VCE 3/4 biology exam revision
1/586
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
587 Terms
Research question
a testable achievable and specific question that an investigation sets out to answer
Testable
you must be able to measure the factors you are interested in
Aim
the objective of an investigation
Dependant variable
the factor/s measured in the experiment that are charged when the IV is manipulated
Independent variable
the factor/s that are manipulated in an experiment
Controlled/constant variables
factors that are kept constant throughout an experiment.
Extraneous/uncontrolled variables
factors that are not kept constant or account for throughout the experiment
Hypothesis
a testable statement that describes how you think your independent variable will affect your dependant variable, including direction of change
if [change in IV] then [change in DV]/(When compared to [control group]) because [why]
Method
the steps followed in a scientific investigation
Methodology
the strategy or overarching framework followed in a scientific investigation
Case study
An investigation of an event or problem that involves a real or hypothetical situation. Includes; historical analysis, role-play of an imagined situation, or designing a solution to a real-world problem
Classification and identification
classification is the arrangement of individuals or objects into logical. manageable sets. Identification is used to recognise where new individuals or objects belong in these sets
Controlled experiment
An investigation into the impact of an IV on a DV, controlling for all other variables
Correlational study
observing and recording events that have not been manipulated or controlled to understand associations that exist between variables. Typically still measures the effect of an IV on a DV, but the IV is not manipulated by the experiment and some conditions may be less controlled than a laboratory experiment
Fieldwork
A correlational study or controlled experiment set up outside a controlled environment usually in a selected ecosystem.Typically still measure the effect of an IV on a DV, but the IV but some conditions may be less controlled than a laboratory experiment
Literature review
The collation and analysis of other people's scientific findings or viewpoints concerning a particular topic. consideration of the reliability of sources and methods is important in literature reviews. THey are used to provide background information on a topic of interest and/or identify potential areas of research.
Modeling
the construction of a model or representation that approximates an object or event. this could be a drawing, an equation, ect. and can be used to describe systems or make predictions.
Product, process or system development
design of an object, process, or system to meet a human need
Simulation
the process of using a model to observe and predict what many happen in a real or theoretical system
Sample groups should be
Representative and unbiased
Experimental group/treatment group
a group of individuals/samples in which the independent variable is manipulated
Control group/ experimental group/control treatment/the control
a group of individuals/samples that are not exposed to the independent variable
Random sampling
ensures that each member is equally likely to be included
Systematic sampling
involves taking samples at regular intervals along and environment gradien
Stratified sampling
when a population has clearly defined zones or characteristics, and you wish to sample proportionately from each zone, you may wish to use stratified sampling
Judgement/selective sampling
the researcher/an expert-chooses which individuals to sample according to their needs. Judgment sampling can be biased and leads to unrepresentative data, and should only be used when necessary
Convenience sampling
taking a group of individuals based on who is easy to reach, which leads to biased and unrepresentative samples that make results unreliable.
Personal error
mistakes or miscalculation due to human fault. Can be eliminated by performing the experiment again, and for measurements relying on human accuracy get multiple people to make the same measurement
systematic error
error which causes results to differ by a consistent amount each time,typically due to faulty equipment, which affect accuracy and cannot be minimised by repeating the experiment. To avoid them re-calibrane instruments, or use more reliable equipment
random error
errors which are caused by unpredictable variations in the measurement process and result in a spread of readings. To avoid them replicate the experiment, increase the sample size, or use more precise measuring equipment.
Uncertainty
a quantification of the error associated with a measurement, often represented by the symbol ±
Valid
a measurement or experiment that actually tests what it claims to be testing
Accuracy
how closely a measurement is to the true value
True value
the value that would be obtained by a perfect measurement without the influence of error
precise
two or more measurements that closely align with each other
Repeatable
an experiment/measurement which scientists, using the method they designed can obtain the same result multiple times
Reproducibility
an experiment/measurement in which a group of scientists, using methods designed by others, can obtain the same results as another group's experiment
Replicaion
the process of running your test/experiment multiple times
-Increasing replication allows scientists to determine if their results are precise.
-Replication allows scientists to take the average of their results which reduces the impact of outliers and random error, which could improve the accuracy of the experiment
Numerical variables
a factor that is measured as a number
Continuous data
variables that can take any value between a set of real numbers.
Typically graphed using line graphs or scatter plots
Discrete numerical data
variables that can be counted and takes a particular value.
Typically graphed using a bar graph
Categorical variables
a factor that is qualitative, typically describing characteristics
Categorical oriental data
variables that can be logically ordered eg size
-typically graphed using a bar chart or pie chart
Categorical nominal variable
variables that cannot be ordered in a logical sequence eg gender
-typically graphed using a bar chart or pie chart
Title
-can be written as a question or statement that describes the main phenomenon you are trying to describe.
-it should be one sentence and in present tense
Introduction
-justifies why you needed to perform your experiment
includes;
1.background information
-why the system or model is important to study
-the broader implications of answering your particular question
-any prior research that has been undertaken
-Any gaps in knowledge, and how your experiment could fill in those gaps
2.The aim of the experiment
3.The variable being tested
4.The hypothesis
5.The final sentence usually suggests the big-picture influence of the experiment
-should be 1-4 paragraphs long in mostly present and future tense
Methodology
outlines all the materials and steps you took during an experiment
Structure;
Sample-who/what is being investigated and how many
Group-Division of sample into experimental group and any control group
Control variables-All variables that are being kept the same
IV
DV
Equipment-Any equipment used and draw and label complex experimental setups
Time-What period of time will the investigation run prior to collecting the results
Outliers, averages
Repeat/reproduce
should be no longer than half a page and written in past tense
Discussion
-determines if the data obtained supports the hypothesis and to explore the implications of the findings.
Structure of a paragraph
1.Restate key data
2.State if the results supported or refutes your hypothesis
3.Discuss if your findings support or differ from prior research
-Be sure to reference source
4.weight up strengths and weaknesses of the data to determine if the results can be trusted
-Identify reasons why these results may be invalid or unreliable referring to errors
-Precision accuracy and uncertainty of data
-Problems with experiment design
-Other studies that contradict your data
5.Identify reasons why the results may be limited- what is the date not telling us that would be useful
6.Suggest how the method could be charged to overcome any problems
7.Identify any strengths that support the validity, reliability, and scope of the results
-Should be at least 1 paragraphs, but is 3-4 paragraphs, and is mostly present tense
Conclusion
Conclusion-summarises the study
Structure
1.Was the hypothesis supported or rejected and justification of why
2.Summary of limitations and improvements
3.The broader implications of the results
-Future research
-Impact of scientific knowledge
-The impact on society/environment
-One paragraph in a mix of tenses but most present tense.
Bioethical approach
a decision making framework that helps guide ethical behaviour
Consequence based approach
an approach to bioethics that aims to maximise positive outcomes while minimising negative outcomes
*Duty/rule-based*-an approach to bioethics that promotes the responsibility of the agent above all else, and places importance in the duty of each individual
*Duty/rule-based*
an approach to bioethics that promotes the responsibility of the agent above all else, and places importance in the duty of each individual
Virtue-based approach
an approach that places importance on the duty of each individual goodness of the agent, and promotes acting in accordance with the values of a 'moral' person, such as honesty and compassion
Ethical Concepts/principles
Integrity, Justice, Beneficence, Non-maleficence, Respect
Integrity
an ethical concept that encourages a full commitment to knowledge and understanding as well as the honest reporting of all sources of information and results
Justice
an ethical concept that encourages fair consideration of competing claims, and ensures that there is no unfair burden on a particular position or course of action
Beneficence
an ethical concept that seeks to maximise benefits when taking a particular position or course of action
Non-maleficence
An ethical concept that discourages causing harm, or when harm is unavoidable, ensuring that the harm is not disproportionate to the benefits from any position or course of action
Respect
an ethical concept that encourages the acknowledgment of the intrinsic value of living things, and considers the welfare, beliefs, customs, and cultural heritage of both the individual and the collective
Social
the influence of the technology on society rather than just one or two individuals
Ethical
a sense of right and wrong in producing or obtaining the technology due to morals and beliefs
Economic
The availability of funds to obtain or produce technology
Biology
The effect of technology on other living organisms in an particular environment
Tertiary structure
The overall three-dimensional shape formed by R-group interactions between amino acids
Condensation reaction
when monomers link to form polymers producing water as a byproduct
peptide bond
The chemical bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid
Quaternary structure
Two or more folded polypeptide chains joined together
function of a protein's shape
A protein's shape determines its ability to bind molecules and perform its function
Denaturation
Any change to a protein's 3D structure that prevents proper function
Disease caused by errors in protein formation
Misfolded proteins can cause disease by failing to perform vital functions or by accumulating and disrupting cellular function
Biomacromolecules
A large biological polymer
Biomolecule
Substances produced by cells and living organisms
Lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids are biomolecules
Protein secretory pathway process
1.Proteins are produced at ribosomes
2.Proteins fold in the rough endoplasmic reticulum
3.Proteins move to the Golgi apparatus via transport vesicles
4.Proteins are modified and packaged into secretory/golgi vesicles for export via exocytosis
Exocytosis
Bulk transport that moves large substances out of the cell
process of exocytosis
1.A vesicle containing secretory products is transported to the plasma membrane
2.The vesicle membrane fuses with the plasma membrane
3.Secretory products release into the extracellular environment
Operator
A DNA code section where repressor protein can bind
-if the operator is bound to the repressor, RNA polymerase cannot bind to the prompter, and thus transcription cannot occur
-This occurs when the correct level of mRNA has been produced
polymer
A molecule made up of a large number of smaller repeating units
Monomer
A molecule that forms bonds with other identical molecules to create the repeating units of a polymer
Nucleotide
The monomer of nucleic acids that join together to form DNA or RNA
components of a nucleotide
they consist of a phosphate group sugar and nitrogenous base
DNA structure
DNA is a polymer with a double helix structure
DNA strands are Anti-parallel
The complementary DNA nitrogenous bases
cytosine is complementary to guanine and adenine is complementary to thymine
Number of hydrogen bonds formed between DNA bases
adenine and thymine form two hydrogen bonds
cytosine and guanine form three hydrogen bonds
Purine bases
have two carbon-nitrogen rings.
Adenine and Guanine
Pyrimidine bases
have one carbon-nitrogen ring
Thymine and Cytosine
RNA
The intermediate step in converting DNA's coded information into proteins
Amino acids
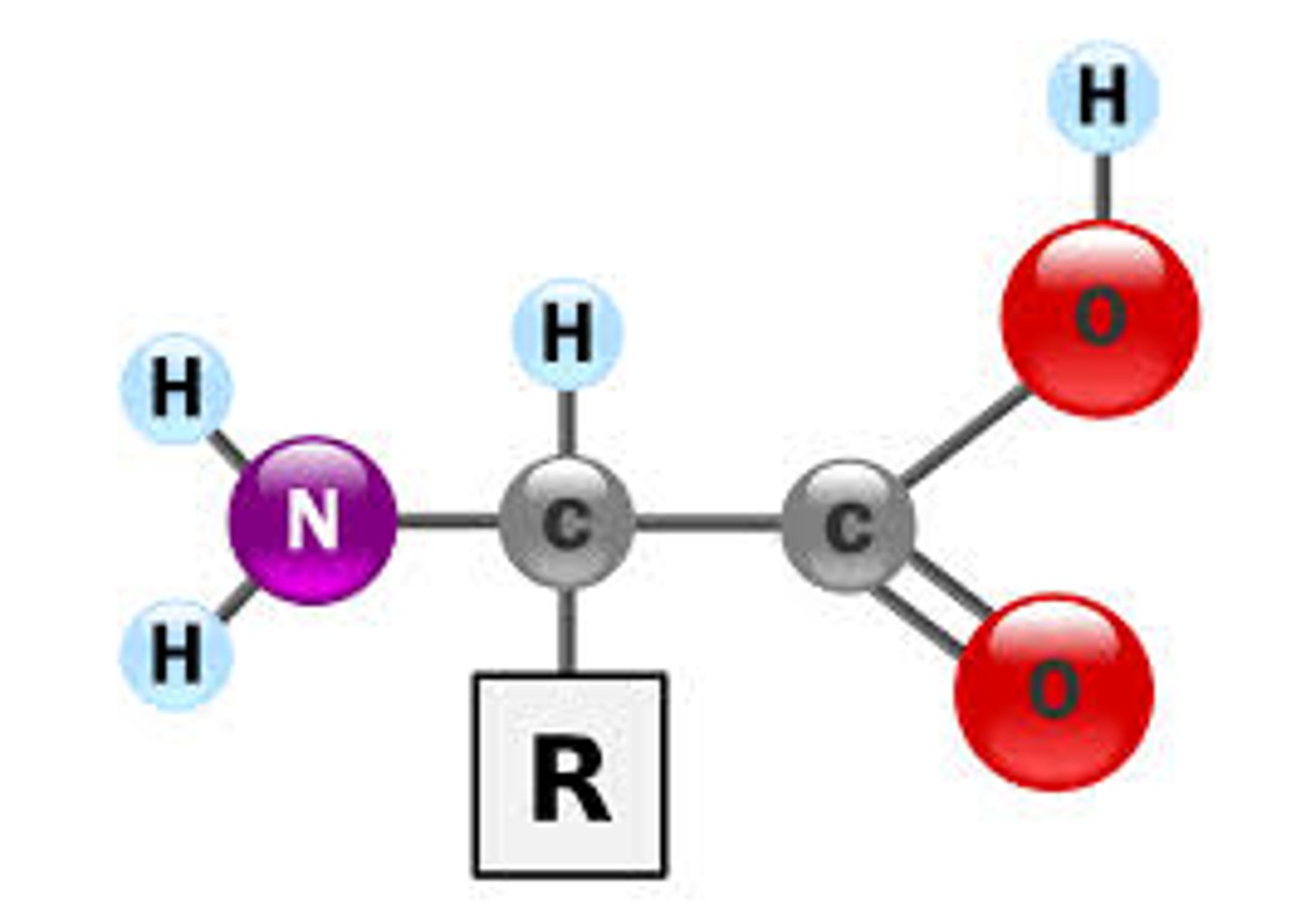
Gene expression
The conversion of the code in the DNA of a gene into protein though protein synthesis
Transcription
The process through which a gene, is used to make a molecule of messenger RNA
Process of transciption
1. Initiation: In the nucleus, RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region upstream of the structural gene, unwinding its double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases
2. Elongation:RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template strand (3 prime to 5 prime), bringing free-floating RNA nucleotides into line via complementarity.
3. Termination: When RNA polymerase reaches the termination sequence, transcription ends and pre-mRNA detaches in the nucleus
RNA polymerase
An enzyme that reads template strands and adds complementary nucleotides to create an mRNA transcript
post-transcription modifications (RNA processing)
1. In the nucleus, Pre-mRNA's introns are spliced out using enzymes called spliceosomes
2. Exons are then joined together, however, may be reshuffled/discarded via alternative splicing to create new mRNA variations
3. Then, a poly-A tail and methyl-guanine cap are added to the 3" and 5" end (respectively) which protects the mRNA against enzyme degradation and maintains a level of stability
Exon
a region of a gene that contains genetic information that codes for the specific protein to be synthesised
Intron
a region of a gene that contains sequences that do not code for the protein to be expressed
Translation
The process of using mRNA information to create a protein
-Occurs at ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on the rough endoplasmic reticulum
-Free ribosomes make proteins for cell use
-Attached ribosomes make proteins for export or secretion
Process of translation
1. In the cytosol, a ribosome attaches to the 5 prime end of the mRNA 5" end, exposing its first codon (start codon). 2. A tRNA molecule with a complementary anticodon binds to the mRNA codon, bringing its associated amino acid into line. This continues for each codon 3. Adjacent amino acids form peptide bonds via condensation polymerisation to produce a polypeptide chain The 'stop' codon denotes the end of translation, causing the polypeptide (primary structure) to detach from the ribosome
The proteome
The complete set of proteins that a cell or organism can express
The human body contains an estimated 80,000 to 400,000 proteins
polypeptide
Polymers made from a series of amino acids
-The amino acid sequence determines protein structure
-Attraction and repulsion between amino acids cause the polypeptide chain to fold into a specific 3D shape
Primary structure
The amino acid sequence in the polypeptide chain
Secondary structure
Hydrogen bonds between amino acid backbones form alpha-helices or beta-pleated sheets, in the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum