hsc exam 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/726
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
727 Terms
1
New cards
what is anatomy
•It is the __scientific study of the structures of the body__ and the relationship of these structures to one another.
2
New cards
what is anatomy linked to?
•The study of anatomy is linked to **dissection** to obtain a 3-dimensional concept
3
New cards
what is anatomy subdivided into?
a. **gross anatomy** (or macroscopic anatomy)
b.microscopic anatomy
c.**radiographic anatomy**
d.neuroanatomy
e.developmental anatomy
b.microscopic anatomy
c.**radiographic anatomy**
d.neuroanatomy
e.developmental anatomy
4
New cards
how can anatomy be studied?
It can be studied with a __**regional approach, systemic**__ __**approach, or clinical approach**__
5
New cards
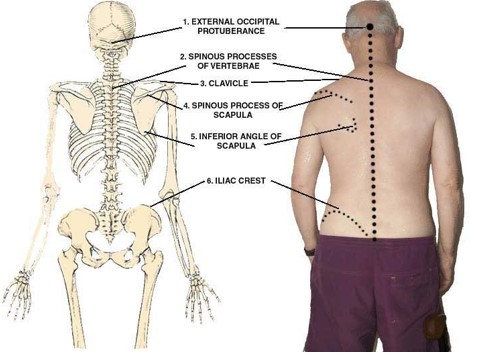
what is surface anatomy?
It is the study of the configuration of the surface of the body, especially in relation to its internal parts.
6
New cards
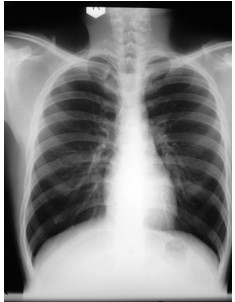
*Radiographic Anatomy is…*
best for imaging bone (e.g., fractures)
7
New cards
types of radiographic anatomy
X-rays (2D)
CT (computed tomography) (3D)
CT (computed tomography) (3D)
8
New cards
how does radiographic anatomy work?
It is the “transillumination” of the body by a highly penetrating beam of x-rays that allows the tissues of different densities\* within the body to be shown as images of differing densities on the x-ray film. \*(density=m/v)
9
New cards
how does bone appear on a radiographic anatomy?
A tissue or organ that is relatively dense, like bone, absorbs (stops) more x-rays than a less dense tissue - shows a white image on the film (**Radiopaque**)
10
New cards
how does soft tissue appear on a radiographic anatomy?
A tissue or organ of lower density, like soft tissue, allows more x-rays to pass through it – shows as black on the film (**Radiolucent)**
11
New cards
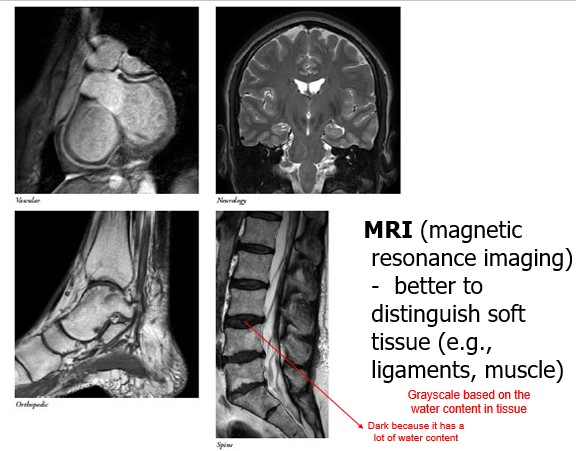
what is an MRI and what is it used for?
**MRI** (magnetic resonance imaging)
\- better to distinguish soft tissue (e.g., ligaments, muscle)
\- better to distinguish soft tissue (e.g., ligaments, muscle)
12
New cards
what is a MRI based on?
water content
13
New cards
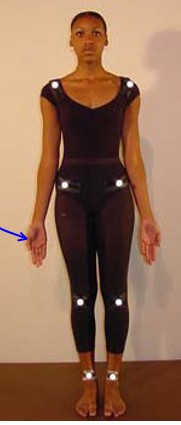
what is anatomical position?
Standard reference position of body adopted worldwide to describe location of different structures
14
New cards
what does anatomical position look like?
•Upright posture
•Thumbs pointed out (laterally)
•Feet together
* *forearms are supinated*
•Thumbs pointed out (laterally)
•Feet together
* *forearms are supinated*
15
New cards
Supinated
(of a hand, foot, or __limb__) turned or held so that the palm or sole is facing __upward__ or __outward__.
16
New cards
anatomical planes are…
Movements are that described as occurring in a plane
17
New cards
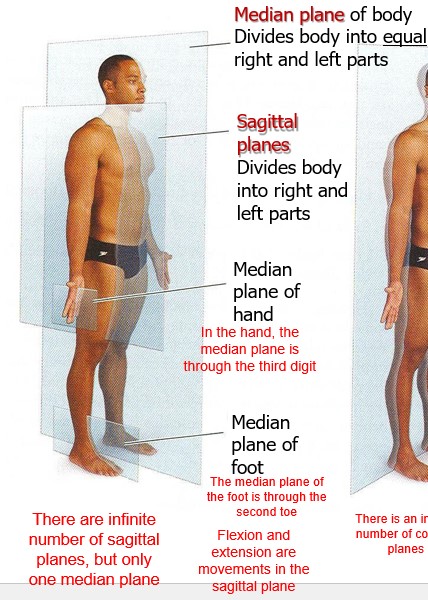
median plane
plane of body Divides body into __equal__ right and left parts
18
New cards
Sagittal planes
Divides body into right and left parts
19
New cards
true or false
There are infinite number of sagittal planes, but only one median plane
There are infinite number of sagittal planes, but only one median plane
true
20
New cards
where is the median plane of the hand?
In the hand, the median plane is through the third digit
21
New cards
where is the median plane of the foot?
The median plane of the foot is through the second toe
22
New cards
what types of movement are in the sagittal plane?
Flexion and extension
23
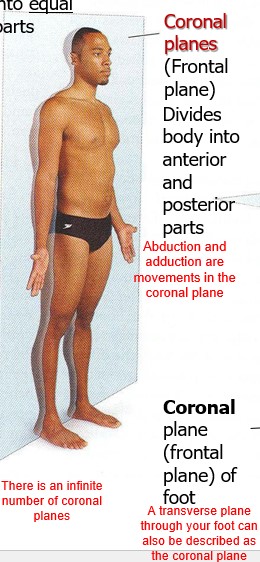
New cards
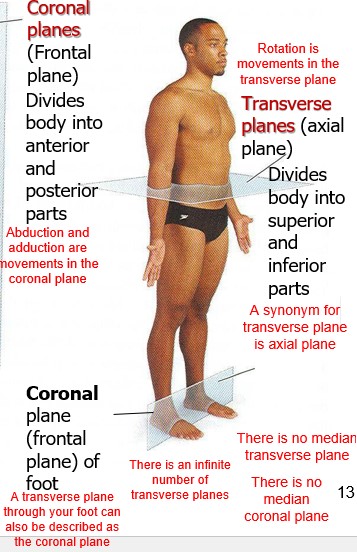
coronal planes (Frontal plane)
Divides body into anterior and posterior parts
24
New cards
true or false
there is only one coronal plane
there is only one coronal plane
false
There is an infinite number of coronal planes
There is an infinite number of coronal planes
25
New cards
true or false
There is no median coronal plane
There is no median coronal plane
true
26
New cards
what types of movements are in the coronal plane?
Abduction and adduction
27
New cards
Transverse planes (axial plane)
Divides body into superior and inferior parts
28
New cards
true or false
A transverse plane through your foot can also be described as the coronal plane
A transverse plane through your foot can also be described as the coronal plane
true
29
New cards
true or flase
there are an infinite number of median transverse plane
there are an infinite number of median transverse plane
false. There is **no** median transverse plane
30
New cards
how many transverse planes are there?
infinite
31
New cards
what type of movement is in the transverse plane?
rotation
32
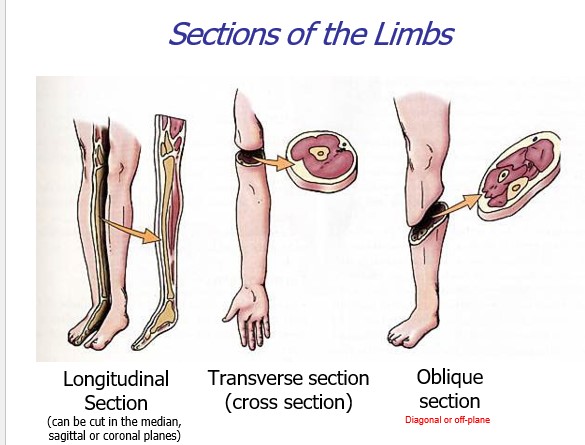
New cards
what are the sections of the limbs?
longitudinal section, transverse section, and oblique section
33
New cards
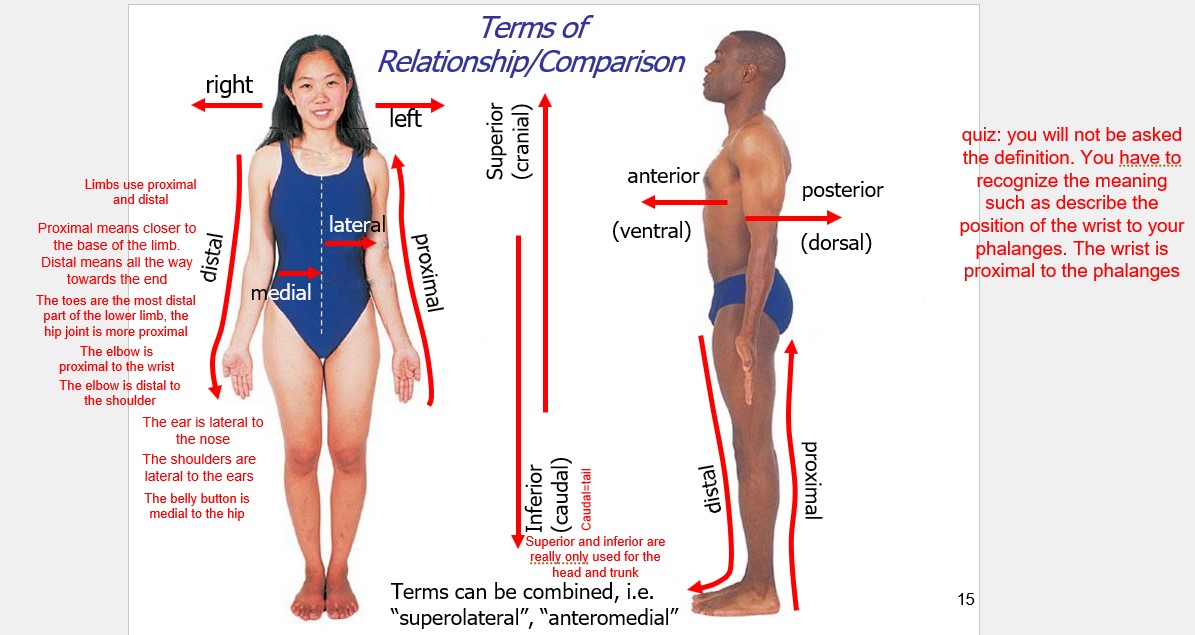
terms of relationship/ comparison
It is written in the opposite way the arrow points
34
New cards
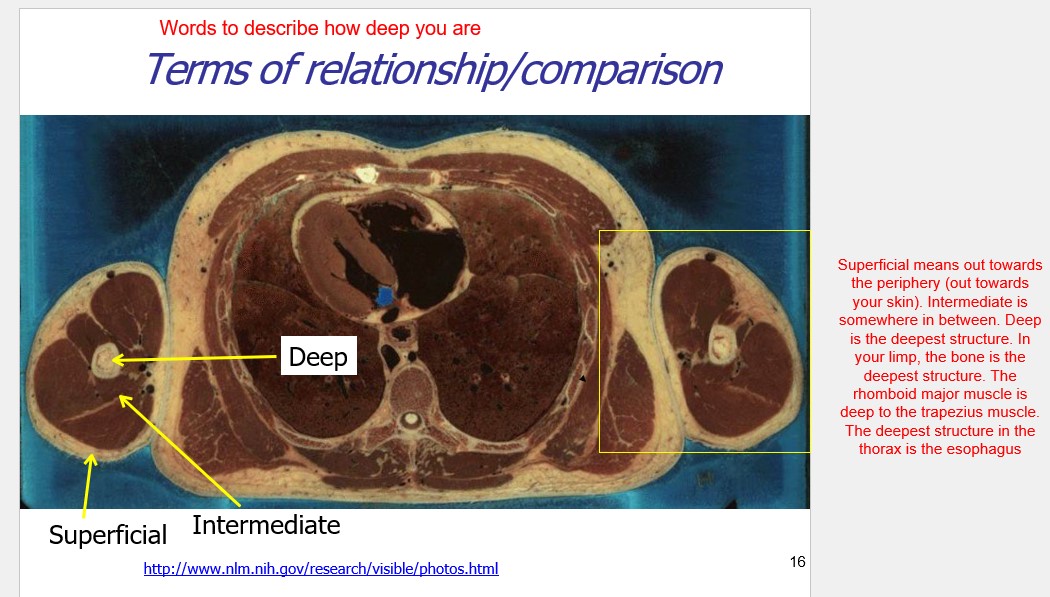
what words describe how deep you are
superficial, intermediate, and deep
Superficial: on top of – the skin is superficial (on top of) the bones
Deep: under – the rhomboid major muscle is deep (under) the trapezius
Superficial: on top of – the skin is superficial (on top of) the bones
Deep: under – the rhomboid major muscle is deep (under) the trapezius
35
New cards
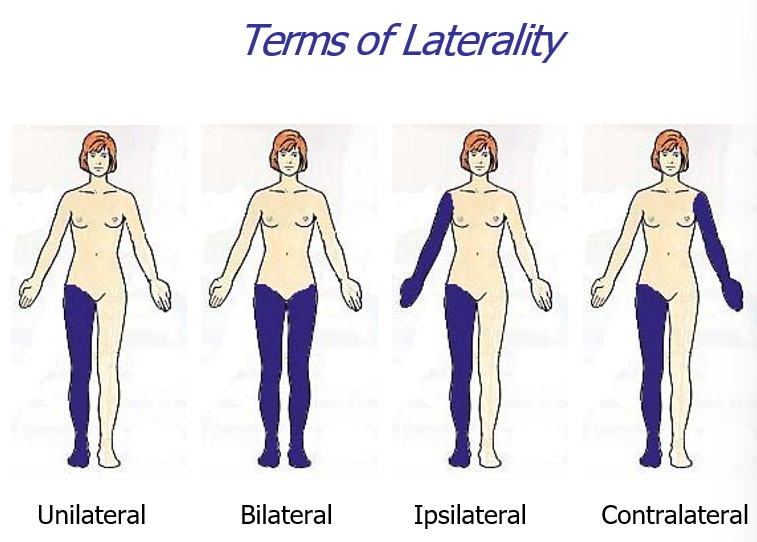
terms of laterality
unilateral, bilateral, ispilateral, contralateral
36
New cards
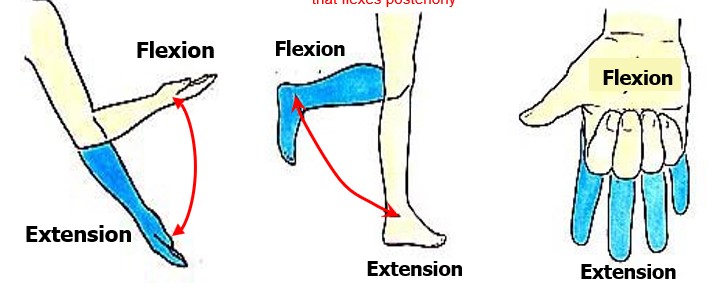
what types of movement occur in the sagittal plane?
flexion and extension
37
New cards
what is flexion?
Flexion decreases in angle
38
New cards
what is extension?
Extension is bringing it back into anatomical position
39
New cards
what is the beginning point of anatomical position
180 degrees
40
New cards
what is the end point of anatomical position?
< 180 degrees
41
New cards
true or false
The knee is the only joint that flexes posteriorly
The knee is the only joint that flexes posteriorly
true
42
New cards
true or false
Flexion of the elbow is the same as flexion of your forearm
Flexion of the elbow is the same as flexion of your forearm
true
43
New cards
what is hyperextension/hyperflexion?
refers to movement beyond normal range of motion
Beyond anatomical position (or an injury)
Beyond anatomical position (or an injury)
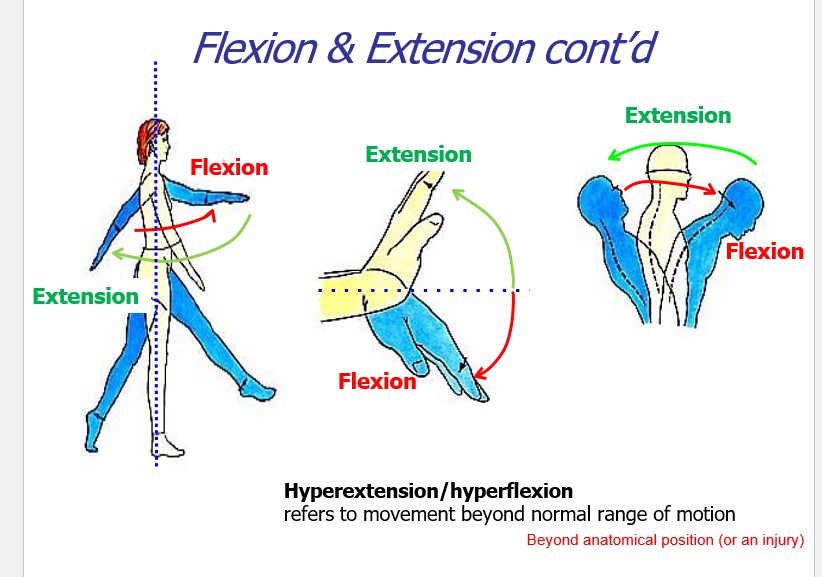
44
New cards
what types of movements occus in the coronal plane?
abduction and adduction
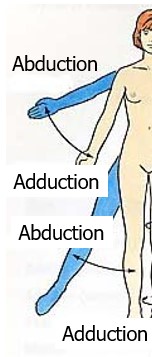
45
New cards
what is abduction?
Abduction is away from the center.
46
New cards
what is adduction?
Adduction is back towards anatomical position
47
New cards
which joints cannot abduct or adduct?
elblow and knee
48
New cards
true or false
abduct your shoulder is the same as abduct your arm
abduct your shoulder is the same as abduct your arm
true
49
New cards
what is medial rotation
rotational movement towards the midline
ex: An example of medial rotation is turning the legs at the hip so that the toes point toward one another. Reaching the arm across the waist toward the opposite side of the body is also an example of medial rotation.
ex: An example of medial rotation is turning the legs at the hip so that the toes point toward one another. Reaching the arm across the waist toward the opposite side of the body is also an example of medial rotation.
50
New cards
what is lateral rotation
rotational movement away the midline
ex: As an example, when the leg is laterally rotated, it is turned out at the hip causing the toes to turn away from the body. Lateral rotation of the elbow turns the arm so that the palm of the hand is facing forward.
ex: As an example, when the leg is laterally rotated, it is turned out at the hip causing the toes to turn away from the body. Lateral rotation of the elbow turns the arm so that the palm of the hand is facing forward.
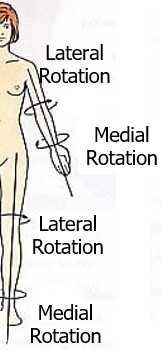
51
New cards
what is supination?
when your radius and ulna bones are parallel. (carrying a bowl of soup). In anatomical position, you are in supination. Palm faces up
52
New cards
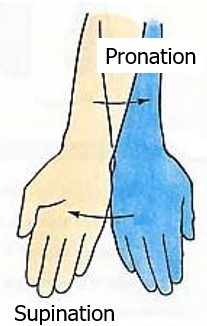
what is pronation
palm faces down
53
New cards
medial and lateral rotation versus supination and pronation
Don't confuse pronation and supination with medial and lateral rotation. Both pairs are rotational movements, but pronation and supination are specialized. In internal (or medial) rotation and external (or lateral) rotation of the arm, the radius and ulna stay parallel, and all the movement is at the shoulder (or at the hip in the case of rotation of the leg). Pronation and supination (of the arm only) are entirely due to the radius and ulna, with no movement at the shoulder.
54
New cards
what is circumduction
combination of flexion, abduction, extension and adduction
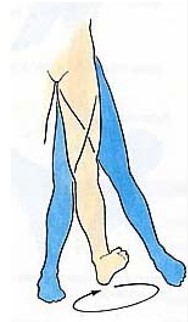
55
New cards
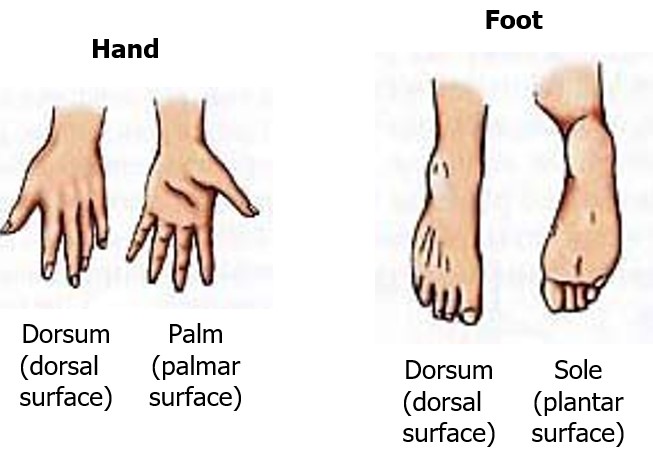
special terms of hand and foot
56
New cards
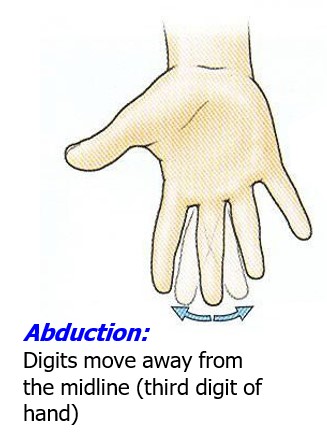
abduction of digits
Digits move away from the midline (third digit of hand)
57
New cards
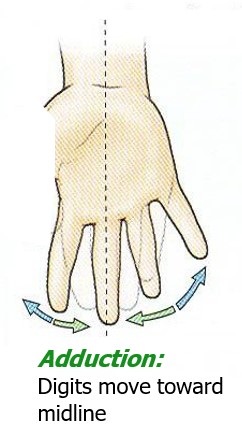
adduction of digits
digits move toward midline
58
New cards
abduction/ adduction of the thumb (hallux)
Abduction of the thumb is pulling it up off of your palm. Adduction is bringing it back down toward your palm
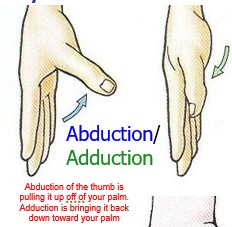
59
New cards
flexion/ extension of the thumb (hallux)
The movements of the thumb are referred as being turned 90 degrees. Flexion of the thumb passes across your palm
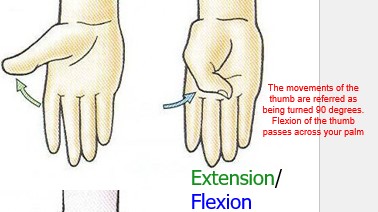
60
New cards
opposition/ reposition of the thumb (hallux)
Opposition: pinky and thumb come together
Reposition is going back into anatomical position
Reposition is going back into anatomical position
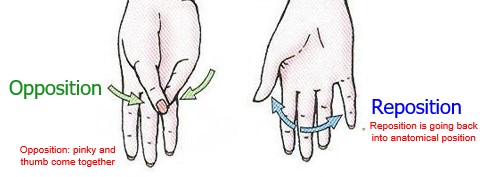
61
New cards
lateral bending
Lateral bending is flexion in the coronal plane (you can’t just say flexion because flexion is movement in the sagittal plane
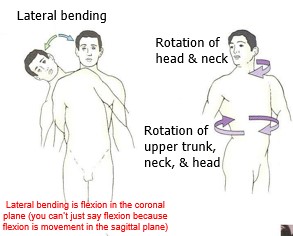
62
New cards
elevation and depression
Elevation is moving up superiorly
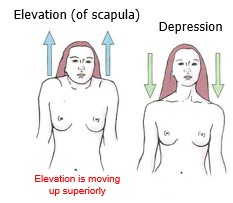
63
New cards
retrusion and protusion of mandible
Protrusion brings your jaw forward
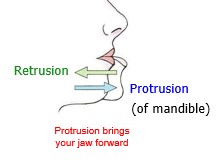
64
New cards
protraction and retraction
Protraction is pushing forward
Retraction is brining it back
Retraction is brining it back
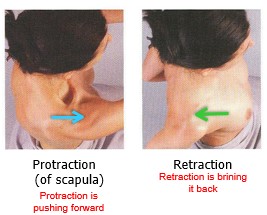
65
New cards
what bones are part of the axial skeleton?
Skull, vertebral column, vertebrae, the ribs, the sternum, sacrum
66
New cards
what bones are part of the appendicular skeleton?
Upper and lower limbs
67
New cards
what cartilage is part of the costal cartilage
Between the ribs and sternum
68
New cards
what cartilage is part of the articular cartilage?
Within all of your joints
69
New cards
skeletal system
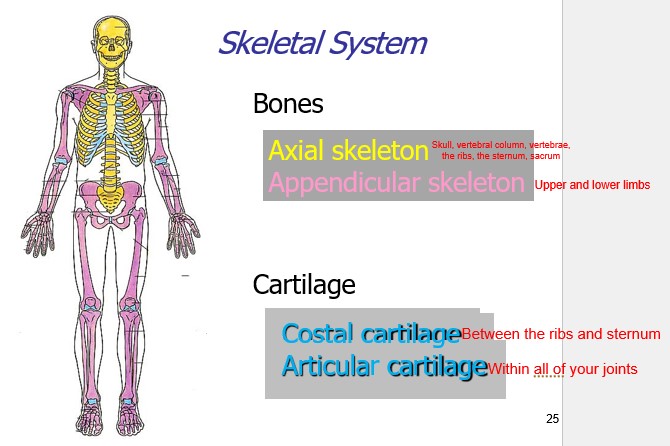
70
New cards
functions of bone
•__Protection__ of vital organs
•Structural __support__ of the body
•Acts as __levers__ for muscles to produce movement
•__Reservoir__ for calcium and phosphorous
•Contains marrow where __blood cells are formed__
•Structural __support__ of the body
•Acts as __levers__ for muscles to produce movement
•__Reservoir__ for calcium and phosphorous
•Contains marrow where __blood cells are formed__
71
New cards
true or false
bones stop growing
bones stop growing
false. Bones are living tissues. They are continuously growing
72
New cards
what are the 2 types of bones?
spongy bone and compact bone
73
New cards
what is spongy bone?
* spongy bone usually occur more in the ends
* they are trabecular and cancellous
* It is known to be a shock absorber and distribute the forces that come down on the joints across to the entire bone
* they are trabecular and cancellous
* It is known to be a shock absorber and distribute the forces that come down on the joints across to the entire bone
74
New cards
what is compact bone?
cortical, dense
75
New cards
what is medullary?
(marrow) cavity
76
New cards
what is red marrow
* for younder adults
* Active in blood formation (hematopoesis)
* Active in blood formation (hematopoesis)
77
New cards
what is yellow marrow
* for older adults
* Inert and fatty
* Inert and fatty
78
New cards
sections of bone
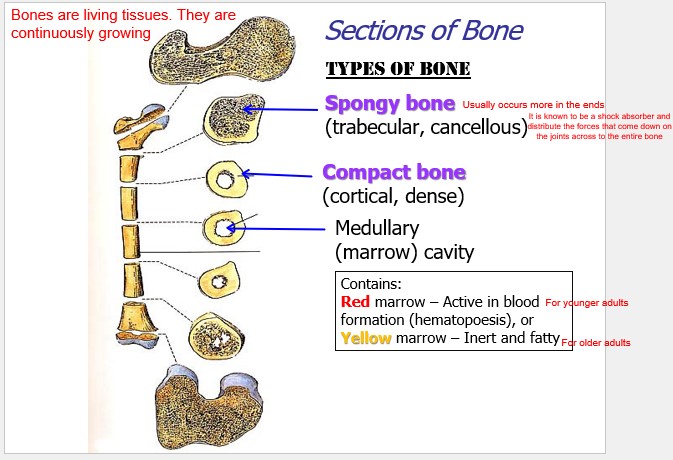
79
New cards
examples of long bone
humerus, phalanges, clavicle
80
New cards
examples of short bone
tarsals, carpals
81
New cards
examples of flat bone
some cranial vault bones, ribs, sternum
82
New cards
examples of irregular bone
vertebrae, sphenoid
83
New cards
example of sesamoid bone
patella (develop within tendons)
84
New cards
examples of pneumatic bone
mastoid part of temporal bone, paranasal sinus
85
New cards
example of accessory (supernumary) bone
in foot
86
New cards
types of elevation bone markings (things that stick out off of the bone)
Crest
Line
Protuberance
Epicondyle
Malleolus
Spine
Process
Trochanter
Tubercle
Tuberosity
Line
Protuberance
Epicondyle
Malleolus
Spine
Process
Trochanter
Tubercle
Tuberosity
87
New cards
types of depression bone markings (indentations)
Fossa
Groove
Notch
Groove
Notch
88
New cards
types of articulation bone markings (This is a joint. Where 2 bones come together and move against each other)
Condyle (rounded end)
Facet (flatter end)
Facet (flatter end)
89
New cards
types of hole bone markings
foramen (pl. foramina)
90
New cards
what is ossification
process of bone formation
91
New cards
what is osteoblast
bone forming cells
92
New cards
what is osteocytes
bone cells
93
New cards
what is osteoclasts
bone resorption cells
94
New cards
what is Chondrocytes
cartilage cells
95
New cards
what is Chondroblasts
cartilage forming cells
96
New cards
true or false
Bone is a living tissue which undergoes continuous change.
Bone is a living tissue which undergoes continuous change.
true
97
New cards
how much of the bone in the body replaced with new bone every year?
10-15%
98
New cards
bones are developed from what
condensations of mesenchyme (embryonic connective tissue)
99
New cards
the condensations undergo ossification by
intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification
100
New cards
intramembranous ossification is also known as
direct ossification