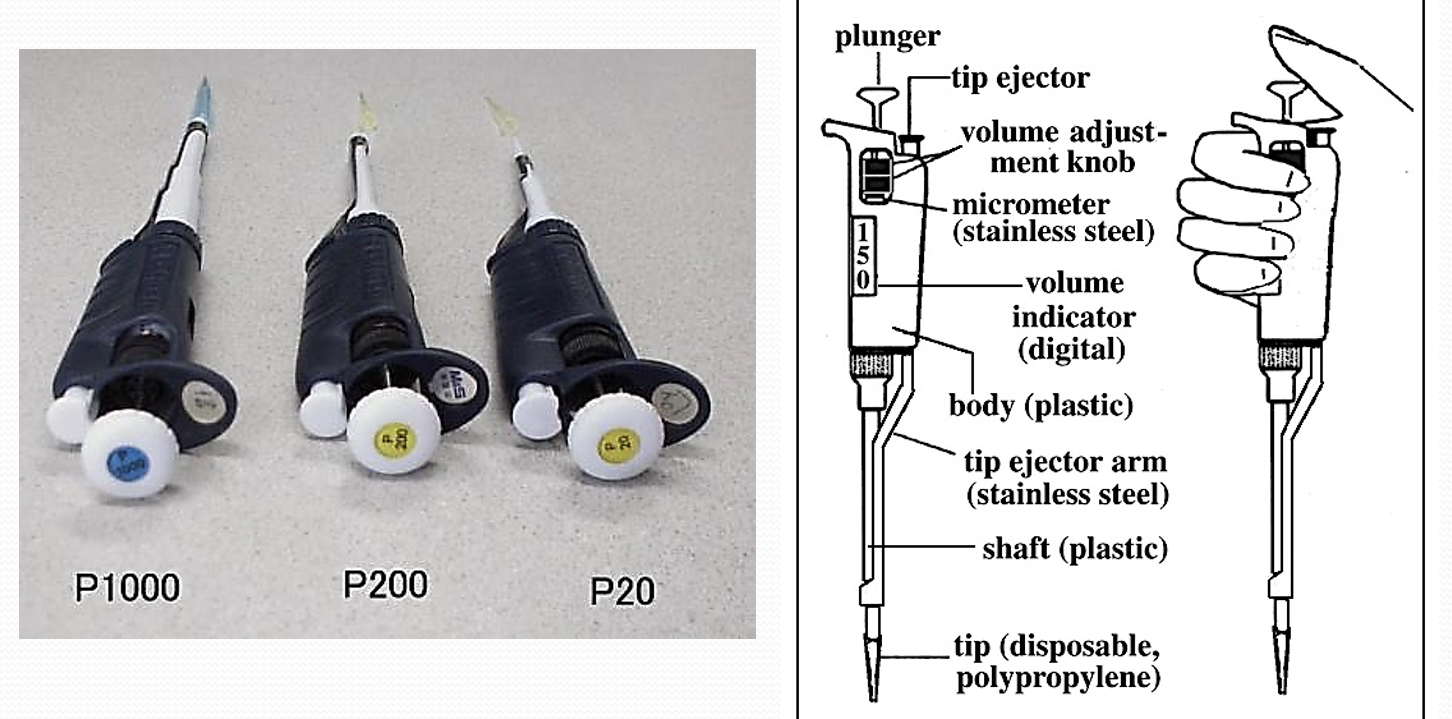
Micropipettors
Accurate, precise, and rapid dispensing of volumes
From 1-10,000µL
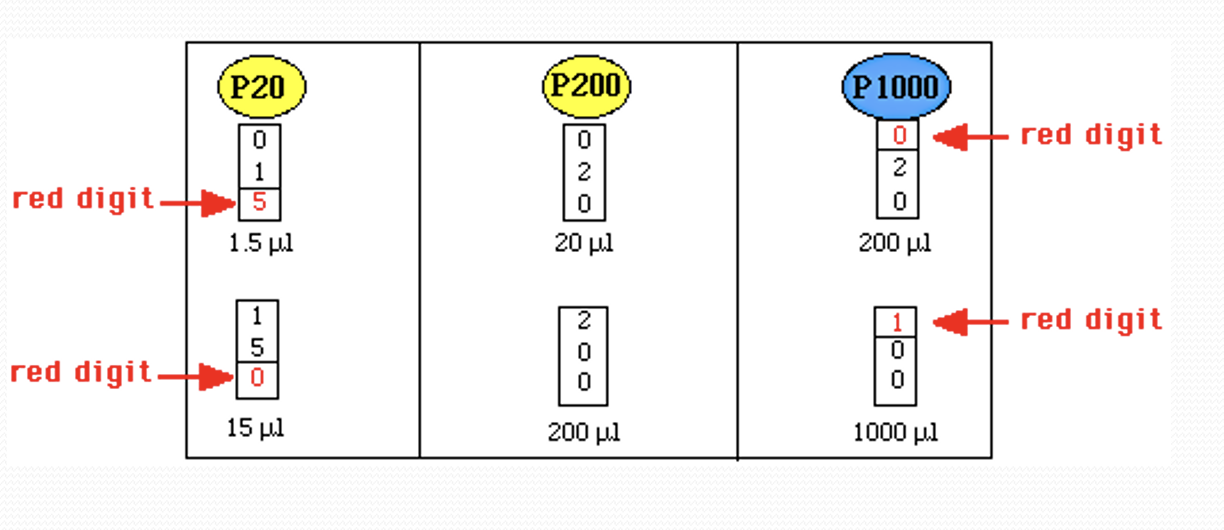
The “0” is the decimal point
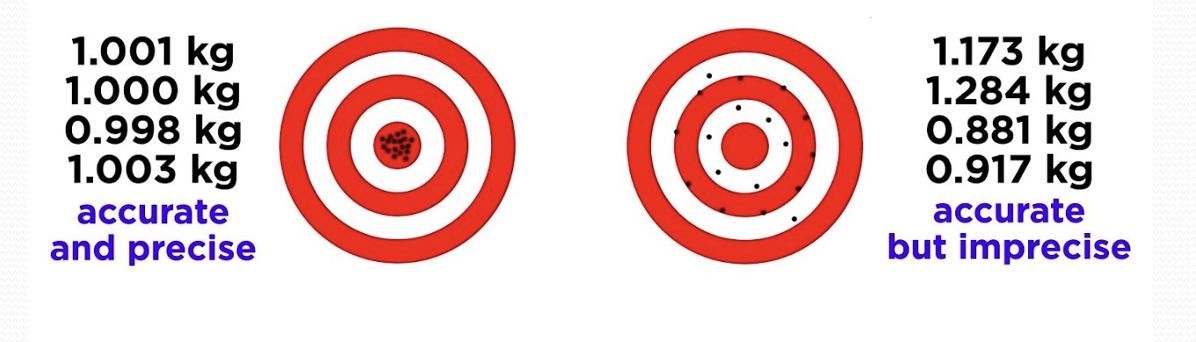
Precision
Extent of agreement among repeated measurement

Accuracy
Difference between experimental value and expected (true) value
Standard Deviation (S.D.)
How widely spread or dispersed the values in a data set are from the average or expected value
A low standard deviation means that most of the numbers are close to the expected value. A high standard deviation means that the numbers are more spread out
Percent Error
% Error = (measured - true value)/true value * 100
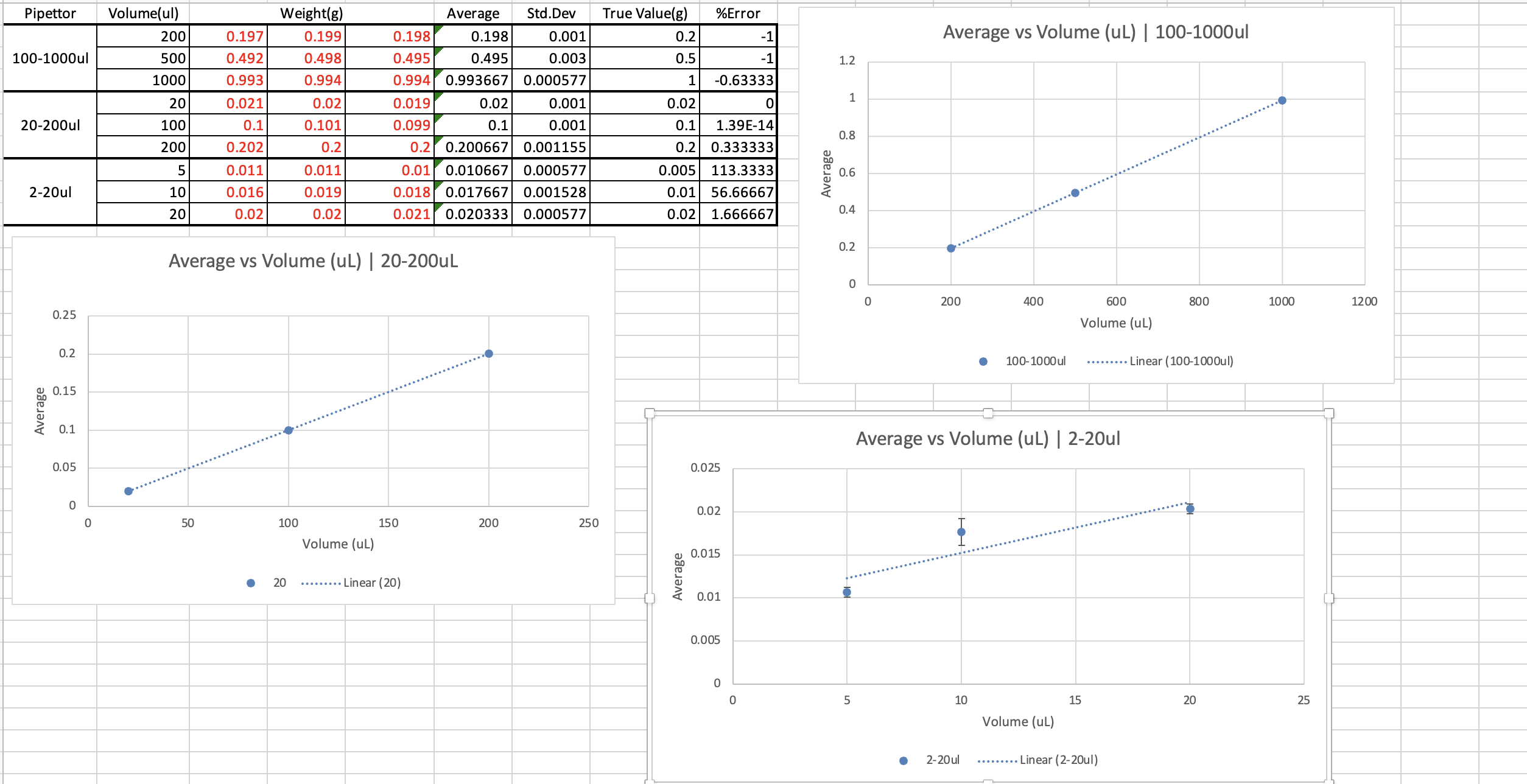
Lab 1 Experiment
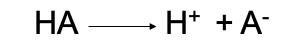
Strong Acid
A compound containing a hydrogen ion that it can give up to the solution (dissociation is complete)
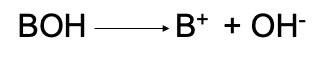
Strong Base
A compound that yields a hydroxyl ion when dissolved in water (dissociation is complete)
Weak Acids
Don’t dissociate completely in water
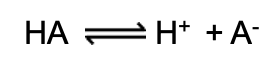
Assessing Acid Strength
Equilibrium constant or dissociation constant
Tendency to lose protons/hydrogen ions
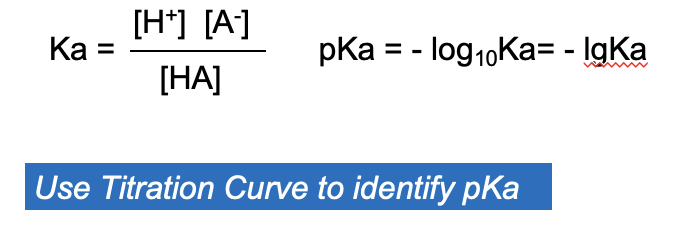
Titration
A technique to determine the concentration of an unknown solution
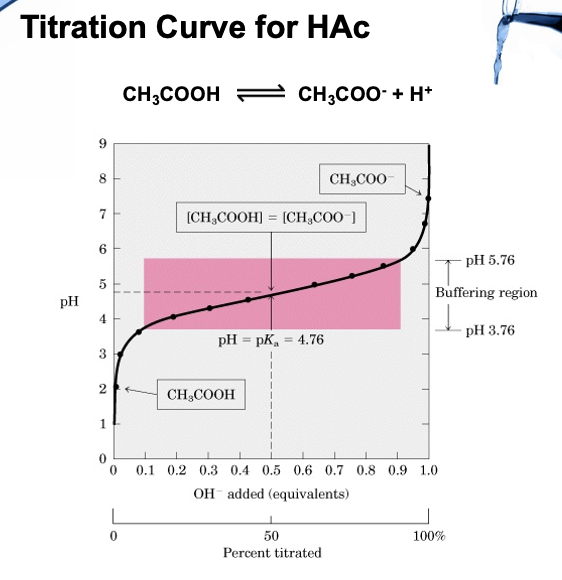
Equivalence Point
At the equivalence point in an acid-base titration, moles of base = moles of acid and the solution only contains salt and water
Buffers
Solutions containing a weak acid and its conjugated base are capable of resisting changes in pH upon addition of small amount of acid or base
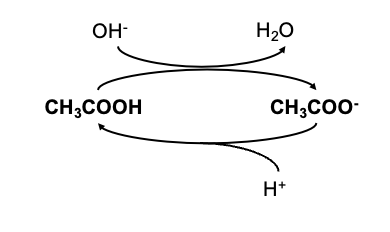
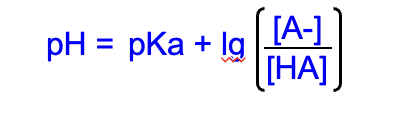
Henderson-Hasselbach Equation
Lab 2 Experiment