W10-11: Sedimentary Rocks
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Knowt for W10-11 exam focused on Sedimentary Rocks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Sedimentary Facies
Bodies of sediment that are recognizably distinct from adjacent sediments. Individual depositional environments produce bodies of rock with specific characteristics (composition, texture, structures, bedding, fossils)
Depositional Environment
A specific type of place in which sediments are deposited, such as a floodplain, beach face, or sand dune. Each place produces a sedimentary facies characteristic of that place.
Facies Assemblage
A genetic grouping of facies that correlates with a particular depositional system
Depositional System
A set of genetically and geographically related depositional environments, e.g., the below storm-wave-base, between storm-wave- and fair-weather-wave-base, above fair-weather-wave-base, and shore face environments that characterize beaches
Depositional Systems Tract
All of the depositional systems present in a given area at a given time in Earth’s history
Walther’s Law of Facies
A vertical sequence of facies is the product of a series of laterally-adjacent depositional environments
Progradation
Seaward outbuilding of successive strata; that is, stacking strata such that a depositional system in an overlying layer lies seaward of the equivalent system in the underlying layer (sediment supply > accommodation space)
Aggradation
Vertical stacking of successive strata; that is, stacking strata such that a depositional system in an overlying layer lies directly above the equivalent system in the underlying layer (Sediment supply = accommodation space)
Retrogradation
Landward migration of successive strata; that is, stacking strata such that a depositional system in an overlying layer lies landward of the equivalent system in the underlying layer (sediment supply < accommodation space)
Transgression
A geologic event caused by a relative rise in sea level that results in retrogradational stacking of strata
Regression
A geologic event caused by a relative fall in sea level that results in progradational (seaward) stacking of strata
Sequence Stratigraphy
An area of stratigraphy that describes sedimentary deposits based on their stacking patterns and interprets them in terms of variations in sediment supply and in the rate of change of accommodation space.
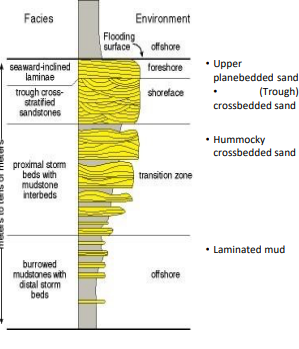
Upper Plane-Bedding
Parallel laminations that indicate rapid flow
Cross-bedding
Laminations at an angle to bedding that indicate intermediate flow
Ripples
Small dune-forms that indicate low flow
Hummocky-bedding
Small piles of sediment surrounded by depressions. These form below fair weather wave base and above storm wave base.
Parallel Laminations
Parallel bedding formed by variations in the sedimentation rate of fine-grained sedimentM
Mud Cracks
Desiccation cracks in clay-rich sediments that indicate subaerial conditions and transitions between wet and dry periods (as found in desert climates)
Bioturbation
Disruptions in and on beds (e.g. burrows) caused by moving (feeding) organisms
Massive Bedding
Homogenous beds with no sediment sorting or laminations
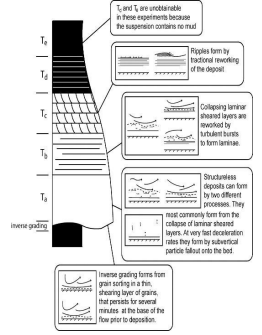
Turbidite Sequence
Point Bar Sequence
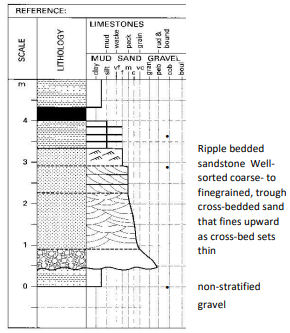
Beach Sequence