Concept 7.4: Active transport uses energy to move solutes against their gradients
1/7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
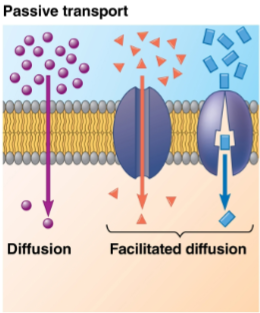
Facilitated diffusion
A passive method of transport that requires no energy due to the molecules only moving down their concentration gradient
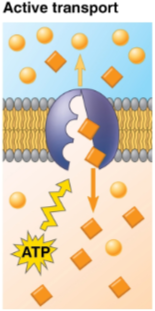
Active transport
Transport that requires energy — usually in the form of ATP hydrolysis — to move substances agains their concentration gradient
Requires carrier proteins specifically
Allows cells to maintain solute concentrations that differ from their environment
Membrane potential
The voltage across a membrane created by differences in the distribution of positive and negative ions across a membrane
Electrochemical gradient
Two forces that drive the diffusion of ions across the membrane that ions diffuse down:
Chemical force (the ion’s concentration gradient)
Electrical force (the effect of the membrane potential on the ion’s movement)
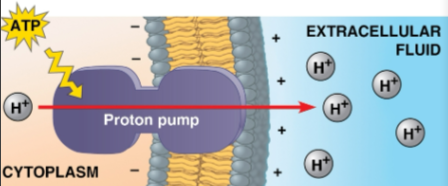
Electrogenic pump
A transport protein that generates voltage across a membrane, storing energy that can be used for cellular work
Animals have the sodium-potassium pump
Plants, fungi, and bacteria have the proton pump that transport H+ ions out of the cell
Cotransport
Transport that occurs when the active transport of a solute indirectly drives transport of other substances
Downhill solute movement may couple to uphill transport of another substance against its own concentration gradient
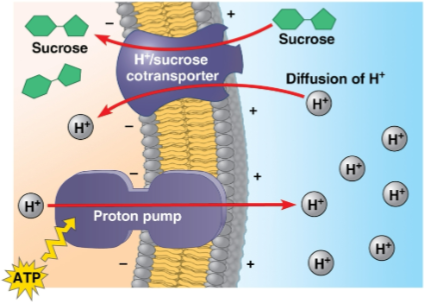
Proton pump
Pump present in plants that generate an H+ gradient across the cell membrane
An H+ cotransporter allows sucrose to be coupled to its active transport into the cell, enabling its transport around a plant body
Sodium-potassium pump
Pump present in animals that transport Na+ out of the cell to maintain the electrochemical gradient while using ATP in the process
Sodium in waste is reabsorbed to maintain a constant level in the body
Drinking concentrated salt and glucose solutions can enable recovery from a rapid, life-threatening loss of sodium too fast for reabsorption