Mouth Ulcers
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
What are the key symptoms of this condition?
Small (<1 cm), round or oval ulcers
Grey-white base with a raised red rim
Painful – pain is the main presenting symptom
Shallow ulcers, occurring singly or in small crops (≤5)
Rarely affect gingiva
Heal within 7–14 days, with recurrence every 1–4 months
What are the treatment options available?
Treatment is symptomatic, as ulcers are self-limiting:
Topical corticosteroids (e.g. hydrocortisone buccal tablets)
Choline salicylate gel for pain relief
Benzydamine mouthwash/spray for short-term analgesia
Local anaesthetic gels (e.g. lidocaine, benzocaine)
Protectorant pastes to reduce irritation
Chlorhexidine mouthwash to reduce severity and recurrence
Who is eligible to take these treatments?
Adults and children ≥12 years: most treatments including corticosteroids, benzydamine, chlorhexidine,benzocaine
≥16 years: choline salicylate
Local anaesthetics: age-dependent (e.g. lidocaine ≥7 years)
Pregnant and breastfeeding patients: most topical treatments are safe
Children <10 years: routine treatment not recommended → consider referral
What are the main differential diagnoses to consider?
Major aphthous ulcers – larger (>1 cm), multiple, slow healing
Traumatic ulcers – irregular borders, clear history of injury
Herpetiform ulcers – numerous pinpoint ulcers, posterior mouth
Herpes simplex infection – systemic symptoms, gingival involvement
Oral thrush – creamy white plaques
Oral carcinoma – painless, persistent solitary ulcer (>3 weeks)
When should the patient be referred?
Refer if any of the following are present:
Ulcer lasts longer than 14 days
Ulcer >1 cm in diameter
More than 5–10 ulcers present
Painless ulcer
Associated eye involvement or systemic symptoms
Children under 10 years
Suspicion of trauma without clear cause
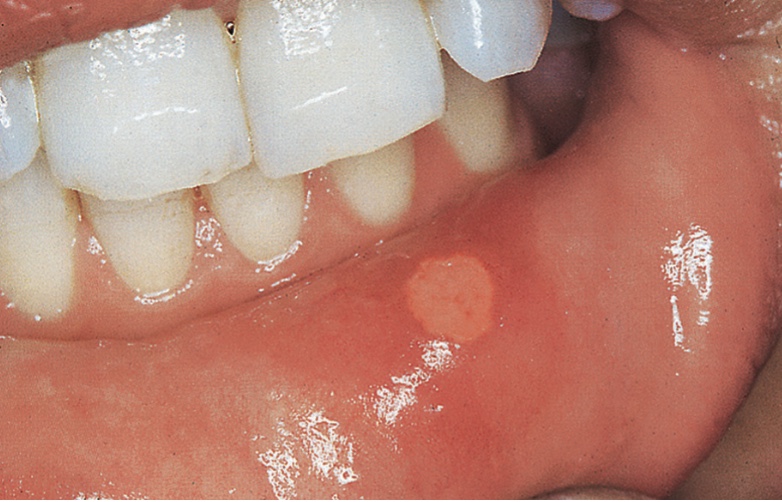
What condition is this?
Minor Aphthous Ulcer
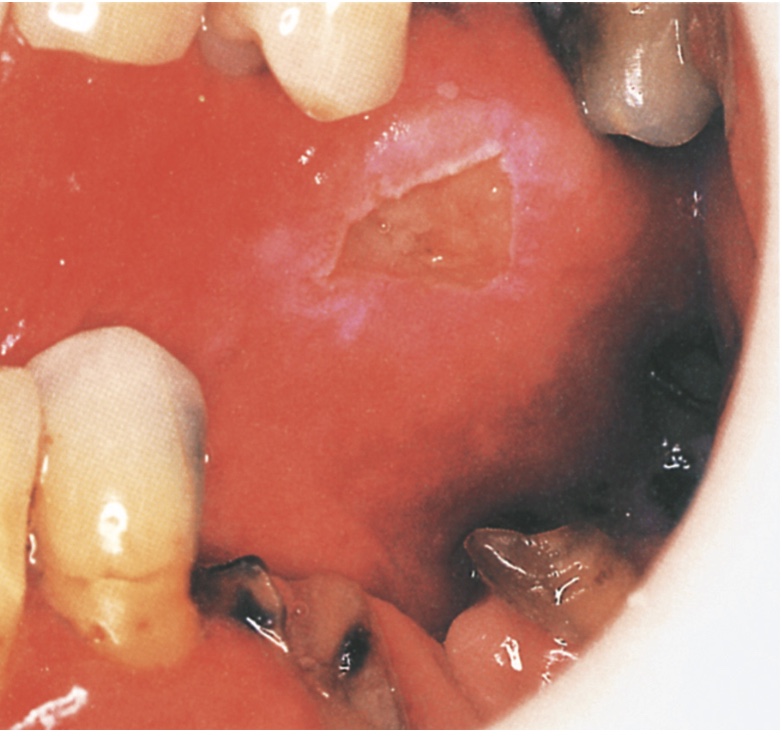
What condition is this?
Ulcer caused by trauma
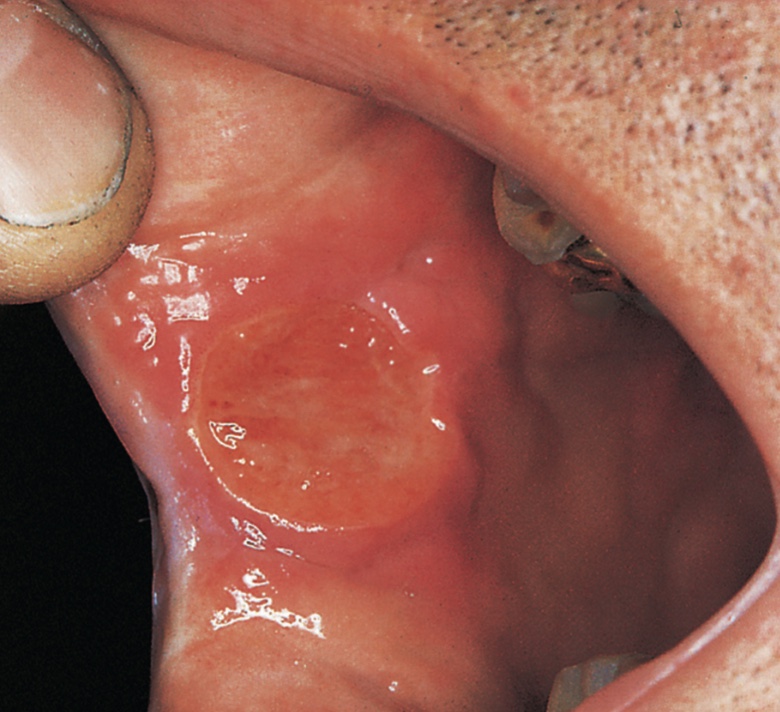
What condition is this?
Major aphthous Ulcer
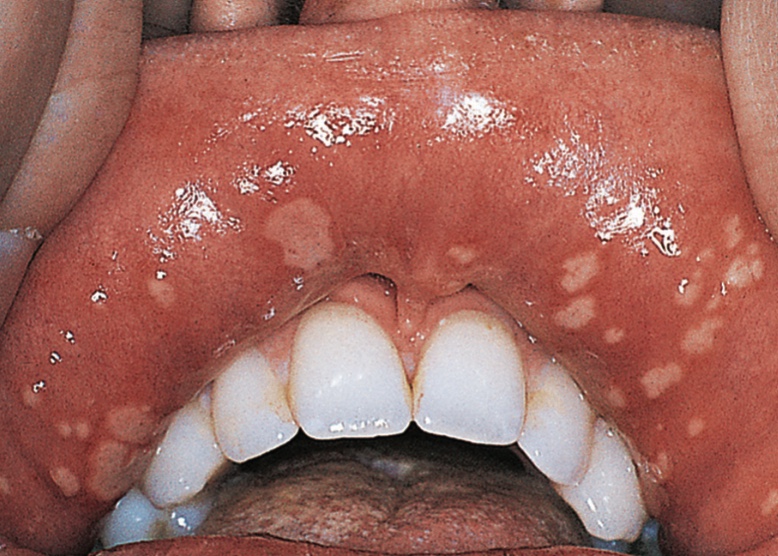
What condition is this?
Herpetiform Ulcer