Miscellaneous Knowledge
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
When to give oxygen therapy?
When sats are below 92%
Wean off when sats are above 94%
What is the purpose of oxygen therapy
relieve hypoxemia
maintain oxygenation to tissues and organs
Nasal cannula considerations
upto 4L/min
High flow nasal cannula considerations
15-60L/min
Provides continous pressure and flow rate can be changed
Simple mask considerations
5-10L/min
Non-rebreather mask considerations
10-15L/min
has reservoir bag that also contains O2
CPAP mask considerations
continous airway pressure
Keeps airway open
Venturi mask considerations
3-10L/min
Contains air + O2
Different coloured valves allow different flow rate and FiO2
What is FiO2
Fraction of inspired oxygen
RA is 21%
Cancer
A group of diseases characterised by abnormal and unregulated cell growth
Cancer pathology
Unwanted cell proliferation: cancer cells don’t respond to normal signals to stop/reduce growth
Control of growth signals: cancer cells secrete their own growth signals and/or upregulate growth factor receptors
Disables cellular apoptosis: Cancer cells don’t undergo normal self-destruction
Restoration of telomeres: normal cells aging leads to progressive shortening of telomeres and cell death, Restoration of telomeres allows cancer cells to divide indefinitly
Malignant tumour chracteristics
cancerous cells
rapid, unregulated growth
lack of cellular differentiation
absence of normal tissue organisation
metastisize
General cancer symptoms
Fatigue
Pain
weight loss
Systematic symptoms from location
Cancer treatments
Surgery
Radiation
Immunotherapy
Hormone therapy
Chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
ionising radiation destroys DNA and cells, but damage can occur to non cancerous cells.
Radiation therapy side effects
Redness in skin
hair loss
nausea
vomitting
fatigue
reduced blood cell count
Immunotherapy
Manipulation of immune system to stimulate action against cancer cells
Hormone therapy
Inhibits hormone production for hormone dependent cancers e.f. reproductive cancers
Chemotherapy
Use of non-selective cytotoxic drugs to target vital cellular/metabolism processes essential to cell growth/replication. Given in cycles to allow non-cancerous cells recovery time.
Chemotherapy side effects
fatigue
nausea
vomitting
hair loss
infertility/sterility
growth suppression
impaired wound healing
reduced blood cell numbers
Complications from treatment
immunosuppression
Neutropenia
Immunosuppression
When treatment destroys white blood cells increasing risk of infection and resulting in poor wound healing
Neutropenia
Suppression of bone marrow resulting in reduced neutrophil production from chemo drugs. Infections may progressive rapidly without early symptoms, so protective isolation is important.
Febrile neutropenia
medical emergency
Pre-operative considerations
Medical history
Medications
Alcohol/drug intake
Allergies
Last food/fluid intake
metal/surgical inplants
surgical consent
Physical prep e.g. bowel prep
Intraoperative considerations
Safety checklist: Sign in, time out, sign out
Surgical counts
Pressure injury assessments
Local, GA, Sedation, regional e.g. epidural
Side effects of anaethesia
Memory loss
confusion
difficulty passing urine
N+V
Post-operative considerations
Level of consciousness
airway
vitals
respiratory status
pain
Post-operative complications
Hemorrage / hypovolemic shock
Caused by loss of blood, where HR and vasoconstriction increase to maintain blood pressure
Signs and symptoms of hemorrage/hypovolemic shock
increased HR
tachyapnoea
Decreased BP
Prolonged cap refill
Pallor
oliguria
Treatment for hemorrage / hypovolemic shock
IV fluids
Maintain airway
Control hemorrage
Oxygen
Blood transfusion
Components of blood
Red cells
Plasma
Platelets
Why give red cells
correct anaemia
Tissue oxygenation
Why give plasma
Restore hemostasis / blood volume
Why give platelets
Help clotting through platelet plug/fibrin net
Considerations for giving blood to patients
valid group and screen
Prescription
Informed consent
Vasuclar access
Documentation
2 RN with seperate checks
Positive ID (NHI, DOB, full name)
Adverse effects of blood transfusion
Febrile non-hemolytic transfusion reaction (Temp > 38C)
Minor allergic reaction
Moderate allergic reaction
Anaphylaxis
Hypotensive reaction (Systolic BP <80 or falls >30)
Acute hemolytic transfusion reaction (N+V, tachycardia, fever, chills, pain, hypotension)
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction (worsening anaemia, renal failure, hemoglobinuria)
Blood transfusion observations
Baseline obs
Full set of Obs at 15 mins (remain in the room)
Every 60 minutes
After each unit
Blood transfusion timeframes
Four hours from issue
ECG placement
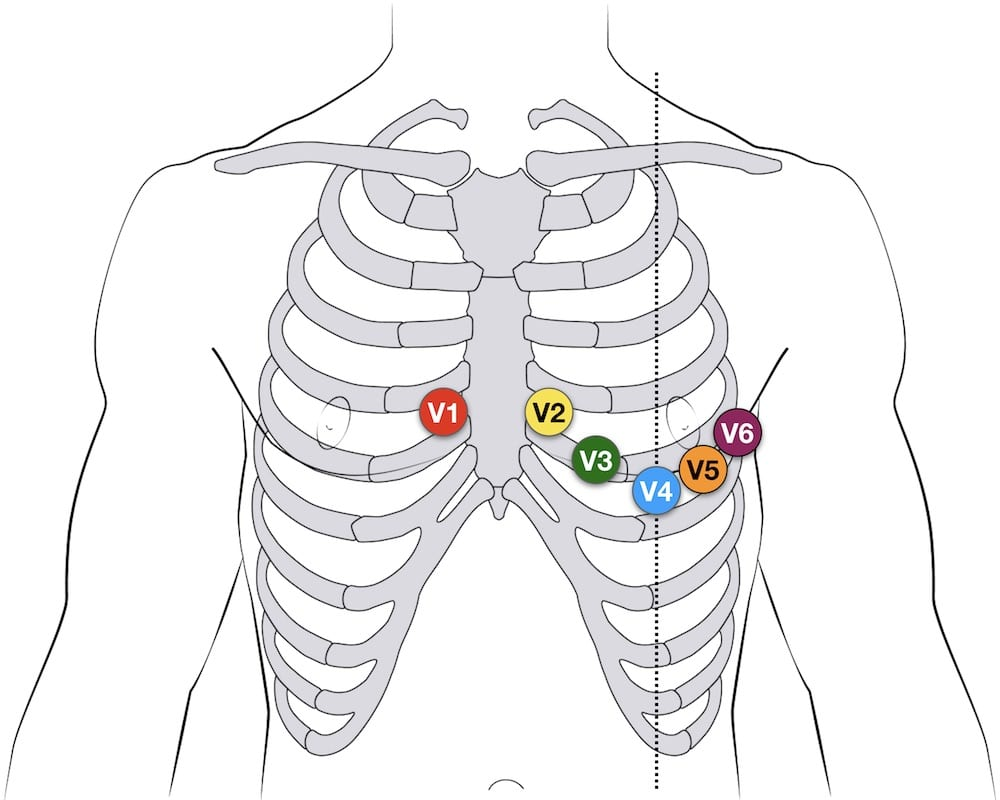
V1/V2 = fourth intercostal space
V3 = in between V2/V4
V4 = Nipple line
V5/V6 = same intercostal space as V4
Resuscitation considerations
Compression-to-ventilation ratio be 30:2 for all ages.
Chest compressions should be provided at a rate of approximately 100 – 120 /min
DRSABCD
NZ Resuscitation guidlines
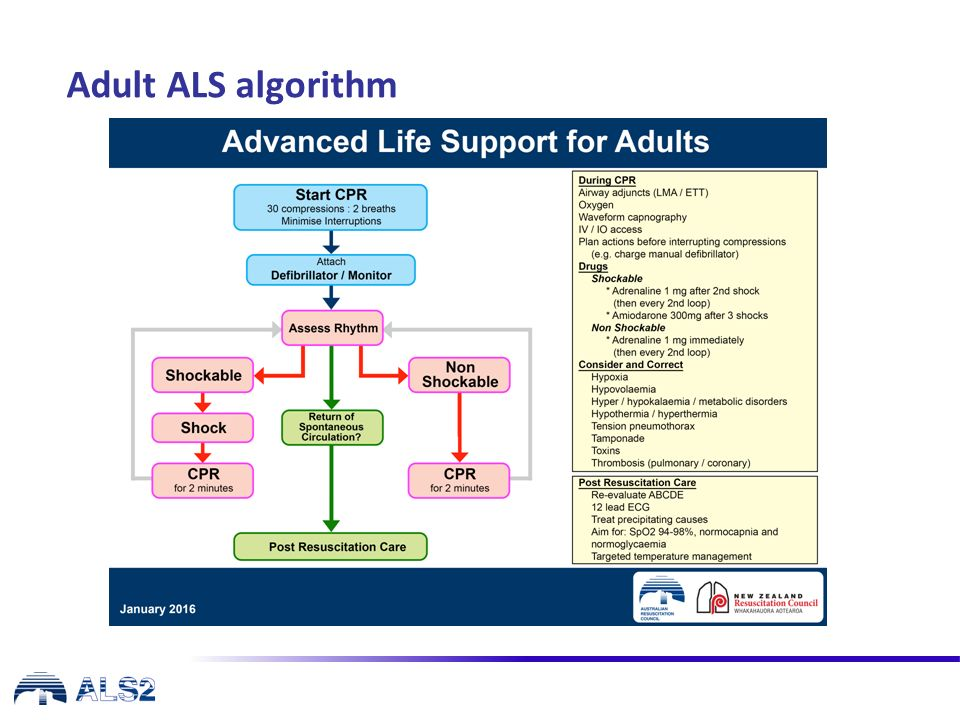
Resuscitation drugs
Shockable drugs
Adrenaline: 1mg after 2nd shock, then every second loop
Amiodorone: 300mg after 3rd shock
Non-shockable drugs
Adrenaline: 1mg immediatly, then every second loop
Pandemic
Exponential disease growth affecting several countries and populations
Epidemic
An unexpected increase in disease specific to a geographical area
What diseases are notifiable
Measles
Rubella
Salmonella
Campylobacter
Crytosporidium
Hepatitis A
Giardia
E. coli
Shigella
Streptococcal
Pertussis
What is a notifiable disease
Diseases that are notifiable to the Medical Officer of Health to enable prevention and control. The primary purpose of notification is to enable public health officials to respond quickly and effectively to potential outbreaks, epidemics, and other public health emergencies.
Who must notify about notifiable diseases
Health practitioners
Laboratories
School principals and childcare centres (in outbreaks)
Employers (for work-related infectious diseases)
Notifications are made directly to Public Health Units (PHUs) — part of Te Whatu Ora | Health New Zealand.
What are nursing responsibilities in relation to notifiable diseases
Legal Duty
Know which conditions are notifiable.
Notify immediately if required (some diseases are urgent, e.g. meningitis, measles).
Understand regional PHU protocols.
Infection Control
Implement standard, contact, droplet, or airborne precautions.
Use PPE and environmental cleaning practices.
Patient Communication
Inform the patient of their diagnosis with empathy.
Educate about preventing transmission.
Public Health Collaboration
Work with PHUs for:
Contact tracing
Mass immunisation
Quarantine or isolation advice
Community outbreak response
Documentation
Key notifiable disease issues
Underreporting (especially in rural or Māori communities)
Late notifications delaying outbreak response
Misinformation or stigma reducing patient disclosure
Workforce strain during outbreaks (e.g., RSV, norovirus, COVID-19 surges)
Five moments of hand hygiene
Before touching a patient
- Before a procedure
- After a procedure or blood/fluid exposure risk
- After touching a patient
- After touching a patient’s surroundings
Contact precautions
MDRO, diarrhea
- Risk in direct contact and indirect contact
- Standard precautions and use of PPE
Droplet precautions
Influenza, RSV
Risk in coughing, sneezing, or talking
Used when there is spread through close respiratory or mucus membrane
contact
Use of PPE
Airborne precautions
Covid-19, TB
- Risk in droplets or particles suspended in the air
- UseofPPE+N95
Complex precautions
Used when there is more than one mode of transmission e.g. droplet and contact, norovirus
Types of MDRO
MRSA(methicillin-resistantstaphylococcusaureus) § ESBL(extendedspectrumbetalactamase)
VRE(vancomycin-resistantenterococcus)
CPO(carbapenemase-producingorganisms)
Donning PPE
Gown, Mask, Goggles, Gloves
Doffing PPE
Gloves, Gown, Goggles, Mask
Palliative care
Holisitic, person-centred care that aim to not hasten or postpone death but improve quality of life for termianlly ill patients
Considerations when talking to bereaved family
facilitate open, honest conversations
Create opportunities for familial input
Assess level of understanding and amount of knowledge wanted
Provide options for ongoing care/support
Support through legal processes
Ensure awareness of after death processes e.g. funeral arrangements
Euthanasia
Deliberately bringing about the death of a person to end what is considered an intolerable existence
Key considerations for euthanasia
A health practitioner cannot raise discussion around ‘assisted dying’
Must determine competence to make an informed decision and can communicate that decision in some way
A person can change their mind at any time
Must encourage discussion with family, friends and counsellors
Must ensure decision is free from pressure
Eligibility criteria for euthanasia
over 18
NZ permanent resident or citizen
Suffering from terminal illness likely to end life in 6 months
advanced state of irreversible decline
experiencing unbearable suffering
competent to make informed decision
Spirituality
The spiritual essense of a person is their life force. It determines who we are, where we come from and where we are going
Grief
the emotional reaction to loss
Types of grief
Anticipatory grief
Complicatred grief
Disenfranchised grief / ambiguous loss
Delayed grief
Youth sexual health risk factors
Poor knowledge
Psychosocial maturity
Embarrassment recieving sexual health advice
Lack of easy access to care
What is PRIME nursing
Emergency ‘24hr’ on call practitioner in rural areas (Primary Response in Medical Emergencies)
What is rural nursing
an area of nursing where nurses look after residents of rural communities across the lifespan and respond to a range of health needs through a broad scope of practice
Health outcomes for rural people
Poorer health outcomes
Lower life expectancy
mental health challenges
Poorer access to health and support services
Service accessiblity issues in rural areas
Geographic factors: distance, weather
Inconsistent data coverage: impacting telehealth
Challenges attracting and maintaining staff (distance to work, hours, lack of cover)
Inequities between access to primary, secondary and tertiary healthcare because of less local options
Taking time off to attend appointments becayse of service hours
Airway issues and considerations in an emergency
Recognise signs and symptoms of airway compromise e.g. cyanosis
Clear obstructions e.g. suctioning, back blows, chest thrusts
Secure airway e.g. head tilt, jaw thrust (Infant head should be kept neutral)
Provide ventilatory support e.g. oxygen therapy
Monitor vitals
Chocking ANZCOR guidelines
Assess effectiveness of cough
effective cough = mild airway obstruction
ineffective cough = severe airway obstruction
Mild airway obstruction interventions
Encourage coughing
consistent checks
Send for help
Severe airway obstruction interventions
if responsive:
send for help
5x back blows, 5x chest thrusts (alternate)
For infants face head down across thighs
if unresponsive
send for help
CPR
EWS esculation pathways (yellow)
EWS=1-5
Increase monitoring
address pain. fever or distress
EWS esculation pathways (Orange)
EWS=6-7
discuss with NIC
HO review
EWS esculation pathways (Red)
EWS=8-9, or any vital sign in red zone
Registrar review in 20 minutes
EWS esculation pathways (Blue)
EWS=10+, or any vital sign in blue
Call 777
Hypothermia
Average temp lower than 36 degrees
Signs and symptoms of hypothermia
confusion
drowsiness
loss of consciousness
shivering
cyanosis
cold, pale skin
Hypothermia treatment
Warm IV fluids
Heating pads
Remove wet clothing
Signs and symptoms of shock
Altered LOC
cold, clammy skindizziness
dry mucus membranes
hypotension
tachycardia
oliguria
Sepsis
Microorganism infiltrates blood triggering a systemic inflammatory response that causes severe hypotension and tachycardia
Signs and symptoms of sepsis
slurred speech
extreme shivering or fever
passing no urine
skin mottled or discoloured
impending sense of doom
severe breathlessness
Sepsis 6 treatment
Blood cultures
Lactate levels
anti-biotics
fluids
Oxygen
monitoring urine output
AED pad placement
Adults: anterior to lateral
Small children/infants: front to back