6th Gr. Ratios
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Additive reasoning
focuses on the use of addition and subtraction for comparisons.
Multiplicative reasoning
focuses on the use of multiplication and division for comparisons.
Ratio
is a comparison of two quantities using division. Ratios may be written in 3 ways. (ex. The ratio of boys (12) to girls (14) in Mr. Levine's class maybe written as 12:14, 12 to 14, or 12/14 (fraction form))
Terms of a ratio
Are the quantities x and y in the ratio. The terms of the ratio 12:14 are 12 and 14.
Equivalent ratios
are ratios that represent the same part-to-part or part-to-whole relationship. (ex. 2:3 and 4:6 are equivalent ratios.)
Percent
is a part-to-whole ratio where the whole is equal to 100.
Part-to-part ratio
compares parts.
Part-to-whole ratio
compares a part of a whole to the total number of parts.
Qualitative reasoning
comparing ratios without measuring or counting quantities. Use qualities (describing with adjectives).
Quantitative reasoning
comparing ratios by measuring or counting quantities.
Tape diagram
illustrates number relationships by using rectangles to represent ratio parts.
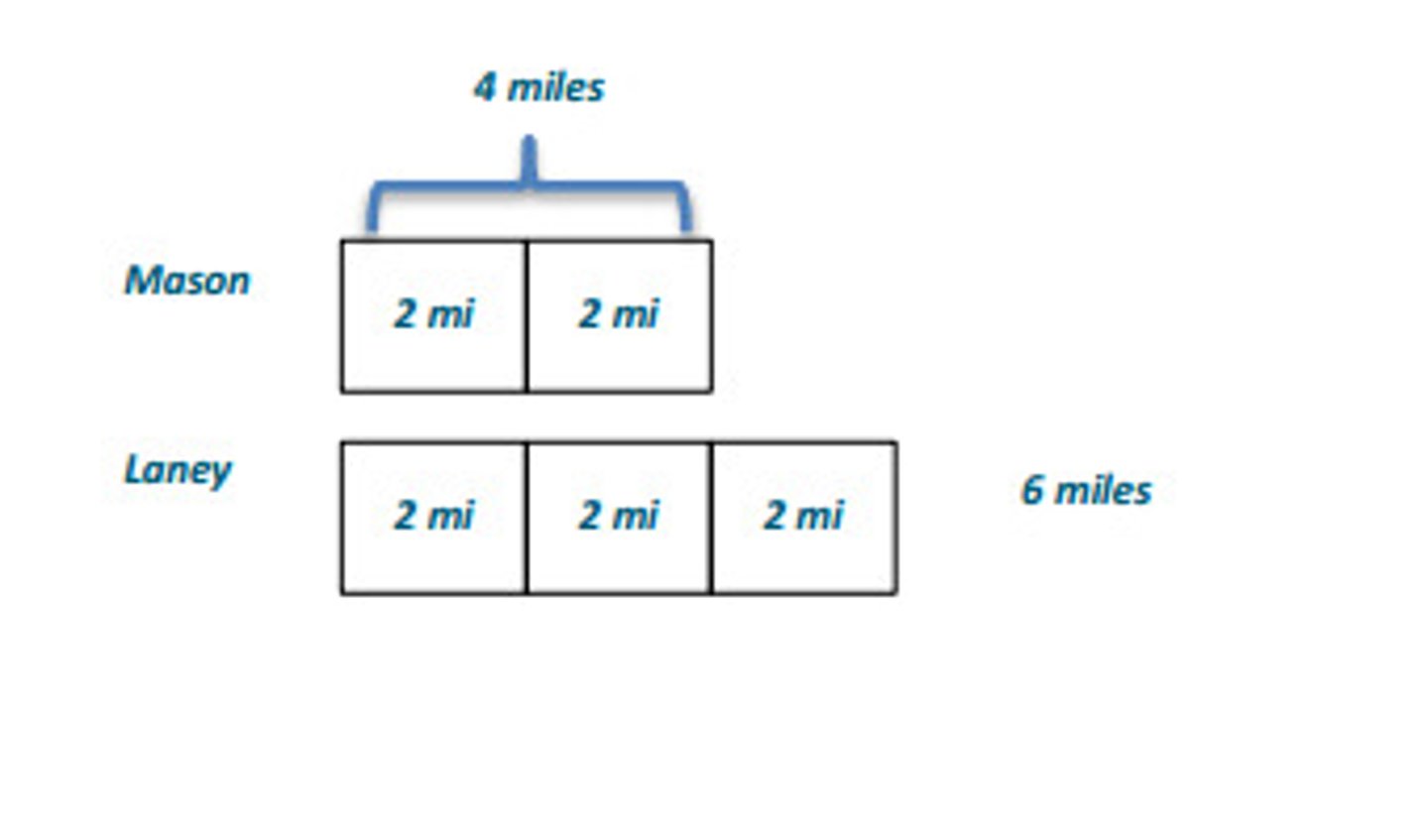
Rate
is a ratio that compares two quantities measured in different units.
Proportion
is an equation that states that two ratios are equal. In a proportion, the quantities composing each part of the ratio have the same multiplicative relationship between them.
Scaling up
means you multiply both parts of the ratio by the same factor greater than 1.
Scaling down
means you divide both parts of the ratio by the same factor greater than 1 or multiply both parts of the ratio by same factor less than 1.
Double number line
e is a model made up of two number lines used together to represent the ratio between two quantities. The intervals on each number line maintain the same ratio.
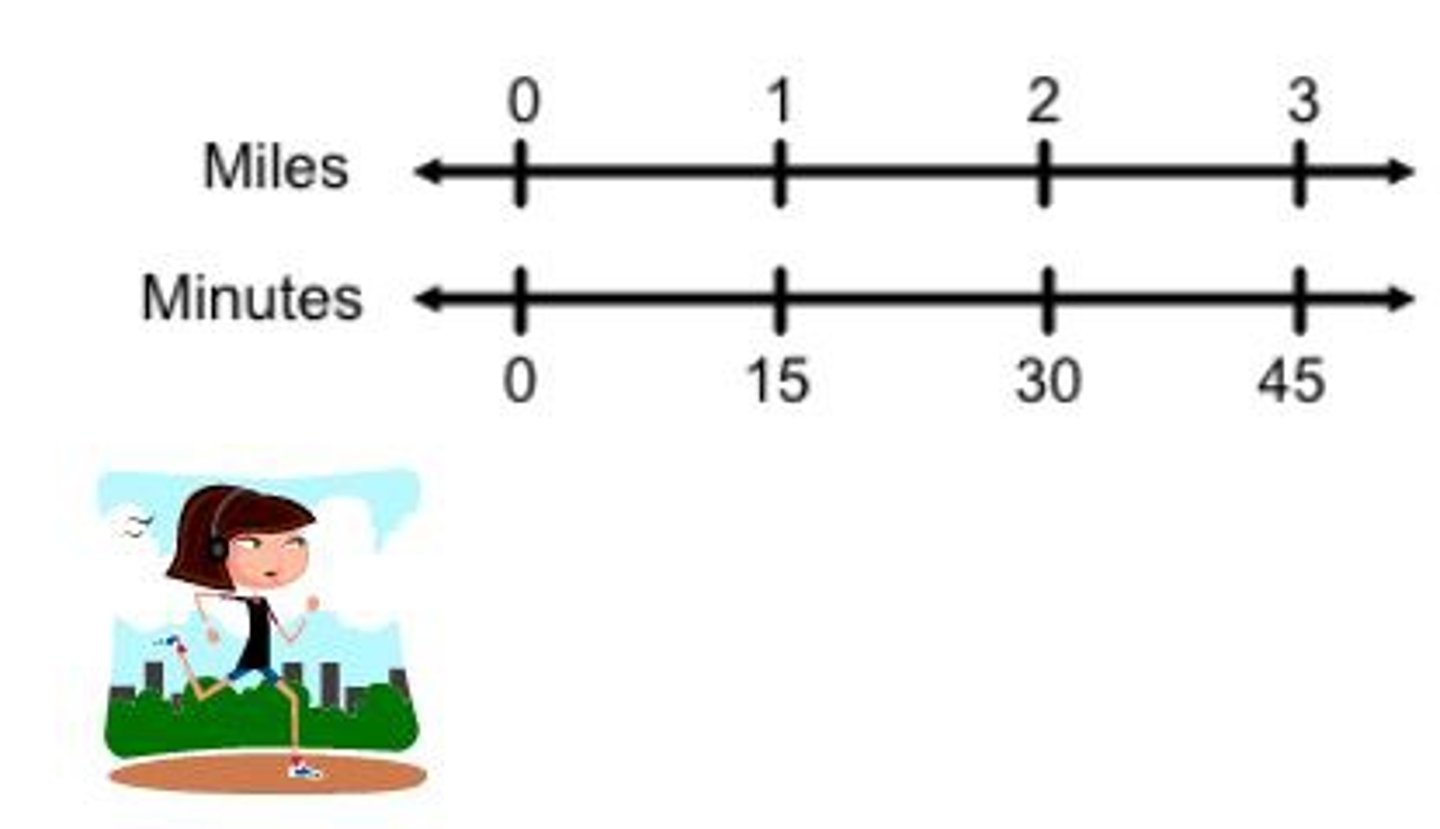
Linear relationship
When a set of points graphed on a coordinate plane forms a straight line.