SAM Exam 4 - GI
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
Pathophysiology of vomiting
CNS reflex → medulla
CRTZ, vestibular, vagal, pain, stress
Receptors:
Dogs: dopamine, histamine
Cats: α2, serotonin
Metabolic Alkalosis: Pyloric Obx → Vomit → loss HCl = ↑ HCO₃ + ↓ Cl
Tx: 0.9 % NaCl + KCl

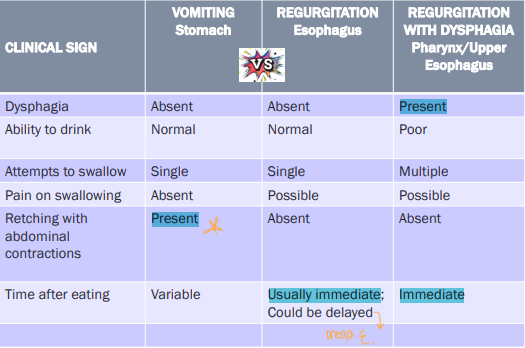
Vomiting
Et: GIT dz, renal dz, hepatic dz, pancreatitis, toxins, pain
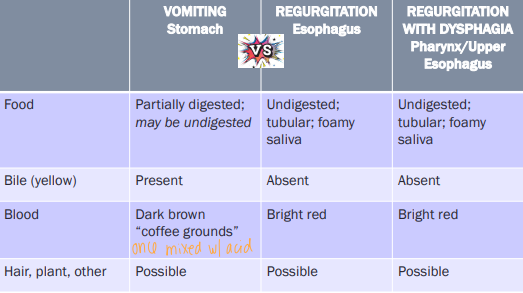
Cs: abdominal contractions, salivation, digested food + bile
Active forceful expulsion GI and intestinal contents
Dt: metabolic alkalosis, ↓ Cl + K, Min database, endoscopy
Acute < 24h & BAR = symp Tx
Chronic > 3w = workup
Tx: withhold food 24h, small bland meals, oral fluids, antiemetics, maropitant + ondansetron (refractory)
Stepwise Diagnostics for Upper GIT
Severity:
Test: >3w, ADR, FB
Symptomatic Tx: <24hrs, hydrated, BAR, No Bld/FB
Anatomy: history, video, observe eating, oropharyngeal exam (awake + sedated), rads of skull + pharynx + thorax
Rule out non-GIT before GIT related
Fxn: fluoroscopy, endoscopy, neuromuscular evaluation
Exclude mechanical obx

Vomiting Syndromes
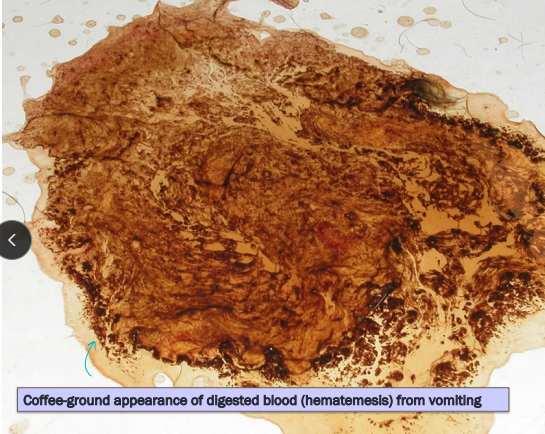
Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Et: Sepsis, Ulcers
Cs: Hematemesis, melena, pale MM, anemia, iron deficiency(chronic) : (acid makes blood brown)
Sepsis/DIC: petechiae, fever, systemic illness, abnormal coagulation tests
Ulcer: localized GI signs, normal coagulation, anemia
Dt: Rads, Contrast GI studies, Fluoroscopy, US
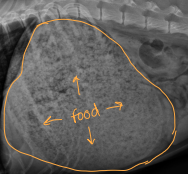
Delayed Gastric Emptying
Et: Outflow obx, opioids, anesthetics, Post-surgical vagal nerve damage, Parvo
Cs: Food in vomitus >10h post eating, projectile vomiting, bloating after eating, burping, metabolic alkalosis (acid loss from body)
Dt: Normal Rads(chest/abd.), Contrast GI studies(thickening), Fluoroscopy(funct. dysphagia), US(mass/hernia)
Exclude mechanical obx by imaging and endoscopy
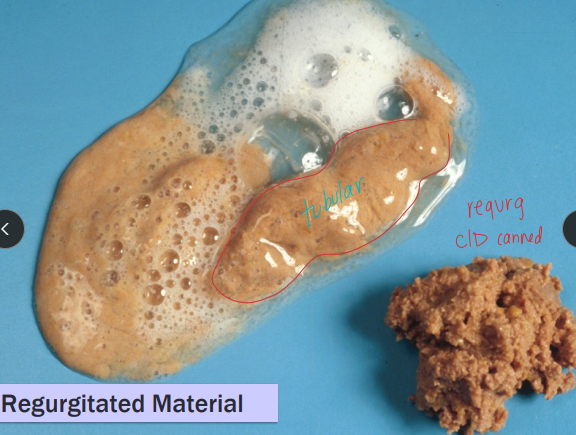
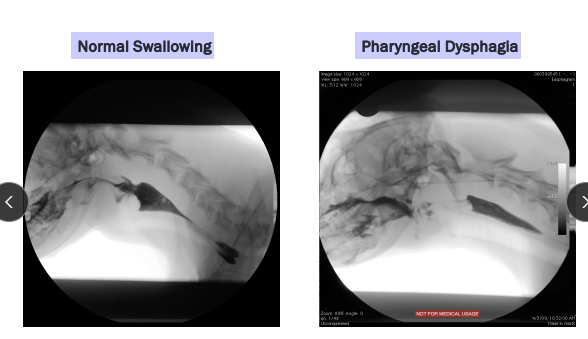
Regurgitation
Et: Megaesophagus, MG, PRAA, reflux, FB, hiatal hernia
Where:
With dysphagia: Oropharynx + prox esophagus
Normal swallowing: Lower esophagus
Sig: GSD, Shar Pei, Golden, Bulldog
Cs: No warning, no abdominal effort, tubular foamy material, undigested food
Passive expulsion undigested post eating + No bile
Dt: Imaging endoscopy, MG test (AChR Ab), Oral exam (awake + sedated)
Comp: Aspiration pneumonia, malnutrition, weight loss

Endoscopy vs Gastric Surgery
Endoscopy & biopsy
What: Non-invasive, atraumatic diagnostic tool
Upper and Lower
Why: Direct visualization of mucosa
Pro: No Sx incision, Quick recovery, Immediate
Takes 10-15 biopsies in area of interest
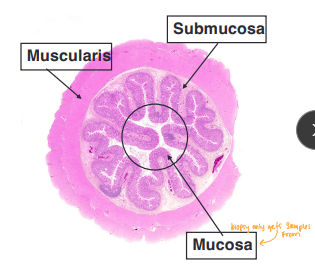
Con: Cannot access submucosa or muscularis, Cannot diagnose mural or extra-luminal dz
Surgery
Why: full-thickness biopsies, large or mural masses, large obx FB removal, when limited endoscopic access
Pro: Allows evaluation of entire abdominal cavity, correct mechanical obx directly
Dysphagia
Et: Dental dz, oropharynx dz
Where:
Only Dysphagia: Oropharynx
With Regerg: Oropharynx + prox upper esophagus
Cs: Difficulty chewing + swallowing
Dt: Oral exam (awake + sedated), imaging, endoscopy
Comp: Aspiration pneumonia, malnutrition, weight loss
Localizing Vomiting, Regurgitation and regurg w/ dysphagia
Sildenafil
MOA: relax GES, ↑ emptying, ↓ regurg
Use: canine esophagitis
canine esophagus is skeletal muscle
Cisapride + Metoclopramide is not effective
Famotidine(pepcid) + Cimetidine
MOA: H2-blocker
↓ gastric acid, gastroprotective
No promotility effect
Use: short-term acid suppression (2-3 d)
Adjust dose in renal disease
Omeprazole (prilosec)
Proton Pump Inhibitor
MOA: inhibits parietal cell ATPase
↓ gastric acid, gastroprotective
Better than H2-blockers
Use: 30 mins before food, taper if used >3-4w(prevent rebound acid hypersecretion), dosed q 12h
Sucralfate
Rx: Aluminum salt of sucrose sulfate
Local effects
MOA: Binds to ulcer base, inactivates pepsin, adsorbs BA, ↑ PG
Site gastroprotective
Use: Separate from oral drugs by >1h
Metoclopramide
Promotility Drugs
MOA: ↑ACh, D2 antagonist, 5-HT4 agonist, 5-HT3 antagonist
↑ prox GIT motility, antiemetic
No colon effect
Use: parvo
not canine esophagitis, not effective centrally in cats, not obx
canine esophagus = skeletal muscle
Cisapride
Promotility Drugs / constipation
MOA: 5-HT4 agonist
Full GIT promotility drug
No antiemetic action
Use: Compounded drug
esophagitis: cats, may worsen regerg, not cardiac dz
canine esophagus = skeletal muscle
Azithromycin + Erythromycin
MOA: Motilin agonist
↑ motility in GES, stomach, SI, colon
Use: Azithromycin cheaper
Ranitidine(no good) + Nizatidine
MOA: Inhibit AChE, ↑ ACh, H2 blocker
↑ motility in stomach, SI, colon
Use: Short-term gastric acid + hypomotility Tx
Apomorphine + Ropinirole
MOA: D2 agonists
CRTZ stim
Use: Induce emesis in dogs
not cats they have ↓ D2 receptors in CRTZ
Xylazine + Dexmedetomidine + Mirtazapine
MOA: α2 agonists
Use: Induce emesis in cats, appetite stim
Good for anorexic cats
Maropitant
MOA: NK1 antagonist
block Substance P in vomiting center, CRTZ, vagal afferents
Use: Anti emetic
Pancreatitis (#1), Obx, parvo, vestibular vomiting, motion sickness, chemo, refractory
Ondansetron
MOA: 5-HT3 antagonist
Use: antiemetic + anti-nausea
Chemo, Pancreatitis, Obx, vestibular vomiting (#1), refractory
Phenothiazine tranquilizers
Rx: Chlorpromazine or prochlorperazine
MOA: D2, H1, M1 blockade
Use: sedating, antiemetic
contraindicated in dehydration/hypotension
Diphenhydramine
MOA: H1 antihistamine
Use: antiemetic
vestibular vomiting, motion sickness

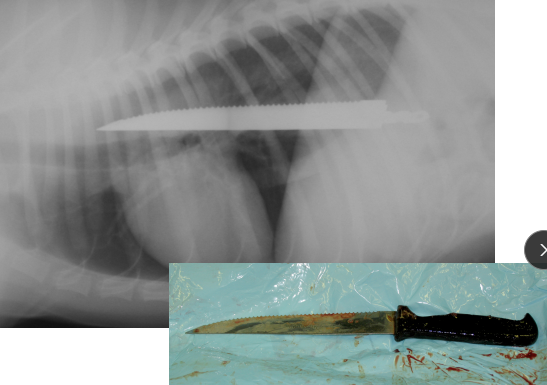
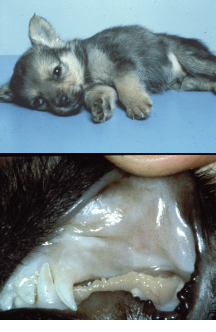
Esophageal Foreign Body
Et: located at cervical, thoracic inlet, base of heart, diaphragm
Sig: young
Cs: acute regurg, dysphagia, gagging, salivation
Dt: rads, endoscopy
Tx: urgent endoscopic removal or surgery
Comp: perforation, esophagitis, stricture, aspiration pneumonia
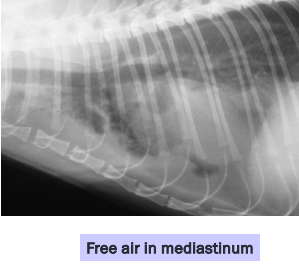
Esophageal Perforation
Et: Air in mediastinum or pleural space
Cs: peri-esophageal swelling, pain, resp distress
Dt: Serial rads
Tx: NG tube feeding, Antibiotics, fluids: heals w/ symptomatic therapy
Sx if Large
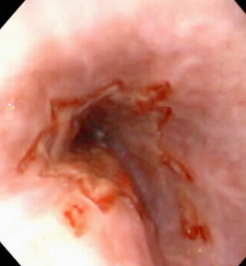
Esophagitis
Et: anesthesia: reflux, caustic injury(chemical), FB, Doxycycline (C), hiatal hernia, bulldogs
Endogenous: Gastroesophageal reflux(gastric acid)
Sig: Young, GSD/Shar Pei
Cs: regurg 1-3d post GA
Dt: endoscopy w/ erythema, erosions, ulcers
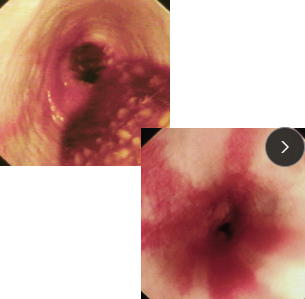
Tx: Omeprazole, Sucralfate, Metoclopramide (C), Cisapride (C), Corticosteroid, tube feed, sildenafil (D)
Prevention w/ pre-op omeprazole (12h + 3h pre-op)
Comp: stricture
multi balloon dilations over 5d
↑ recurrence, guarded px
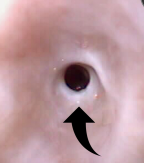
Esophageal Stricture
Abnormal narrowing of the esophageal lumen d/t fibrous tissue
Common causes:
Gastroesophageal reflux during anesthesia
2º to esophageal foreign body
Oral doxycycline, clindamycin tabs (cats)
Other (caustic agents, esophageal surgery)
Strictures form when esophagitis involves deeper layers (submucosa/muscularis) which heal with fibrous tissue
CS: regurgitation, ravenous appetite, weight loss
Solid > liquid foods
occurs w/in 3-14 d after injury
TX: balloon dilation, sx resection
Steroids, G tube : medical treatment

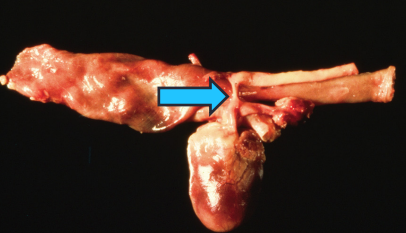
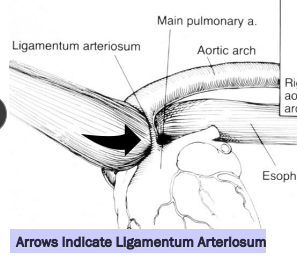
Persistent Right Aortic Arch
Et: vascular ring traps esophagus, constriction near heart base
Sig: Young <6m, onset at weaning
Cs: regurg.
solids > liquids
Dt: thoracic rads, contrast esophagram or CT
Tx: Sx
Comp: residual dilation when delayed
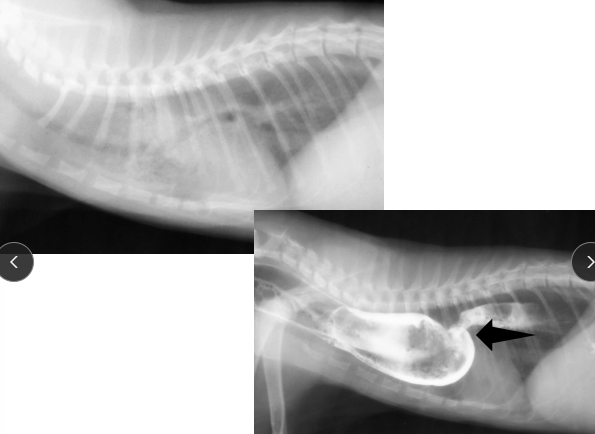

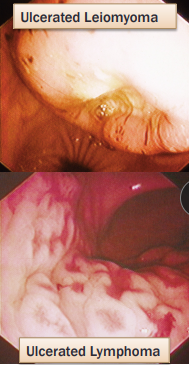
Esophageal Neoplasia
Sarcoma: Spirocerca lupi
Squamous cell carcinoma: old cats
Leiomyoma/sarcoma: dilated esophagus of dogs
CS: Asymptomatic (early)
Obstruction (advanced)
TX: Surgical resection (distal leiomyoma)
prognosis guarded except: Leiomyoma
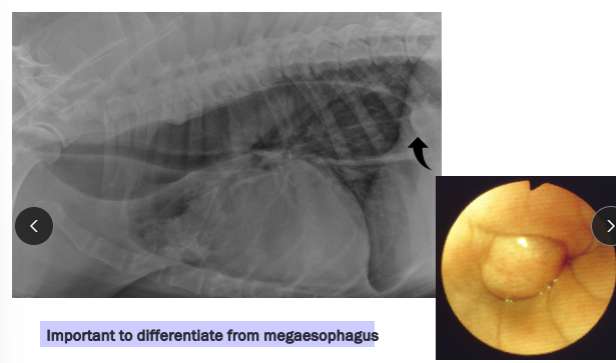
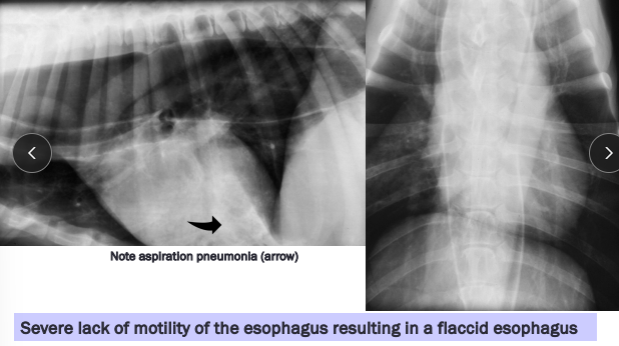
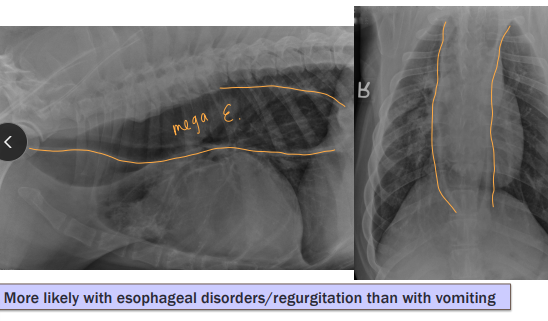
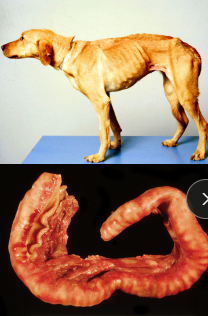
Megaesophagus
Et: Congenital, Idiopathic (#1 dogs), MG, Hiatal hernia, Reflux esophagitis
R/O: Esophageal Obstruction → cause diffusely dilated esophagus
Sig:
Congenital: kittens + GSD/Shar Pei puppies
Acquired: GSD, Golden
Cs: Regurg after weaning, Diffuse dilation, weight loss
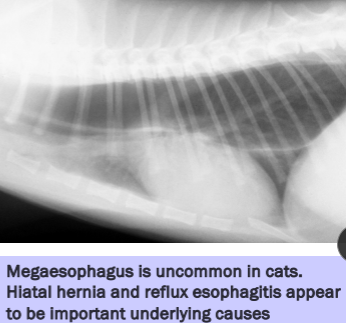
Cats: Uncommon, Hiatal hernia and reflux esophagitis underlaying causes
Dt: lab work, Rads, barium esophagram, AchR antibody (MG 25%)**, cortisol, lead, thyroid
Tx: upright feeding (Bailey chair), small soft meals, G tube feeding, pyridostigmine (MG), immunosuppressives (MG)
Avoid promotility agents
Px: May improve but not normal
better w/ MG, recurrent pneumonia

Breed-related esophageal disorders
Congenital idiopathic megaesophagus: GSD, Shar Pei
Myasthenia gravis: GSD, Golden
Focal MG: Facial, pharyngeal, laryngeal, esophageal muscle involvement only (≥1)
Cricopharyngeal achalasia: Golden
Hiatal hernia or reflux esophagitis: Shar Pei, Bulldog
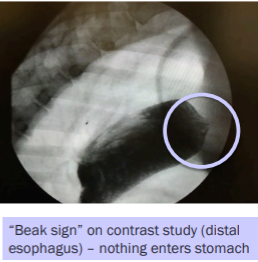
Achalasia-like Syndrome
Et: Primary esophageal motor dz
degen of the myenteric plexus, poor GES relax, unorganized peristalsis
Sig: megaesophagus in dogs
Dt: “Beak sign” on distal esophagus contrast
Tx: Sildenafil
Relaxes GES
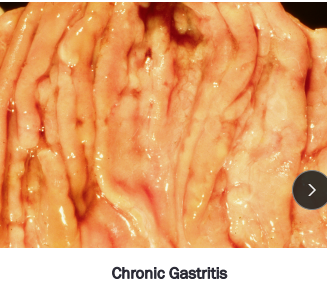
Gastritis
Inflammation of the gastric mucosa: requires biopsy
Lymphoplasmacytic most common
Cats = part of diffuse IBD
Acute
Et: idiopathic (#1), dietary indiscretion, NSAIDs, antibiotics, chemo
Cs: Sudden vomiting, healthy otherwise → spon. resolves
Diarrhea = gastroenteritis
Dt: history + Cs
biopsy not done, no indepth Dt
Tx: self-limiting 24-48h, no food 24h, bland diet, fluids, antiemetics
Chronic
Et: idiopathic (#1), allergy, toxin, drugs, Helicobacter(G-), Parasitic (Physaloptera rara, Ollulanus tricuspis(vomit eating)), Bilious vomiting syndrome(dogs)→ am bile vomiting / feed b4 bed
Dog: Beef, dairy, wheat
Cat: Beef, dairy, fish
Cs: vomiting food/bile for weeks/years, otherwise healthy
Dt: min database, biopsy, fecal, xrays
Tx: Therapeutic trials #1 → Novel diet 4-6w, Fenbendazole 2-3w, Omeprazole 2-3w, Biopsy(tx fail), Pred (post biopsy), diet therapy cont.
Helicobacter
Et: normal flora
Infection ≠ dz
Cs: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting
Pet: mild gastritis, no ulcers, asymptomatic
Humans: ulcers, gastritis + gastric cancer
Dt: gastric biopsy
cannot culture
Tx: Metronidazole, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, omeprazole (14-21d), Bismuth (pepto) 6 m (D)
Recurrence common w/in 6 m
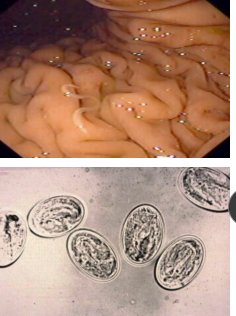
Physaloptera rara
Et: Nematode in stomach + proximal duo
Insects, rodents, snakes
Cs: gastritis, chronic vomiting
Dt: fecal float unreliable
Tx: Fenbendazole, Pyrantel, Ivermectin
Bilious vomiting syndrome
Et: night-time duodeno-gastric reflux of bile
Cs: Morning bile vomiting otherwise healthy, chronic gastritis
Tx: Sm meal at bed, Metoclopramide, Omeprazole
Avoid fasting
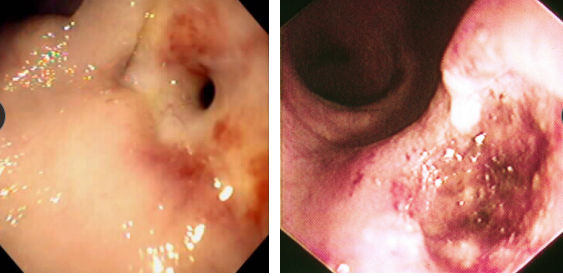
Gastroduodenal Ulcers
Et: NSAID, Steroid, GDV, MCT, renal dz, hepatic dz, sepsis
NSAIDs block PG synthesis → ↓ mucus, bicarb, blood flow → mucosal erosion
NSAID + steroid = ulcer
Cs: Hematemesis, melena, anemia, pale MM
Dt: Endoscopy (#1), regen/ iron-deficiency anemia, ↓ protein, thick mucosa
Determine GI or systemic
Tx: Fluids, (PPI) Omeprazole, Sucralfate
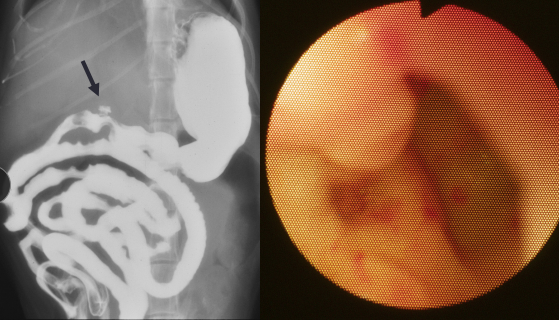
Gastric Foreign Bodies
Et: Obx at pylorus or intestines, Metal toxicity (zinc or lead), pressure necrosis, perforation
Post-1983 pennies contain zinc
Cs: acute vomiting, Obx
Dt: metabolic alkalosis (pyloric outflow obx), repeat rads before endoscopy
LAB: Hypochloremic, hypokalemia metabolic alkalosis with obstruction
Tx: Apomorphine (sm + smooth), endoscopic removal, Sx
Dont induce: Sharp, caustic, Obx, shock, airway compromise, corrosives
Hairballs
Et: swallowing hair during grooming
all cats don’t vomit hairballs
excess grooming from fleas, skin dz, anxiety, GI motility dz
Sig: long-haired cats
Nasopharynx: Vomited though nose
Esophagus: Obstruction, esophagitis, stricture
Intestine: Obstruction
Tx: grooming(lion clip), ↑ fiber diet, Laxatone (NOT mineral oil), Metoclopramide, Cisapride
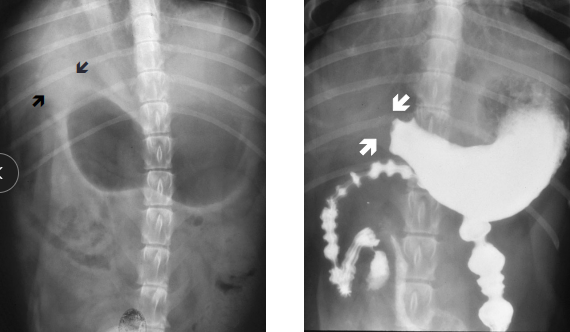
Delayed Gastric Emptying
Et: Mechanical Obx, Extramural compression, Fxn Obx
Sig:
Young: congenital pyloric stenosis, FB
Old: antral pyloric hypertrophy (D), neoplasia
Cs: acute or chonic vomit >10h after eating, projectile vomiting
Dt: metabolic alkalosis, imaging
Hypochloremic, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis
Tx: Sx, fluids→0.9% NaCl w/ KCL(metabolic alkalosis), cisapride→ (post gastric antony or fxn delay ONLY), ↓ fat canned diet, Sm frequent meals
Promotility drugs are contraindicated if Obx
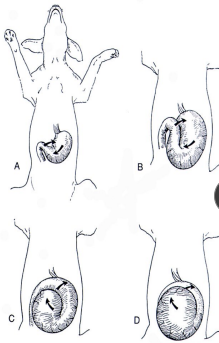
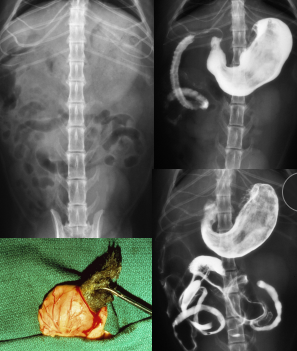
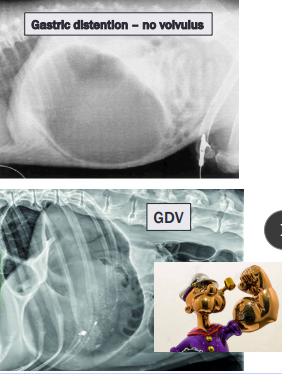
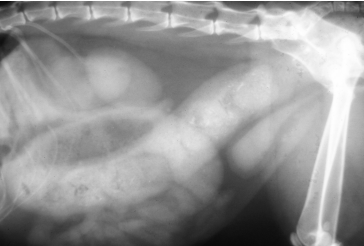
Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus (GDV)
Et: Rapid distention of stomach with air + volvulus @ axis
Compression of caudal vena cava → ↓ venous return → hypovolemic shock
EMERGENCY
Sig: Old, Lg, deep chest, rapid eating, aerophagia, raised food bowls, anxiety
Cs: non-productive retching, salivation, distention, tympany, tachycardia, weak pulse, shock
Dt: R-Lateral abdominal rads, double bubble, ↑ PCV, metabolic acidosis, coagulation defects
Tx:
Initial: LRS shock fluids, O2, Gastric decompression (NG tube or trocarization), Antibiotics
Sx: Emerg Gastropexy
Prevent: Prophylactic gastropexy, slow feeding, sm meals
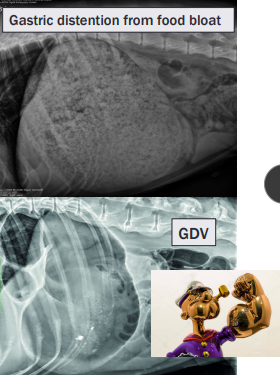
Food Bloat
Et: over - eating
Cs: acute distention, panting, drooling, retching
Dt: r/o GDV →R-Lateral abdominal rads w/ uniform food-filled stomach
No volvulus present, rule out GDV
Tx: fluids, analgesics, gastric lavage
Supportive
resolves < 24-48hr, good Px
Gastric Neoplasia
Malignant: Adenocarcinoma (dogs), Lymphoma (cats)
Benign: Leiomyoma (dogs), Polyps (cats and dogs)
CS: Chronic vomiting, weight loss, +/- hematemesis; +/- anemia
GI bleeding, delayed gastric emptying, vomiting, anorexia, weight loss
Dx: gastroscopy, biopsy
TX: Surgical resection, chemo(lymphona)
Prognosis: poor w/ malignant
Diarrhea
Et: Diet, Toxins, NSAIDs, antibiotics, Parasites, infectious dz, endocrine dz, IBD, EPI
Cs: <3w = acute, >3w = chronic
Dt: fecal float, CBC, biochem, rads
systemic signs or chronic→ req tests
Rule out non-GI causes before
Mild → tests optional
Tx:
Acute: self-limiting, deworm, Fenbendazole, Fluids, Probiotics, fiber, Loperamide, Bismuth subsalicylate
No empirical antibiotic
Chronic: cobalamin, steroids (post biopsy, entropathy + IBD), diet trial, fiber, antibiotics, probiotics
Stepwise format
Protocol for treating chronic diarrhea
Stepwise before biopsy
Anthelmintic: Fenbendazole (whipworms)
Fiber supp: psyllium or high-fiber diet
Diet trial: novel/hydrolyzed protein
Probiotics
Antibiotics: tylosin or metronidazole
If unresponsive → biopsy (confirm IBD)
Corticosteroids: Chronic enteropathy, IBD
Steroids only after biopsy
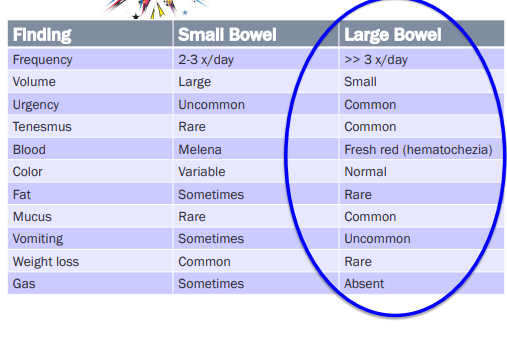
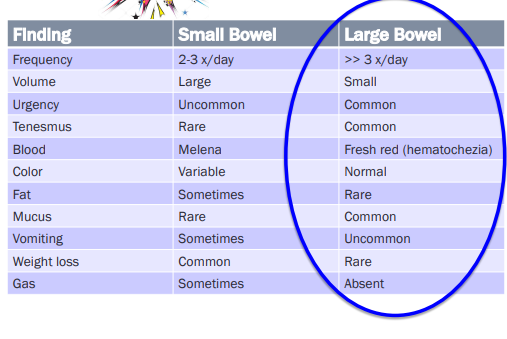
Localizing Diarrhea
Small Bowel
Et: hyperthyroidism, dysbiosis, hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s), EPI, Giardia, IBD, FeLV, allergies, dysbiosis, Lymphangiectasia, Neoplasia, Histoplasmosis
Cs: 2x daily, lg volume, watery, weightloss, gas, fatty stool, melena
Urgency, Mucus, Tenesmus rare
Large Bowel
Et: Whipworms (Trichuris vulpis), Tritrichomonas, IBS, Lymphocytic plasmacytic colitis, Neoplasia, Histoplasmosis
Cs: >3x daily, Sm volume, Urgency, tenesmus, fresh red blood (hematochezia), Mucus
No vomiting, weightloss, or gas
Serum biochemistry in a diarrhea patient
↓ albumin + globulin: PLE
↑ globulins: BD, FIP
↓ Na + ↑ K: Addison’s disease, whip worms
↓ Cholesterol: small intestinal malabsorption, PLE
↑ ALT/ALP: liver disease, enteritis
Small Intestine Dihareha
↑ T4: hyperthyrpoid cats
Chronic Small Intestine Dihareha
Cortisol/ACTH stim: hypoadrenocorticism (Addison’s)
Chronic Small Intestine Dihareha
Neutropenia: viral (parvo) or bacti
Low fasting serum TLI: EPI
Folate + cobalamin tests
↓ folate: proxl small intestinal dz, malabsorption
↑ folate: small intestinal bacti dysbiosis
↓ cobalamin (B12): EPI, ileal dz, dysbiosis, villus atrophy, mucosal inflam
Normally absorbed in the ileum
Distal small intestinal malabsorption
Gastric Supplements
Probiotic:
MOA: Modulate immune response (↑ IgA, ↓ inflam), strengthen intestinal barrier, inhibit pathogen colonization
Ex: Enterococcus faecium, Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium
Live microorganisms
Prebiotic:
MOA: Promotes gut flora
Ex: FOS, Inulin, Pectin, Psyllium
Fiber
Use: Large bowel diarrhea, Fiber-responsive diarrhea, IBS, Acute diarrhea recovery
Synbiotic: Combo prebiotic + probiotic
Cobalamin:
MOA: Deficiency worsens intestinal dz
villus atrophy and mucosal inflam
Why: chronic enteropathy
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
MOA: intestinal flora modification
How: Stool from healthy donor transplanted
normalize microbiome
Use: GI dz, parvo, Chronic enteropathy
Opioids
Rx: Loperamide (Imodium), Lomotil (Diphenoxylate & atropine)
MOA: ↑ absorption, ↓ secretion, ↓ motility, ↑ anal tone
First pass metabolism, does not pass BBB
Use: acute diarrhea
Control urgency, cramping, frequency
Avoid: infectious/bacti diarrhea, MDR1-deficient dogs (Collies), cats
Anticholinergics
Rx: Atropine, Aminopentamide (Centrine), Dicyclomine, propantheline
MOA: ↓ all motor activity, ↓ secretion
↓ peristalsis + ↓ non-propulsive motility
Use: Not recommended
Risk: Ileus, worsen diarrhea, constipation, tachycardia
Pepto-Bismol
MOA: GI protectant, Coat mucosa, inhibit bacti, Bind toxins, Anti-inflam
Remains in lumen
Use: Avoid in cats (salicylates)
Gastric Diets
Novel
What: one protein + carb source not previously eaten
Why: Food allergies or chronic enteropathies
Hydrolyzed
What: Proteins broken into small peptides
Why: chronic or refractory diarrhea
Diet history unclear or “been on everything.”
Highly digestible low-fat
What: Easily digestible, ↓ fat, ↑ fiber
Why: Acute diarrhea, dietary indiscretion, chronic small bowel diarrhea, fat intolerance
High fiber diet
Why: Large bowel diarrhea, Fiber-responsive diarrhea, Constipation, IBD
Intestinal Dysbiosis
Et: Flora imbalance, secondary to chronic dz
Cs: diarrhea that respond to antibiotics
Dt: ↑ Folate, ↓ cobalamin
Tx: Metro, Tylosin
Chronic Enteropathy / IBD
Et: Allergy, IM, genetics
Food/Antibiotic/steroid responsive or Non-responsive
Lymphocytic-plasmacytic (#1), Eosinophilic, Neutrophilic , Granulomatous
Sig: Middle-aged, tradis in cats
Triaditis: IBD, pancreatitis, cholangitis
Breeds: GSD, Shar pei, boxers, basenji
Cs: Chronic vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, thickened intestines, enlarged LN, ascites/edema (alb < 1.5)
Dt: CBC, chem, TLI, cobalamin, US, biopsy
FeLV/FIV, T4, Resting cortisol(addiosn’s)
Therapeutic diet trials before biopsy: Diet x2 → flora mods → steroids
Dysbiosis index:
<0 normal, 0-2 equivocal, >2 dysbiosis
Tx: Diet, probiotics, pred (#1), Vit B12, Budesonide, Chlorambucil (C), Cyclosporine/atopica, Azathioprine (D)
65% respond to diet alone
Novel protein, hydrolyzed 2-3w → rechallenge
Fiber: LG bowel signs
Canine Parvovirus
Et: Incubation 4–7d, fecal-oral
Intestinal crypt cell necrosis → necrosis → vomiting + hemorrhagic diarrhea
BM → neutropenia
Lymphocytes → lymphopenia + immunosuppression
Sig: puppies 6w-6m, Rottweilers, Dobermans, Pits, GSD, Labs
Cs: Acute vomiting, bloody diarrhea, lethargy, anorexia, dehydration, fever, cardiac dz
Dt: Marked neutropenia + lymphopenia, ELISA SNAP test
Tx: fluids, Convenia, antiemetic, pyrantel, famotidine, vax, isolate
Px: 90% survival with ER care, outpatient possible
Panleukopenia
Et: feline parvovirus
Sig: kittens 8-12 w
Cs: Fever, anorexia, lethargic, vomiting, mild diarrhea, peracute death, cerebellar hypoplasia,
end stage = hypothermia, DIC
Dt: Marked neutropenia + lymphopenia, ELISA K9 SNAP test
Tx: fluids, antiemetics, antibiotics, early nutrition,
Prevention: vaccines
Px: poor, high mortality
Minor Viral Diarrhea
Enteric Coronavirus
Et: Fecal-oral, shed 6–9 days
may mutate to FIP in cats
Cs: mild malabsorptive diarrhea(occ. blood), Anorexia, lethargy, vomiting, fever(cats)
Dt: Fecal PCR
Tx: Supportive
Prevention: non-core vaccines
Canine Rotavirus
Sig: uncommon, in puppies <3 months
Cs: Subclinical or mild gastroenteritis
DX: PCR
Tx: Supportive, no vaccines
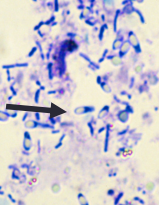
Clostridium
C. difficile + C. perfringens(safety pins)
Dt: PCR + ELISA toxin test
culture isolation ≠ disease, find strain + toxin
Toxin A + B
Found in healthy animals(C. perfringens): type A causes issues
CS: Fatal acute hemorrhagic diarrhea
Small, large, or diffuse bowel signs
Dx: culture, PCR, ELISA + ELISA toxin test
Tx: Metro(difficile), self limiting, symptomatic
Antibiotics only if systemic dz
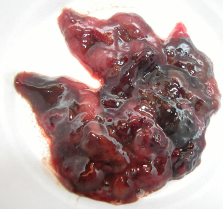
Acute Hemorrhagic Diarrhea Syndrome (AHDS)
Et: C. perfringens in young small dogs
Cs: Acute vomiting, hematemesis progressing to hemorrhagic diarrhea, Intestinal necrosis and inflammation
“raspberry jam”/bloody
**** hemoconcentration → PCV > 60% ****
Dx: clinical dx, no test
Tx: fluids!*, symptomatic
No antibiotics unless fever, shock, abnormal WBC
Ampicillin 1st choice
Px: Excellent
Campylobacter
ID: Motile slender curved rod (G-)
Et: many healthy carriers, zoonotic
Cs: diarrhea(young), fever, vomiting → “pet store puppies”
stress, over crowding, coccurrent dz
Dt: Fecal smear (gull-wing), culture, PCR
Tx: Erythromycin, azithromycin, enrofloxacin
Salmonella
G- bacilli
Raw food diets higher risk, pig ears
Et: healthy carriers, zoonotic
Cs: Vomiting, diarrhea, fever, lethargy
Acute 3-5 days post exposure
Dt: Fecal culture (x3), PCR
Tx: self limiting, supportive care
Ampicillin + enrofloxacin only if systemic dz
E. coli Granulomatous Colitis
AKA “ boxer colitis or “Histiocytic Ulcerative Colitis”
Et: invasive E. coli
Sig: Young, Boxers, Bulldogs, Mastiffs.
Cs: severe Chronic large bowel diarrhea, weight loss, inappetence
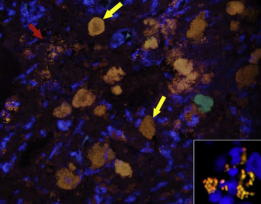
Dt: Hypoalbuminemia, anemia(GI loss), Colon biopsy (inflammation, PAS+ macrophages, FISH: Fluorescence in situ hybridization)
culture: not helpful for dz, helpful in tx
Tx: Enrofloxacin based on c/s from the biopsy
Px: Good, improve 1w, full dose for remission
Fungal Diharreah
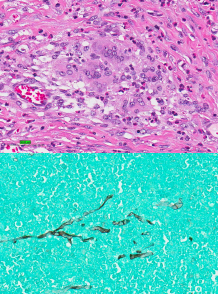
Histoplasmosis
Et: Soil-borne, Mississippi & Ohio River valleys
Cs: multisystemic (GI(colon), liver, spleen, lungs, eyes, bones)
LG/SM bowel diarrhea, wt loss, fever, thickened bowel loops
Dt: Cytology (rectal/liver/spleen FNA), biopsy, urine ag test
Tx: Itraconazole, fluconazole, amphotericin B (≥6 months).
Pythium insidiosum
Gulf coast southern US
Et: GI tract, granulomatous masses
Focal or multifocal segmental thickening
Stomach, SI, colon, ± esophagus
CS: vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, wt loss
Dt: Cytology or biopsy, ELISA(antibody), PCR(antigen)
Tx: Sx, itraconazole + terbinafine, pred
Px: poor
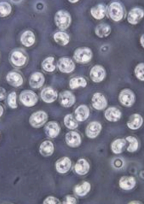
Giardia
Et: Fecal-oral, cysts survive months, dogs + cats
Protozoal Diarrhea
Cs: young, small bowel diarrhea ± mucoid, weight loss(chronic)
Dt: Fecal ZnSO₄ flotation, smear(floating leaf), ELISA, PCR
Tx: Fenbendazole, Metro
Treat all animals, bathe, disinfect enviro
Tritrichomonas foetus
Feline Trichomoniasis
Only trophozoite form unlike giardia
Et: Colonizes colon/ileum
Protozoal Diarrhea
Sig: young cats
Cs: Chronic large bowel diarrhea, blood, mucus, incontinence, cow pie, ± fecal incontinence - otherwise healthy cats!
“waxes and wanes” = Weeks to years
Dt: Fecal PCR, fecal smear(jerky movement)
fresh diarrheic feces (lima bean size)
Tx: Ronidazole, spontaneous resolution w/i 2y but remain PCR +
Cryptosporidiosis
Et: C. parvum, Zoonotic
Protazoal Dihareah
Cs: small bowel diarrhea
Puppies or kittens with concurrent disease or immunocompromised
Dt: fecal Immunoassay or PCR
Px: poor, difficult to eliminate
Coccidiosis
Et: Protozoal Diarrhea
Sig: young animals
Cs: Mild–severe diarrhea, sometimes blood
Dt: Fecal flotation.
Tx: Sulfadimethoxine, TMS, Ponazuril.
Px: Good
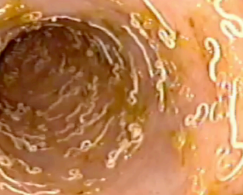
Whipworms
Et: Trichuris vulpis
Dogs, rare in cats
Cs: Large bowel diarrhea, hematochezia
Dt: Fecal flotat (false neg common), colonoscopy
Tx: Fenbendazole repeat in 3m
Consider therapeutic trial of fenbendazole!!
Roundworms
puppies and kittens
Et: Toxocara + Toxascaris
Cs: Diarrhea, ± vomiting, poor growth/hair coat, “pot-belly”
Dt: Fecal float
Tx: Pyrantel, Fenbendazole
Hookworms
Et: Ancylostoma + Uncinaria
Sig: young
subclinical in adults
Cs: Anemia(pale MM), melena, diarrhea, Blood loss/iron-deficiency anemia, Failure to thrive
Tx: Pyrantel, Fenbendazole
Tapeworms
dogs and cats
Et: Dipylidium, Taenia
Transmission by fleas
Cs: Anal irritation, NOT diarrhea
Tx: Praziquantel, Episprantel, control fleas
Strongyloides stercoralis
Et: protazoa
Sig: puppies → shelters/pet stores
Cs: mucoid/hemorrhagic diarrhea, lethargy
Dt: Fresh feces or Baermann
Tx: Fenbendazole, thiabendazole, ivermectin.
Px: guarded with serve CS ± pneumonia
Prototheca zopfii
Rare
Et: Algal infection → tissue invading
colon, eyes, skin
Cs: bloody diarrhea (LG bowel signs)
Dt: Cytology, biopsy
Tx: Amphotericin B
Px: poor.
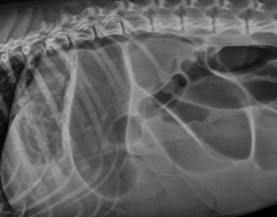
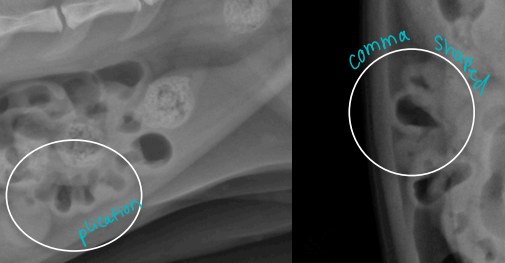
Intestinal Obstruction
Et: FB (#1), intussusception, neoplasia
More Proximal obx = more severe vomiting
Linear: #1 cause of Obx
Cats young (#1)→ base of tongue
Dogs older→ pylorus
Cs: Vomiting, dehydration, lyte imbalance, ± aneroxia, depression, abd. pain, ± shock/sepsis
Dt: PE, Palpation, survey Rads #1 ± contrast, US(more sensitive)
dilated loops, stacking, gas pattern
Comma-shaped gas bubbles
Tx: pre anes. fluids, Sx once stable, cut string under tongue,
monitor if simple: Healthy cat (present only 1-2 days) → sx in 12-24h if not better
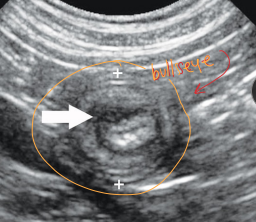
Intussusception
One intestinal segment (intussusceptum) into an adjacent segment (intussuscipiens)
“Sausage loop” on PE
Young animals
Et: idiopathic, enteritis, motility dz, parasites
intussusceptum into intussuscipiens common at ileocolic jxn
Cs: Vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, lethargy, pain, “sausage-like” mass, hematochezia
Dt: Palpation, rads, US
Tx: Sx reduction or resect

Intestinal Adenocarcinoma
Most common primary neoplasm of GI tract
Dogs
CS: vomiting if causing obstruction; weight loss,
diarrhea
diffuse thickening or focal, circumferential mass
lesions
Dt: contrast radiographs, explore sx
Apple core lesions w/ contrast = focal
Tx: surgery, good prognosis if fully resected
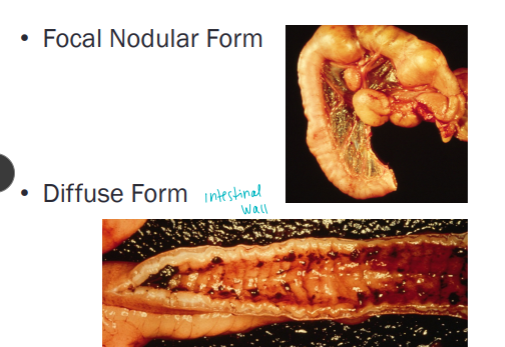
Intestinal Lymphoma
Both can be focal or diffuse
Most common in cats
Large cell (lymphoblastic) High grade
Most common in dogs, can occur in cats
CS: Acute (days to weeks): Weight loss, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, GI perforation
Small cell (lymphocytic) Low grade T-cell
Most common in cats
LGITL
CS: chronic (weeks to months) GI signs indistinguishable from chronic inflammatory enteropathy
Mimics lymphocytic plasmacytic enteritis (LPE)
May need immunohistochemistry or PARR (PCR) to differentiate
Dx: cytologic (lymphoblastic only) or histopathologic (both) or PCR antigen - PARR
Biopsy: gold standard
Tx: Chemo → lymphoblastic lymphoma do not do as well
Pred + chlorambucil (cat SM cell)
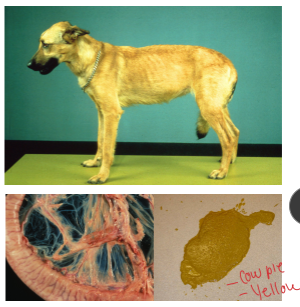
Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI)
Et: 90% loss of pancreatic enzyme secretion
Pancreatic acinar atrophy: hereditary GSD, young dogs1-4 y, Most common: DLA-88
exocrine function preserved: no diabetes
Inflammation and fibrosis absent: pancreas
2ndary Chronic pancreatitis(acquired): cats, small dogs
older onset, may have diabetes
Cs: dysbiosis, ravenous appetite + weight loss, yellow Cow-patty, greasy stool, fart
Cats less obvious clinical, mostly just weight loss
Chronic small bowl diarrhea
Dt: ↓ TLI (#1), Cobalamin ↓
Dogs: < 2.5
Cats: < 8
Tx: Life long: Pancreatic enzyme supp, Cobalamin supp, digestible diet, Tylosin
Px: excellent, lifelong therapy
Protein-Losing Enteropathy
General: dogs > cats
Et: Chronic bowel dz, Hookworms, histoplasmosis
Loss of albumin and globulins into intestines
Cs: panhypoproteinemia, edema, ascites, effusion, diarrhea, vomiting, weight loss
Edema: Transudate fluid
Dt: ↓ Albumin**, ↓ Globulin-**, fecal α1-proteinase inhibitor, Imaging + biopsy
a1 test - not till others are r/o: UPC, bile acids
Lymphangiectasia subtype
Et: Primary, Obx CHF, portal hypertension
Lacteals rupture with lymph loss and cholesterol
Sig: yorkies
Cs: Weight loss, small bowel diarrhea, ascites, effusion
Dt: ↓ Albumin, ↓ Globulin, ↓ Cholesterol, ↓ Ca, lymphopenia, US w/ thick striations/speckling, Biopsy
Tx: ↓ fat diet #1, Cobalamin supp, Pred, Aspirin, clopidogrel, Octreotide
Small vs. Large bowel diarrhea
Chronic Colitis
Inflammation limited to colon (cats +/- small bowel)
CS: Dogs: Mucoid diarrhea, Hematochezia, Frequent defecation, Vomiting and weight loss (rare)
Large bowel signs
Cats: Hematochezia, diarrhea
Dx: r/o other LG bowel dz
Tx: Therapeutic trials prior to biopsy
Modified fiber diet, probiotics, Pred, sulfa(risk KCS)
If diet fails: biopsy→ Lymphocytic-plasmacytic inflammation most common, idiopathic
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBD)
Et: Stress**
travel, boarding, separation, noise/storms
Cs/Dt: Recurrent idiopathic large bowel diarrhea with normal biopsy
Tx: Fiber, Probiotics, Metro, Anti-anxiety meds
Constipation
Infrequent or difficult evacuation of dry, hard feces
Et: Bones, Dirty litter box, Anal sac dz, Pelvic fracture, Arthritis, CKD, ↑ Ca
Large intestine dz
Cs: ↓ defecation, dry feces, straining, Paradoxic Diarrhea (Liquid leaks during straining)
Dt: rads, palpation
Tx: Fulids, Lactulose, Miralax, Enemas (avoid in Sm animals), Manual deobstipation, fiber
Treat underlying issue!!
Megacolon
Et: Over weight cats
Cats: primary dz, idiopathic smooth muscle dysfunction, perm dilation
Dogs: secondary to stricture or obx
Cs: constipation, anorexia, lethargy, weight loss, paradoxical diarrhea
Dt: enlarged colon & painful colon on PE, rectal exam, rads
dehydration, hypokalemia, pre-renal azotemia may be present
Tx: Fluids 12-24h, Enemas, Lactulose, Miralax, Fiber, Cisapride, Subtotal colectomy (refractory)
NO Fleet enemas in cats → ↑P, ↓Ca, death
Long term: Fiber-enriched diet, Metamucil, Oral laxative
Cholestasis**
Et: Impaired bile flow**
Extrahepatic: gallbladder, common bile duct
mechanical
Intrahepatic: functional
Cs: icterus, vit K malabsorption
Dt: ↑ BA, ↑bilirubin, ↑ cholesterol
Tx: parenteral Vit K1, Sx (extrahepatic)
Sulfasalazine
MOA: acts locally in colon
Use: for large bowel colitis only
Ineffective for small intestinal IBD
Risks: KCS, monitor tear production
Anal Sac Disease
Et: impaction, sacculitis, abscess
small breeds, obesity, diarrhea, allergic skin dz
Sig: common in dogs, rare in cats
Cs: scooting, licking, biting, tail chasing, blood on feces, dyschezia
Tx: express sacs, antibiotic-steroid infusion, compresses, Sx, fiber, weight loss, manual expression, weight loss
Rectal diseases
Anorectal Prolapse
Et: Secondary to diarrhea or straining
Dt: Differentiate from intussusception
probe can pass deeper in intussusception
Tx: Replace + purse-string suture
Anorectal Stricture
Et: Fibrous narrowing of lumen, congenital or post-inflammation
Cs: painful defecation
Dt: palpation ± imaging
Tx: dilation (balloon/tapered syringe dilation (mild), Sx (severe)
Comp: fecal incontinence
Rectal Polyps
Sig: Older dogs
Cs: hematochezia, dyschezia, blood with normal stool
Dt: rectal palpation, colonoscopy
Tx: Sx
Px: good
Perineal diseases
Hernia
Et: Weak pelvic diaphragm, rectal sacculation, constipation, perineal bulge
Sig: Older intact males
Cs: dyschezia, perineal swelling, bladder entrapment (emerg), depression, vomiting
Dt: rectal, imaging, Post-renal azotemia
Tx: Sx
Fistula
Et: Painful ulcers/sinus tracts around anus, IM (T-cell)
Sig: Mid age GSD
Cs: tenesmus, hematochezia, dyschezia, pain!!, discharge, anorexia, diarrhea, weight loss
Tx: Cyclosporine ± Ketoconazole, Tacrolimus 0.1% ointment, Novel diet
Exocrine Pancreatic Carcinoma
Uncommon
Older dogs and cats
High metastatic rate (liver, nodes) @ dx
CS: Lethargy, anorexia, weight loss, vomiting
7-day median duration of signs in dog
Palpable abdominal mass in cats; previous hx diabetes
mellitus
Dx: cytology, biopsy, necropsy; ↑ liver enzymes, bilirubin
and pancreatic enzymes
mimic acute pancreatitis in dogs and increase cPL
Tx: Chemo?
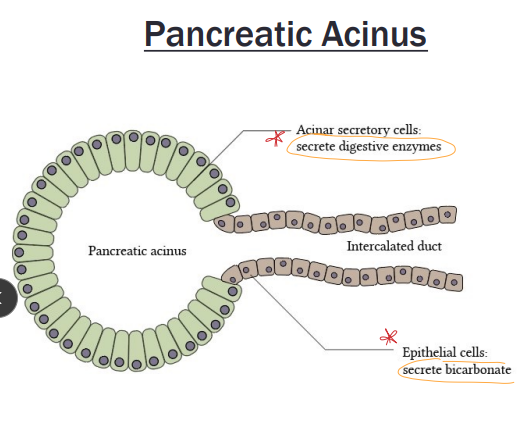
Acute Pancreatitis
Premature activation of trypsinogen within the pancreas
Et: Idiopathic (#1), Dietary indiscretion, DM, Cushing’s, Hypothyroidism, Schnauzers hypertriglyceridemia
Sig: Old, obesity, dogs
Cs: Acute vomiting, anorexia, lethargy, dehydration. inflammation, abd. pain → edematous: self limiting
Cats subclinical: Increased liver enzymes, bilirubin
Triaditis
Dt: biopsy (#1), ↑ PL snap + US, ↑ bilirubin
Diagnosis of exclusion
Snap is NOT definitive also + with kidney failure
NEGATIVE test rules out pancreatitis
Rads have ↓ sensitivity + specificity
Soft tissue density in area of pancreas with displacement of duo to the right
Tx: Fluids (LRS + K + Ca), analgesia, Maropitant, Ondansetron, ↓ fat diet, avoid table scraps
Avoid NSAIDs
Risks: Organ failure, DIC, SIRS, mortality 50%
necrotic > edematous
• Abscess*
• Pseudocyst*
• Biliary obstruction*
Chronic Pancreatitis
Et: idiopathic (#1), IBD, Cholangitis, Biliary obx, DM, Hepatic lipidosis, drugs
Sig: Older, cats
Cs: subclinical Cats
Dogs: chronic intermitting GI signs
can cause EPI and DM
Dt: Suspicion, low-grade inflammation
Lymphocytic-plasmacytic inflammation, fibrosis and
atrophy most common
US + PL will look normal
Snap is NOT definitive, + w/ kidney failure
Rads have ↓ sensitivity + specificity
Tx: ↓ fat diet, Steroids
Triaditis in Cats
Pancreatitis
Cholangitis
Cat pancreatic and bile ducts join → predisposed to triaditis
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Functional Categories of the Liver
Metabolic: Carb + protein + fat metabolism, Detoxification
gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, cholesterol, bile acids, lipoproteins, albumin, coagulation factors, urea synthesis
Avoid drugs needing hepatic activation
Reduce doses of those inactivated by liver
↑ NH3, ↑coags, ↓ glucose, ↓ chloesterol, ↓ BUN, ↓ albumin, ↑ bile acids
Circulatory: Receives portal and arterial blood, regulates blood flow
Liver has large reserve → Cs at <30% fxn
R CHF → Venous congestion → backup of blood into liver → hepatic enlargement
Liver maintains low blood ammonia, normal BUN
NH₃ produced in colon → hepatocytes convert to urea
MOST COMMON LIVER DISEASE IN DOGS THAT CAUSES PORTAL HYPERTENSION IS CIRRHOSIS
Secretory + Excretory: Bile synthesis +secretion, Bilirubin excretion
Portosystemic Shunts
Et: Portal Blood bypasses liver
Single congenital: no portal hypertension
Multiple acquired: secondary to portal hypertension
Sig: Yorkie, Cairn, Maltese, Schnauzer, Wolfhound, Lab
Extra: Small dogs, cats
Intra: Large-breed
Cs: Hepatic atrophy, Microcytosis, Ammonium biurate crystals, HE, PU/PD, stunted growth, urate uroliths, Hepatic encephalopathy: ammonia toxicity is key
Dt: Nuclear scintigraphy ↓ BUN, ↓ albumin, ↓ cholesterol, ↓ glucose, ↑ BA → post prandial
Tx: Protein-restricted diet, lactulose, antibiotics, ameroid constrictor Sx (extra), radiology coil embolization (intra).
Sx for congenital NOT acquired
Px: Good with closure; cats ↑ post-op risk.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Et: congenital/acquired PSS, hepatic necrosis, cirrhosis, urea cycle enzyme defects
Ammonia + toxins affect CNS
Cs: anorexia, lethargy, drool, head pressing, circling, ataxia, blind, seizures, coma
Can wax and wane
Tx: PSS Sx, ↓ diet protein, lactulose
Portal Hypertension
Et:
Prehepatic: portal vein thrombus/mass
Intrahepatic: cirrhosis, congenital hypoplasia
Posthepatic: CVC obstruction, R heart failure, pericardial effusion
Cs: Ascites, Acquired PSS (not post-hepatic), Hepatomegaly (post-hepatic), Gastric ulcers
↑ hydrostatic pressure → ascites
Cholestasis
Et: Impaired bile flow, ↑BA, bilirubin, cholesterol in blood
Extrahepatic: gallbladder, common and main bile duct
mechanical
Intrahepatic: functional
Making this distinction is clinically important since
mechanical causes may be corrected with surgery
Cs: icterus, vit K malabsorption
Tx: parenteral Vit K1, Sx for extrahepatic
Icterus
Run PCV FIRST!
Et: Pre-hepatic hemolysis, Hepatic dz, Post-hepatic biliary obx
Cs: Bilirubinuria (orange urine), acholic feces (gray)
Dt: serum bilirubin >2.5 mg/dl, PCV, US
Normal PCV = not pre-hepatic
US for post-hepatic obx
Ascites in Liver Disease
Portal hypertension: ↑ hydrostatic pressure
Hypoalbuminemia: ↓ oncotic pressure
Renal sodium and water retention: secondary effect