endocrine system U8
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What other system is the endocrine very close in contact with and for what reason
Works with nervous system. Important for homeostasis
What is endocrine communication and what type of messengers does it involve
Considered indirect communication as cells do not need to by in close proximity (distant signalling) and involves chemical messengers called hormones
Are endocrine or nervous effects longer lasting and why
Endocrine communication has LONGER LASTING effects then nervous conductions as hormones enter directly through blood stream and hormones last longer in synapse then neurotransmitters
How are hormones carried to effect target organs
Carried in bloodstream so they can reach multiple targets
Endocrine vs exocrine
Endocrine-involves hormones to blood
Exocrine-creates secretions to body surface
What is paracrine vs autocrine communication
Paracrine-near signalling where stimulation is limited to neighbouring cells in the same tissue
Autocrine-self signalling. Where stimulation only effects the single cell that secretes the hormone
Endocrine-distant signalling through bloodstream
What are hormones
Chemical messengers
What can the binding of a hormone cause
Altered rate of genetic activity
altered rate of protein synthesis (rapid)
change in membrane permeability
3 classifications of hormones
Amino acid derivatives
Peptide hormones
Lipid derivatives
What are amino acid derivative hormones and the ones to know
Small molecules from tyrozenes. → catecholamines (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine), thyroid hormones
What are peptide hormones and ones to know
Long or short→glycoproteins, TSH, ADH
Lipid derivatives and ones to know
Ones to know: steroids (estrogen, testosterone, calcitrol), eicosanoids like prostaglandins
What is special about steroids
The bond to plasma proteins which give them extended action and longer effect on the body
How do hormones travel in related to the blood
Either freely in blood (which attach to receptors) or attached to a carrier protein. But in both cases a hormone MUST attach to receptor
How are hormones recycled
Can be broken down by liver and kidney if not used
What stimuli control hormone secretion
Humoral stimuli, hormonal stimuli or neural stimuli
Humoral stimuli
Refers to changes in extra cellular environment (ECF)→for example insulin secretion
Hormonal stimuli
Changes in the levels of circulating hormones (hormone amount triggers hormone release)
Neural stimuli
Arrival of neurotransmitters at neuromuscular junctions which triggers nervous system (fight or flight), hypothalamus activation
Major functions affected by hormones
Mobilization of body defences
regulation of cellular metabolism
regulation of water, electrolyte and nutrient balance
Growth and development
Reproduction
What type of effects can hormones have on the other hormones
Permissive- Strengthens other hormone
Synergistic- works together with other hormone
Antagonistic-works in opposite to other hormone
What do hormones rely on to exert their effects
Target receptors in target organs
2 types of target receptors deemed by location
Extra cellular receptors-found on cell membrane
Intra cellular receptors-inside cell
Where can target receptors be found
May be on another endocrine organ causing inhibition or secretion of another hormone
In which ways can the number of target receptors by impacted
Up regulation and down regulation
What is up regulation
Process where lack of hormone leads to increase in receptors
What is down regulation
Where tissue becomes less responsive or turns off receptor due to an abundance of hormone (think type 2 diabetes)
Role of second messengers in endocrine response
While the hormones acts as the first messenger. Second messengers are needed to actually cause cell change
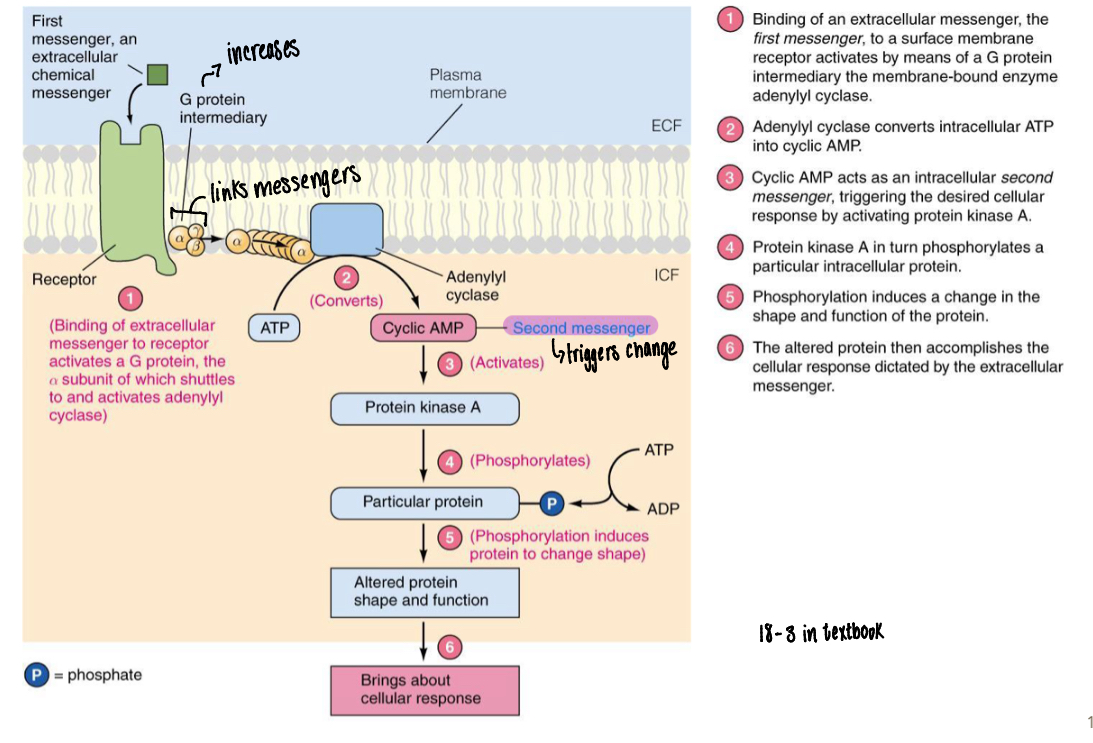
What are the second messengers needed and their functions
G proteins- link first and second messengers (stimulated receptor to cyclic AMP)
Cyclic AMP and calciuum- cyclic AMP acts as the second messengers to trigger change and desired cellular response to induce phosphorylation
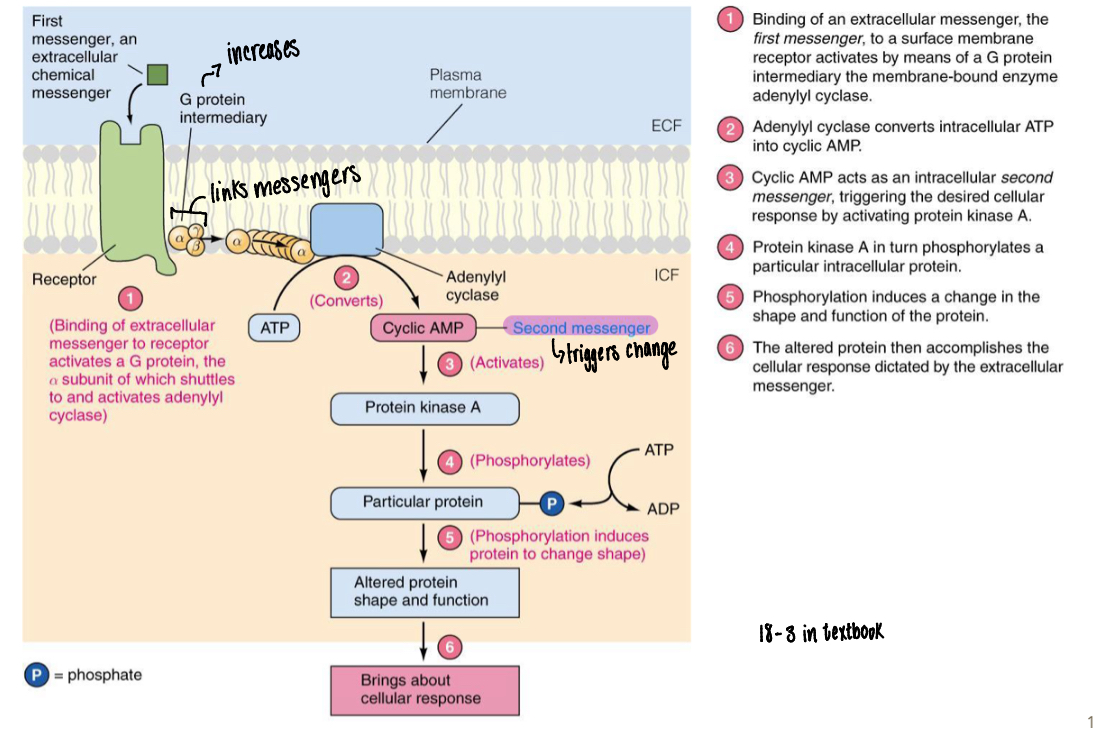
Where is the hypothalamus and pituitary gland located, what connects them
Pituitary is a small gland located at the base of the brain that sits in sella turcica (bone depression in sphenoid)
Connected to hypothalamus by a thin connecting stalk called INFUNDIBULUM to provide constant communication between the two
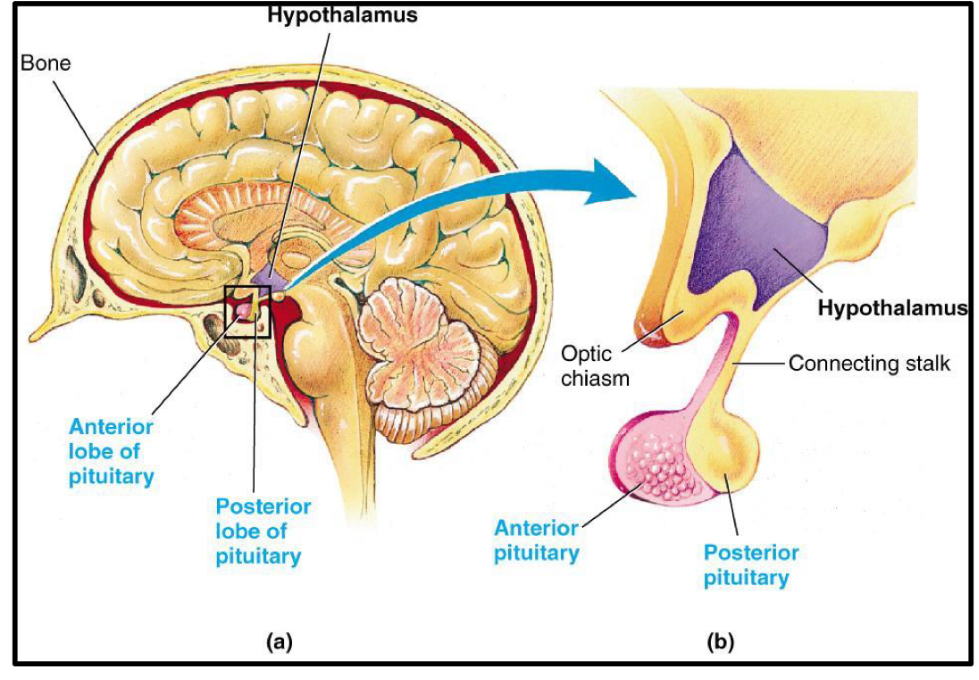
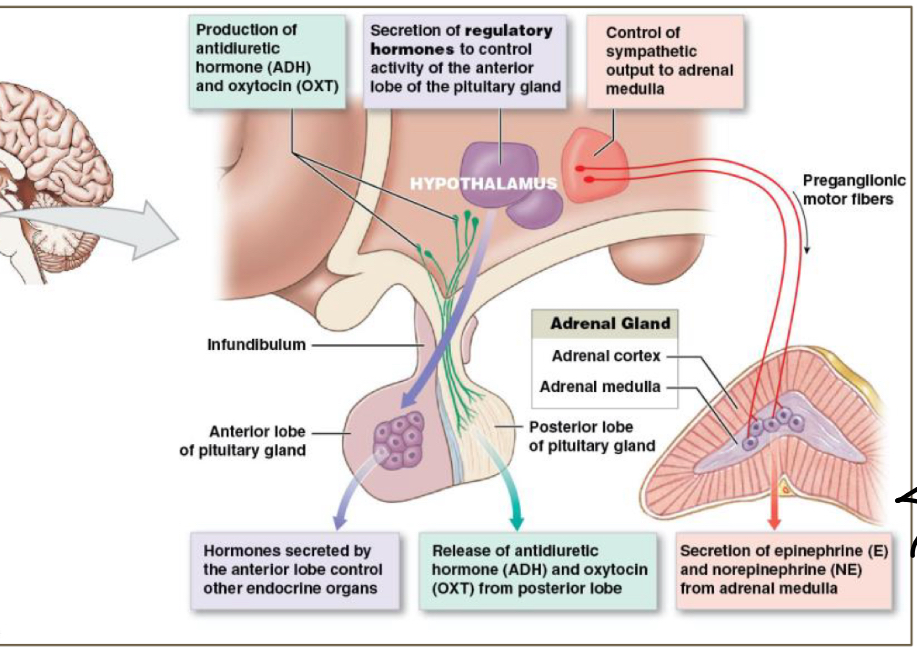
Functions of the hypothalamus
Functions as an endocrine gland (produces OXYTOCIN AND ADH) - sends to post pit to be secreted
Secretes regulatory hormones that control activity of endocrine cells in ANTERIOR PITUITARY
Contains autonomic centres that controls endocrine cells o the adrenal medulla
Regulates functions of both pituitary lobes
Another name for the pituitary gland
Hypophysis
Functions of the pituitary gland, the lobes of the pituitary and the amount of hormones they secrete
Secretes 9 important hormones
Consists of 2 lobes
Posterior pituitary- 2 hormones
Anterior pituitary-7 hormones
Second name for posterior pituitary, type of tissue its composed of and hormones it secretes
NEUROHYPOPHYSIS- composed of neural tissue and secretes oxytocin and ADH
Another name for the anterior pituitary, tissue its composed of and hormones it secretes
ADENOHYPOPHYSIS, consists of glandular epithelial tissue and secretes: TSH, GH, FSH, LH, PRL,ACTH, MSH
What controls release of hormones from both lobes
Hypothalamus
What is ADH
Antidiuretic hormone or VASOPRESSIN which is released in response to hypothalamic osmoreceptors (blood pressure changes and solute concentration). MADE in hypothalamus SECRETED from POSTERIOR PITUITARY
Functions of ADH
PRESERVE WATER
Decreases urine production directly
Decreases sweating
Increases vasoconstriction
Impact of decreased ADH
Increased fluid loss and dehydration. Impacted by alcohol, caffeine ingestion, head trauma.
Oxytocin effects as a reproductive hormone in boys and girls
In men-causes contraction of sperm duct and ejection of sperm
In women-contraction of uterus (orgasm) which causes movement of sperm toward uterine tubes
Functions of oxytocin in labour and delivery and breast feeding
Contraction of uterus for delivery of infant and prevention of uterine bleeding
Causes a let down of milk from mammary glands (in fact suckling stimulates hormone)
What is SIADH
Syndrome of inappropriate ADH-often related to head trauma or tumours where TOO MUCH ADH causes a lot of water retention and high blood pressure
What is diabetes insipidus
TOO LITTLE ADH, causes lots of dilute urine production and causes extreme dehydration. (HAS NOTHING TO DO WITH INSULIN)
Name for overproduction of urine
Polyuria
Name for extreme thirst and hunger
Thirst-polydispia
Hunger-polyphasia
What is portal circulation in ant. Pit.
The idea that 2 capillary networks are connected. They provide efficient means of communication. Ensures all hypothalamic hormones entering portal vessels reach target cells in anterior lobe
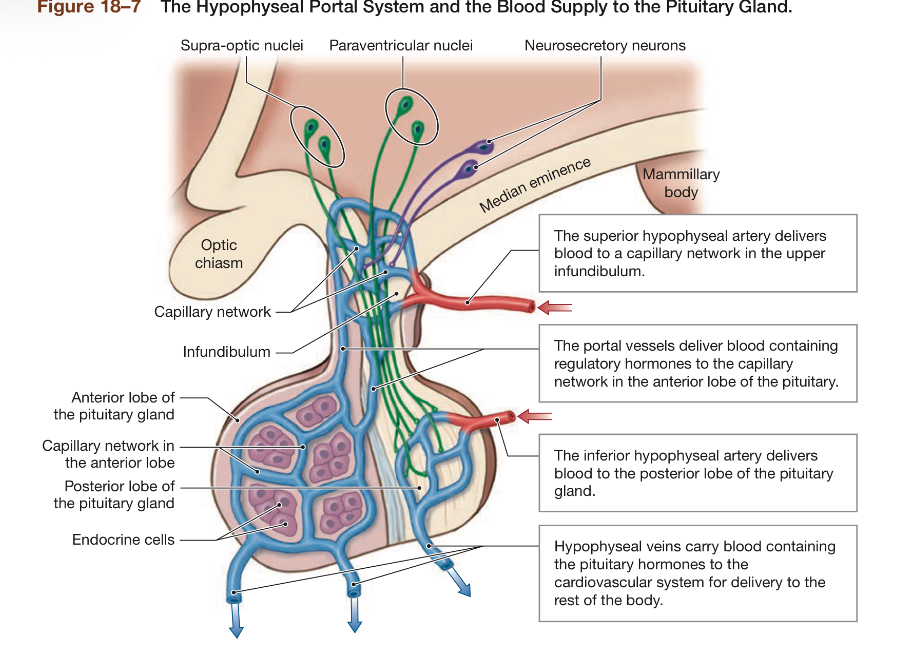
process of portal circulation
Regulatory hormones from hypothalamus enter portal circulation→capillary circulation→fenestrated capillaries (very permeable) around endocrine cells of anterior pituitary→endocrine hormones released to blood stream→to systemic circulation via HYPOPHYSEAL veins
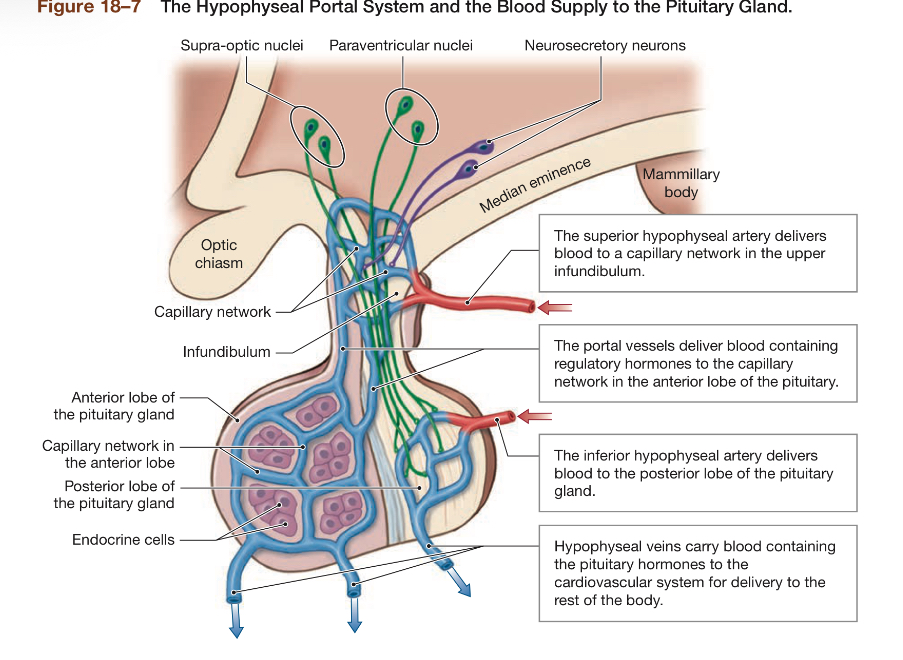
Which hormones regulate anterior pituitary hormone secretion
Hypothalamic releasing hormone (RH)
Hypothalamic inhibiting hormone (IH)
7 hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary
Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Growth hormone (GH)
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Prolactin (PRL)
Melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH)
What is TSH describe negative feedback loop
Also known as a thyrotropin , creates a negative feedback loop in which hypothalamus stimulates pituitary which stimulates thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormones.
As circulating concentrations of thyroid hormones rise, rates of TRH and TSH decline
What is ACTH, describe negative feedback loop
Also known as corticotropin stimulates release of steroid hormones by the adrenal cortex effects glucose metabolism such as cortisol
What are gonadotropins and which hormones are considered these
Regulate activity of the gonads (testes and ovaries). Stimulated by GnRH of the hypothalamus.
FSH and LH are gonadotropins
What is FSH
Follicle stimulating hormone: promotes sperm and egg maturation. Stopped by inhibin
What is LH
Luteinizing hormone- induces ovulation in females, promotes ovarian secretions of estrogen and progesterone. In males, stimulates release of testosterone and androgens
What is prolactin
Helps stimulate mammary gland development in females. Stimulates milk production by the mammary glands
What is the growth hormone, another name for it and what does it do
Somatotropin that stimulates cell growth and division by accelerating rate of protein synthesis in myocytes and chondrocytes
Follow path that growth hormone uses to stimulate cell growth
GH release→somatomedin hormones (insulin line growth factors released by liver)→increased uptake of amino acids→formation of proteins→increased cell synthesis
Main targets of GH
Bones, cartilage and skeletal muscles
Results of hyposecretion (Too little) of GH In kids and adults
In kids→Dwarfism
In adults→ decreased strength and bone mass
Results of hyper secretion (too much) of GH in kids and adults
In kids→gigantism
In adults→acromegaly (bones get thicker instead of longer)
How does thyroid hormone effect growth
Growth is stunted in kids with hypothyroidism
Hyper secretion does not cause excessive growth
How does insulin effect growth
Deficiency often blocks growth
Hyperinsulinism often spurs excessive growth
Androgens effect on growth
Plays a role in pubertal growth spurt, stimulates protein synthesis in many organs
thyrotropin releasing hormone
Stimulates secretion of TSH and PRL
Corticotropin releasing hormone
Stimulates release of ACTH
Where is thyroid gland
On anterior trachea, bow tie gland inferior to thyroid cartilage, not typically visible or felt through skin
What joins lobes of thyroid gland
Isthmus- bow tie
What are follicular cells
Cells bound to plasma proteins which are considered the functional cells of the thyroid that produce two iodine containing hormones
Thyroid hormones
Tetradiodothyronine (thyroxine or T4) -90% of thyroid
Tri-iodothyronine (T3)
Both depend on iodine molecules which can be obtained from our diet
What are C (clear) cells
Cells contained in thyroid that secrete peptide hormone CALCITONIN WHICH DECREASE CALCIUM IN BLOOD
Are thyroid hormones lipophilic or lipophobic
Lipophilic hormones
What type of effects do T3 and T4 have on the body
Impact rate of metabolism→by altering rate of protein synthesis in target cell.
Caloregenic→effect on metabolic rate and heat production
Thyroid hormones effect on other systems
Permissive to GH→aids growth
Nervous system growth and function
Sympathetic effect on cardiovascular and nervous system
Calcitonin role in body
Stimulates calcium excretion by kidneys and prevents calcium reaborbtion by GI tract. Decreases calcium levels in blood by putting it into bones and maintaining bone mass
What is hypothyroidism caused by
Failure of thyroid gland
secondary to TSH, TRH hormone deficiency
Not enough iodine in diet
Symptoms of hypothyroidism
Always tired, chilled, hair loss and weight gain
What is cretinism
Congenital disorder which effect mental and physical growth stemming from hypothyroidism from birth
What is myxedema
Face swells and characterized by thick hard skin on lower legs resulting from hypothyroidism
Treatment for hypothyroidism
Synthroid replacement therapy→synthetic supplement of thyroid hormones
Hyperthyroidism symptoms
High metabolism, weight loss, irritability
What is Graves’ disease
Autoimmune disorder which is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism BODY ATTACKS THYROID. And will aggressively produce thyroid stimulating immunoglobins and characterized by fluid retention in odd places (exophthalmos)
What causes goiters is it more related to hypo or hyper thyroidism
Occurs in both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism and primarily caused by low iodine levels
Where are your parathyroid glands
4 glands (2 on each side) embedded in posterior thyroid
Principle cells make PTH
What is the function of the parathyroid glands
Produce and secrete PTH in response to blood calcium levels
PTH effect on blood calcium levels
Increases calcium levels in blood by stimulating osteoclasts to break it down from bones. Though too much calcium in blood causes neurological damage
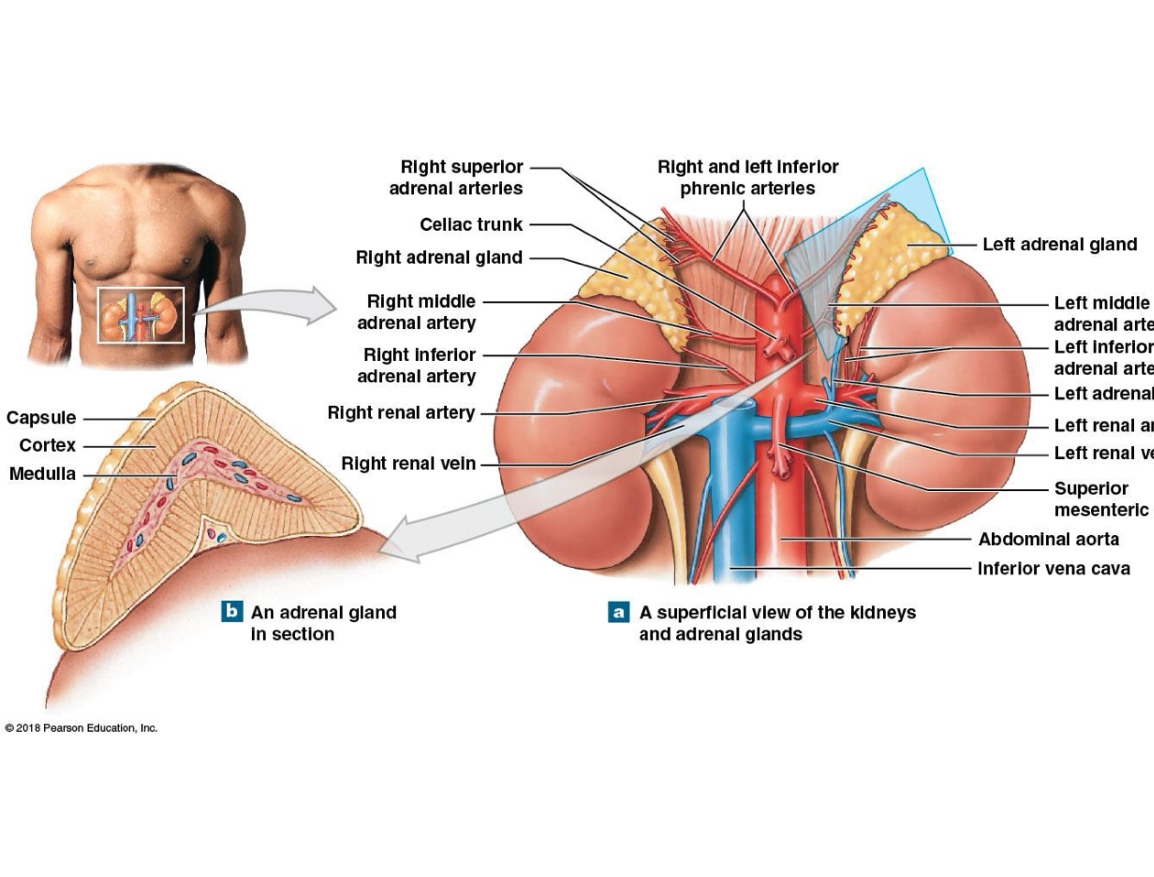
Where are your adrenal glands found
Sits on top of each kidney embedded in a capsule of fat which is important structures
Regions of adrenal glands
Adrenal cortex-outer portion that secretes corticosteroids
Adrenal cortex-inner portion that secretes catecholamines
Areas of the adrenal cortex
Zona glomerulosa- top layer, aldosterone
Zona fasciculata-middle layer, cortisol and cortisone
Zona reticularis-bottom layer, androgens
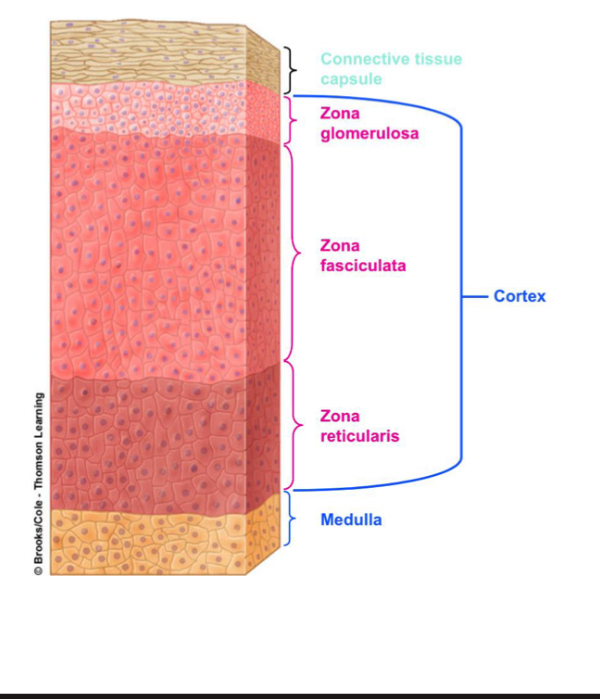
What are mineralocorticoids. Main hormone
Zona glomerulosa- steroid hormones that impact fluid and electrolyte balance primary hormone is aldosterone
Aldosterone effects and relationship with ADH
Decreases blood pressure. Promotes the reabsorption of Na sodium and in turn excretes potassium and hangs onto water as well.
Increased effect in presence of ADH
What are glucocorticoids and main hormone
Zona fasciculata-steroid hormones that impact glucose metabolism (increase fuel availability)
Main hormone is cortisol
ANTI INFLAMMATORY response and slows immune response
What stimulates cortisol secretion and how does it effect body
Stimulated by ACTH. Targets most cells to increase glucose synthesis and is sometimes activated in stress repsonses to make fuel more available
BODIES MAIN STRESS HORMONE
Cortisol effect on healing
If too much is secreted it can make your immune system more susceptible and in turn decreased healing rates and increases chances of getting sick
Androgens, where are they produces and what do they do
Zona reticularis- impact development of secondary sex characteristics and are estrogen and testosterone precursors
Diagnosis names for too little or too much cortisol
Too much→cushings disease (moon face)
Too little→addisons disease
During long term stress the constant cortisol stimulating messes with one’s homeostasis
What is mainly responsible for controlling hormone released from adrenal medulla
Sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
What hormones are produced by adrenal medulla
Epinephrine (80%) and norepinephrine
How do epinephrine and norepinephrine interact with plasma receptors
Bind to alpha and beta receptors on plasma membranes
Where is pineal gland found
Epithalamus
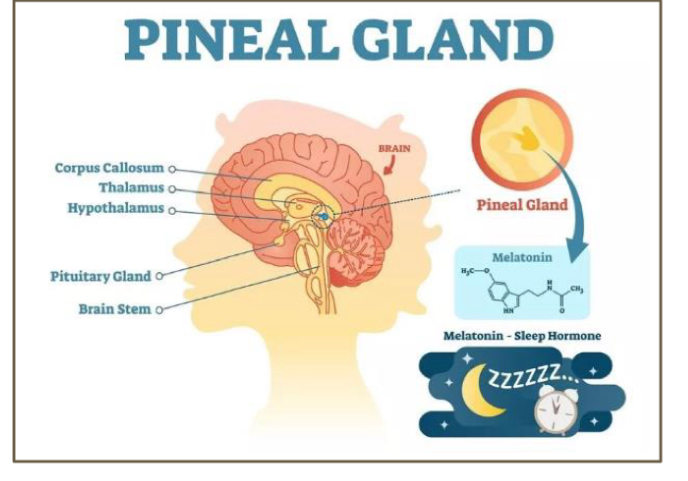
Primary function of pineal gland
Contains secretory cells called pinealocytes that synthesize melatonin
Its primary function is to influence circadian rhythm