Soils Exam 2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
The 1° soil particels
Defined on the basis of EFFECTIVE DIAMETER and include sand, silt, and clay.
The three types of soil particles are
Sand, Silt, and Clay
Sand
2 - 0.05 mm diameter
Irregular in size and shape
Primary mineral is quartz (siliceous)
Big pores
Low soil organic matter which means little material holding it together. This leads to high erosion rate
Does not compact well
Silt
0.05 - 0.002 mm diameter
Irregular size and shape
high pH resistance and water holding
Somewhat good compatibility (depending on how much weight there is)
Susceptible to wind and water erosion
Clay
< 0.002mm diameter
< 0.001mm diameter is “colloidal”
Aluminosilicates base = crystalline structure
Fe & Al oxide base = between crystalline to amorphous structure
Slow drainage rate with poor aeration. This causes high water holding capacity
High soil organic matter and fertility
Very compactable
LARGE SURFACE AREA
When soil is aggregated (clumped)
The soil is not susceptible to wind/water erosion
When soil is dispersed (not clumped)
The soil is susceptible to wind/water erosion
Is Poorly Drained soil ALWAYS poorly aerated?
NO. Poorly Drained soil is NOT always poorly aerated
The 2° soil particles
Defined as the aggregation of 1° particles
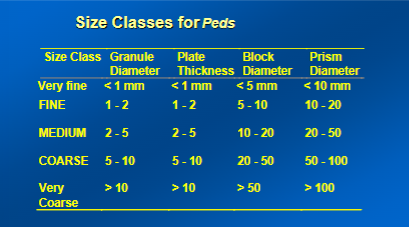
Soil Structure is characterized by
Shape, Grade, and Size
What are the different shapes of soil?
Granular (porous)
O horizon
Crumb (very porous)
O horizon
Platy
Horizontal plates
Not very porous
B horizon
Angular Blocky
Block shape
Subsoil
Sub-angular blocky
Similar to angular block but not as sharp edges
Columnar
Columns shaped
Found in dry, calcified regions
Prismatic
Vertical orientation
Bx horizon
Example: Fragipan
What are the different grades of soil?
Weak
Poorly formed, in distinct peds, barely observable in place
Moderate
Well formed peds evident in undisturbed soil
Strong
Well formed peds distinct in undisturbed soil
What are the different sizes of soil?
Very Fine
Fine
Medium
Coarse
Very Coarse
Aggregated Formation (Soil Structure Genesis)
Physical Processes
Wetting and drying
Freezing and thawing
Physical effects of roots and other organisms
Aggregated Stability (Soil Structure Genesis)
Soil organic Matter
Microbial decomposition products
root exudates
fungal hyphae exudates (glomalin)
Inorganic Material (interacts with organic material)
Silicate Clay
Fe and Al oxides
Cations (polyvalent = flocculation)
Ex: anything with more than one cation (+2, +3, +4)
Some are monovalent = dispersion (anything with one cation (+1))
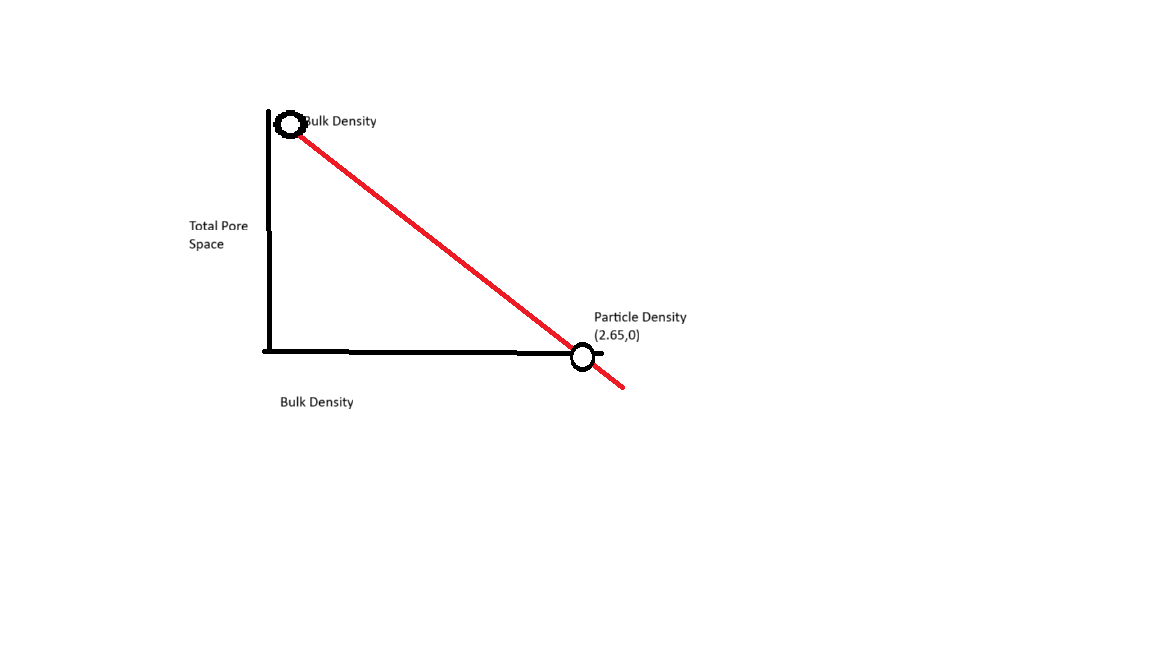
Bulk Density (Db)
Mass per unit volume of DRY UNDISTURBED soil
Particle Density (Dp) always equals
2.65 Mg/m3
This is the general particle density of things around Central New York
Another term for Dp is Specific Gravity
Total Pore Space (TPS) %
Volume solids = (Db/Dp)*100
Volume pores = 100 - volume solids
TPS = 100 - [(Db/Dp)*100]
TPS = (1 - Db/Dp)*100
Does Db have pores? What about Dp?
Db = WITH pores
Dp = WITHOUT pores
Structure = fn (Clay, SOM)
Aggregated has stability and holds things together
When SOM comes together = HUMIFIED
Horizons Oe and Oi are NOT humified
What must you have in order have water stable aggregates?
You must have CLAY
Sands do not form water stable aggregates
Smaller particles come together to form large particles
Water Stable aggregates
Clusters of soil particles bound together that resist falling apart when wet
What is the most important thing to remember when it comes to Structure and texture?
You can always change or alter soil structure but you can NOT change texture
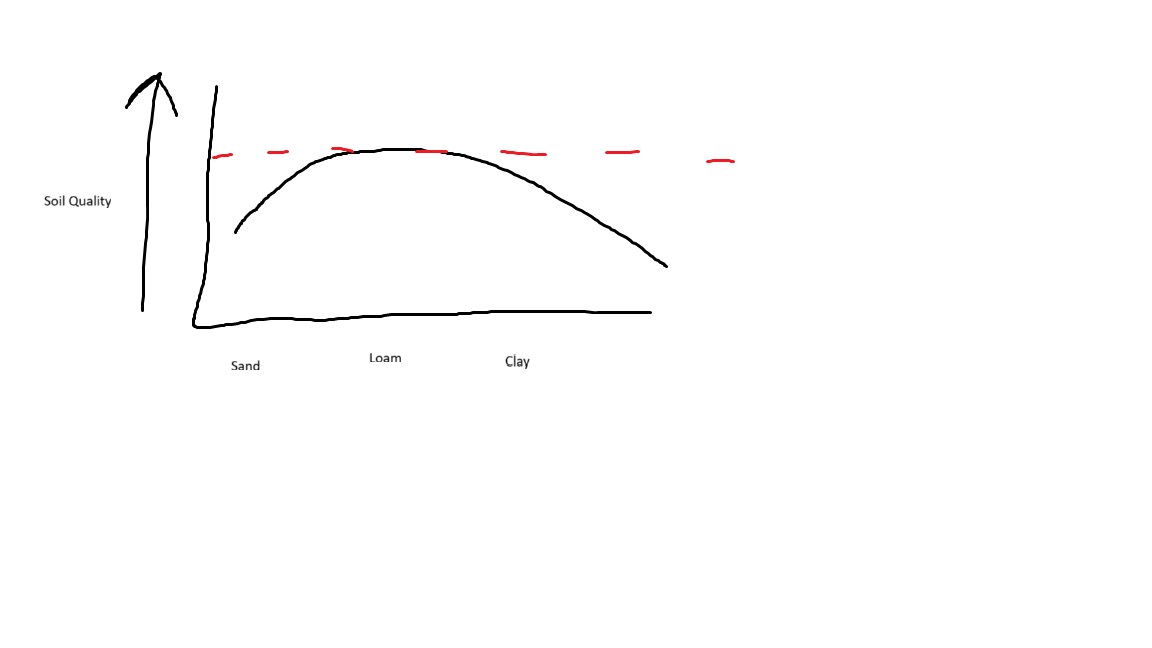
Relation between Site Quality and Soil Texture
What’s up with the red line?
The max quality of undisturbed, not touched soil
Structural development can improve this
Structure can work with texture in order to improve this
Limitations on Sand:
Nutrients and Minerals
Water retention
Limitations on Clay:
Lack of drainage and large pores
Little to no aeration
What is an easy way to measure volume
Displacement by water
Specific Gravity
AKA Dp (Particle Density)
Usually a property of crystal structure and chemical composition
Example: Quartz and feldspar is the bulk of the minerals for the central New York region. The average specific gravity for these minerals is 2.65 Mg/m3
That is where the 2.65 comes from
Bulk Density (Db) vs Particle Density (Dp)
As Bulk Density increases, Total Pore Space decreases
Example Db and Dp Problem. Given the Db = 2.0 Mg/m3, compute the TPS
TPS = (1 - Db/Dp)*100
TPS = (1 - 2.0/2.65)*100
TPS = (1 - 0.755)*100
TPS = 0.245 ×100
TPS = 24.5%
Factors that influence TPS and Db
Texture
Structure
Organic Matter
Depth
Management Practices
Texture (Factors that Influence TPS and Db)
Bulk Density decreases with finer textured surfaces
This means Total Pore Space INCREASES
Example
Cultivated Surface
Sand & Sandy loam: 1.2-1.8 Mg/m3 Density; 55-32% TPS
Silt & Clay loam: 0.9-1.5 Mg/m3 Density; 66-43% TPS
Structure (Factors that influence TPS and Db)
Bulk density is lower for well developed granular structure