Precipitation Measurements: Interception
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Who designed the first non-recording rain gauge.
Essentially a funnel directing rain into a bottle.
Total precipitation = liquid form + solid form
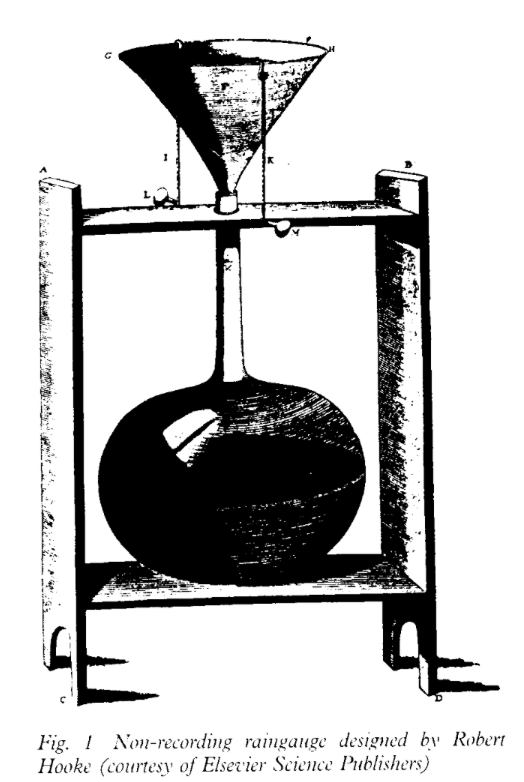
What are the different types of rain gauges?
Manual rain gauges - standard 5 inch rain gauge used by the met office, which water is measured manually with a graduated cylinder.
Mechanical recording rain gauges - motors are used to turn drums on to which are fixed paper charts. As they rotate, a pen traces a record of the rain on to the chart.
Data-logging rain gauges - modern tipping buckets are double sided, like a sea saw fills with rainfall and then tips. Tips every 0.1-1mm and triggers a magnetic switch. This connects to a data logger lots of switches = heavy rain.
Means unattended operation for long hours.
Limitation - records in steps but met office weighs bucket as it fills.
Other electronic gauges - detects the raindrops directly as they fall on passing through a beam of infrared light. Instantaneous rate of rainfall, which can be converted to accumulated totals over set times.
Not cheap and they require considerably more power than a tipping-bucket logging gauge.
Name a manual recording gauge.
Tilting syphon
tilt syphon gauge tells us distribution over that day.
Bias in reading the level.
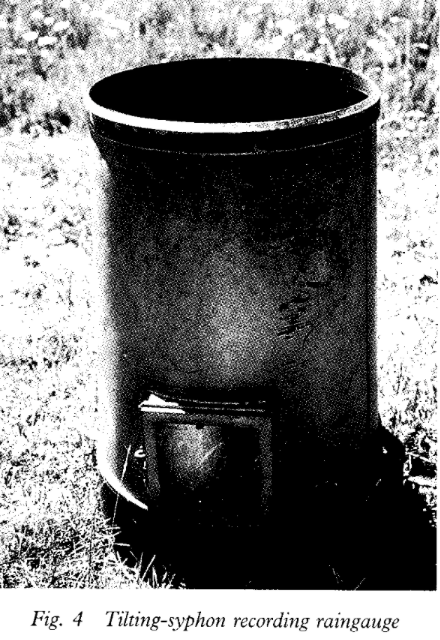

What is a serious drawback to manual and mechanical recording gauges?
They need human operators
Their geographical distribution has been restricted to populated places, much of the earth’s surface is not monitored.
What does a tipping-bucket rain gauge look like?
Water can be evaporated or lost when rainfall has stopped in the bucket.
Small amount of rain can be lost as the bucket tips.

What are the limitations of rain gauges?
One gauge is not representative of the whole area, rainfall is never uniform in intensity with time.
Need more gauges in mountainous areas or areas of localised rainfall.
Mountains add to spatial variation due to wind effects.
For a 20m high building needs to be minimum 14m away from building. At least 2x and 4x.
What are radar measures?
Measure rainfall intensity remotely over large areas, reflecting the signal back to the receiver.
only applicable to certain types of cloud and so is not universally applicable.
cost benefit of 3:5
What are some rain gauge errors?
Levelling - If the funnel is not levelled when installed, the amount of rainfall caught will be too small in non windy conditions and too large in windy conditions. Need to be perpendicular to ground surface.
Precision of manufacture - not manufactured properly can affect its catch.
Evaporation - rain can stick to the surface of the funnel and evaporate when it stops raining. Large rain droplets more prone.
Splash - gauges installed on hard surfaces, like concrete, can suffer insplash errors in heavy rain. Large raindrops can also cause outsplash.
Wind - the greatest error. Increase of wind speed with height. In mountainous areas error is 50 percent or more for drizzle and even more for snow as crystals are easily deflected.
What combats the wind problem?
The turf wall - breaks the force of the wind.
However, the area between the turf wall and the gauge can become filled with snow.
Shields - deflect the wind downwards.
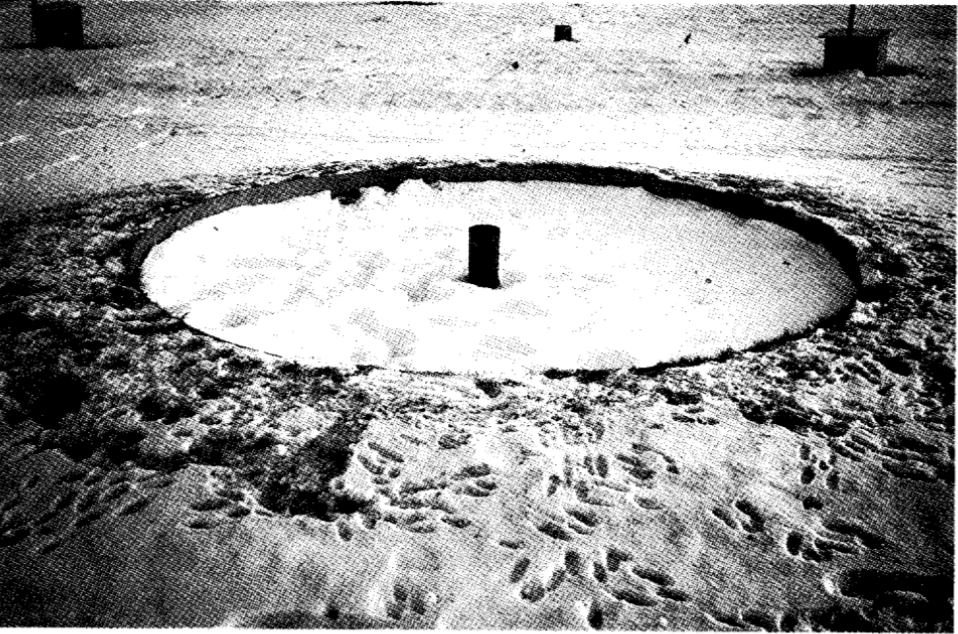

What is a pit gauge?
Pit gauge - rim is located at ground floor and anti splash featured.
Gives most reliable rainfall estimates.
Can become filled with sand, snow or vegetation.
What is interception loss?
Some precipitation does not reach the surface because it is caught by vegetation (e.g., trees) and evaporated back into the atmosphere.
Net rainfall = the remaining water which reaches the ground beneath the vegetation.
Throughfall and Stemflow
rainfall that falls through spaces in the vegetation canopy.
water trickling along twigs and branches.
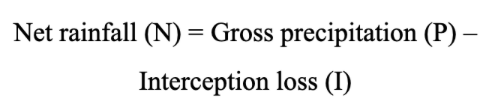
What does interception loss depend on?
type of vegetation - woodland and grasses.
Density of vegetation - more trees = more intercepted.
dependent on short-variations in rainfall.
What is the neutral hypothesis?
Interception losses are essentially evaporative, used either to evaporate water from the leaf (transpiration) or to evaporate from the surface of the leaf (interception).
The overall amount of water loss from a catchment by evaporation of intercepted water is the same as what would have been lost by transpiration if the leaves had been dry.

What is transpiration?
A gradient process.
Water moves from a region of high concentration (inside the leaf) to a region of low concentration (the surrounding air).
No transpiration if vapour pressure tends to 0.
Why is the neutral hypothesis incorrect?
Vegetation evaporates at a faster rate than transpiration. When leaves are wet, rate of evaporation is 2-5 times if the leaves were dry.
Transpiration requires a living plant and evaporation does not.
Transpiration required during the day time, need light. Evaporation can occur 24 hours a day.
Why does intercepted water evaporate at a faster rate?
Intercepted water has a high surface area to volume ratio - increases evaporation.
Advection energy, energy travelling horizontally above the forest canopy. Advection removes latent heat by carrying away the moist, cooled air produced by evaporation and replacing it with warm, dry air, allowing evaporation (and latent heat flux) to continue.
Wet leaves have short circuiting of aerodynamic resistances, atmosphere accommodates more water vapour.
What are the factors affecting interception loss from vegetation?
Interception capacity - water collected from leaves. Start of rain interception capacity will be high as leaves are dry.
High interception capacity = need high evaporation.
Wind speed - proportional to evaporation, means high interception capacity.
Amount of precipitation, duration and frequency important.
Interception losses is higher at drizzle or light rain for that duration of rainfall event.
Heavy rainfall will overwhelm the interception capacity of the leaf.
As rainfall increases so does interception loss.
When do you have the highest interception capacity?
Highest interception capacity occurs when the canopy can store the most water before it starts dripping or draining. In practice, this is when vegetation is dense, dry, and fully developed before a rainfall event.
more frequent rainfall events = less intercepted
What is the Horton equation (1919)?
Interception = water held on vegetation + water evaporated during storm

What is Merriam’s equation (1960)?
Modelled as a negative exponential function.
As rainfall total increases, interception loss decreases.
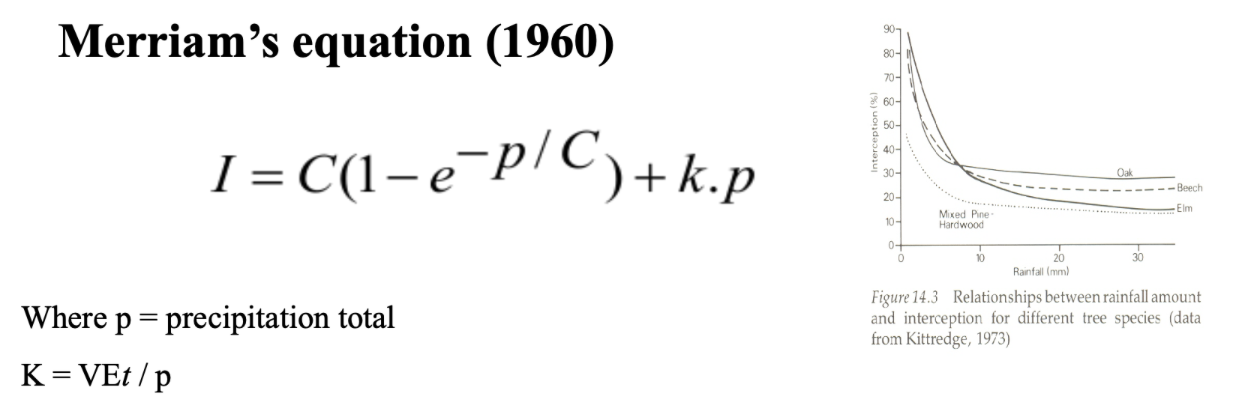
What is Calder’s annual formula?
estimates the total annual evaporation of intercepted rainfall
Upland Britain has some of the highest interception losses in the world.
What are the factors affecting measuring gross precipitation?
Field site - easy to measure in an open field site.
Stem flow and through fall - rough surface is harder for the trickle effect in stem flow. Through fall depends on drip points of the leaves.
Water balance approach - deciduous or coniferous.
Greater interception loss from coniferous pine than from deciduous hardwoods that drop their leaves in autumn.
If trees further part = increased wind speed = more evaporation = less interception.
