Microbial Diseases of the Skin and Eyes
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Epidermis
Thin outer portion of skin; composed of layers of epithelial cells
Keratin
Waterproofing protein coating outer layer of epidermis
Dermis
Inner, thick portion of skin; composed mainly of connective tissue
Human Skin
• Perspiration and sebum contain nutrients and keep skin from drying out
• Salt inhibits microbes
• Lysozyme hydrolyzes peptidoglycan
Mucous Membranes
• Line body cavities that lead to the outside: Digestive tract, Respiratory tract, Urogenital tract.
• Part of the first line of defense against pathogens.
• Secrete mucus that helps trap pathogens
Normal Microbiota of the Skin
Gram-positive, salt-tolerant bacteria
Staphylococci e.g Staph. epidermidis
Micrococci
Diphtheroids e.g Cutibacterium (Propionibacterium) acnes
• Anaerobic
• lives in hair follicles
• Produces propionic acid, and keep pH low
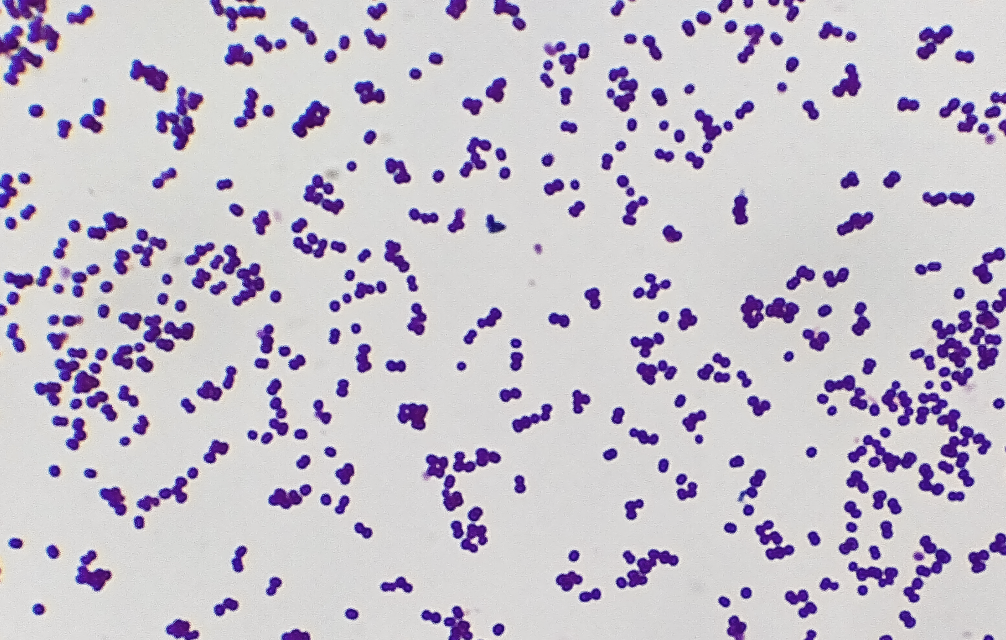
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Gram-positive cocci
Coagulase negative.
90% of normal skin microbiota
Health-care associated pathogen
Can form biofilms on catheters
Forms slimy layer that allows cells to attach
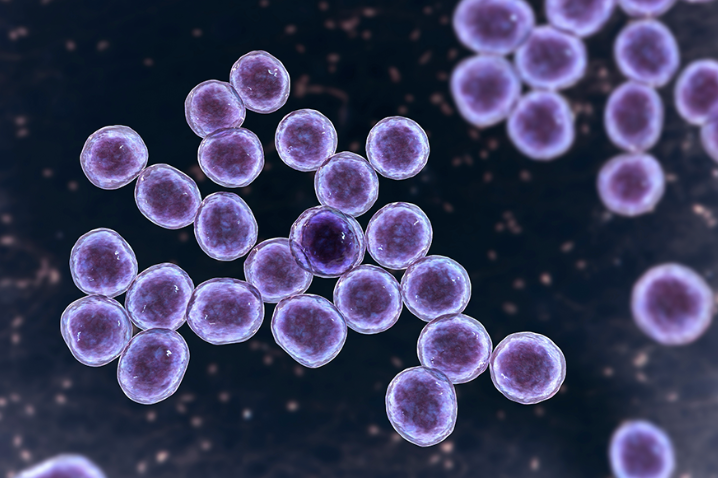
Staphylococcus aureus
Gram-positive cocci
Coagulase-positive
Carried in the nasal passages of 20% of the population
Produces exfoliatin that causes separation of skin layers
Avoids host defenses in the skin - secretes proteins and toxins that kill phagocytic cells
MRSA strains are antibiotic-resistant
Folliculitis
Infections of the hair follicles
Sty
Folliculitis of the eyelash
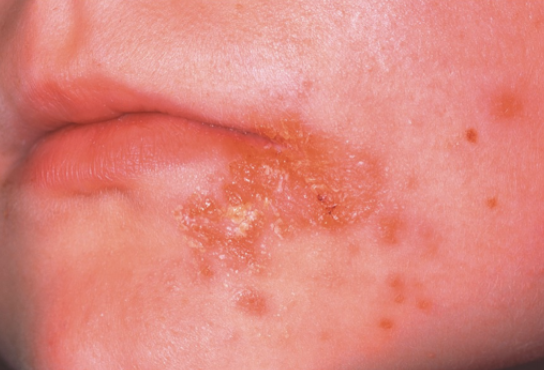
Impetigo
Crusting sores
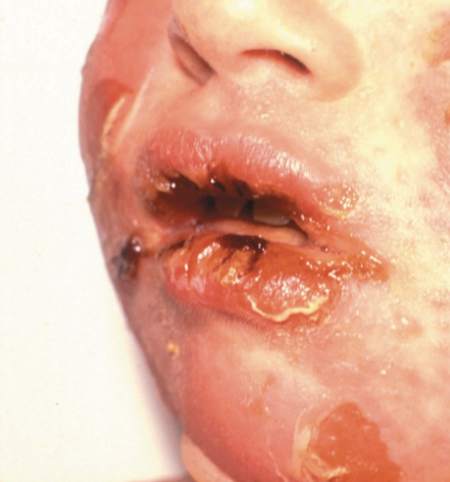
Scalded Skin Syndrome (Staphylococcal Skin Infection)
Type of impetigo where the toxin circulates and causes separation of skin layers
▪ Exfoliative toxin A remains localized
▪ Exfoliative toxin B spreads to distant sites
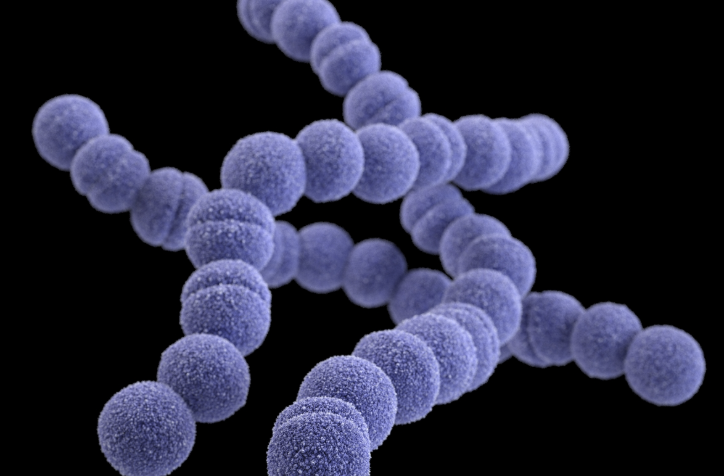
Streptococcus pyogenes
Gram-positive cocci in chains
Associated with a wide range of infections in addition to skin infections
Beta hemolytic: ability of bacteria to completely break down red blood cells (hemolysis) in the agar, leading to a clear, transparent zone around the bacterial colonies.
Produces several virulence factors
▪ Hyaluronidase: digest hyaluronic acid that keeps cells of connective tissue together
▪ Hemolysin that lyses red blood cells
▪ M protein: allows attachment to host cell and helps cell evade phagocytosis
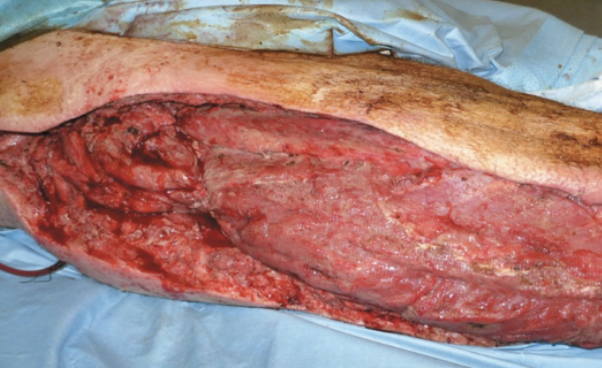
Streptococcus pyogenes - Necrotizing fasciitis
“Flesh-eating” disease
Pyrogenic toxins produced by S. pyogenes acts as a superantigen
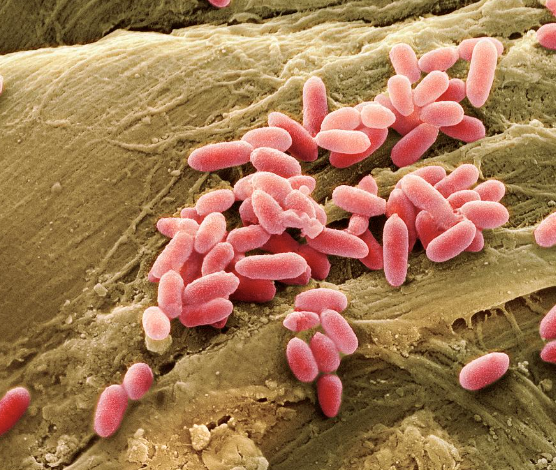
Infections by Pseudomonads - Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Gram-negative, aerobic rod
Pyocyanin produces a blue-green pus
Opportunistic pathogen
Causes:
Pseudomonas dermatitis
Otitis externa, or “swimmer’s ear”
Post-burn infections
Viral Diseases of the Skin
• Many are transmitted via respiratory routes and are systemic
• Many cause problems in children and developing fetuses
Smallpox (Variola)
• Caused by an orthropoxvirus
• Transmitted via the respiratory route, moves into the bloodstream, and infects many internal organs and the skin
• Completely eradicated from the human population by vaccination
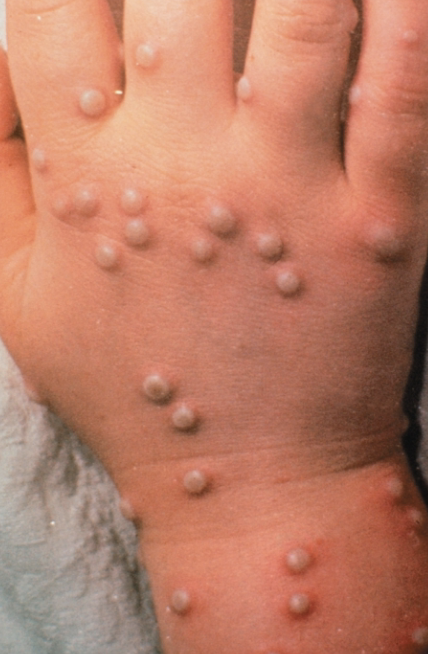
MPOX - Monkeypox
Related to smallpox but less severe
Endemic to small animals in Africa
Spill-overs from animals to humans
Can be transmitted from human to human by prolonged close contact
2022 outbreak in the United States: >30,000 cases
Prevention by the smallpox vaccination
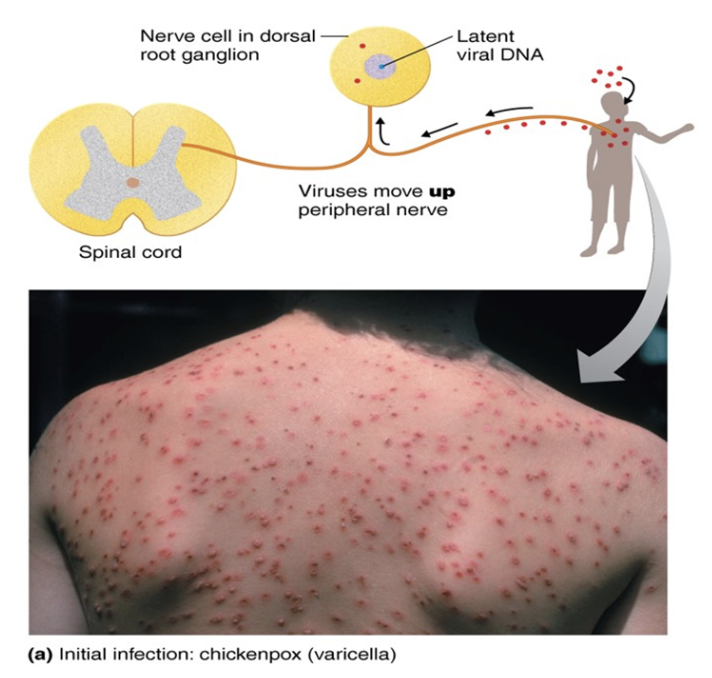
Chickenpox (varicella)
Herpesvirus varicella-zoster (human herpesvirus 3)
Transmitted via the respiratory route
Causes pus-filled vesicles after a 10–14 day incubation
Virus becomes latent in the dorsal root ganglia
Prevented by a live attenuated vaccine
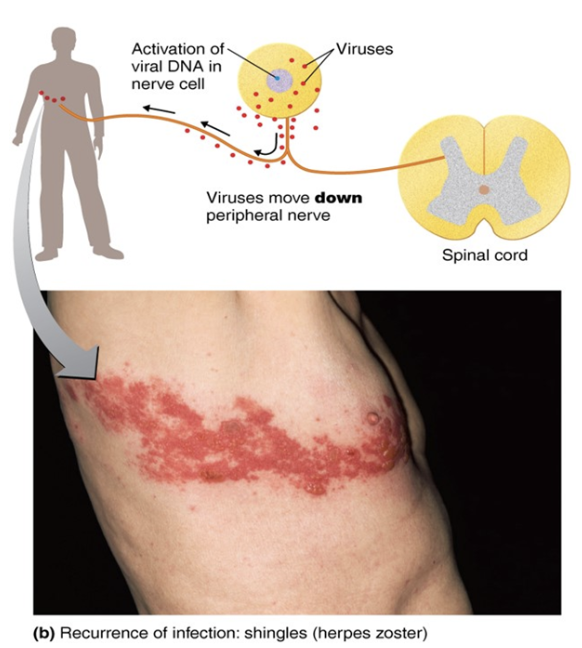
Shingles (herpes zoster)
Reactivation of the latent varicella-zoster virus that moves from dorsal root ganglia along peripheral nerves to the skin
▪ Due to stress or lowered immunity
▪ Highest incidence is in older adultsFollows the distribution of affected cutaneous sensory nerves
▪ Painful pustular lesions over a dermatome
▪ Limited to one side of the body
Shingles (herpes zoster) Cont’d
Postherpetic neuralgia—painful stinging and burning sensation for months to years following shingles
Treatment of shingles: acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir may lessen symptoms
An individual with shingles can shed the virus and infect nonimmune individuals with chicken pox
Prevention: Shingrix® vaccine
Herpes Virus
Human herpesvirus 1 (HSV-1) and 2 (HSV-2)
– HSV-31 is spread primarily by oral or respiratory routes
– HSV-2 is spread primarily sexually, causing genital herpesViruses can remain latent in nerve ganglia
90% of the US population is infected with HSV–1
– Usually develop as cold sores or fever blisters
– Not the cause of canker sores
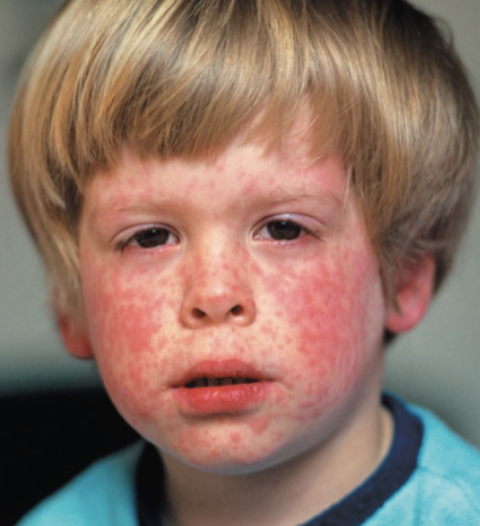
Measles (Rubeola)
Measles virus transmitted by the respiratory route
Virus can be shed for several days before symptoms appear
Cold-like symptoms, macular rash
Koplik’s spots
– Red spots on the oral mucosa opposite the molarsPrevented by the MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine
– Children under 1 year old cannot receive the vaccine
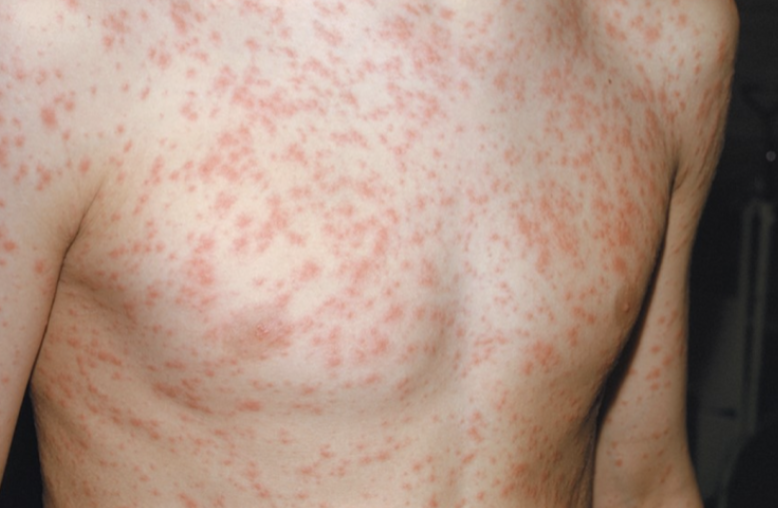
Rubella
German measles
Rubella virus
Macular rash and light fever, milder than measles
Transmitted via the respiratory route; 2-to 3-week incubation
Congenital rubella syndrome
– Fetal damage, deafness, heart defects, mental retardation in 35% of cases
– 15% mortality within first year of lifePrevented by the MMR vaccine
Bacterial Diseases of the eye: Conjungtivitis
An inflammation of the conjunctiva (the outermost layer of the eye and inner layer of eyelids)
Also called pinkeye or red eye
Commonly caused by Haemophilus influenzae
Various other microbes can also be the cause
Bacterial Diseases of the Eye - Ophthalmia Neonatorum
Caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Large amount of pus forms; ulceration of corneas results
– Untreated cases may lead to blindnessTransmitted to a newborn’s eyes during passage through the birth canal
Prevented by treating a newborn’s eyes w/ antibiotics
Bacterial Diseases of the Eyes - Chlamydia trachomatis
Conjunctivitis, or chlamydial conjunctivitis
Transmitted to a newborn’s eyes during passage through the birth canal
Treated with tetracycline
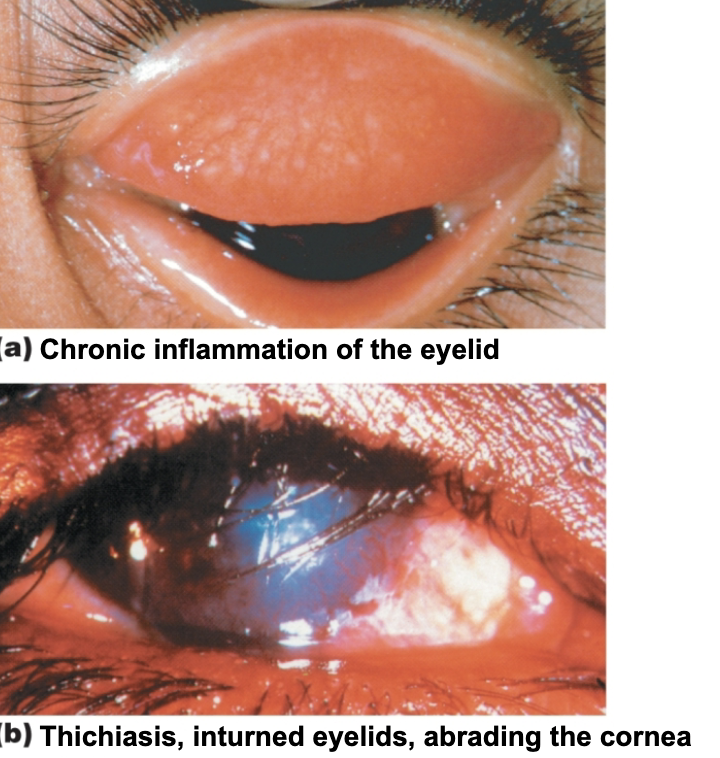
Causes trachoma
Leading cause of blindness worldwide
Infection causes permanent scarring; scars abrade the cornea, leading to blindness
Coagulase-Postive
refers to bacteria that produce an enzyme called coagulase, which can clot plasma (the liquid portion of blood).