biol 1011 exam 4
1/324
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
325 Terms
CHAPTER 13
_____________ is adaptive and occurs only after an immunizing event such as an infection
specific immunity
after final maturation, T and B lymphocytes migrate to ____________ areas in the ____________ organs
separate; lymphoid
3 multiple choice options
T cells, but not B cells constantly recirculate in blood and lymphatics
false
1 multiple choice option
mature B and T lymphocytes migrate in and out of ______________ organs
lymphoid
phagocytic cells such as dendritic cells process and present _____________ to T cells
antigens
specific immunity only occurs after a(n) _________________ event
immunizing
T and B lymphocytes migrate to separate areas of the _____________ organs after maturation
lymphoid
the gene complex giving rise to a series of glycoproteins that are found on all cells except red blood cells and are important in the recognition of self by the immune system is called the ______ complex.
major histocompatibility
3 multiple choice options
after maturation, B cells and T cells ______.
constantly recirculate through blood and lymphatics
3 multiple choice options
for the major histocompatibility complex, ___________ classes of MHC genes have been identified
three
3 multiple choice options
mature B cells and T cells ______.
migrate in and out of lymphoid tissues
3 multiple choice options
all mature T lymphocytes express ______ coreceptors.
CD3
T cells also express ______ coreceptors.
CD4 or CD8
which type of resident phagocyte ingests antigen, migrates to a nearby lymphoid organ, and then processes and presents the antigen to T and B lymphocytes?
dendritic cell
3 multiple choice options
the site of B cell development and maturation is in the human __________.
bone marrow
3 multiple choice options
each individual mature B and T cell has the capacity to respond to a single, unique _______________.
antigen
what is the set of genes that encodes human cell receptors that play a role in recognition of self by the immune system called?
MHC
3 multiple choice options
a conceptual explanation for the development of lymphocyte specificity and variety during immune system maturation is known as the ____________ theory.
clonal selection
3 multiple choice options
the important antigenic characteristic of whole microbes or their parts is that they are recognized as ______.
foreign
2 multiple choice options
which type of cell ingests and degrades a microbe, then processes and displays the microbe's antigens on its surface?
antigen-presenting cell
3 multiple choice options
each individual mature B and T cell has the capacity to respond to ______.
a single unique antigen
3 multiple choice options
since they require some type of MHC recognition on an antigen-presenting cell before they can be activated, we refer to ____________ cells as "restricted".
T
1 multiple choice option
Like B cells, T cells also form _____________ cells which can quickly respond upon secondary exposure to the eliciting antigen.
memory
to become functional, most B cells must interact with T __________ cells that bear receptors for epitopes on the same antigen.
helper
One important characteristic of an antigen is that it be perceived as, ______________ meaning that it is not a normal constituent of the body.
foreign
The two arms of an antibody that bind the antigen are called _______.
antigen-binding fragments
3 multiple choice options
Antigen-presenting cells process and present antigenic determinants on their surface and include B-cells, __________, and dendritic cells.
macrophages
the antibody region that does not bind the antigen is called the _____.
crystallizable fragment
3 multiple choice options
only ________ cells require antigen to be presented on MHC class molecules.
T
2 multiple choice options
a basic immunoglobulin molecule is composed of four polypeptide chains: two heavy chains and two light chains.
true
1 multiple choice option
________ can quickly respond upon second exposure to the eliciting antigen.
Memory T cells
2 multiple choice options
in an antibody molecule, the two heavy chains are bonded to one another through _____.
disulfide bonds
3 multiple choice options
most B cells must interact with cells that bear receptors for epitopes on the same antigen to become functional. What type of cell would this be?
T helper
The principal activity of an ______________ is to immobilize, call attention to, or neutralize the antigen that is complementary to its receptor.
antibody
the Fab fragment of an antibody molecule, with a site that recognizes the antigen, is termed the _________________.
antigen binding fragment
antibodies can cross-link cells or particles into large clumps through a process called ______________.
agglutination
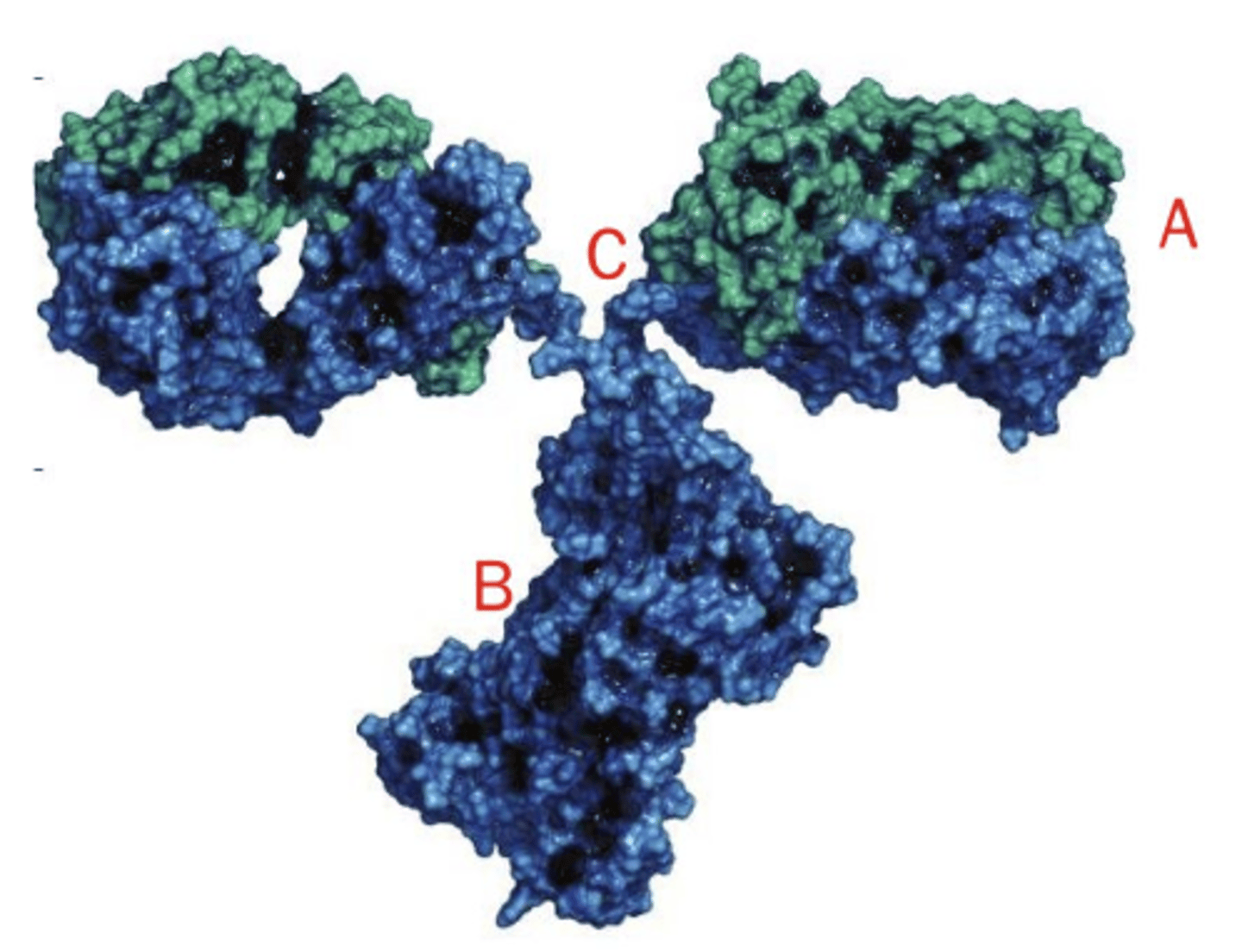
identify the Fc region in this image of an antibody
B
2 multiple choice options
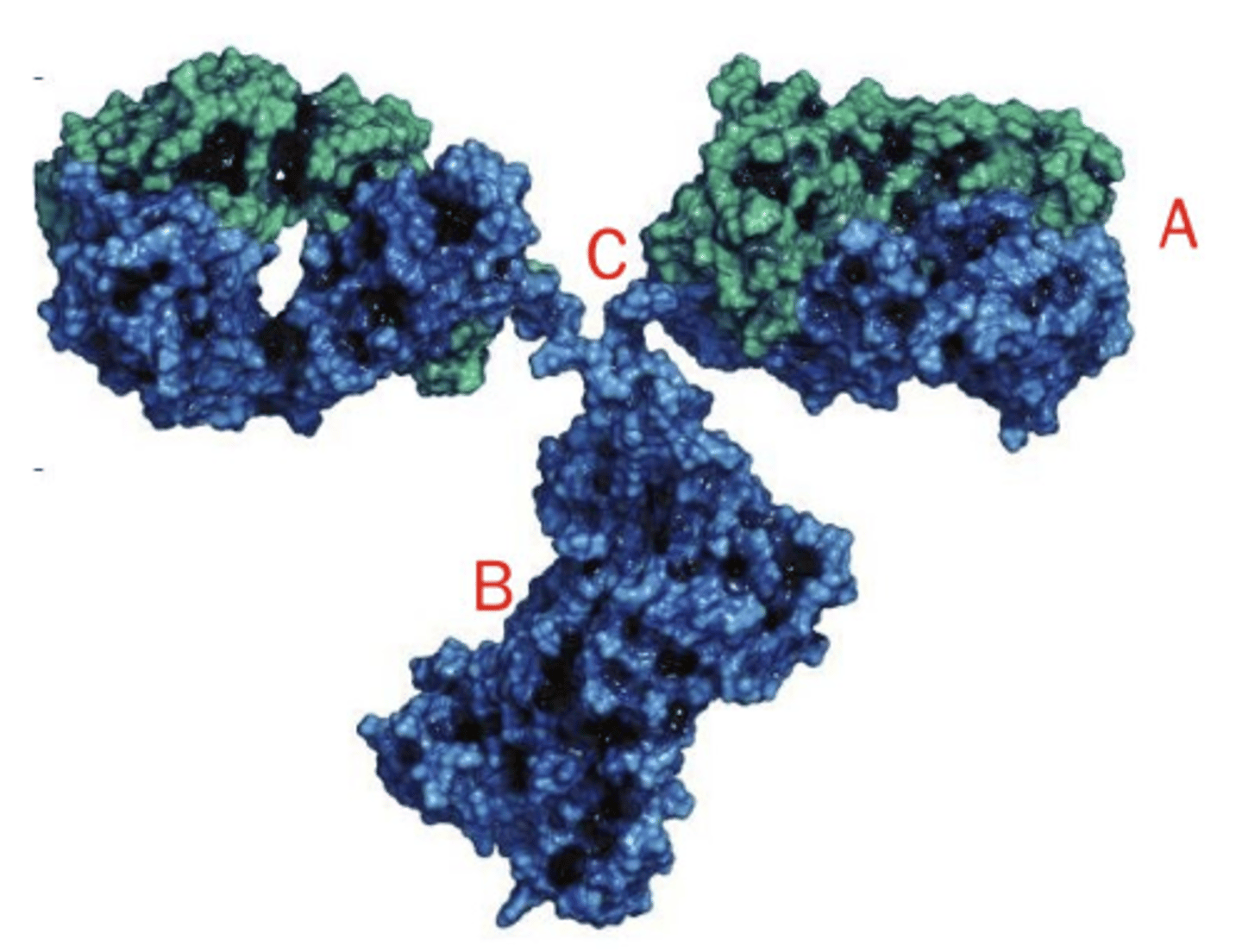
identify the antigen binding site in this image of an antibody
A
2 multiple choice options
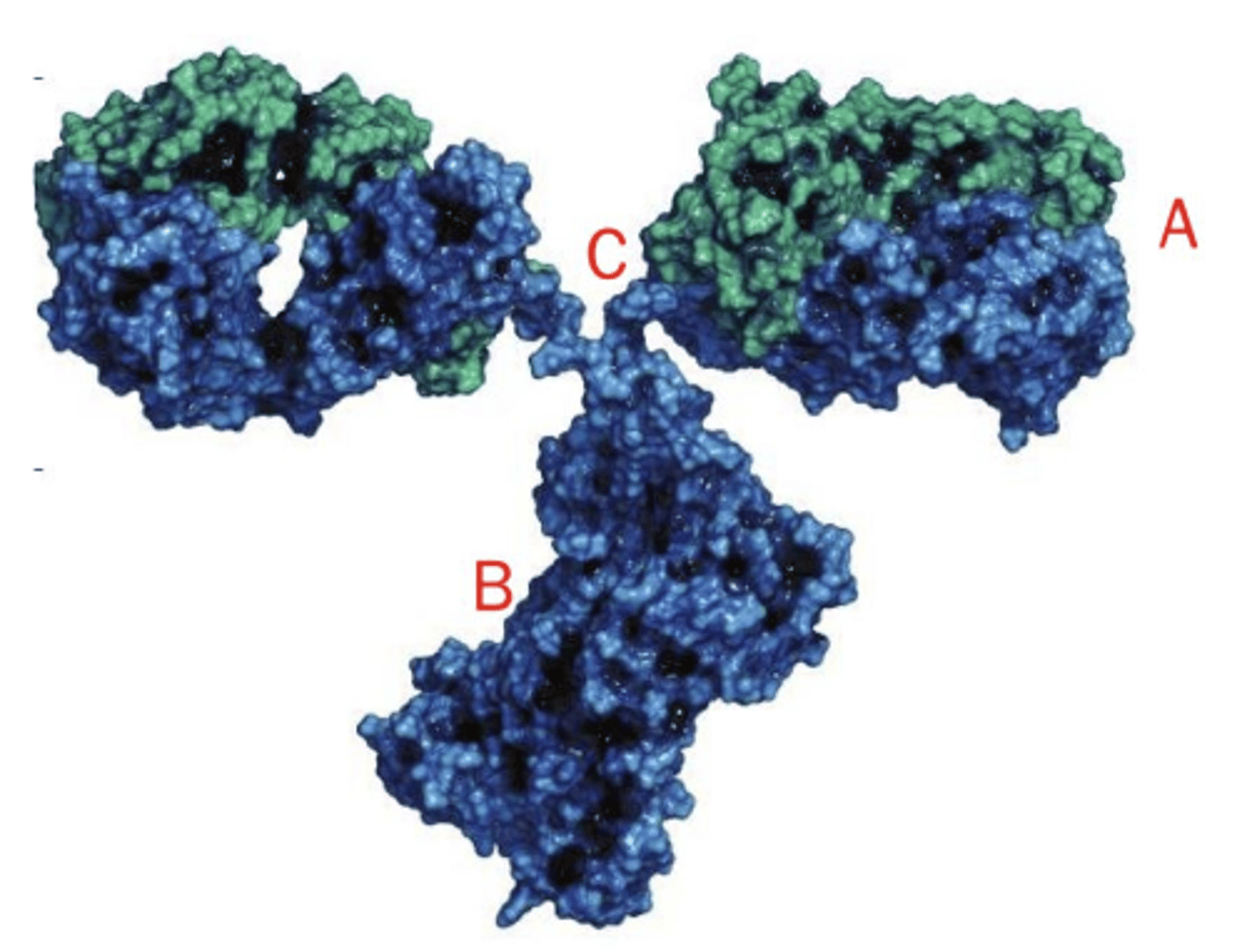
identify the hinge region in this image of an antibody
C
2 multiple choice options
an ____________ refers to a special type of antibody that neutralizes bacterial exotoxins
antitoxin
a toxin that has been neutralized is called a ___________.
toxoid
an antibody molecule has a total of ________ polypeptide chains, including ______ heavy chains and _________ light chains
(4) (2) (2)
3 multiple choice options
the fragment of an antibody that serves as the effector portion of the molecule as it binds to receptors on the membranes of many different cells is the ______________ fragment.
Fc or crystallizable
in an antibody molecule, each light chain is bonded by disulfide bonds to _____.
one heavy chain
3 multiple choice options
the effect of an antibody's Fc fragment binding to an Fc receptor on a cell depends on ______.
the cell's role
3 multiple choice options
the principal activity of an antibody is to _immobilize, call attention and _____________ the antigen for which it was formed
neutralize
this fragment of the antibody molecule binds to phagocytes when antibodies opsonize an antigen
Fc
2 multiple choice options
the concentration (measure) of antibodies in serum is expressed as the _________________.
titer
which type of immunity occurs when an individual is stimulated by an antigen that activates the T and B cell response?
active immunity
1 multiple choice option
deliberately inoculating a healthy person with the dried pus from the pustules of a smallpox patient is called ______.
variolation
____________ is a process by which a person becomes protected against a disease through vaccination
immunization
intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) contains immunoglobulins extracted from ______.
the pooled blood of many human donors
3 multiple choice options
the artificial active immune process called ______________ generates memory cells to a pathogen so an immediate protective immune response is elicited upon entry of the pathogen into the body.
vaccination
there is a vaccine for almost all known pathogenic microbes
false
1 multiple choice option
which of the following is true for vaccines that have been approved and licensed for general use in preventing diseases?
The vaccines may show adverse outcomes, known as complications.
2 multiple choice options
immune serum globulin contains immunoglobulins extracted from the pooled ______ of many human donors.
blood
3 multiple choice options
protection against ______ diseases can be achieved through vaccination.
many, but not all
3 multiple choice options
before vaccines can be marketed they go through years of trials and, upon approval, the vaccines ______.
have numerous complications
2 multiple choice options
CD8 markers bind to MHC class _____ molecules.
I
1 multiple choice option
MHC-I molecules are located on what types of cells?
All nucleated cells
3 multiple choice options
MHC-I molecules normally display "self" proteins, those that are normally produced by a cell.
true
1 multiple choice option
In the case of cancer or viral infection, which MHC class is involved with displaying abnormal proteins to cytotoxic T cells as a signal for destruction?
I
1 multiple choice option
MHC-II molecules are located on what types of cells?
Macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells
3 multiple choice options
Helper T cells require antigen processing and presentation by MHC-_____ molecules.
II
1 multiple choice option
what is the site of maturation of T cells?
thymus
1 multiple choice option
macrophages with antigen fragments displayed on their surfaces are known as ___________________.
antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
when activated by antigen-presenting cells, helper T cells release what cytokine that activates B-cells and cytotoxic T cells?
Interleukin-2
3 multiple choice options
cytotoxic T cells know that a cell is infected because ________.
it has antigens from the disease-causing microbe on its surface
3 multiple choice options
B cells differentiate into ________, which make antibodies.
plasma cells
3 multiple choice options
the immune system responds more swiftly by making antibodies to an antigen after the first exposure because ________.
memory B cells are produced during the first response
3 multiple choice options
antigen-presenting cells release what cytokine to activate helper T cells?
Interleukin-1
3 multiple choice options
cytotoxic T cells kill target cells by ________.
exposing them to chemicals which induces apoptosis.
3 multiple choice options
surface receptors on immune system cells function in ________.
All of these choices are correct.
3 multiple choice options
CHAPTER 14
Immunopathology is the study of disease states associated with _____ of the immune response.
- hypersensitivity
- hyposensitivity
- overactivity
& _____________________
underactivity
what is the mechanism of action of hypersensitivity type I?
allergy and anaphylaxis
3 multiple choice options
what is the mechanism of action of hypersensitivity type II?
IgG- and IgM-mediated cell damage
3 multiple choice options
what is the mechanism of action of hypersensitivity type III?
immune complex reactions
3 multiple choice options
what is the mechanism of action of hypersensitivity type IV?
delayed hypersensitivity
3 multiple choice options
Any substance that provokes an allergic response is referred to as a(n) _________________.
allergen
In a range from mild to severe, the majority of type I allergies can be characterized as relatively ________________.
mild
Airborne environmental allergens such as pollen and house dust are called ______.
inhalants
3 multiple choice options
The study of disease states associated with overreactivity or underreactivity of the immune response is called _______________.
immunopathology
The subsequent exposure to an allergen that triggers an allergic reaction is called a(n) ______ dose.
provocative
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following classification systems is currently used to differentiate hypersensitivity reactions?
Type I to type IV categories
3 multiple choice options
________ is the most profuse and fastest-acting mediator of allergy; its effects include smooth muscle contraction and dilating arterioles and venules.
Histamine
3 multiple choice options
Allergic individuals are acutely sensitive to repeated contact with ______, which do not noticeably affect nonallergic individuals.
allergens
3 multiple choice options
________ is a form of atopic allergy marked by seasonal acute nasal congestion, redness of the eyes, and profuse mucus secretion.
Allergic rhinitis (hay fever)
3 multiple choice options
_______________ is an inflammation of the conjunctiva but not the respiratory membranes.
Conjunctivitis
____________________ is a respiratory disease characterized by impaired breathing due to bronchoconstriction.
Reactive asthma
The majority of type I allergies are severe or life-threatening.
False
Allergens that enter the respiratory tract are called ______________.
inhalants
Atopic dermatitis is commonly referred to as ______.
eczema
3 multiple choice options
Subsequent encounters with the same allergen are referred to as ________________ doses.
provocative
Which are the three most common gastrointestinal symptoms of food allergy?
vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea
3 multiple choice options
The inflammatory reaction to the local injection of allergen, observed as a wheal and flare pattern on the skin, is called ______ anaphylaxis.
cutaneous
3 multiple choice options
anaphylaxis is _______________ and part of the adaptive immune response
IgE mediated
____ anaphylaxis is characterized by sudden respiratory and circulatory disruption that can be fatal.
systemic
A form of atopic allergy marked by seasonal acute inflammation of the eyes and mucous membranes of the respiratory passages is called _________________.
allergic rhinitis (hay fever)