Small Animal Nursing I Lecture 10 - Bandaging Techniques
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
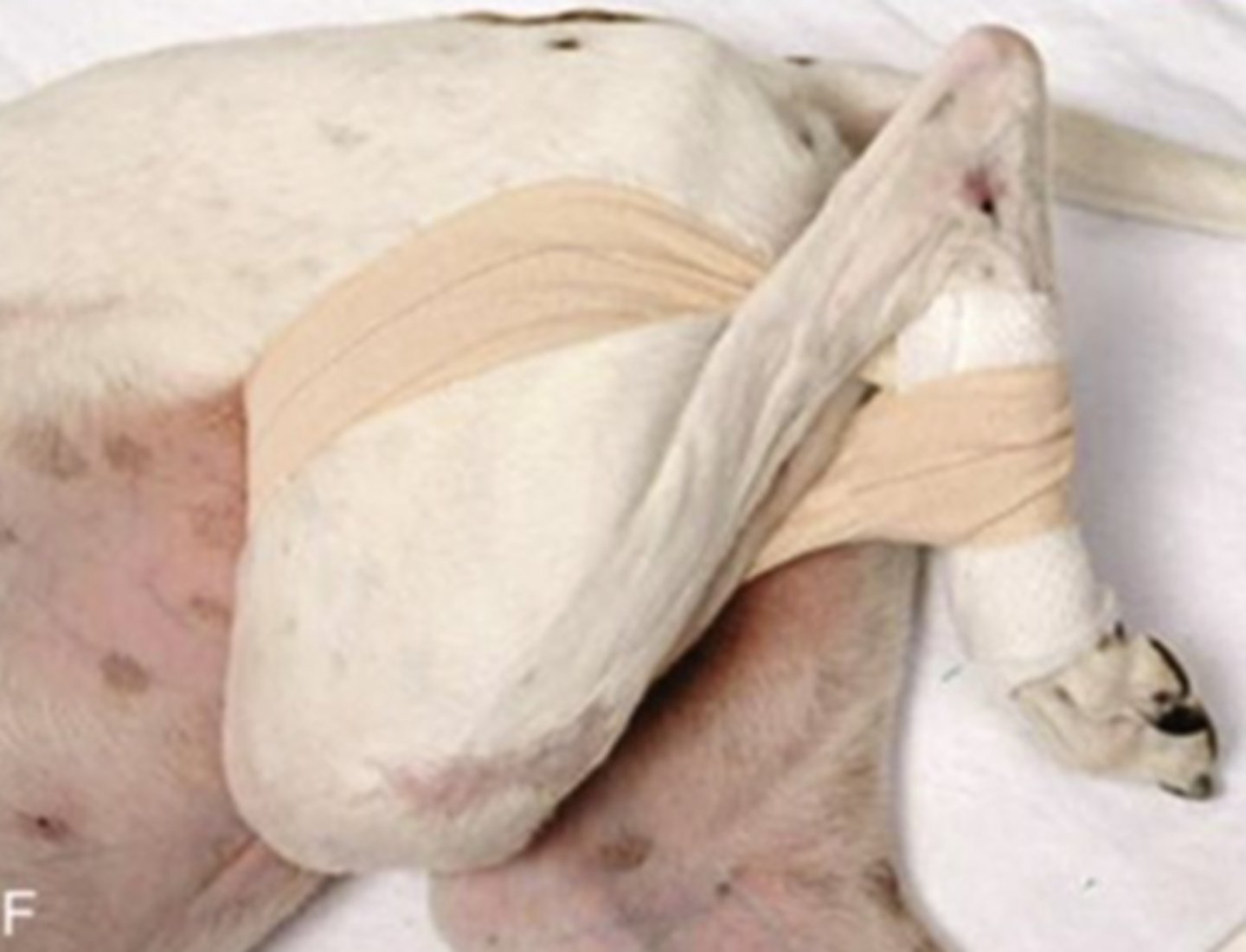
Ehmer sling (Not kept longer than 2-3 weeks to prevent muscle shortening)
A non-weight-bearing sling applied to the pelvic limb to protect the hip joint after injury
Craniodorsal displacement of the femoral head
Identify the pelvic abnormality that causes the limb to be carried close to the body, with the stifle externally rotated
• Used after a non-surgical reduction of a craniodorsal hip luxation
• Used selectively after surgery of the hip joint
• Sling will internally rotate and abduct the femur, forcing femoral head into place
Identify the functions of the Ehmer sling
90-90 flexion sling
A sling using a simple loop of adhesive tape wrapped around the stifle and hock while both joints are maintained at 90 degrees of flexion
To prevent contractures of the quadriceps muscle after repair of a distal femoral fracture in young dogs
What is a 90-90 flexion sling used for?
• Applied immediately after surgical repair of the distal femur
• Maintained for 2-3 days until post-op pain and swelling have decreased
• After removal patients can begin placing weight on the leg
At what point in the healing process is a 90-90 flexion sling applied?
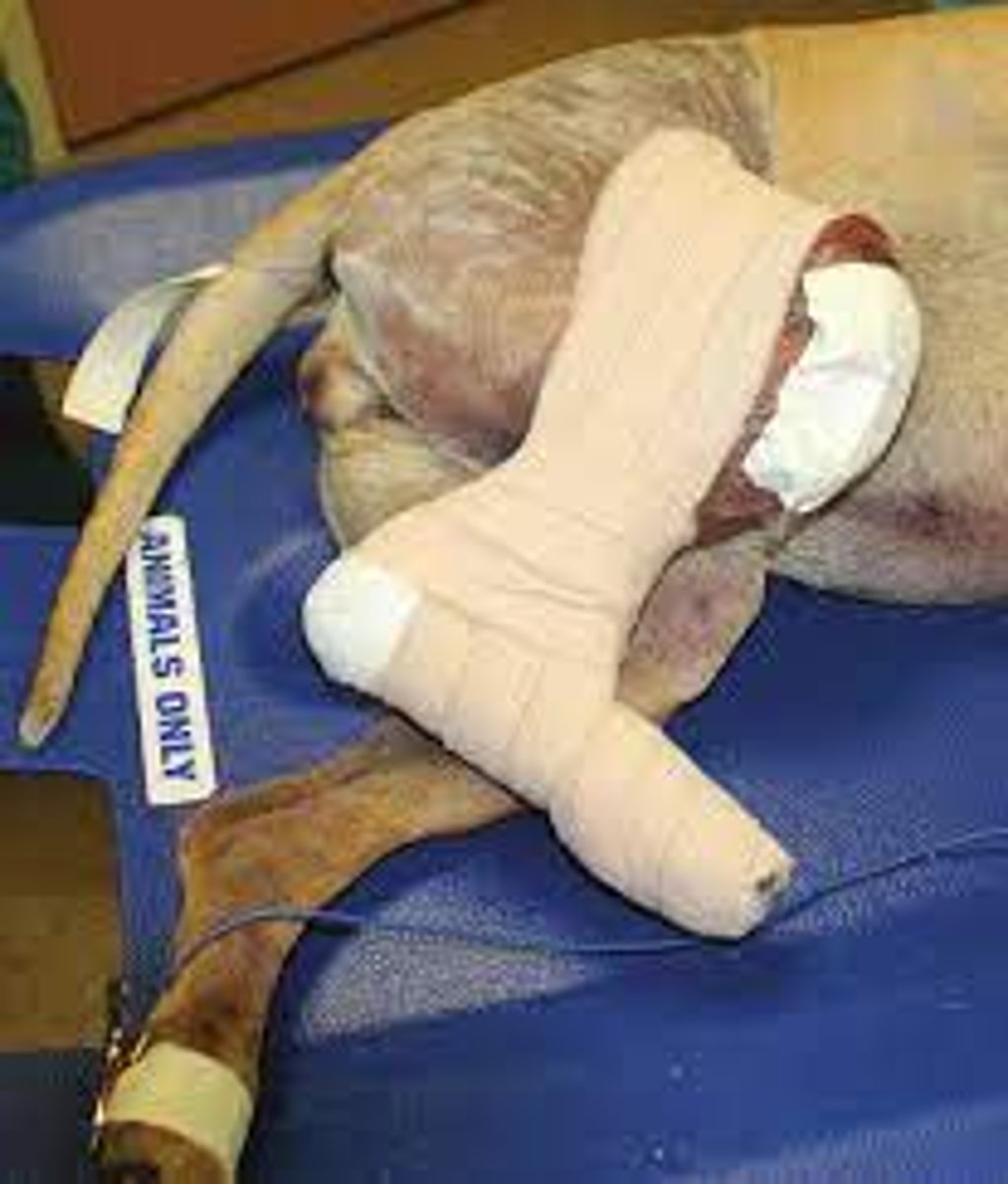
Velpeau sling
A non-weight-bearing sling used to flex the entire forelimb against the thoracic wall, with a soft-padded bandage applied to immobilize the joints
• Applied after the reduction of a medial shoulder joint luxation
• After reconstruction of tenuous (poor blood supply) fracture
When is a velpeau sling applied?
Carpal flexion sling
A simple non-weight-bearing forelimb sling that prevents weight bearing on the carpus but allows movement of the elbows and shoulder joints
Used to relieve tension on the carpal flexor tendon after injury or surgical
repair
What is a carpal flexion sling used for?
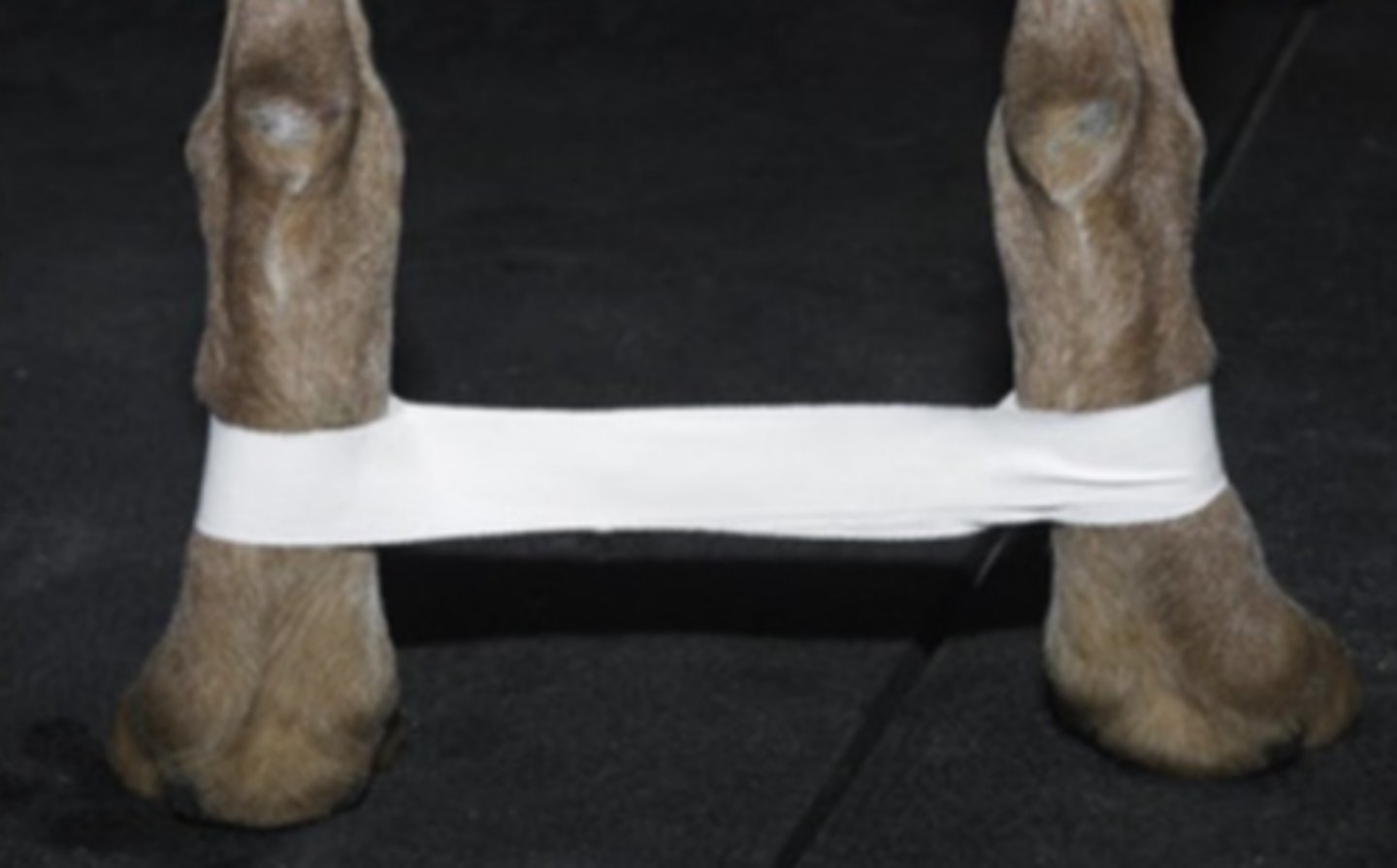
Hobbles
A strip of adhesive tape applied around metatarsal bones of both pelvic limbs to prevent abduction
• Prevent abduction of the pelvic limbs
• Used after reduction of ventral hip luxation
Identify the function of hobbles

Tie-over bandage
Applied to locations on the body where traditional limb bandages cannot be used or would be impractical
• Axillary areas
• Inguinal areas
• Around the pelvis
Identify locations where tie-over bandages are commonly applied
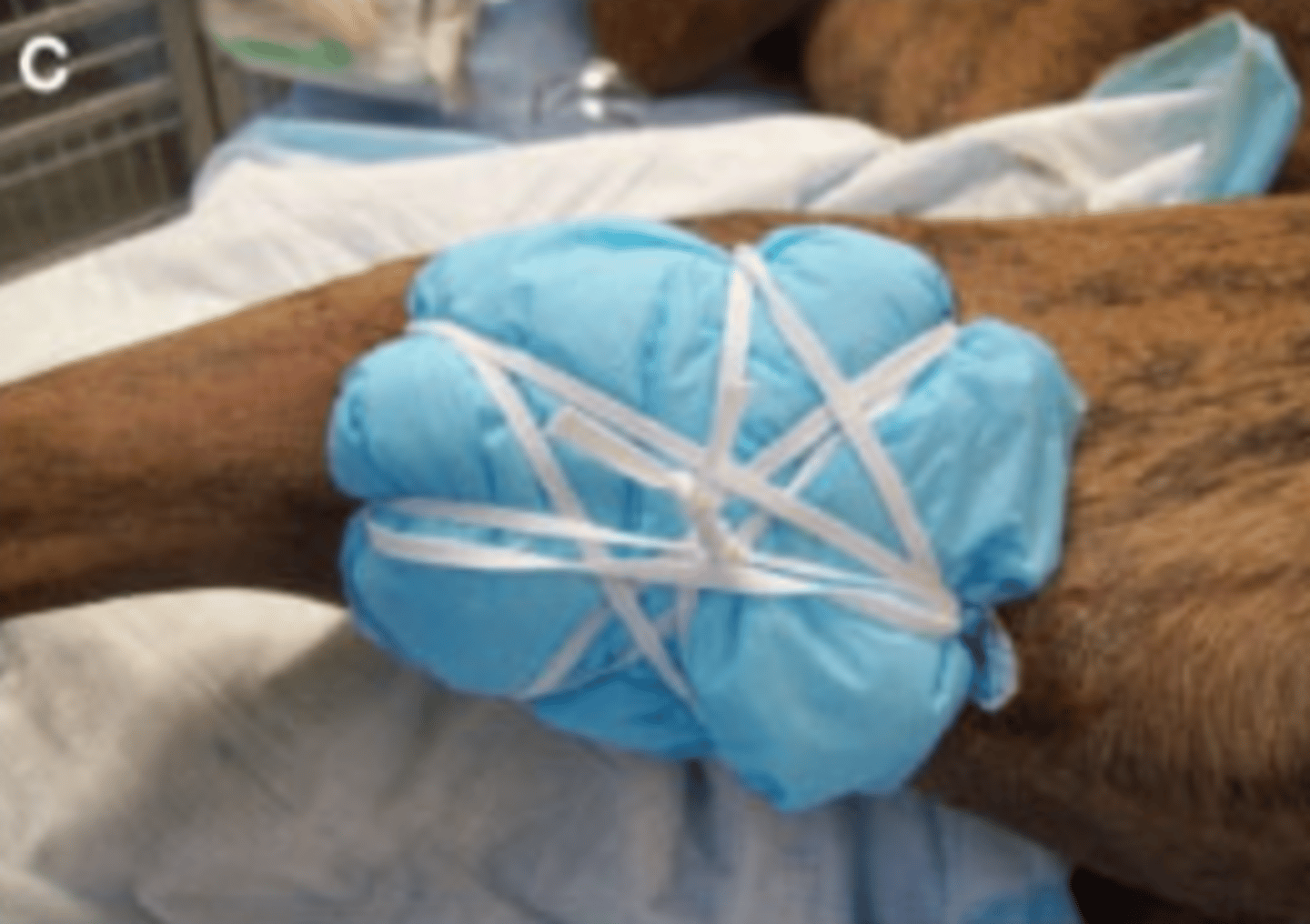
Tie-over bandage (covered with appropriate primary, secondary layers, and a tertiary layer with paper drape)
This type of bandage uses suture loops that encircle the wound edges and are used as anchor points for bandage material
Adhesive drapes
Can be used instead of tie-over skin sutures to hold primary and secondary bandage layers in place
• Used in place of tie-over skin sutures to bandage layers in place
• Also functions as the outer protective layer
• Useful for wounds on flat surfaces, such as the chest or abdominal wall
Identify the function of adhesive drapes
Three-layer soft-padded bandages (stockinette can be used to hold primary and secondary layers in place)
Bandages that encircle body parts such as the head, chest, abdomen, and tail
• To absorb wound drainage
• Provide compression against dead space
• Protect the ear from injury caused by head shaking
Identify reasons a head bandage might be applied to the patient's ear after injury or surgery
• Animals must be closely monitored for respiratory compromise because of airway compression by a tight bandage
• Corneal abrasions if the bandage is placed too close to the eye
Identify complications associated with a head bandage
Figure eight pattern
What pattern is used to apply a chest bandage around the forelimbs to prevent slippage?
• Applying bandage too tightly can restrict respiratory function
• Urination and defecation can be impaired if placed over caudal abdomen or pelvis
• Soiling of the bandage is common
Identify complications associated with a chest bandage
• Muscle atrophy
• Contracture of soft tissues
• Joint changes
What can prolonged immobilization from bandage use lead to?
• Daily inspection of toes for swelling, decreased warmth, or abnormal color
• Bandage must be kept dry and clean
• Patient must wear e-collar to prevent chewing and licking bandage
What does care and monitoring of a distal bandage include?
• Foul odor from the bandage
• Sudden behavior change in the animal
• Increased lameness or biting at the limb
What may indicate that bandage complications are occurring?