Biology Exam 2
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is a conjoined twin?
Identical twins whose bodies are physically attached at some location
Describe cell theory
The realization that all living organisms are made of cells; it was first proposed in 1839 by Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
Prokaryotes
no nucleus, no membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotes
do have nucleus, membrane-bound organelles
Similarities between Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
Cell membrane, genetic material, cytoplasm, ribosomes
What is the role of the cell membrane?
It regulates what enters and leaves the cell. The cell membrane also maintains the environment inside the cell — essential for the many thousands of chemical reactions that occur in cells
What is the function of the nucleus?
Contains genetic material
What is the function of the mitochondria?
Creates ATP (energy)
Describe the theory of endosymbiosis
Eukaryotes evolved from Prokaryotes. Bacterias being engulfed by Prokaryotes; they weren’t digested and they worked together in symbiosis
Chloroplast
Bacteria that can use sunlight energy to produce their own food
Mitochondria
Bacteria that can use oxygen to make ATP
What are the components of the endomembrane system?
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER), rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), ribosomes, golgi apparatus, and lysosomes
Nucleus Components
Membrane & DNA
Nucleus Function
contains genetic material
Mitochondrion Components
Membrane & DNA
Mitochondrion Function
Creates ATP
Mitochondrion: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
all organelles
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Components
Membrane & ribosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Functions
Creates proteins
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
Ribosomes & Golgi apparatus
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Components
Membrane
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Functions
Creates lipids and detoxes
Golgi apparatus Components
Membrane & enzymes
Golgi apparatus Function
Modifies proteins
Golgi apparatus: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
RER, vesicles
Vesicle Components
Membrane
Vesicle Functions
Trafficks proteins
Vesicle: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
RER, Golgi
Lysosome Components
Membrane & hydrolytic enzymes
Lysosome Functions
Digests DD/damaged organelles & macromolecules
Lysosome: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
Damaged/old organelles
Ribosome Functions
Creates proteins
Ribosome: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
RER
Cytoplasm/Cytosol Functions
Contains organelles, cell features
Cytoplasm/Cytosol: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
All organelles, cell features
Cytoskeleton Functions
Supports cell membrane, allows cell movement
Cytoskeleton: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
Cell membrane
Cell Membrane Functions
Protects cell, regulates what enters/leaves
Cell Membrane: Interactions with other organelles/cell features
Cytoskeleton
Mitosis Function
make somatic cells
Meiosis Function
Make gametes
Mitosis Steps/Phases of
PMAT
Meiosis Steps/Phases of
PMAT I and PMAT II
Mitosis occurs in what cells?
Somatic cells
Meiosis occurs in what cells?
Gametes
Is Mitosis genetically identical or different?
Identical
Is Meiosis genetically identical or different?
Different
Mitosis: Number of Divisions
1
Meiosis: Number of Divisions
2
Mitosis: Number of Cells Produced
2
Meiosis: Number of Cells Produced
4
Mitosis: Chromosome number (at end)
46
Meiosis: Chromosome number (at end)
23
Does crossing over occur in Mitosis?
No
Does crossing over occur in Meiosis?
Yes
Does Mitosis produce haploid or diploid cells?
Diploid
Does Meiosis produce haploid or diploid cells?
Haploid
Does Mitosis occur before or after fertilization?
After
Does Meiosis occur before or after fertilization?
Before
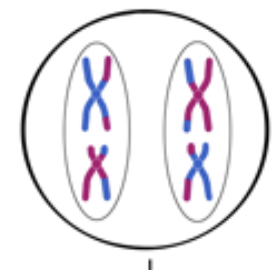
What is a homologue?
Pairs of Chromosomes
Compare testes and ovaries
Testes are in males and produce sperm while ovaries are in females and produce eggs.
Prophase I
CROSSING OVER OCCURS

Metaphase I
INDEPENDENT ASSORTMENT - Line up on metaphase plate
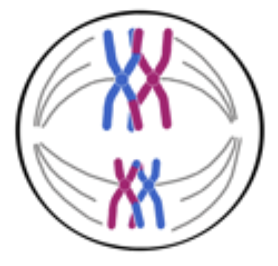
Anaphase I
Pulled a part
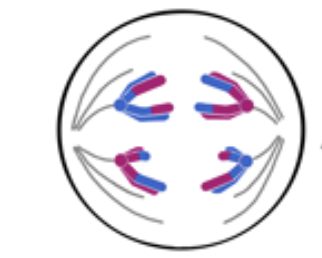
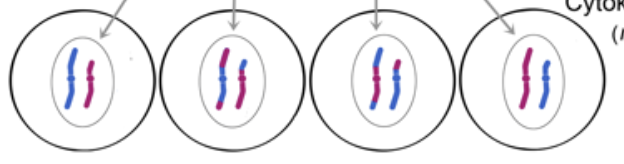
Telophase
Cytokinesis
*Each daughter cell is haploid
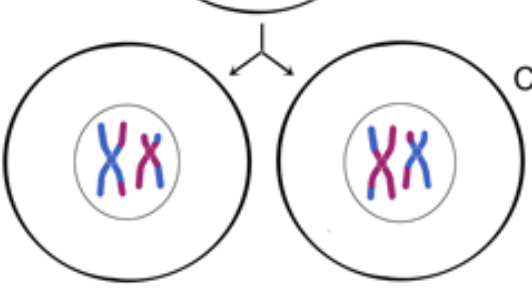
Prophase II
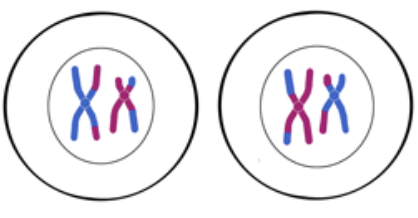
Metaphase II
*Single File Line
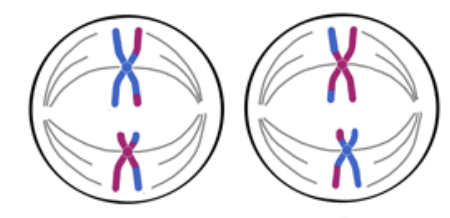
Anaphase II
*Pulled to poles
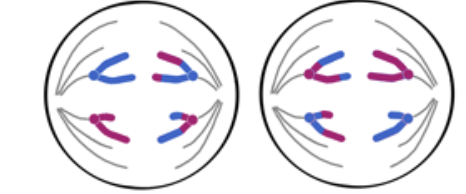
Telophase II
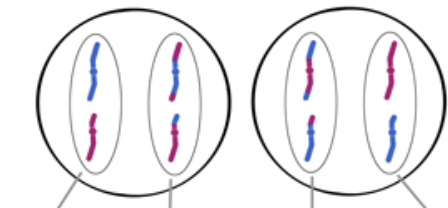
Cytopkinesis
*End result of meiosis is four haploid daughter cells
3 events that create genetic variability
Crossing over (Prophase)
Independent assortment (Metaphase)
Random fertilization