Biol-1115 Lab
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Resolution
Ability to see finedetail
Parfocal
Focus remains constant even when magnification or focal length changes
Working distance
Distance from objective lens to slide
Image reversal
Left-right & top-bottom. Specific to light compound microscope.
Advantages of stereoscopic dissecting microscope:
Ability to observe objects that are too large/ thick.
Ability to observe objects in 3D
Image reversal does not occur.
Total magnification
The product of objective & ocular lenses
Field diameter
Number of millimetres seen in whole field of view through ocular lenses.
Stage micrometer
1 cm ruler on glass slide
Scale
Size of drawing relative to true size of organism. Drawing diameter divided by true diameter of organism in mm
True diameter
The field diameter multiplied by the linear fraction in mm
True size
The actual, unmagnified size of organism on slide
Cross section
Cut at right angles to the longitudinal axis of an object
Longitudinal section
Cut parallel to the longitudinal axis of an object
Median section
Cut along the middle of an object
Radial section
Cut made along a radius of a circular object.
Organelles
Mitochondria, chloroplasts, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus.
Cytoskeleton
A network of microtubules, microfilaments, & intermediate filaments that extends throughout the cytoplasm & serves a variety of mechanical, transport, & signalling functions.
Mitochondria
Where cellular respiration occur & ATP is generated
Food vacuoles
A membranous sac formed by phagocytosis of microorganism or particles to be used as food by the cell
Cilia
Short appendage containing microtubules. Specialized for locomotion or moving fluid past the cell. Primary cilia are non - motile for sensory & signalling.
Flagella
Long cellular appendage specialized for locomotion
Chloroplasts
Specific to plant cells. Absorbs sunlight & uses it to drive the synthesis of organic compounds from carbon dioxide & water.
Lysosomes
Digestive organelle where macromolecules are hydrolyzed.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Network of membranous sacs & tubes; active in membrane synthesis & other synthetic & metabolic processes
Golgi apparatus
Active in synthesis, modification, sorting, & secretion of cell products from endoplasmic reticulum.
Central vacuole
Specific to mature plant cells. A large membranous sac with diverse roles in growth, storage, & sequestration of toxic substances
Cell wall
Specific to plant cells. A rigid structure surrounding the cell.
Centrioles
Specific to animal cells. A structure in the cytoplasm that functions as a microtubule organizing center & is important during cell division. Has 2 centrioles
Ovum
Mature female egg cell.
Plasma (cell) membrane
Membrane enclosing the cell
Chromosome
Cellular structure consisting of one DNA molecule & associated proteins
Nucleus
Holds genetic material in the form of chromosomes. Made up of chromatin. Contains the nuclear envelope, nucleolus, & chromatin.
Nuclear membrane
Membrane enclosing the nucleus
Nucleolus
A nonmembranous structure involved in production of ribosomes; a nucleus has one or more nucleoli.
Epidermis
Simple plant tissue in non woody plants. Outer most layer of cells in animals.
Prokaryotic cells
Lacks any membrane-bound organelles or a true nucleus. DNA is held in nuclei
Eukaryotic cells
Presence of membrane-bound organelles. DNA held in nucleus.
Plant cells
Has a cell wall, central vacuole, chloroplasts, & plasmodesmata. Only has microfilaments & micro tubules in its cytoskeleton.
Animal cells
Has a lysosome, centrosome, & flagellum. Has microvilli & intermediate filaments a part of its cytoskeleton.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Active in protein synthesis, folding, & quality control; covered in ribosomes.
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Active in synthesis of lipids, carbohydrates metabolism, & detoxification; free of ribosomes.
Cytoplasm
Content of the cell enclosed by the cell membrane.
Tissue
Group of similar cells performing a common activity
Histology
Study of tissues
Organ
Group of tissues collectively performing a specific function
Organ system
Group of organs performing a major body function
Indeterminate growth
Continues to grow bigger & taller throughout their lives. (Plants)
Determinate growth
Achieves a mature size & stops growing (animals)
Epithelial tissue
Forms the covering & lining of free body surfaces, internal & external. Functions for protection (surface of skin & lining of internal organs), absorption of nutrients (in intestines), secretion (in kidneys, salivary glands, intestines, thyroid gland), lubrication (in areas where mucus is produced), & exchange of materials by diffusion (lungs & blood capillaries)
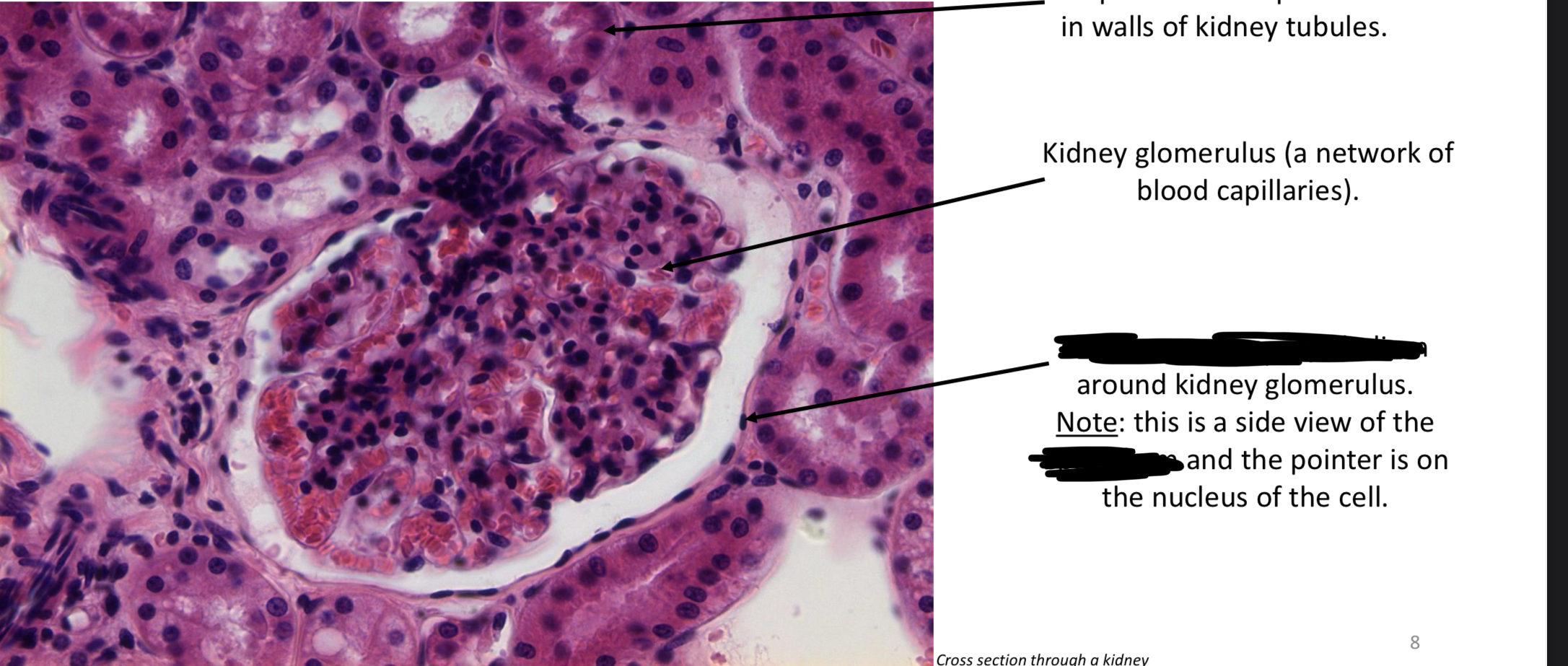
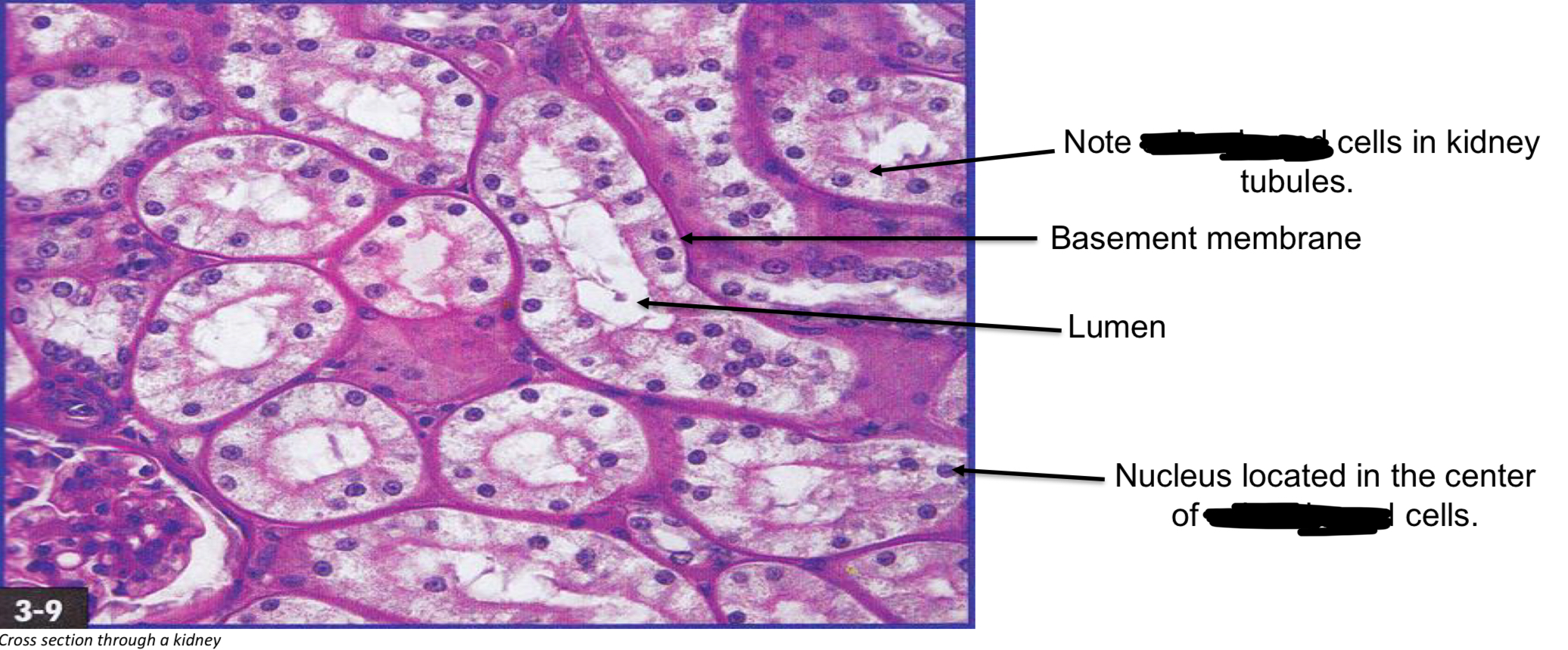
Basement membrane
Separates epithelium from underlaying tissue
Apical (luminal) surface
Free surface of epithelium which is exposed to air (skin) or fluid (stomach)
Microvilli
Located in lumen to increase surface area
Epithelial tissue function
Barrier against mechanical injury, pathogens, & fluid loss
Epithelial cell shapes:
Squamous: flat, scale-like
Cuboidal: appear square in side view, nucleus in center
Columnar: appear rectangular in side view, nuclear towards base of cell
Simple epithelial
Cells are arranged in one single layer
Stratified epithelial
Cells are arranged in two or more layers.
Simple columnar epithelium function
Absorption of nutrients, secretion of digestive juices, & secretion of mucus by goblet cells.
Villi & crypts
Outward finger-like extensions & inward indentations, respectively → increases surface area of small intestine
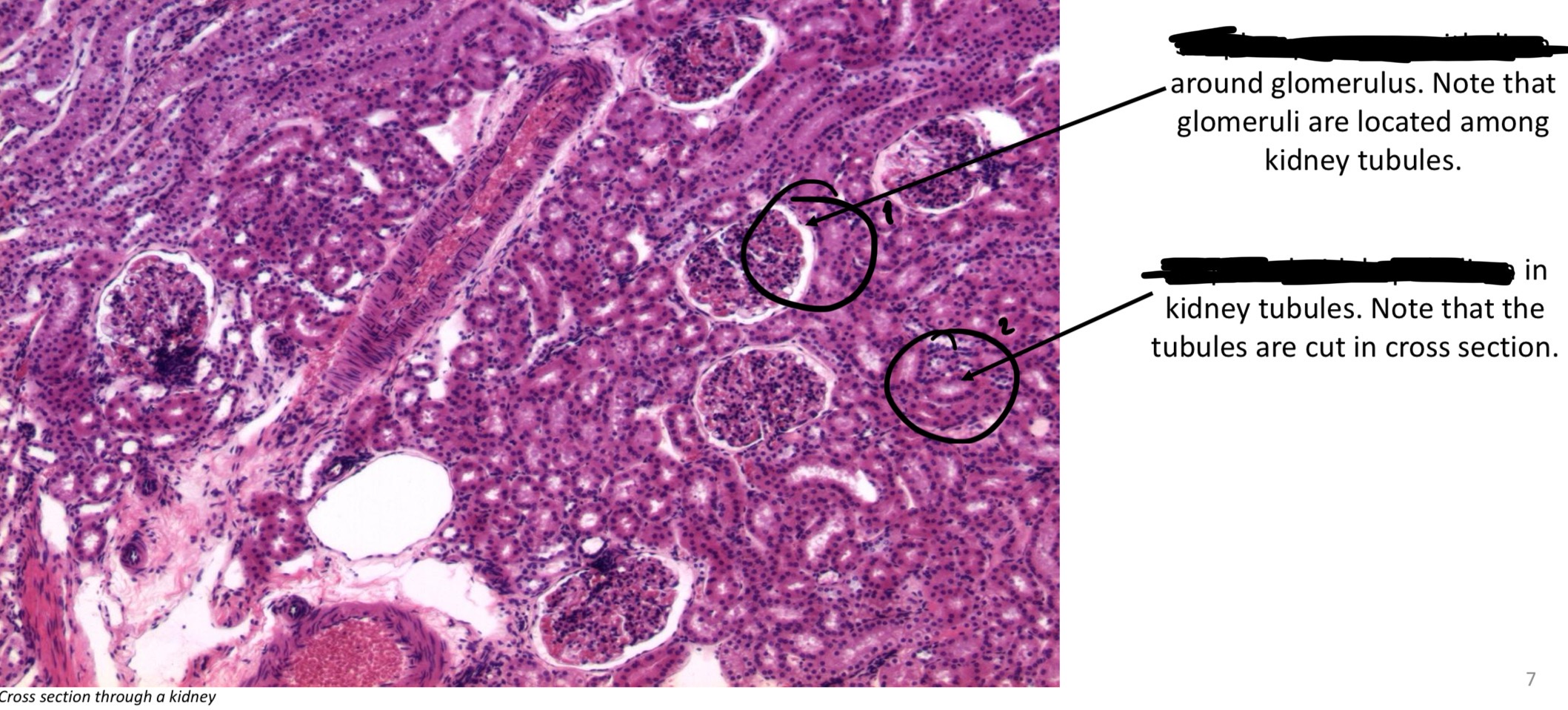
Nephrons
Formation of urine
Simple cuboidal epithelial function
Secretion & absorption. Found in kidneys, thyroid gland, sweat glands, & salivary gland.
Simple squamous epithelium function
Allows substances to easily diffuse through cells to be filtered through → thinnest epithelium → found in kidney walls, internal surfaces of ventral body cavities, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, & heart.
Stratified squamous epithelium (non-keratinized (wet)) function
protection against abrasion & pathogens → oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, vagina, & anus.
Stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized (dry)) function
Known as epidermis: thick → soles of feet, palms of hands. Thin → found everywhere else.
Pseudostratified ciliates columnar epithelium
Protection, secrete mucus by goblet cells, &move mucus by cilia → the nasal cavity, trachea, & bronchi
Goblet cells
Secrete mucus into the respiratory tree. Usually lack stain & cilia.
Glomeruli
Cluster of capillaries at end of kidney tubules where waste is filtered out of blood
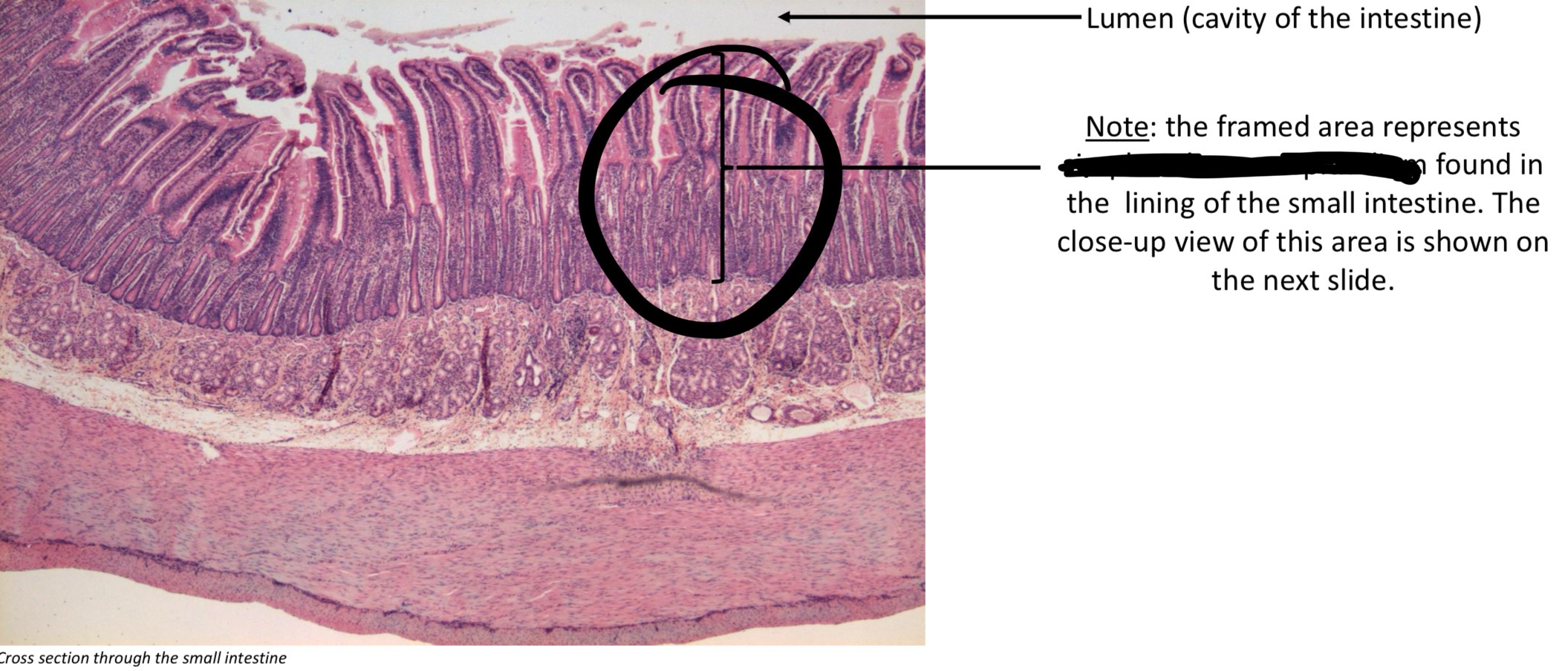
Simple columnar epithelium → small intestine
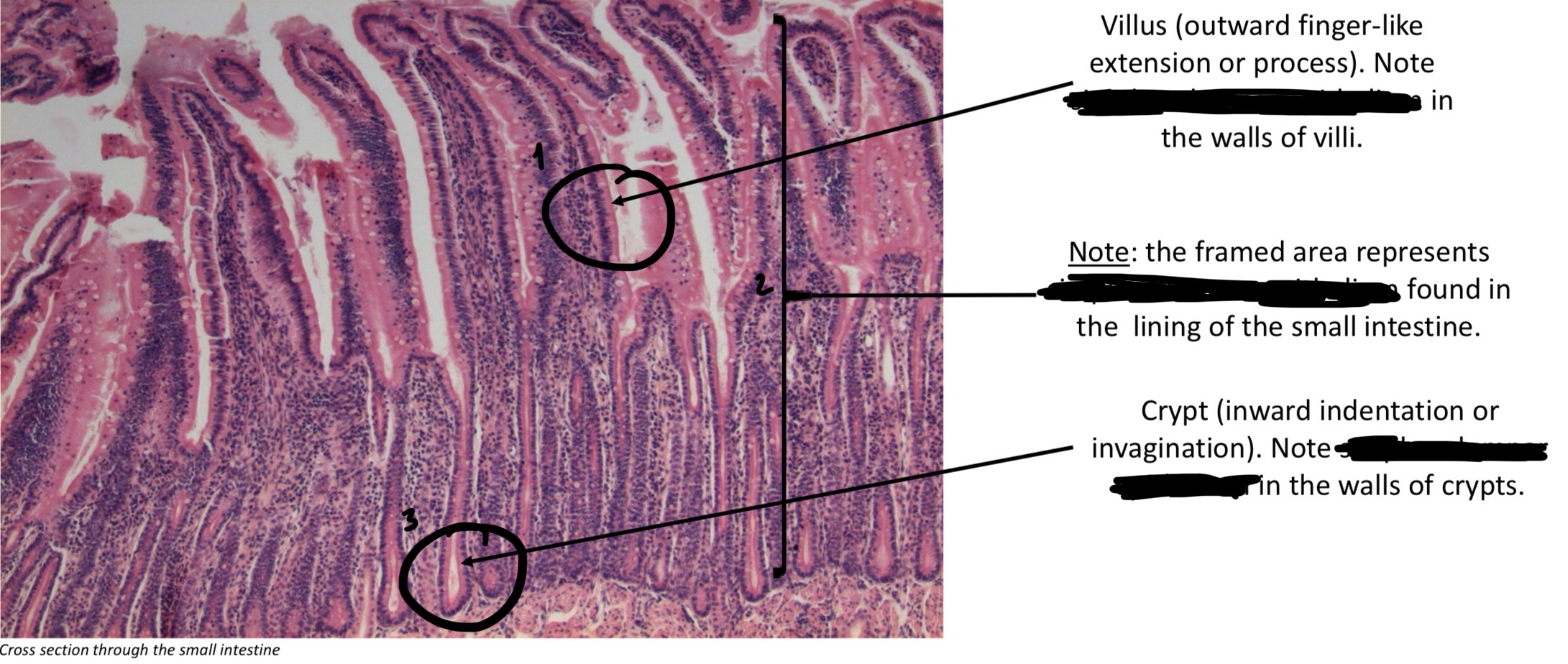
Simple columnar epithelium → small intestine
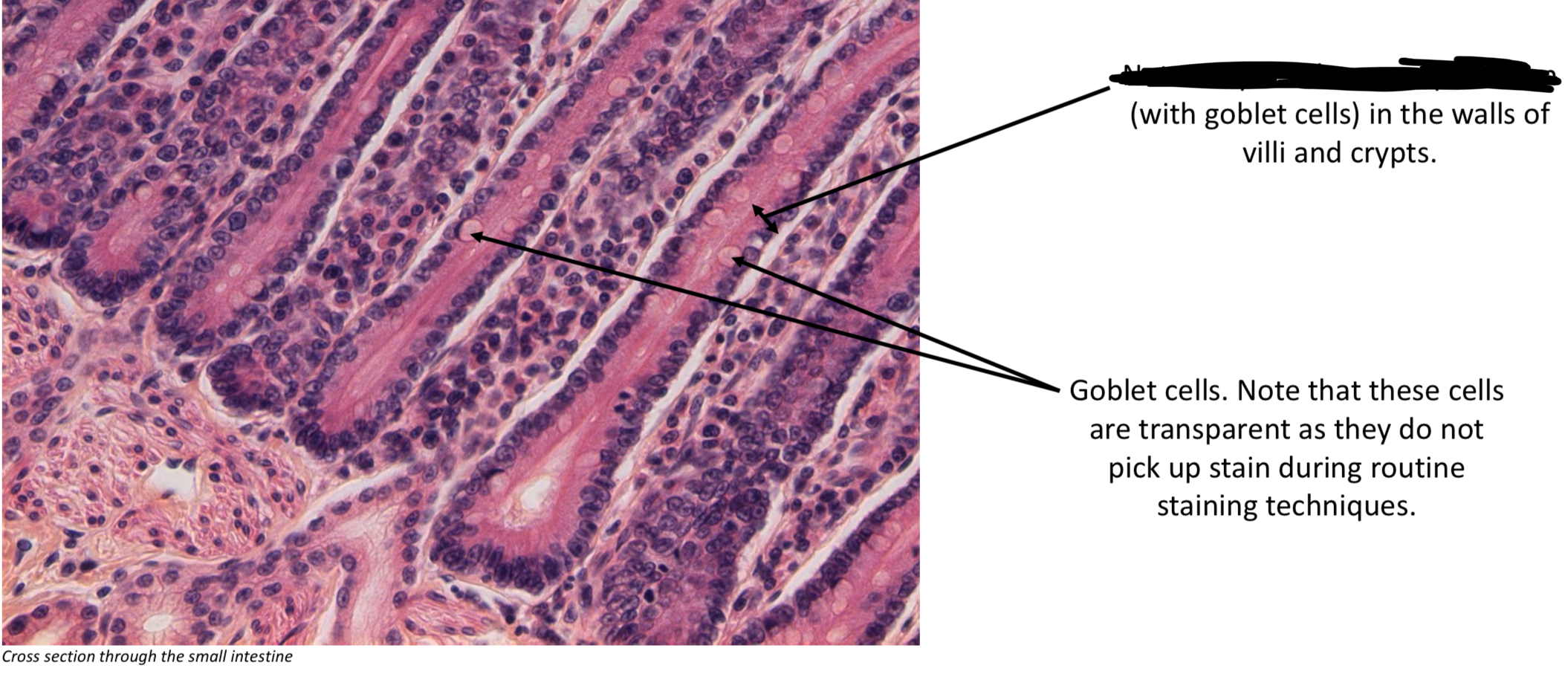
Simple columnar epithelium → small intestine
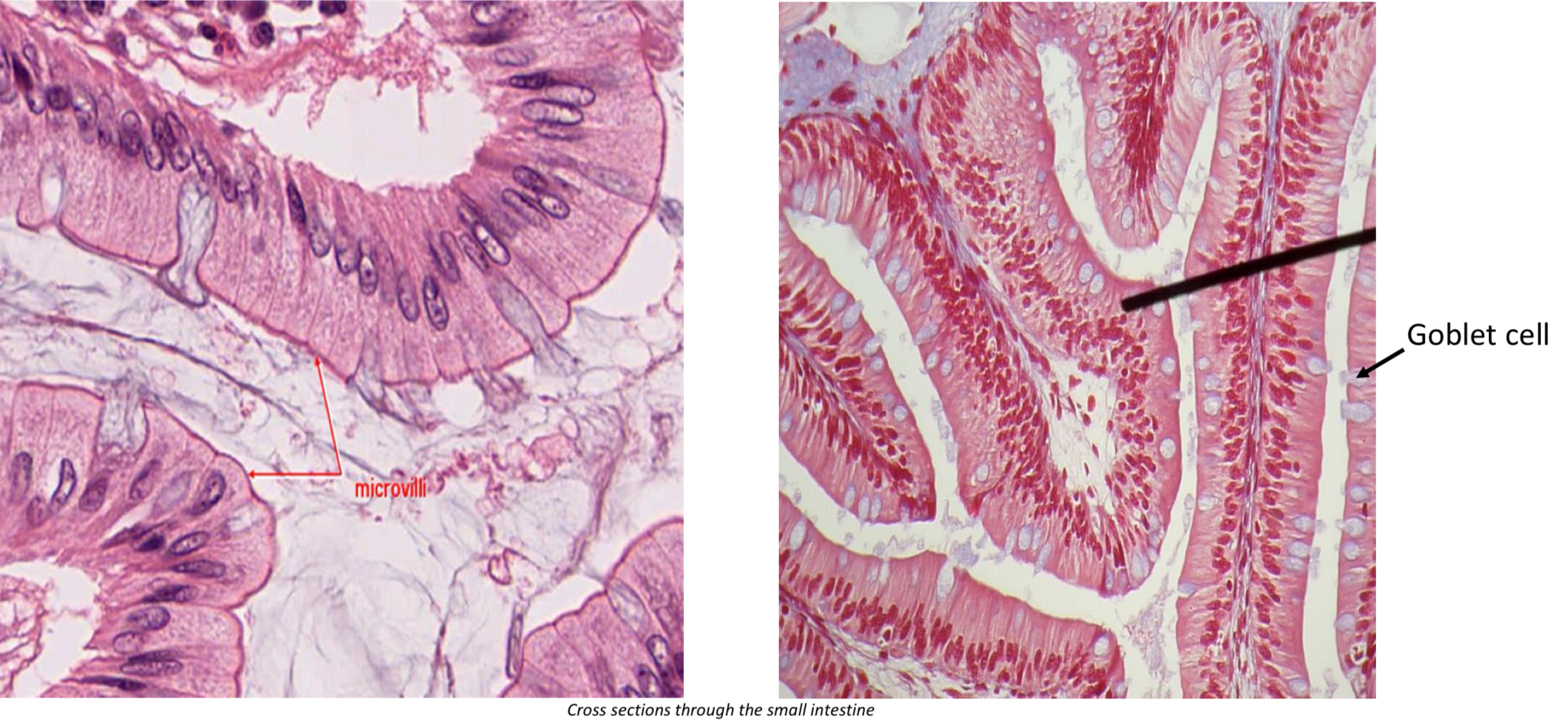
Simple columnar epithelium → small intestine
Simple squamous epithelium
Simple cuboidal epithelium → kidneys
Simple cuboidal epithelium
Simple squamous epithelium → kidneys
Simple cuboidal epithelium → kidneys
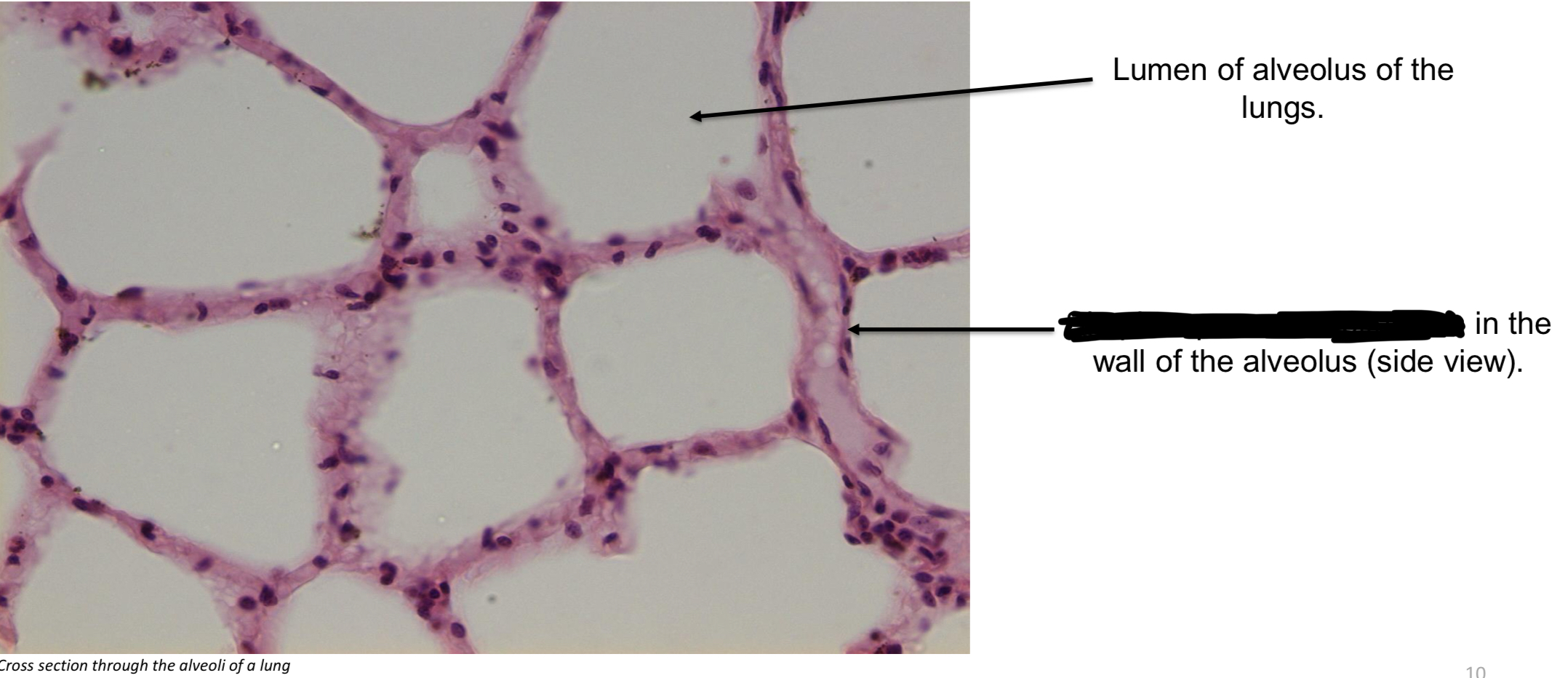
Simple squamous epithelium → alveoli of lung
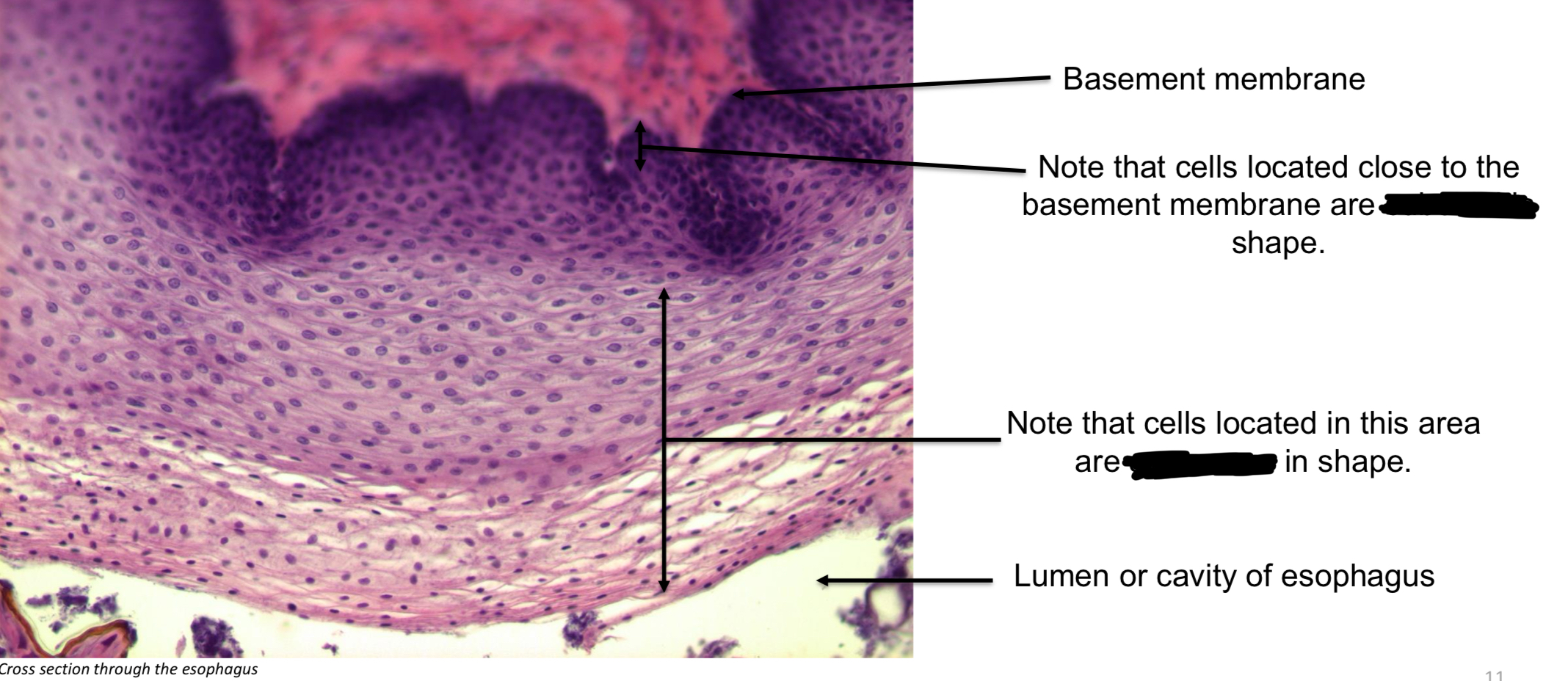
Stratified squamous epithelium, non-keratinized → esophagus
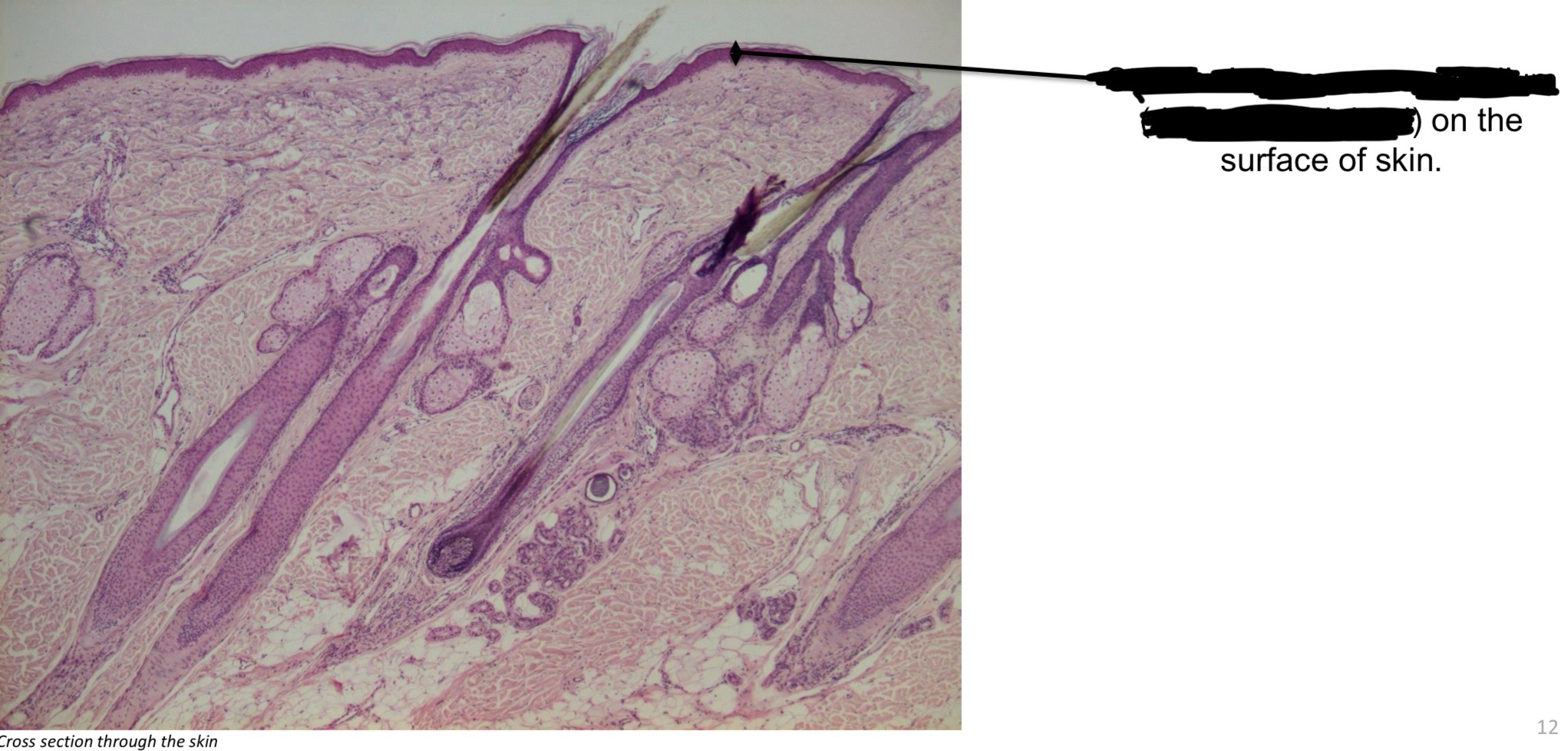
Stratified squamous epithelium, keratinized → skin
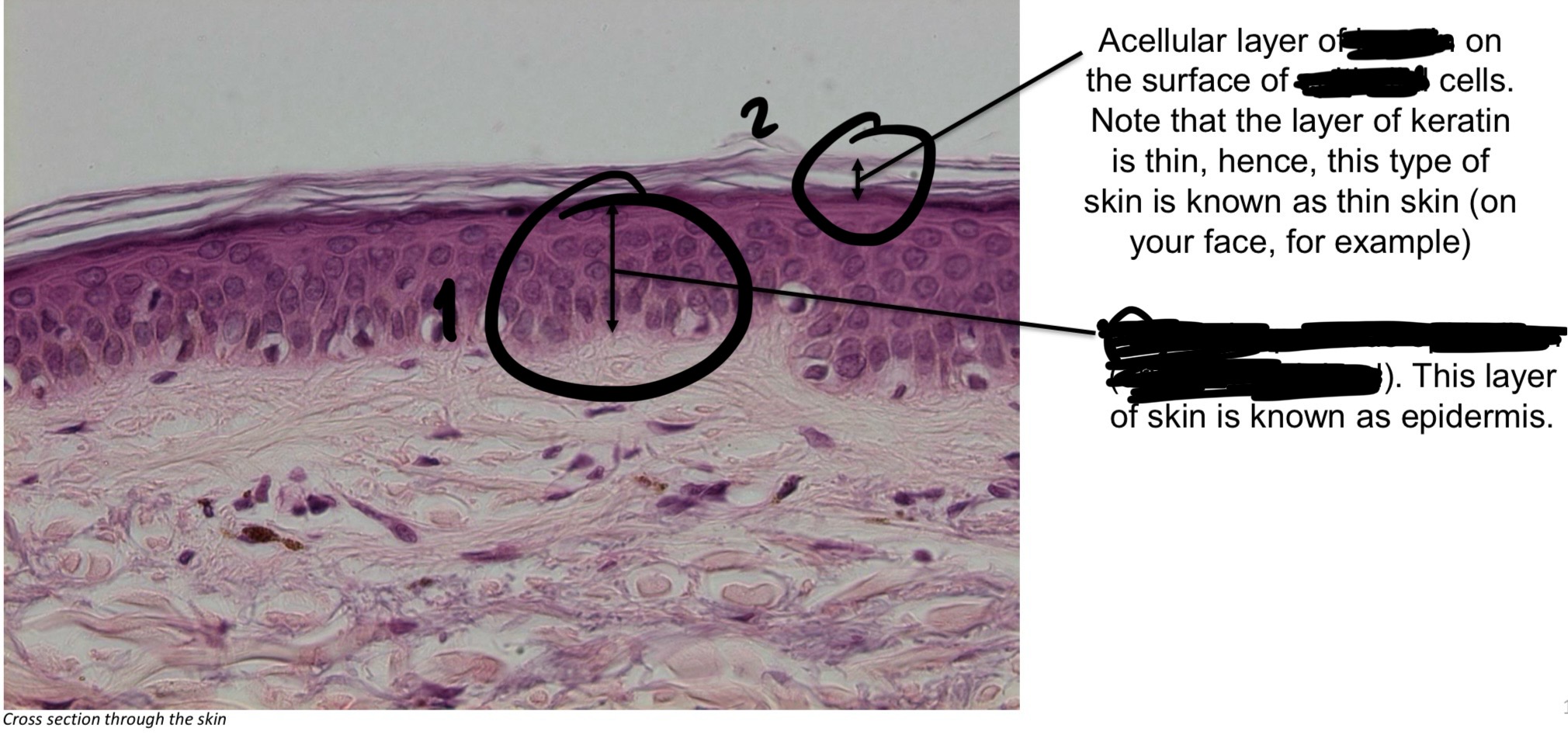
Keratin layer (thin) → ex. Face
Stratified squamous epithelium (epidermis) → skin
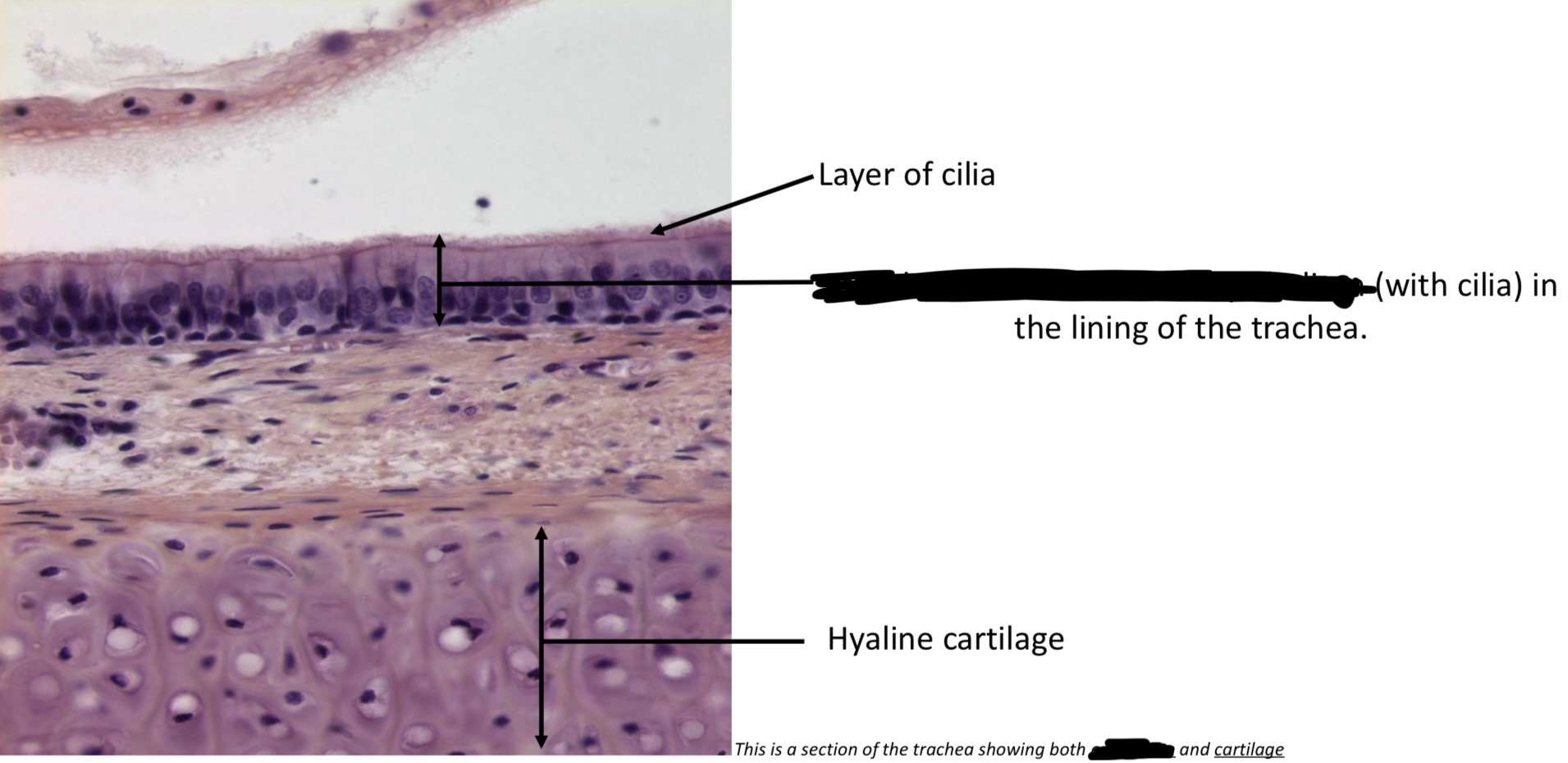
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium, with cilia → trachea
Hyaline cartilage
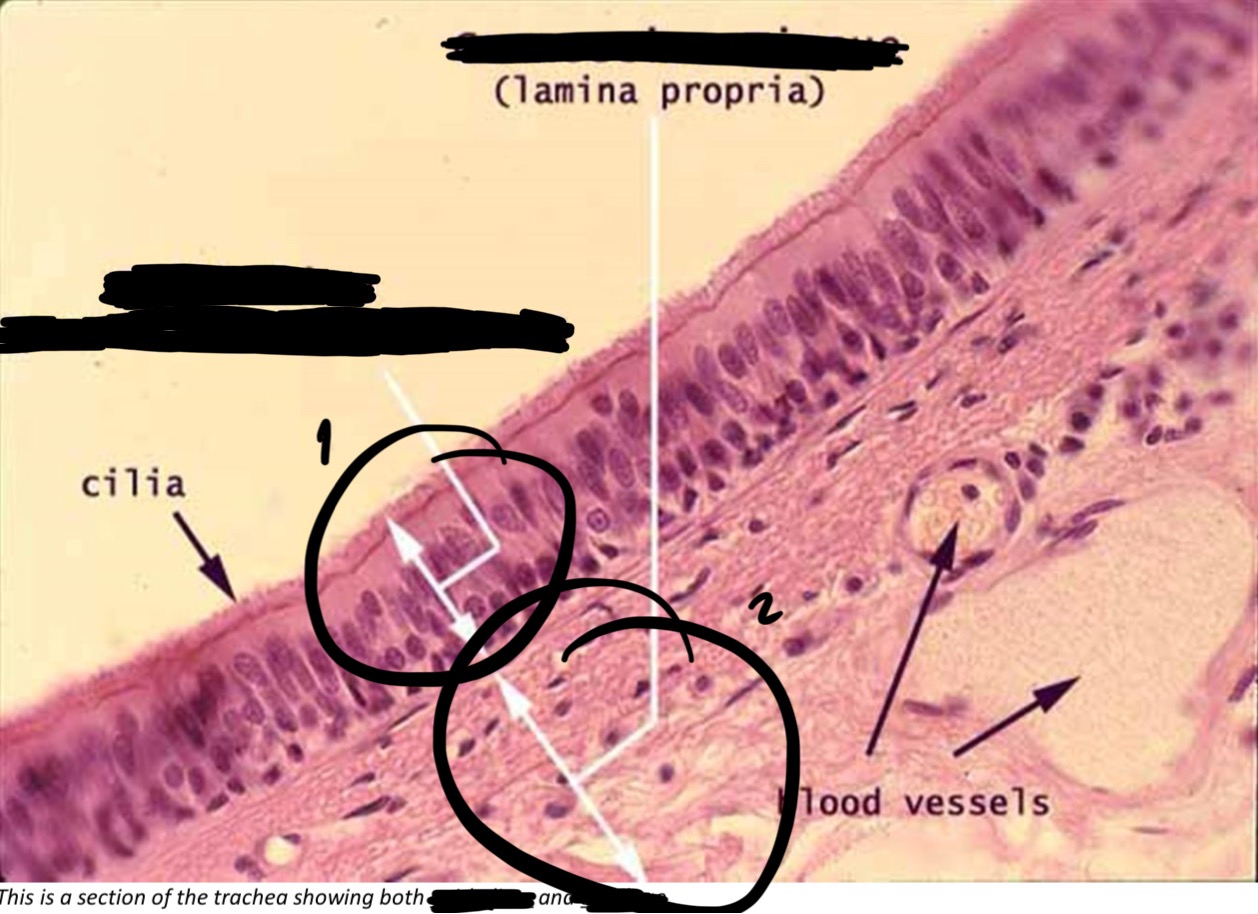
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium, with cilia → trachea
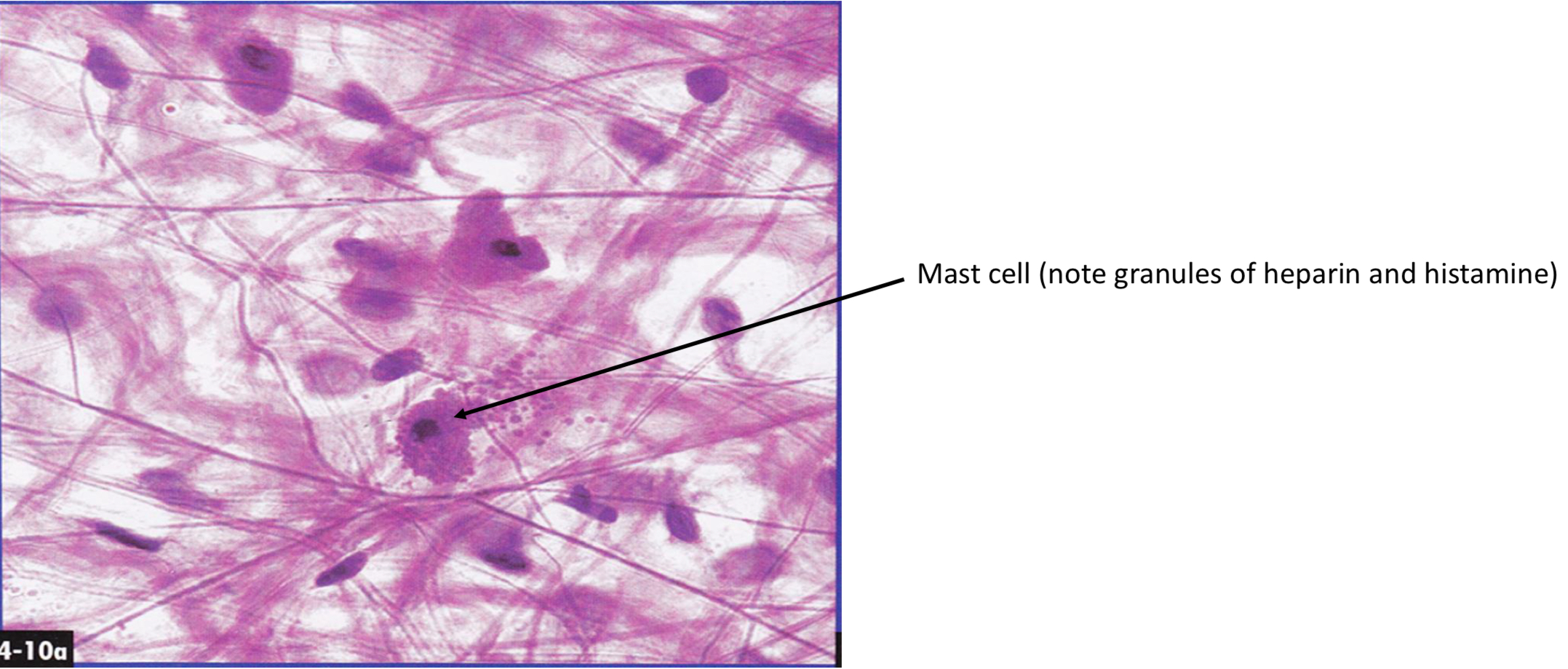
Connective tissue
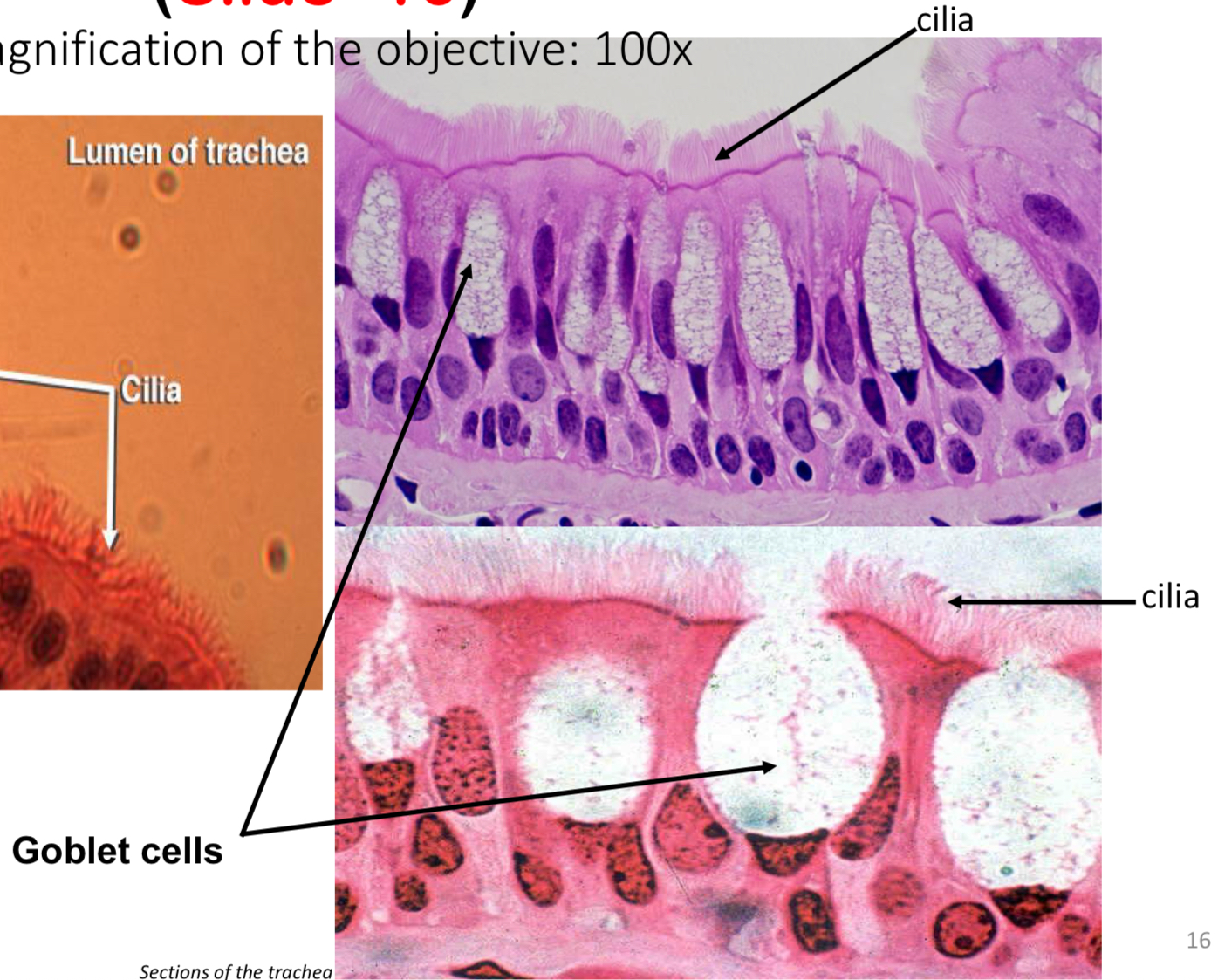
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium, with cilia
Connective tissue
Most abundant, support, anchor, & connect.
Extracellular matrix
Fibres & ground substance in connective tissue
Fibroblasts
Most common cell in connective tissue → produces fibers & other intercellular materials.
Collagen fiber
One of two most common fibers in connective tissue → strength. Imbedded in ground substance
Connective tissue proper
Encompasses all organs & body cavities connecting & separating → areolar (loose), adipose (fat), & dense regular tissue.
Areolar (loose) connective tissue.
Most widespread → attach skin to underlaying tissue, fills space between organs & holds them in place, cushions & protects them. Surrounds & supports blood vessels.
Adipose (tat) tissue
Large internal fat droplet that pushes cytoplasm into thin layer & nucleus is at edge of cell → storage for lipids, pads & protects, & insulates.
Specialized connective tissue
Cartilage, bone, & blood. Cartilage & bone form skeletal framework. Blood is vascular (transport) tissue.
Cartilage
Elastic, pliable, compact non-vascular. → hyaline, elastic, & fibrocartilage
Lacunae
Traps chrondrocytes in matrix.
Chondrocytes
Cartilage cells.
Matrix
Ground substance → structural support.
Elastic fiber
One of two most common fibers in connective tissue → elasticity. Imbedded in ground substance
Blood plasma
Extracellular matrix → water, salts, proteins, glucose, lipids, glycoproteins, hormones, amino acids, & vitamins.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells, most abundant, transport oxygen, carbon dioxide, & nutrients. Lacks nodes but has hemoglobin & cytosteletal elements
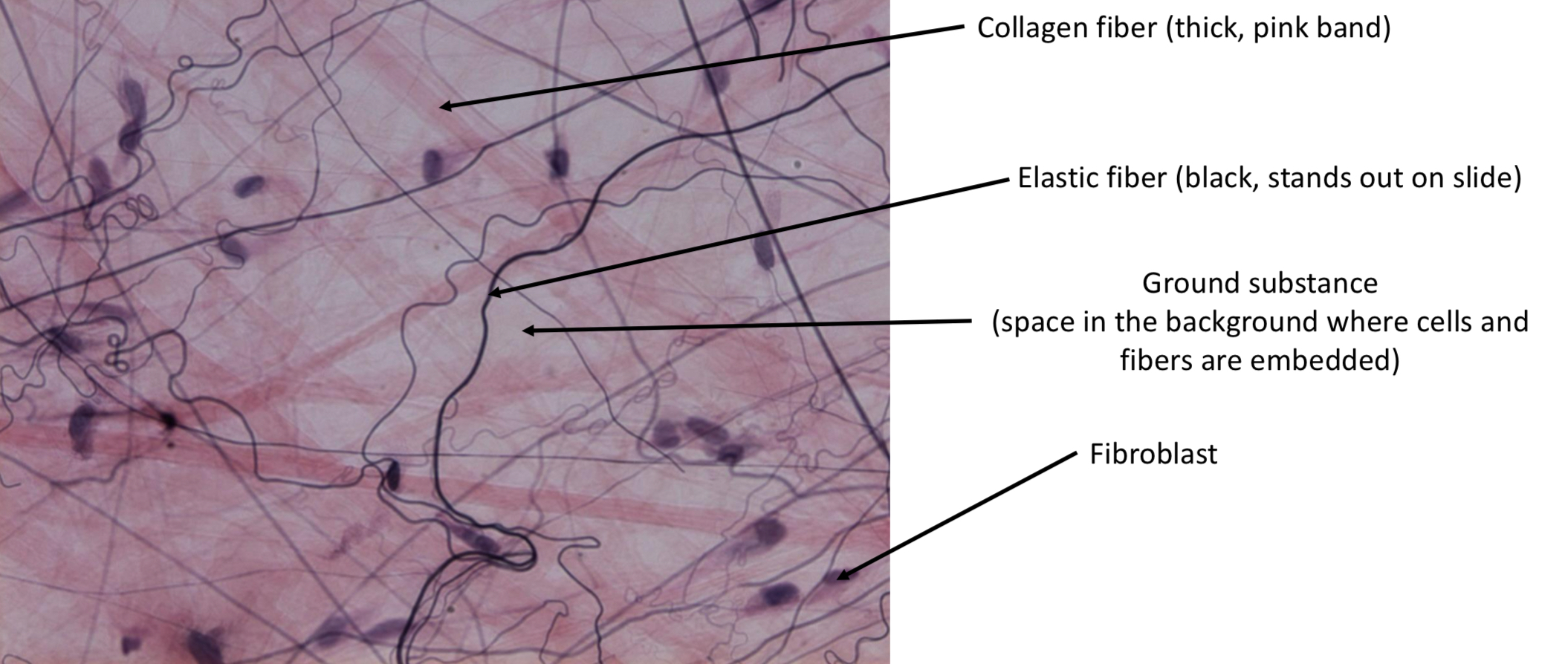
Areolar (loose) connective tissue
Areolar (loose) connective tissue
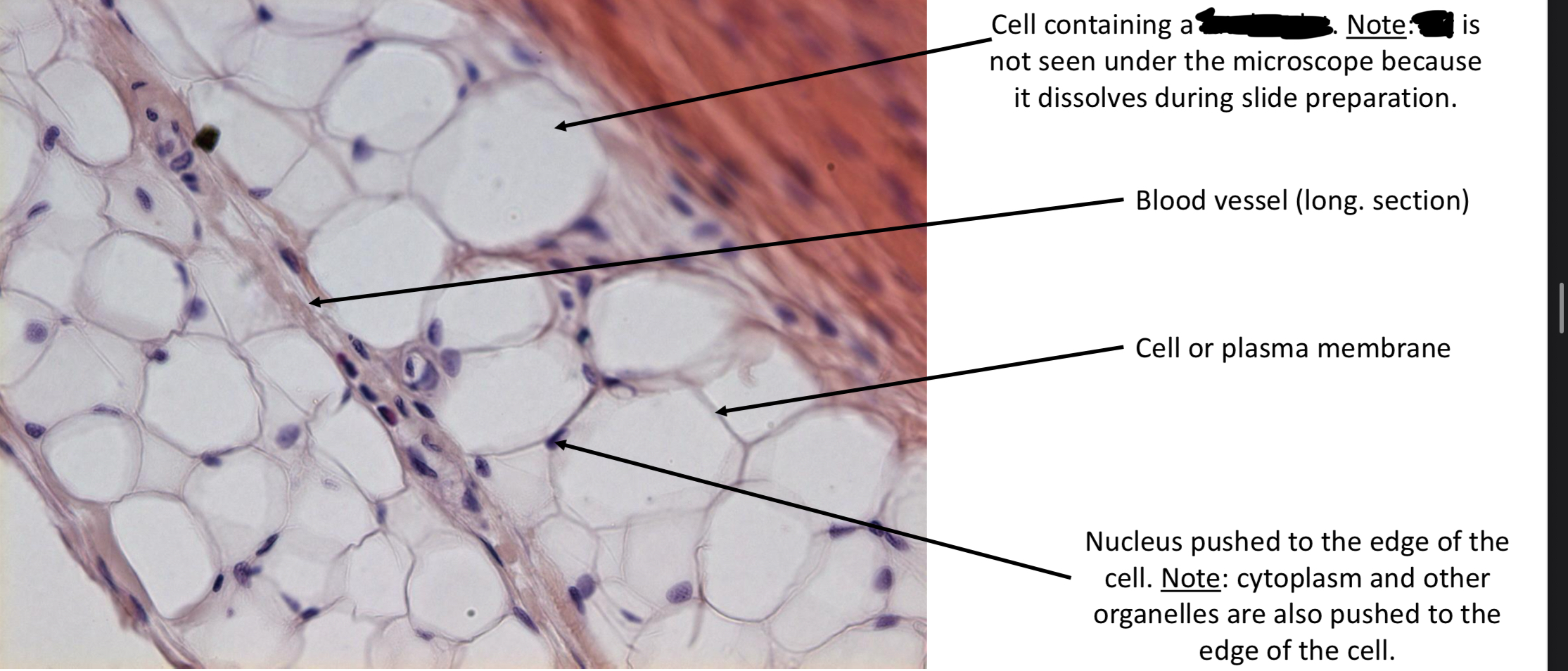
Adipose (fat) connective tissue
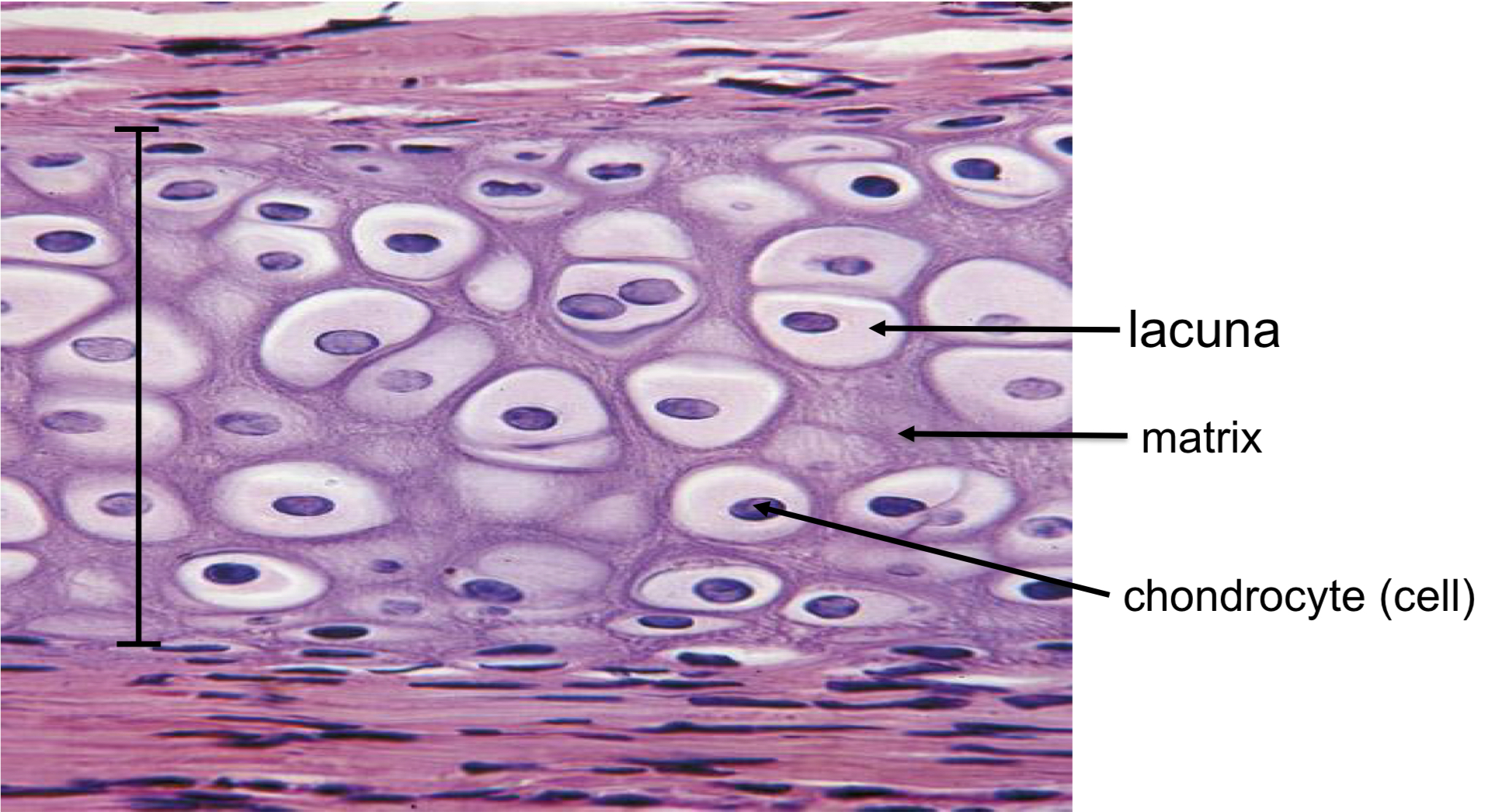
Hyaline cartilage → trachea