Types of Cells & Cell Theory (2A)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Domains for classifying organisms
Domain Bacteria
Domain Archaea
Eukarya
4 kingdoms of eukarya
Protists, Fungi, Plants, Animals
Protists
unicellular or multicellular
some have cell walls (composition varies)
nutrition either autotrophs (make their own food)
or heterotrophs (eat other living things)
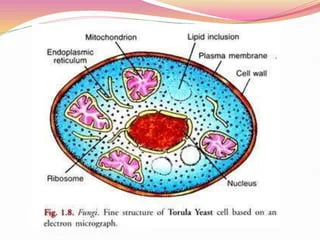
Fungi
unicellular or multicellular
cell walls of chitin
heterotrophs
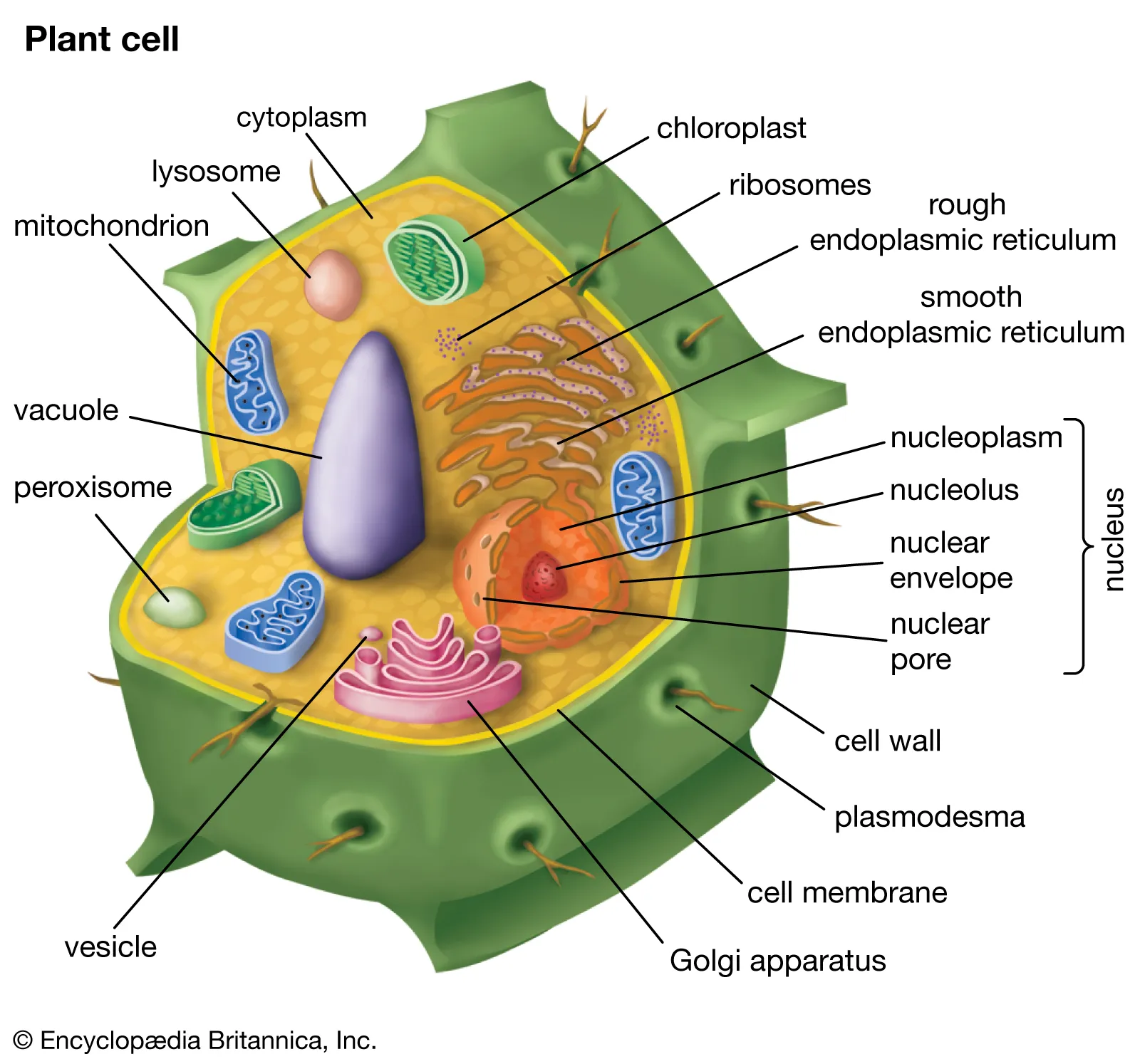
Plants
multicellular
cell walls of cellulose
photosynthetic autotrophs
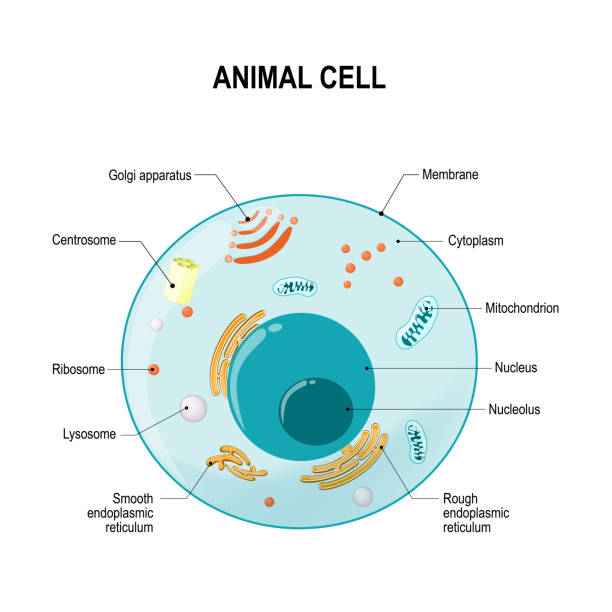
Animals
multicellular
no cell wall
heterotrophs
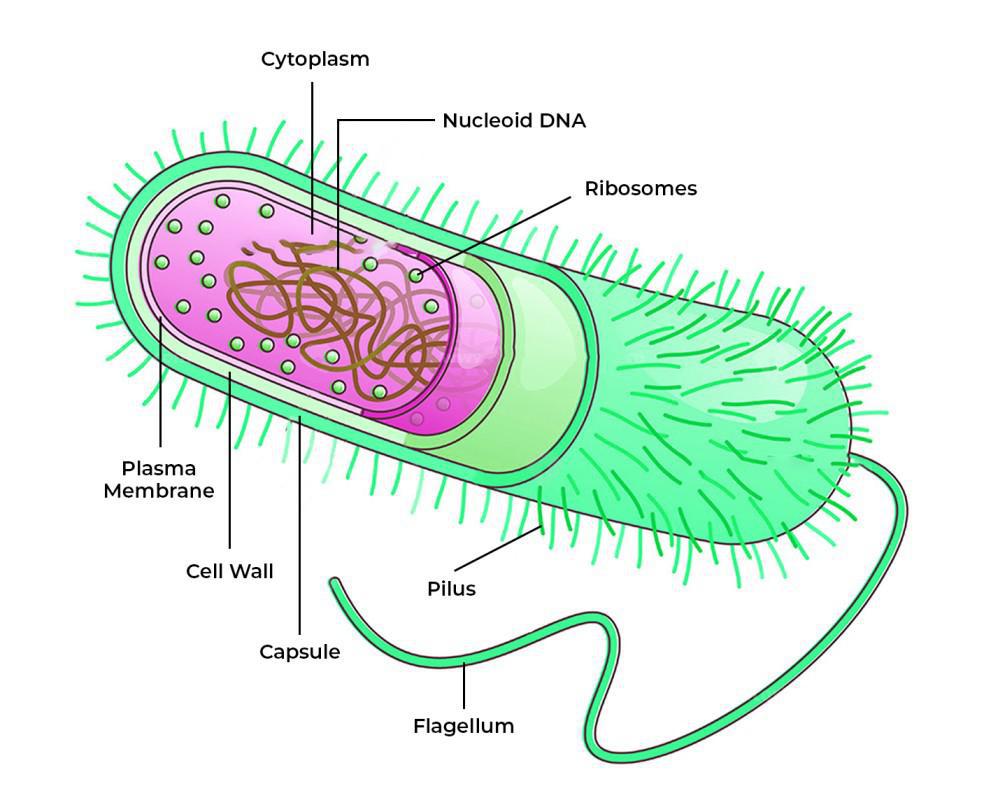
Prokaryotic Cells/Prokaryotes (Overall)
usually unicellular
smaller=between 1-5µm
cells lack a nucleus + other membrane-bound organelles
Parts of a Prokaryote
DNA - 1 circular chromosome (“not packaged”)
found in the nucleoid region
cell wall
OFTEN have extra DNA (plasmids)
external extensions used for attachment (pili)
structure used for movement (flagella)
external protective layer (slime capsule)
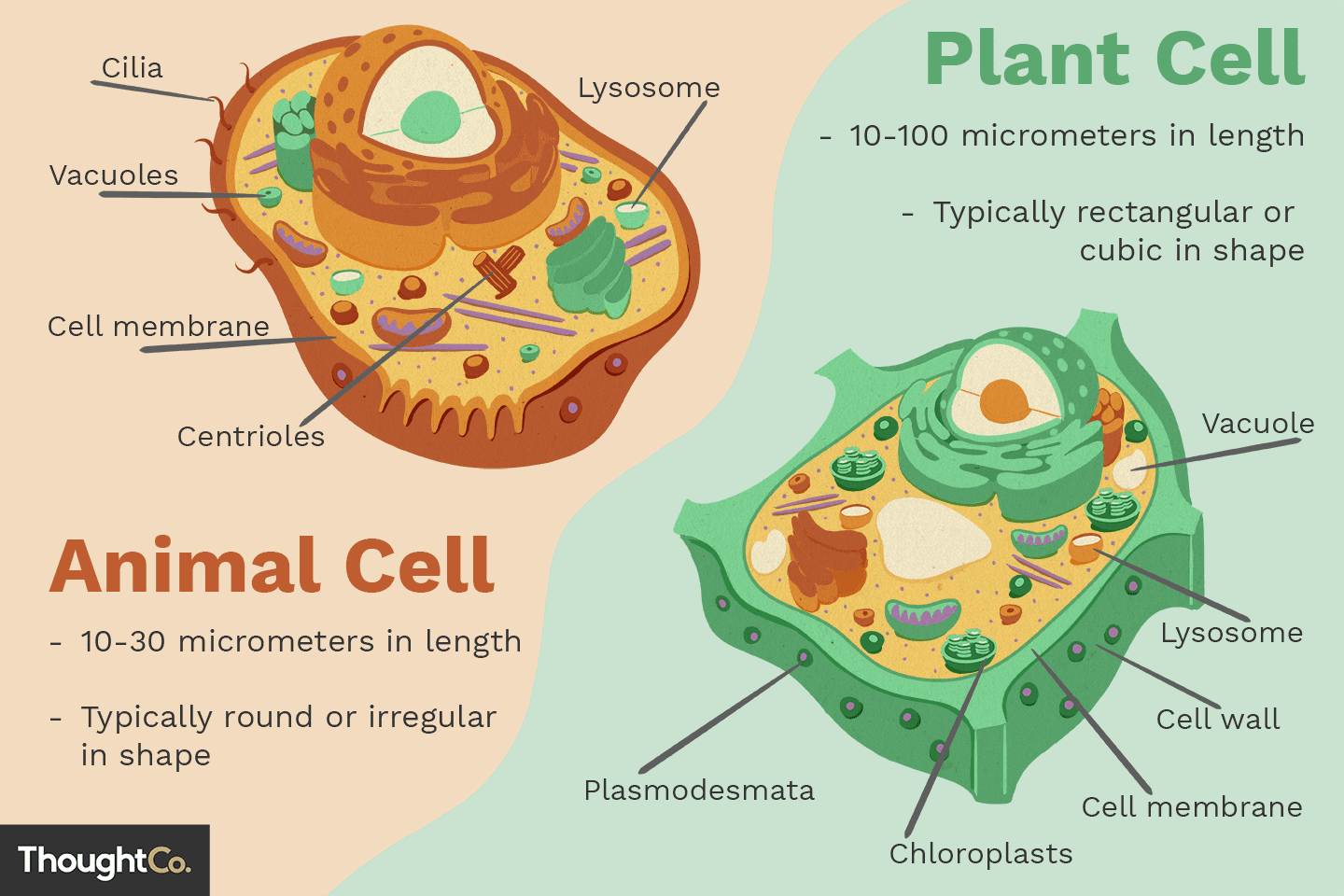
Eukaryotic Cells/Eukaryotes (Overall)
can be unicellular or multicellular
larger=between 10-100µm in length (lots of exceptions)
numerous membrane-bound organelles
allows for compartmentalization
can maintain a unique internal chemistry
Parts of a Eukaryote
all have a double membrane nucleus
DNA is linear, cells have multiple chromosomes
DNA is “packaged” by wrapping it around histone proteins
Cell Theory
All cells come from preexisting cells
Living things are made of one or more cells
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things